Quick betula alnoides seedling raising method based on flower arrangement mud serving as cutting substrate
A technology of cutting substrate and flower-arranging mud can be used in planting substrates, botanical equipment and methods, culture medium and other directions, which can solve the problems of easily contaminated roots, long time for raising seedlings, long time for rooting, etc. The cost of fresh-keeping, the effect of benefiting hair roots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] A method for rapid seedling cultivation of Betula chinensis based on flower cutting mud as a cutting substrate is carried out in a greenhouse, a plastic greenhouse, or a small plastic shed, and comprises the following steps:
[0028] Step 1: Preparation of flower arrangement mud
[0029] Cut the flower arrangement mud into rectangular block-shaped cuttings with a size of 1.6cm×1.6cm×2.5cm, then soak the cut flower arrangement mud in clean water for 3 days, change the water once a day, and soak the flower arrangement mud;
[0030] After soaking, the flower cutting mud is taken out and placed on the seedling tray. The seedling tray is a 105-hole tray with an upper diameter of 3.5 cm, a lower diameter of 1.5 cm, and a depth of 3.5 cm. The bottom of the seedling tray is equipped with a non-porous tray.
[0031] Step 2: Collection and Processing of Cuttings
[0032] Choose strong growth, good buds, no pests and diseases, 0.2-0.5cm in diameter, semi-lignified young branches ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Cutting Propagation Test of Cuttings with Different Lignification Degrees
[0047] This test is carried out according to the steps of Example 1, wherein, in step 2, the young shoots of the current year, semi-lignified, and 1-year-old shoots are selected for testing.
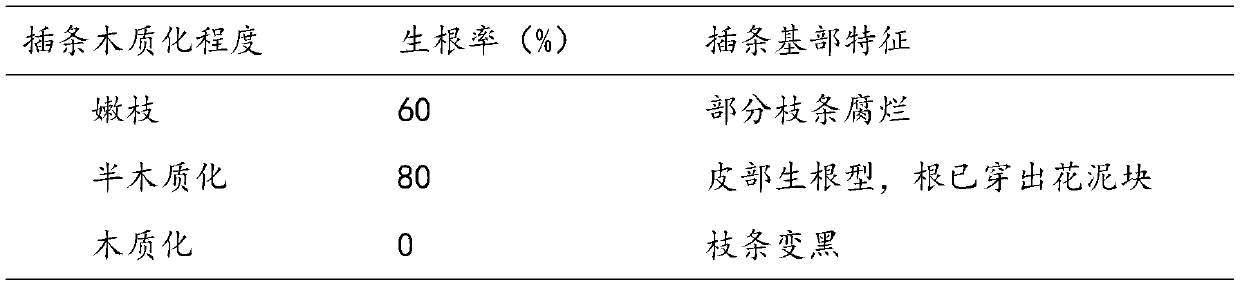
[0048] After step 1-step 5 in embodiment 1, the rooting rate of the Southwestern birch branch of different lignification degree after 1 month is as table 1:
[0049] Table 1 Rooting conditions of branches of Betula chinensis with different lignification degrees
[0050]
[0051] Actual effect: Observe the rooting situation after 3 months of cultivation. The average rooting rate of young shoots and semi-lignified branches cuttings is 65%.
Embodiment 3
[0053] Cutting Propagation Experiments Treated with Different Hormone Concentrations
[0054] This test is carried out according to the step of embodiment 1, wherein, test with clear water, sodium naphthalate 100mg / L, sodium naphthalate 200mg / L respectively in step 2, every processing cutting 15 strains of cuttings, repeat 3 times. The pruned cuttings of Southwestern birch were soaked in liquids of different experimental designs for 16 hours, keeping the branches upright, and submerging 1 / 3 of the length of the cuttings.
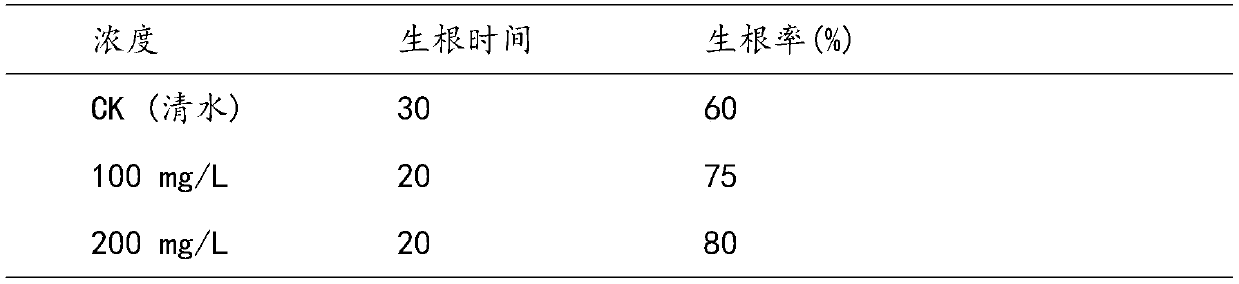
[0055] After step 1-step 5 in embodiment 1, the rooting rate of the Southwest birch branch that different hormone concentration sodium nacetate handles is as table 2:
[0056] The rooting rate of the Southwest birch branch that table 2 hormone concentration sodium nacetate handles
[0057]
[0058] Actual effect: Observing the rooting situation after 1 month of cultivation, it shows that sodium naphthalate 100mg / L or 200mg / L is used for the cuttings of S...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com