A low-maintenance ecological wetland construction method
A technology of ecological wetlands and construction methods, applied in the field of construction of low-maintenance ecological wetlands, can solve the problems of water pollution and purification ability affecting the operating life of wetlands, and achieve the goal of promoting the balance of water ecosystems, reducing disturbance and investment, and improving survival rates Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for constructing a low-maintenance ecological wetland, comprising the following steps:
[0040] Step 1. Ecological survey: Use the groundwater source detector to measure the source of groundwater, select the area with dense springs as the base point, and diverge from the base point to the surroundings. Use lime powder to draw the outline of the lake body on the project site according to the design drawings, and then carry out pile points Piling after layout;
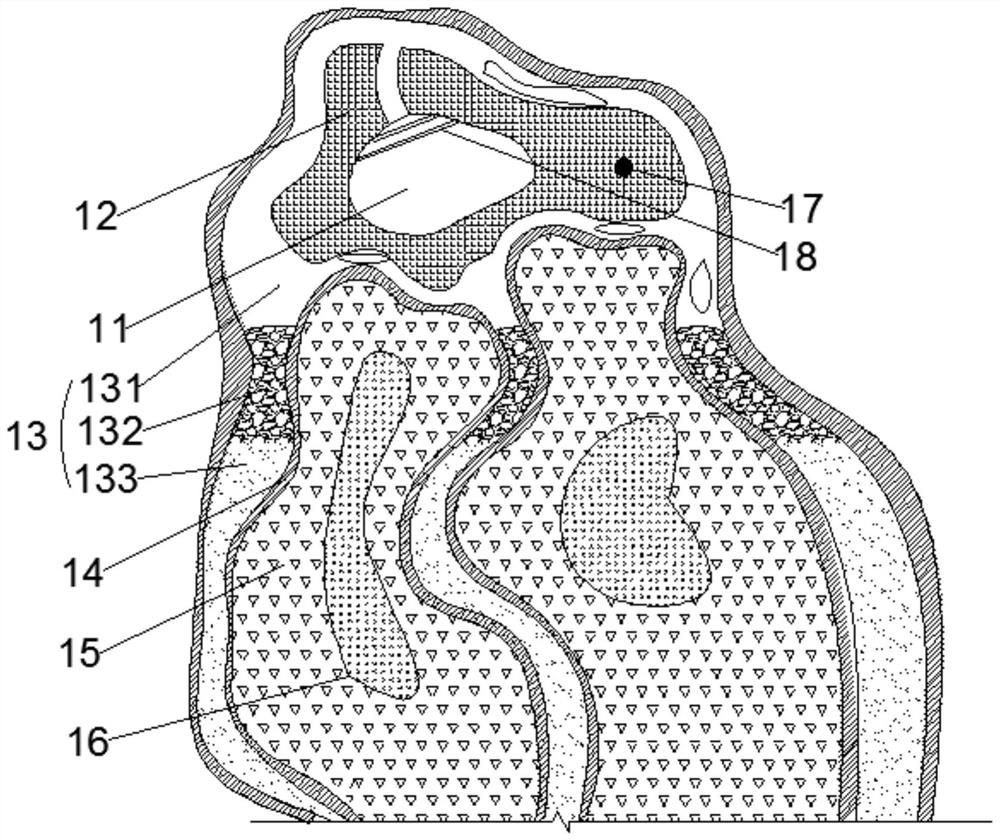
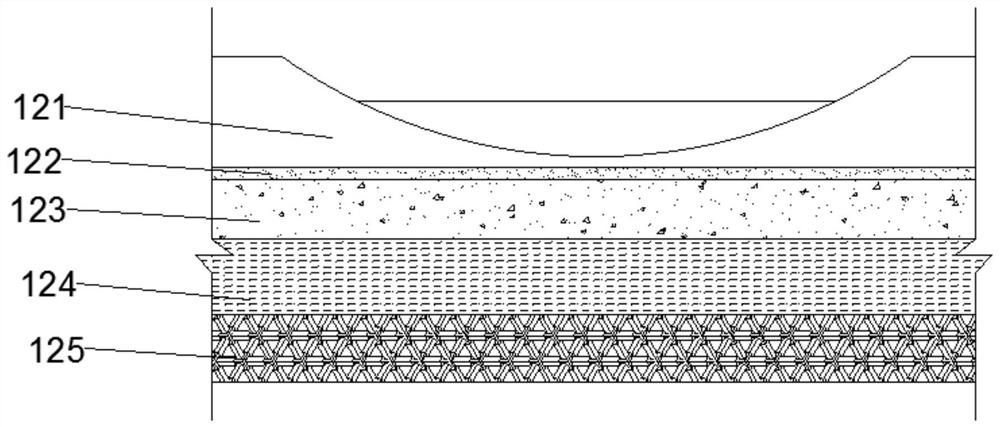
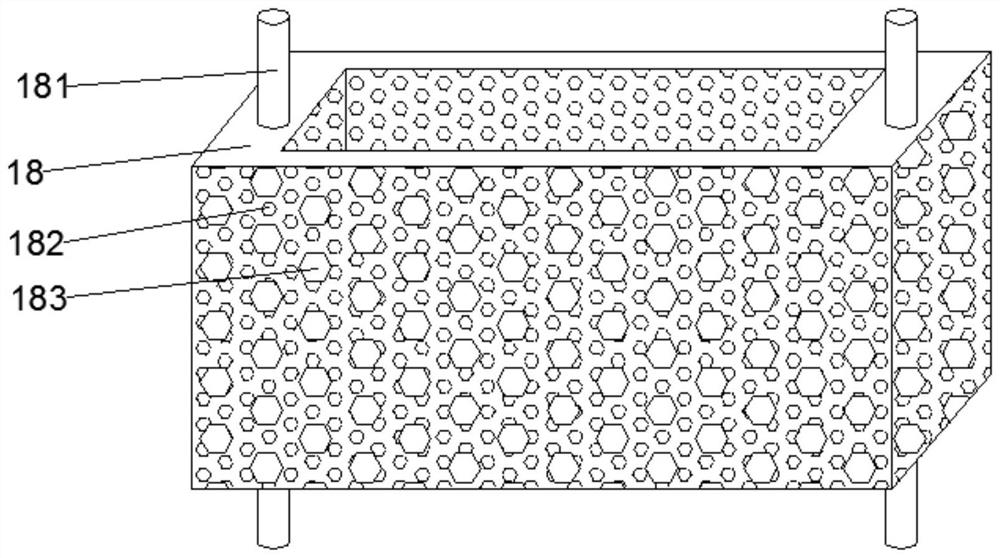
[0041] Step 2. Build an artificial lake: Excavate the artificial lake wetland 11 with excavators, the effective water depth range is 8m, set up drainage outlets and water storage channels, remove debris at the bottom of the lake, install nozzles vertically at springs, and lay geotechnical anti-seepage membranes. Do a good job of anti-seepage at the bottom of the lake, and set up two plant corridors 18 in the lake. The plant corridors 18 are straight structures, and each plant corridor 18 is filled with el...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A method for constructing a low-maintenance ecological wetland, comprising the following steps:
[0054] Step 1. Ecological survey: Use the groundwater source detector to measure the source of groundwater, select the area with dense springs as the base point, and diverge from the base point to the surroundings. Use lime powder to draw the outline of the lake body on the project site according to the design drawings, and then carry out pile points Piling after layout;
[0055] Step 2. Build the artificial lake 11: Excavate the artificial lake 11 with an excavator, the effective water depth range is 9m, set up a drainage outlet and a water storage channel, remove debris at the bottom of the lake, install a nozzle vertically at the spring, and lay a geotechnical anti-seepage membrane. Do a good job of anti-seepage at the bottom of the lake, and set up two plant corridors 18 in the lake. The plant corridors 18 are straight structures, and each plant corridor 18 is filled with...
Embodiment 3
[0067] A method for constructing a low-maintenance ecological wetland, comprising the following steps:
[0068] Step 1. Ecological survey: Use the groundwater source detector to measure the source of groundwater, select the area with dense springs as the base point, and diverge from the base point to the surroundings. Use lime powder to draw the outline of the lake body on the project site according to the design drawings, and then carry out pile points Piling after layout;
[0069] Step 2. Build the artificial lake 11: Excavate the artificial lake 11 with an excavator, the effective water depth range is 6m, set up a drainage outlet and a water storage channel, remove debris at the bottom of the lake, install a nozzle vertically at the spring, and lay a geotechnical anti-seepage membrane. Do a good job of anti-seepage at the bottom of the lake, and set up two plant corridors 18 in the lake. The plant corridors 18 are straight structures, and each plant corridor 18 is filled wi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com