Permanent-magnet traction motor
A traction and permanent magnet technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuits, electric components, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of easy vibration and noise, poor performance, and difficulty in ensuring the plane air gap of the stator and rotor, and achieve simple and easy manufacturing and assembly processes line, improve the power density per unit volume, and have a good shafting structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
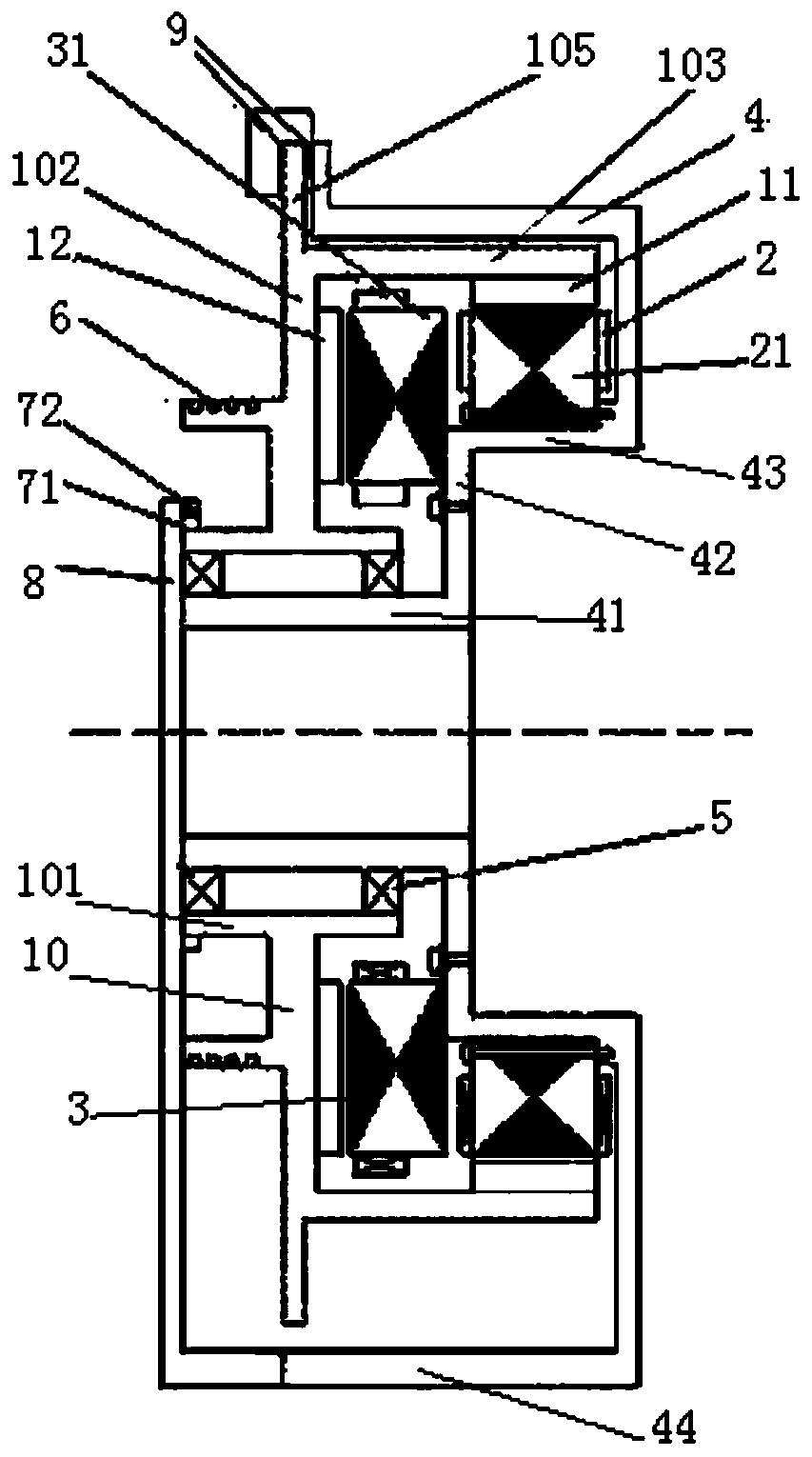
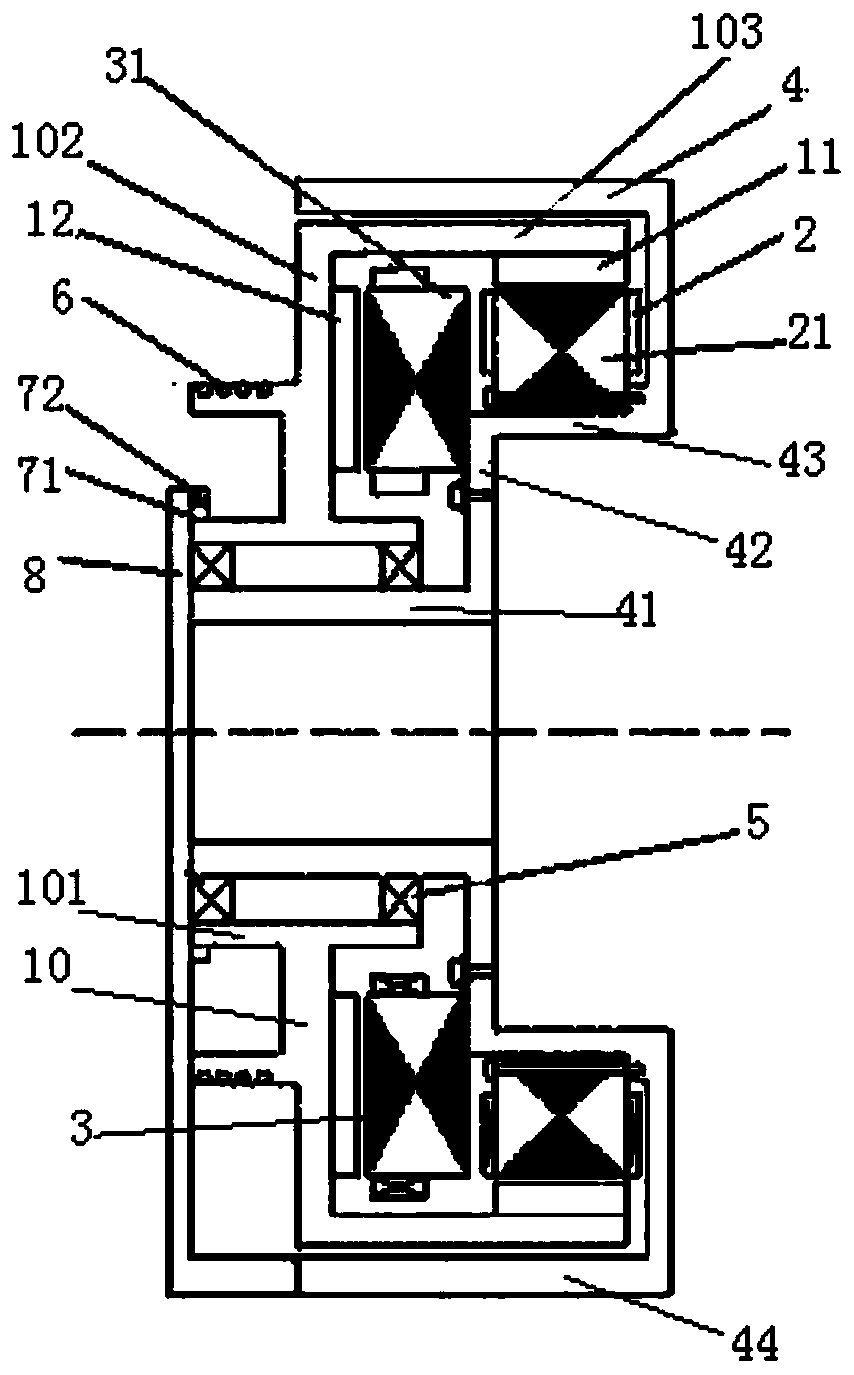
[0050] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the permanent magnet traction motor includes a rotor part, a first stator 2, a second stator 3 and a frame 4;
[0051] The rotor part includes a rotor bracket 10, a first magnet 11 and a second magnet 12;
[0052] The rotor bracket 10 includes a rotor inner tube part 101, a rotor ring plate part 102 and a rotor outer tube part 103;
[0053] The machine base 4 includes an inner tube portion 41 of the machine base, a ring plate portion 42 of the machine base, and an outer tube portion 43 of the machine base;
[0054] The inner tube part 101 of the rotor is in the shape of a round tube; the ring plate part 102 of the rotor is in the shape of a ring; the outer tube part 103 of the rotor is in the shape of a round tube;
[0055] The inner tube part 41 of the machine base is in the shape of a round tube; the ring plate part 42 of the machine base is in the shape of a ring; the outer tube part 43 of the machine base is in the shape o...
Embodiment 2
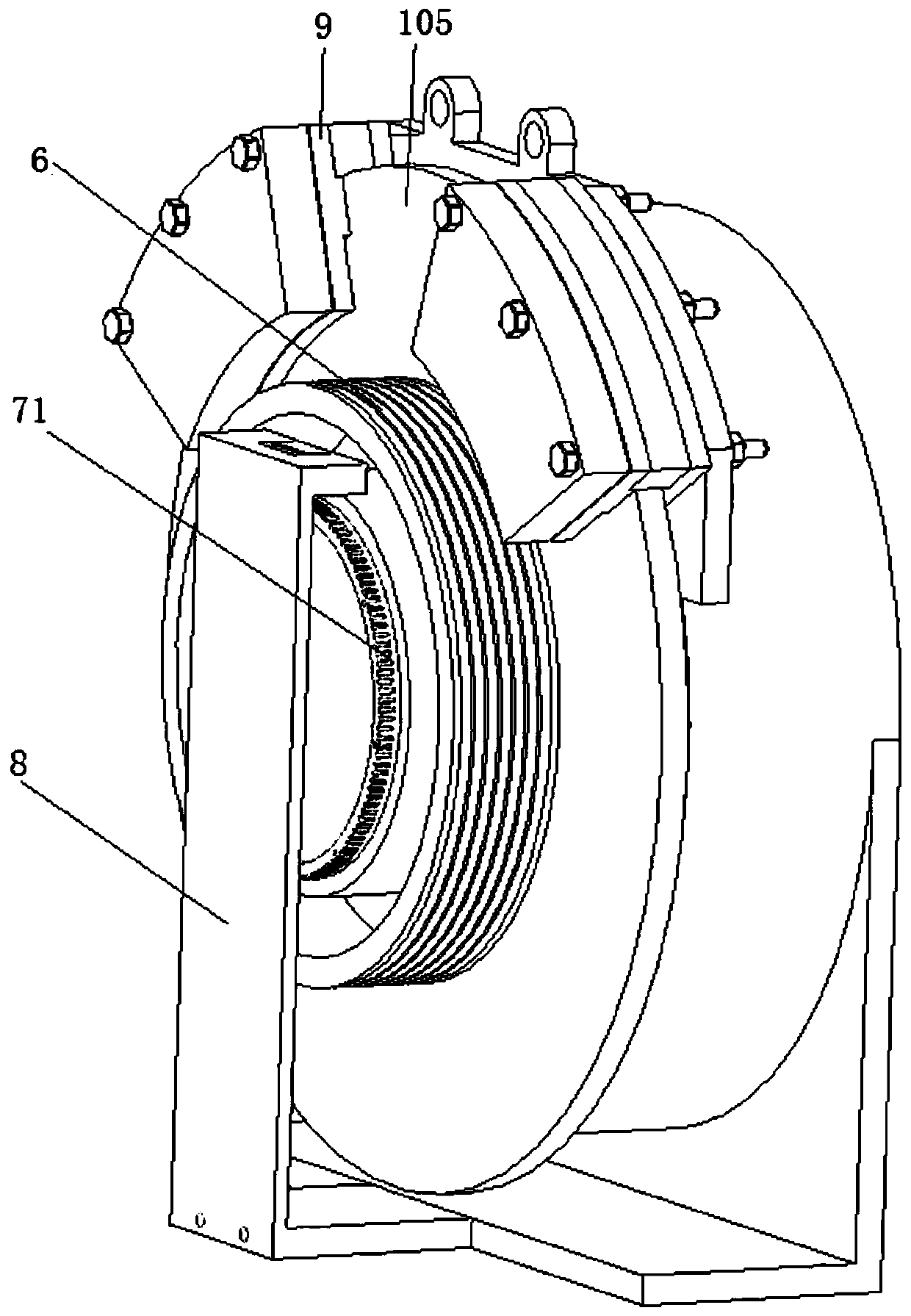
[0069] Based on the permanent magnet traction motor of the first embodiment, the left side of the rotor ring plate portion 102 of the rotor bracket 10 is integrally formed with a round tubular traction sheave portion 6 .
[0070] Embodiment two
[0071] Based on the permanent magnet traction motor of Embodiment 1, a ring-shaped rotor brake part 105 is once formed outward along the outer edge of the rotor ring plate part 102;
[0072] The brake pads 9 are located at the rotor brake part 105, and the left side and / or the right side of the rotor brake part 105 are used as braking surfaces to form a disc brake structure.
Embodiment 3
[0074] Based on the permanent magnet traction motor of Embodiment 1, the base 4 further includes a housing part 44 of the base;
[0075] The right end of the outer shell part 44 of the machine base is fixedly connected with the right end of the outer tube part 43 of the machine base;
[0076] The frame shell part 44 is sleeved on the outer tube part 103 of the rotor;
[0077] The brake is fixed on the shell part 44 of the machine base, the brake pad is in an arc shape, and the outer wall of the outer tube part 103 of the rotor is used as a braking surface to form a drum brake structure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com