Composition for base editing for animal embryo and base editing method
A technology of base editing and composition, applied in the field of base editing composition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] Example 1: Preparation of BE3 mRNA
[0154] By downloading pCMV-BE3 (Addgene; Catalog #73021; Image 6 ) was digested and separated, rAPOBEC1-XTEN (linker) and UGI (uracil DNA glycosylase inhibitor) were inserted into the pET-nCas9(D10A)-NLS vector (see Cho, S.W. et al. Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR / Cas-derived RNA-guidedendonucleases and nickases.Genome Res 24,132-141 (2014)) to construct pET-Hisx6-rAPOBEC1-XTEN-nCas9-UGI-NLS (SEQ ID NO:7; Figure 7 ) Then, it was used as BE3 mRNA template.
[0155] The sequence of each region in pET-Hisx6-rAPOBEC1-XTEN-nCas9-UGI-NLS (SEQ ID NO: 7) is summarized as follows:
[0156] His x6: SEQ ID NO: 8;
[0157] rAPOBEC1: SEQ ID NO: 9;
[0158] XTEN (linker): SEQ ID NO: 10;
[0159] nCas9(D10A): SEQ ID NO: 11;
[0160]Linker: TCTGGTGGTTCT (SEQ ID NO: 14)
[0161] UGI: SEQ ID NO: 12;
[0162] Linker: TCTGGTGGTTCT (SEQ ID NO: 14)
[0163] NLS: SEQ ID NO: 13.
[0164] In the presence of primers (F: 5'-GGT GAT GTC GG...
Embodiment 2
[0165] Embodiment 2: Preparation of sgRNA
[0166] The guide RNA (sgRNA) of the targeting dystrophin gene Dmd and tyrosinase gene Tyr with the following nucleotide sequences was synthesized and used for follow-up experiments:
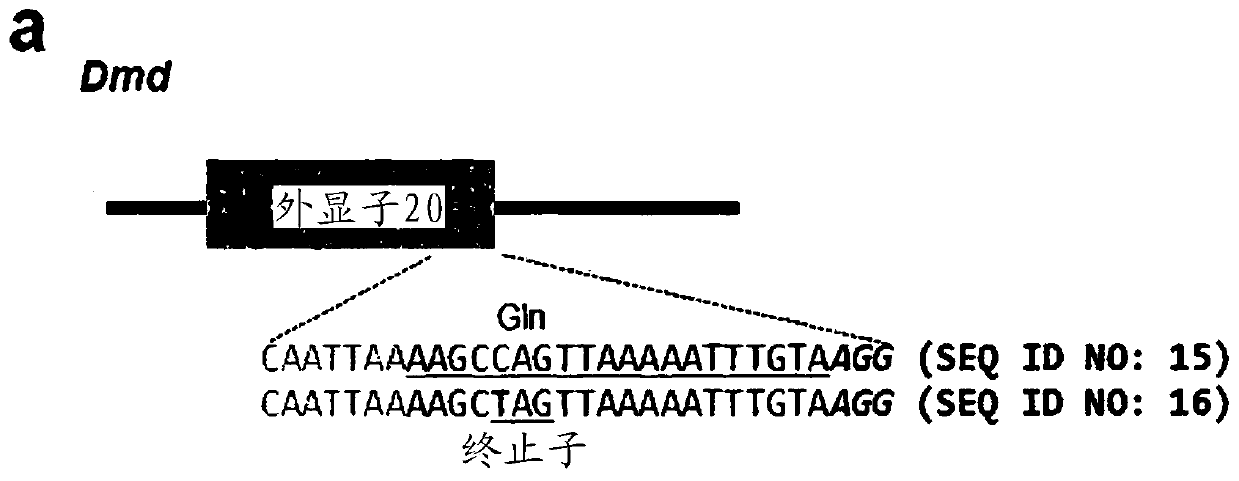
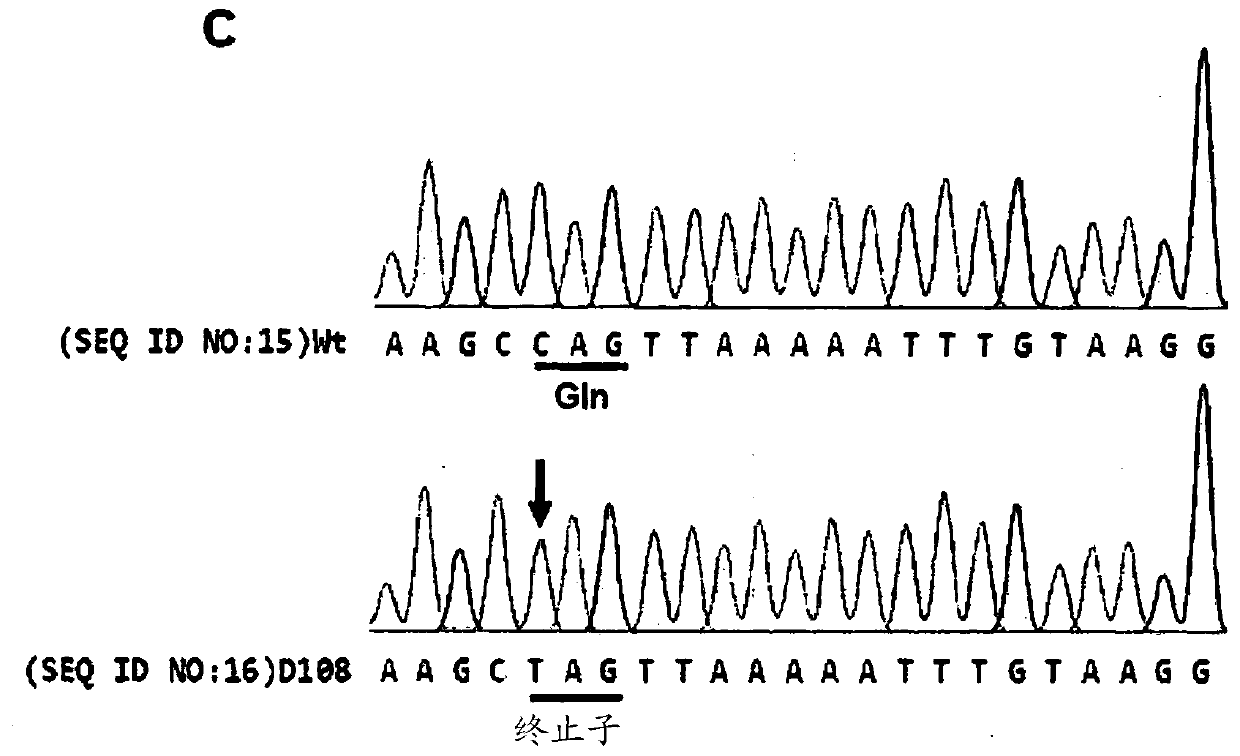
[0167] 5'-(target sequence)-(GUUUUAGAGCUA; SEQ ID NO:1)-(nucleotide linker)-(UAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGC; SEQ ID NO:3)-3'
[0168] (except that "T" is converted to "U", the target sequence is the same as Figure 1a (Dmd) or Figure 2a The underlined nucleotide sequences in (Tyr) are identical in sequence, and
[0169] The nucleotide linker has the nucleotide sequence of GAAA).
[0170] sgRNAs were constructed by in vitro transcription using T7 RNA polymerase (see Cho, S.W., Kim, S., Kim, J.M. & Kim, J.S. Targeted genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9RNA-guidedendonuclease. Nat Biotechnol 31, 230-232 (2013)).
Embodiment 3
[0171] Embodiment 3: the preparation of ribonucleoprotein (RNP)
[0172] Transform Rosetta Competent Cells (EMD Millipore) with the pET28-Hisx6-rAPOBEC1-XTEN-nCas9(D10A)-UGI-NLS(BE3) expression vector prepared in Reference Example 1, and then use 0.5mM isopropyl β-D- 1 Thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was incubated at 18°C for 12 to 14 hours to induce expression. After protein expression, the bacterial cells were harvested by centrifugation and passed through the lysis buffer [50mM NaH 2 PO 4 (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, 1% TritonX-100, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM DTT, and 1 mg / ml lysozyme] to lyse the cell pellet.
[0173] The cell lysate thus obtained was centrifuged at 5251 xg for 30 minutes to remove cell debris. Soluble lysates were incubated with Ni-NTA beads (Qiagen) for 1 hour at 4°C. Subsequently, wash buffer [50mM NaH 2 PO 4 (pH 8.0), 300mM NaCl and 20mM imidazole] to wash the Ni-NTA beads three times, and then wash them with elution buffer [50mM Tris-HCl (pH7.6),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com