Time sequence processing method and device for distributed target InSAR with enhanced space-time coherence
A processing method and coherence technology, applied in the directions of measurement devices, radio wave reflection/re-radiation, and utilization of re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of space-time coherence estimation error propagation, failure, and large space-time coherence estimation errors, etc., to achieve Effect of Uncertainty Reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
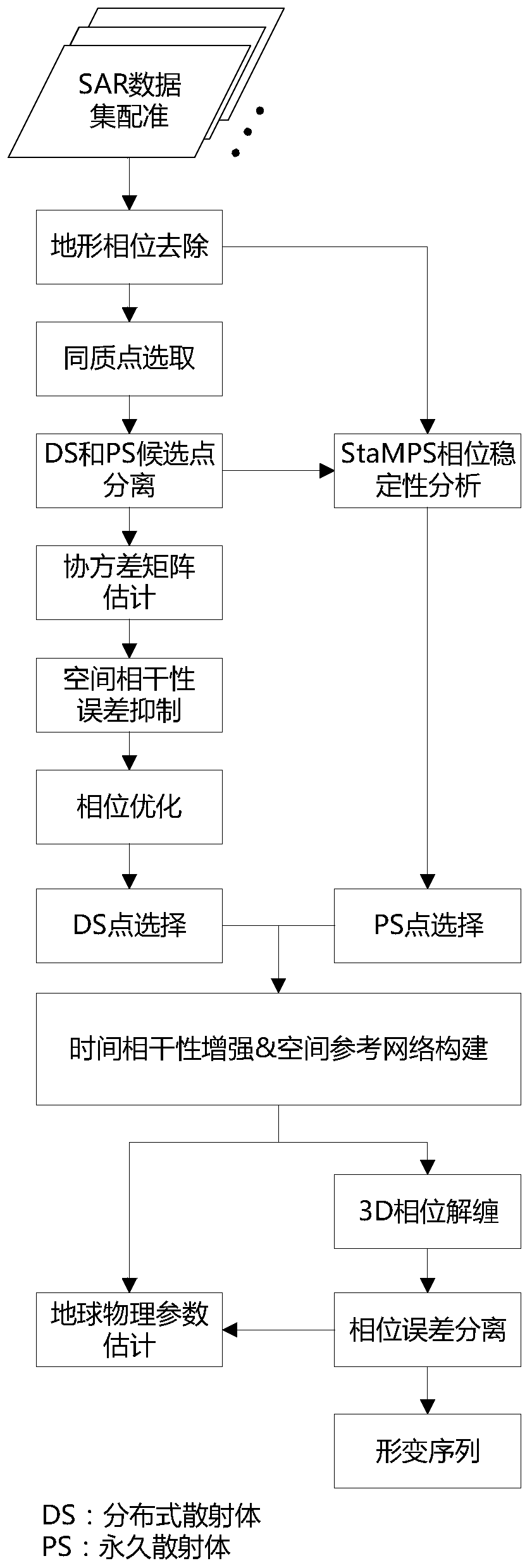
[0058] Embodiment 1: a distributed target InSAR timing processing method with enhanced spatio-temporal coherence, the specific steps are as follows (such as figure 1 shown):
[0059] 1) InSAR preprocessing. Geometric registration is performed on N single-type complex SAR data sequences on the basis of precise orbits and external digital elevation models, and single-view complex image data stacks are obtained. After radiometrically correcting the SAR image, a common main image is selected, and the remaining N-1 SAR images are interfered, and the external DEM is used to remove the topographic phase contribution of the interferometric image.
[0060] It should be noted that the method of the present invention is applicable to any spaceborne SAR data set, and the N-1 images after interference are differentiated to obtain all N(N-1) / 2 images. Therefore, this is a timing processing method that does not lose interfering information.
[0061] 2) Selection of homogeneous points. De...
Embodiment approach 2
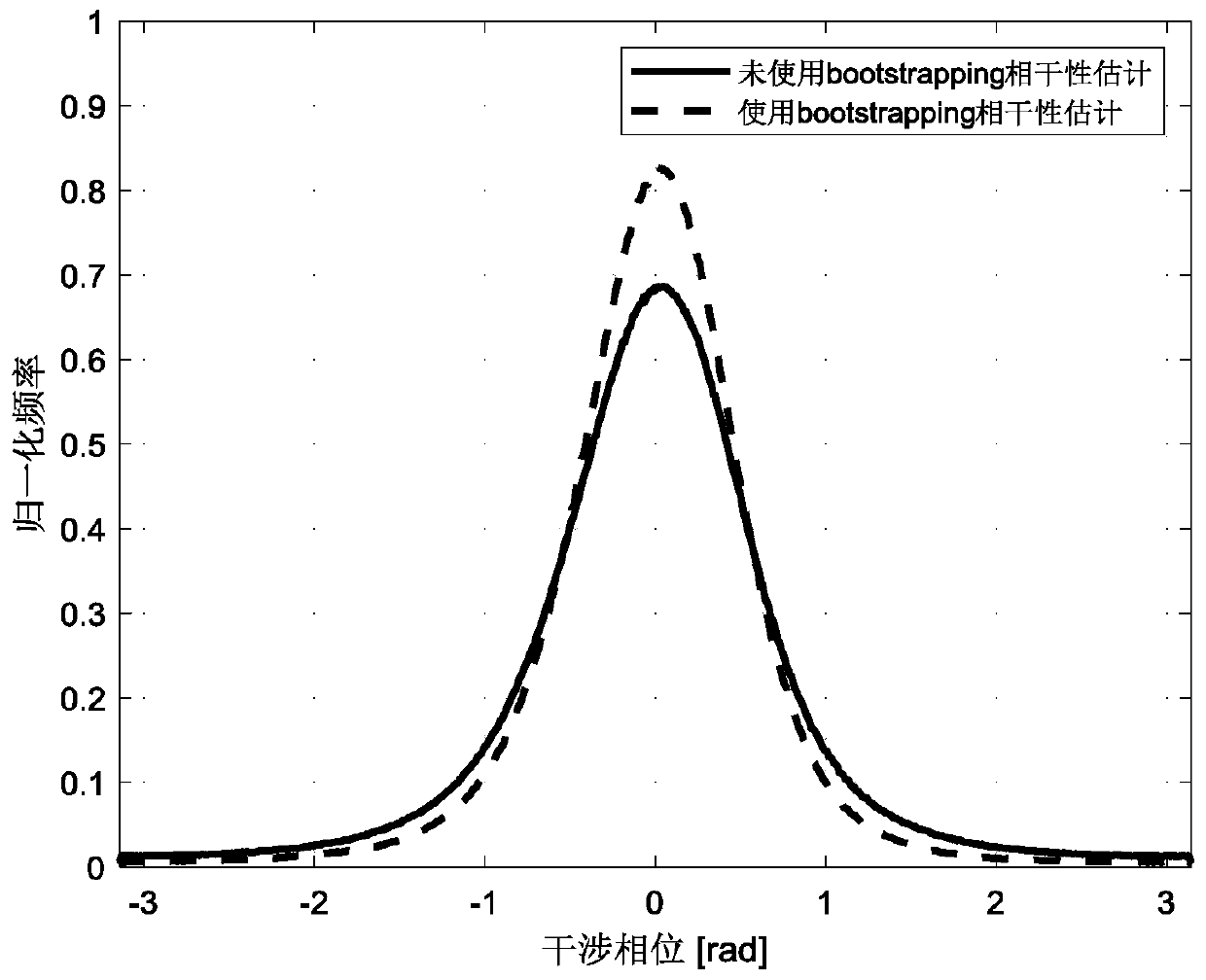
[0076] On the basis of the above embodiment, after step 5) estimates the covariance matrix for each DS candidate point in space one by one, the following bootstrapping estimator is used to weaken the error of the spatial coherence estimation in the covariance matrix, for each The covariance matrix of spatial pixels in the coherence matrix To correct, the expression is as follows:
[0077]
[0078] where R represents the bootstrapping replication number, Represents the coherence matrix samples estimated at each bootstrapping replication. Next, average the variance-reduced variance over all the bias-corrected neighborhood coherence matrix samples:
[0079]
[0080] Optimize the phase using the corrected covariance matrix as follows:
[0081] Obtaining Optimal Phases of Time Series Based on a Maximum Likelihood-Eigenvalue Decomposition Estimator
[0082]
[0083] in Indicates the inversion of the coherence matrix, Indicates the product of Hadamard, Represents...
Embodiment approach 3
[0092] On the basis of the above embodiments, this embodiment uses the Floyd-Warshall multi-source shortest path algorithm in graph theory to select the optimal sub-path of the starting point p and the ending point q.
[0093] First, the PS points are used to form edges with Delaunay triangulation, the purpose of which is to obtain the starting point p and end point q of each edge; this requires first exploring all edges of M PS points. Because the farther the distance between the two points, the more serious the interference from the atmosphere, etc., so the distance needs to be restricted in advance, for example, less than 2000 meters. Estimate the temporal coherence of at most M(M-1) / 2 constrained edges in order to determine the weight of the shortest path algorithm:
[0094]
[0095] where K represents the number of interferograms (single or multi-primary image temporal network), e p,q Indicates the double-difference phase of edges p, q. Convert temporal coherence to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com