Method for controlling outlet temperature of cooling liquid of electronic equipment
A technology for cooling liquid outlet and control electronics, which is applied to structural parts of electrical equipment, cooling/ventilation/heating renovation, electrical components, etc., which can solve the complexity of liquid cooling control system, realize low cost, and break the upper limit of cooling liquid outlet temperature and other problems, to achieve the effect of high reliability, lower system cost, and lower complexity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
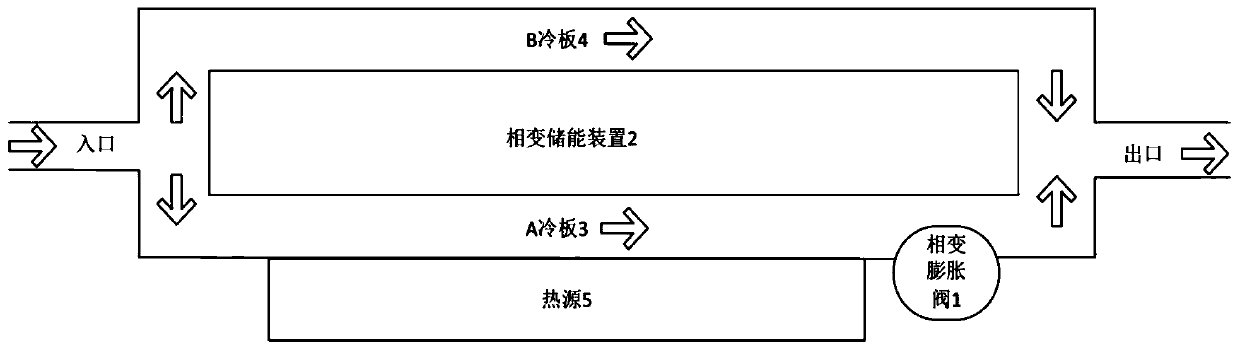
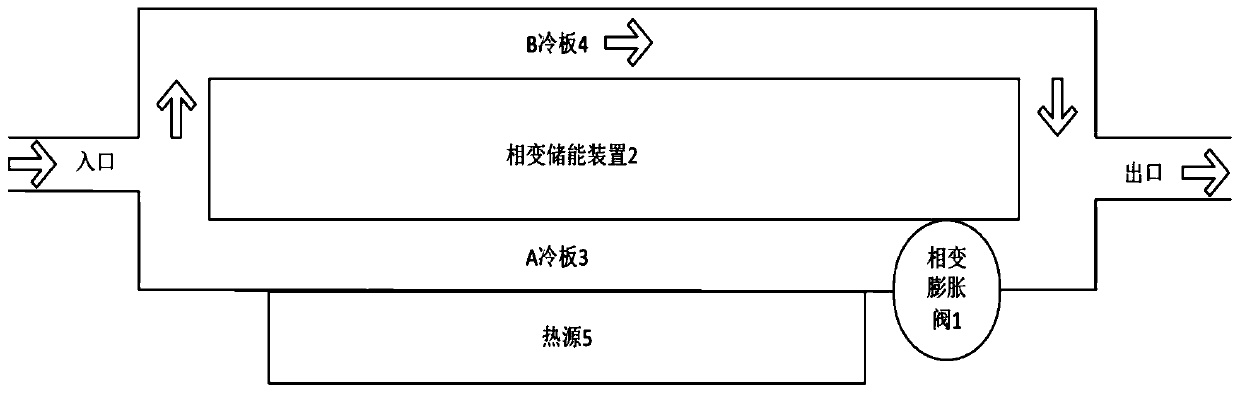
[0023] When the heat source is loaded under typical low heat consumption conditions, the flow channels of cold plate A and cold plate B are connected at the same time, and the phase change energy storage device and the phase change expansion valve are not working. After the coolant enters the liquid cooling system from the inlet, it flows through the The cold plate runner is heated by the heat source and discharged from the outlet of the runner. At this time, because it is a low heat consumption condition, the outlet temperature does not exceed the allowable value.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Load the heat source under typical high heat consumption conditions. The phase change expansion valve located downstream of the flow channel of the cold plate A undergoes a phase change when heated, and the volume expands significantly to block the flow channel of the cold plate A, shut off the flow channel of the cold plate A, and all the cooling liquid flows from the cold plate B Runner through. The heat first passes through the phase change energy storage device before reaching the B cold plate as the final heat sink. During this process, the phase change energy storage device absorbs heat and undergoes a phase change at its phase change point, and the phase change material in it becomes liquid , and release a heat consumption lower than the total heat consumption of the heat source at the contact surface with the B cold plate. Therefore, the coolant flowing through the channel of the cold plate B only needs to absorb a relatively low amount of heat per unit time, s...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Load the heat source again with typical low heat consumption conditions. At this time, the heat release rate of the phase change energy storage device is greater than its heat absorption rate, and the phase change material in it undergoes a phase change again to return to a solid state; at the same time, the phase change expansion valve also undergoes a phase change again, and the volume shrinks, thereby opening A The flow channel of the cold plate makes the liquid cooling system return to its original state.
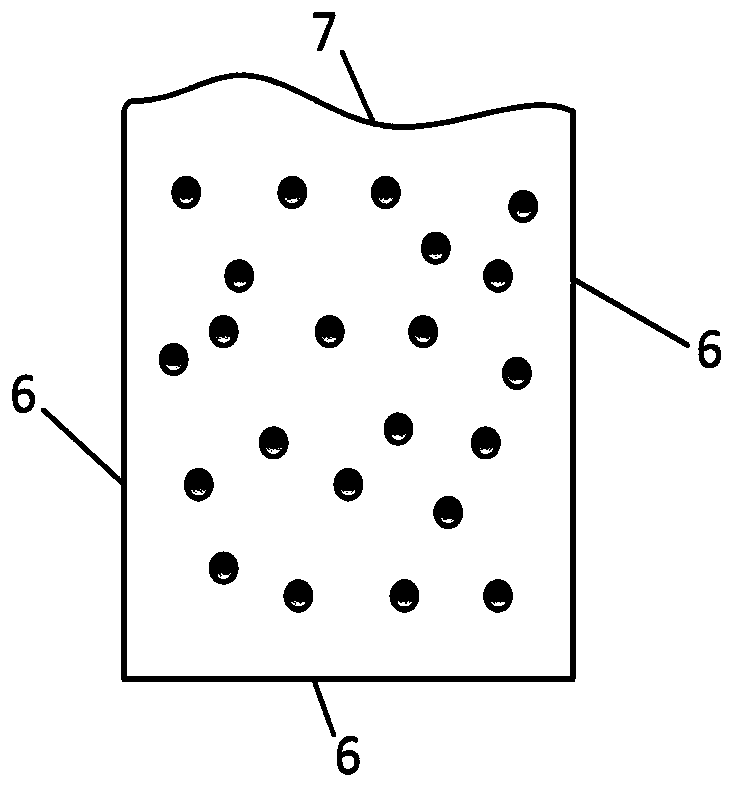
[0028] In an optional embodiment, the phase change material is packed into a box made of aluminum alloy 6 except for the top surface, the top surface of the box is made of flexible material 7, and the box is packaged to form a phase change expansion valve 1 . The phase change material is packaged into the metal cavity to form the phase change energy storage device 2 .
[0029] The phase change energy storage device 2 is connected with the cold plate A 3 and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com