Data transmission method and system between memory database system and data warehouse system
A data transmission method and data transmission system technology, applied in the field of data processing, to achieve real-time efficient processing capabilities and comprehensive data analysis effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
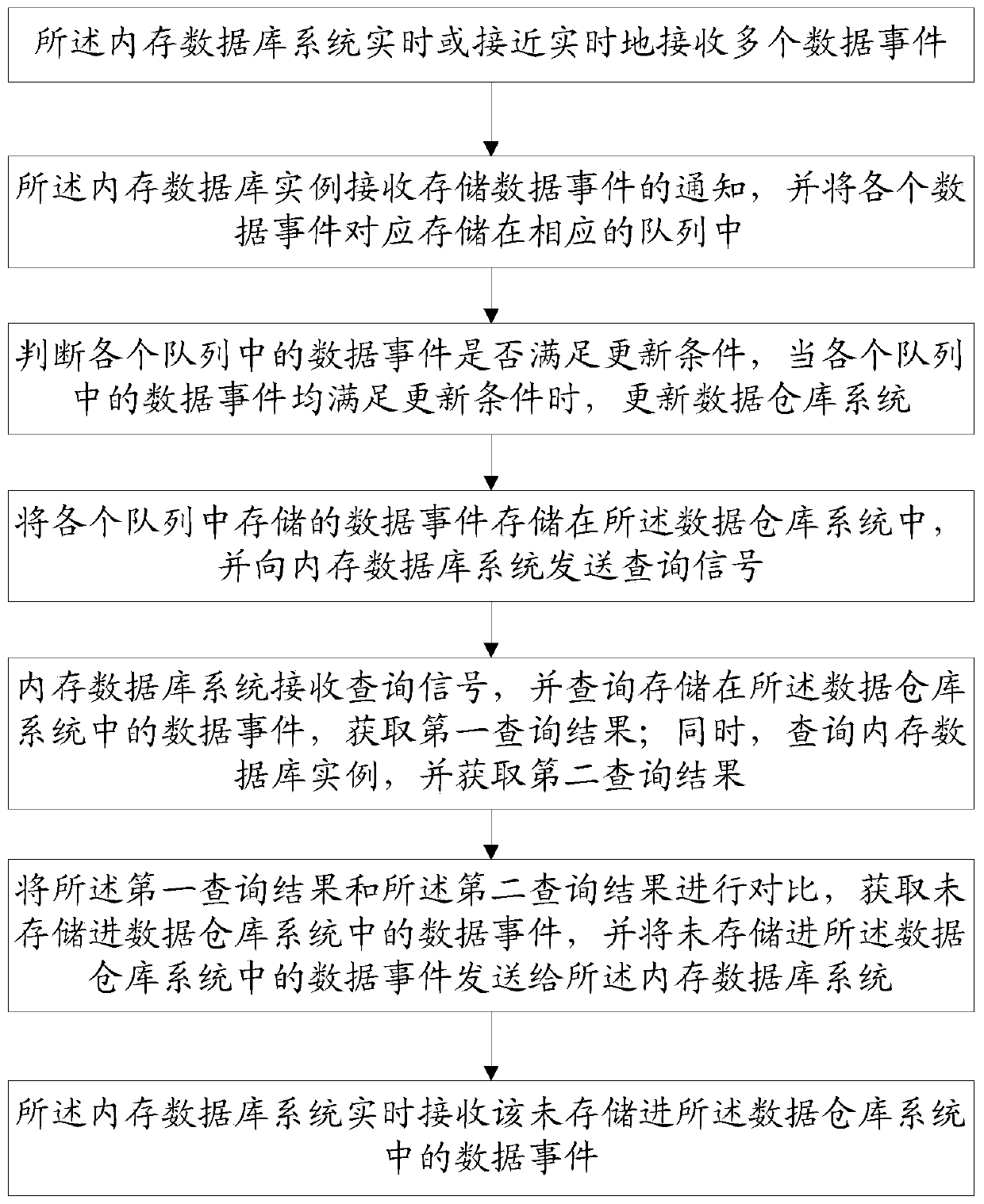
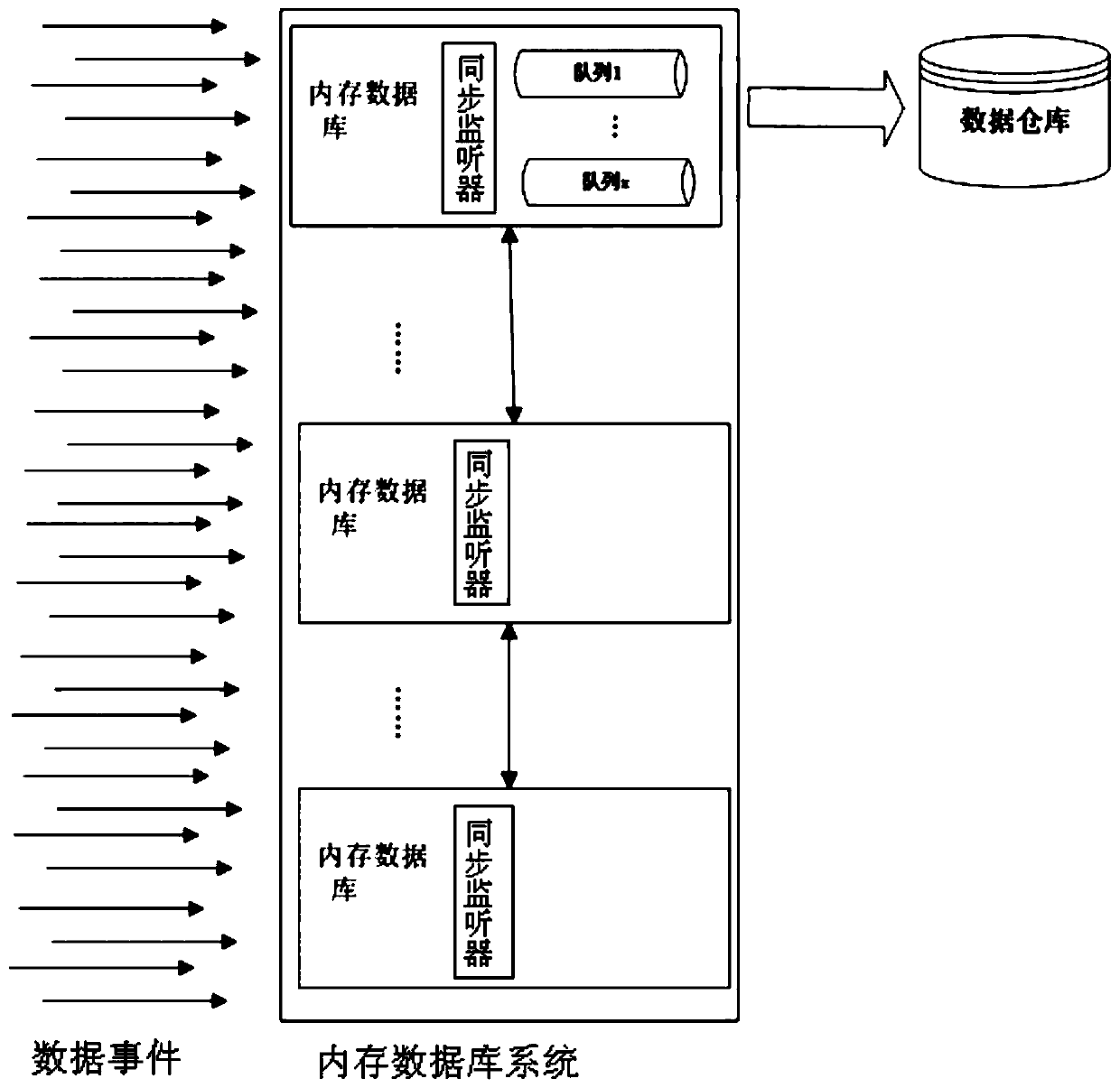
[0042] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 2As shown, this embodiment provides a method for data transmission between an in-memory database system and a data warehouse system, the in-memory database system includes multiple parallel in-memory databases, and the in-memory database system also stores multiple At least one in-memory database instance for in-memory database parallel operation, including the following steps,
[0043] S1. The in-memory database system receives multiple data events in real time or close to real time;
[0044] S2. The in-memory database instance receives a notification of a stored data event, and correspondingly stores each data event in a corresponding queue;
[0045] S3. Judging whether the data events in each queue meet the update conditions, and when the data events in each queue meet the update conditions, update the data warehouse system;
[0046] S4. Store the data events stored in each queue in the data warehouse system, and send a query signal to t...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Such as image 3 As shown, in this embodiment, the in-memory database system includes multiple in-memory databases, and the in-memory databases form an in-memory database instance in parallel, and they are communicatively coupled to the data warehouse system, and the data warehouse system includes at least one data warehouse. Although each in-memory database includes a sync listener, there is only one instance of the in-memory database.
[0061] In this embodiment, although the in-memory database system receives many input data events such that any in-memory database can receive data interactions, the queuing is done by only one instance, the in-memory based database. In this implementation; all queues reside in a single in memory database. Each synchronous listener that receives a data event in its associated in-memory database can go through the process of identifying which queue received the data event and then deliver that information to the appropriate queue. As ...
Embodiment 3
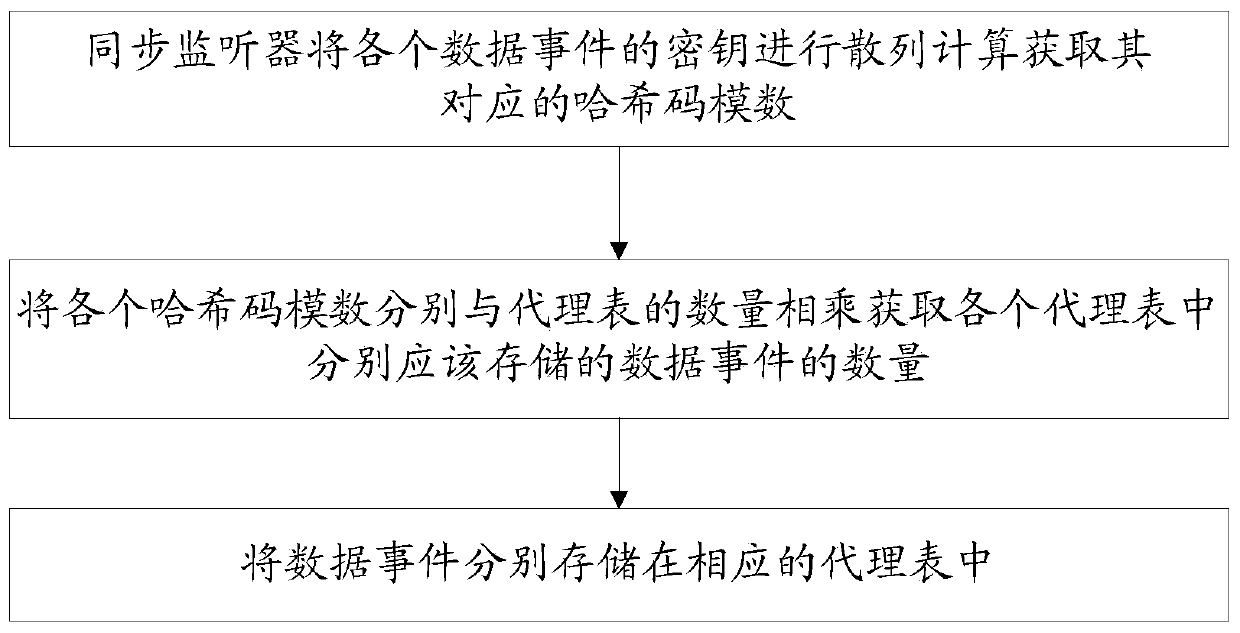
[0063] Such as Figure 4 As shown, in this embodiment, the in-memory database system includes multiple in-memory database instances, which are communicatively coupled to the data warehouse system, and the data warehouse system may include at least one data warehouse. Each in-memory database includes a synchronous listener and also includes a queue; an in-memory database includes a proxy table and related micro-batch listeners. Unlike the second embodiment, the queues in this embodiment are distributed to multiple in-memory databases. An advantage of this configuration is that queues occupy resources that are separate from system resources, which can improve overall throughput. In an embodiment, network hopping is unnecessary in this architecture because the queue for each event is defined in the in-memory database where the event occurred. Each synchronous listener receives data events in its associated in-memory database and passes the received data events to the appropriate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com