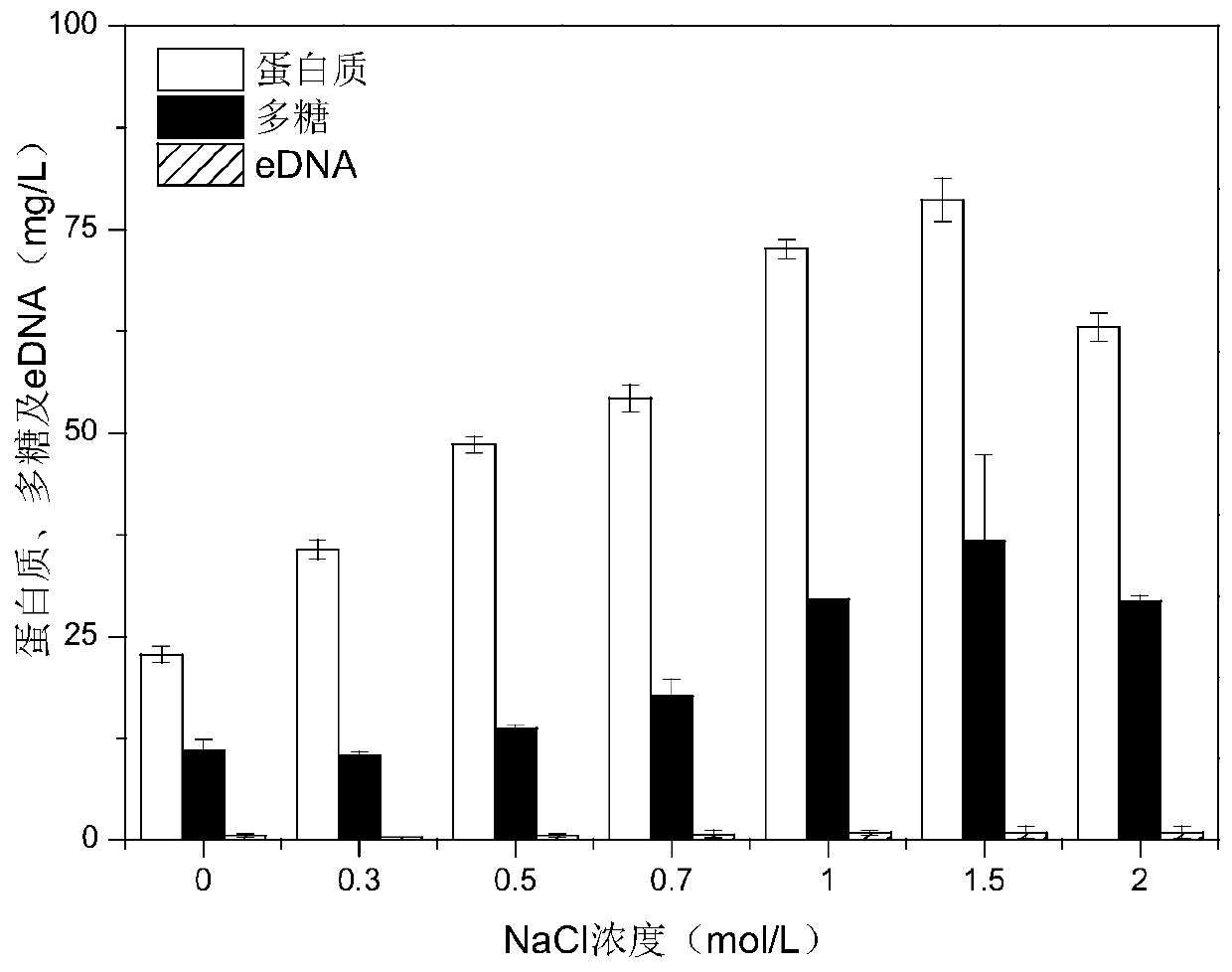
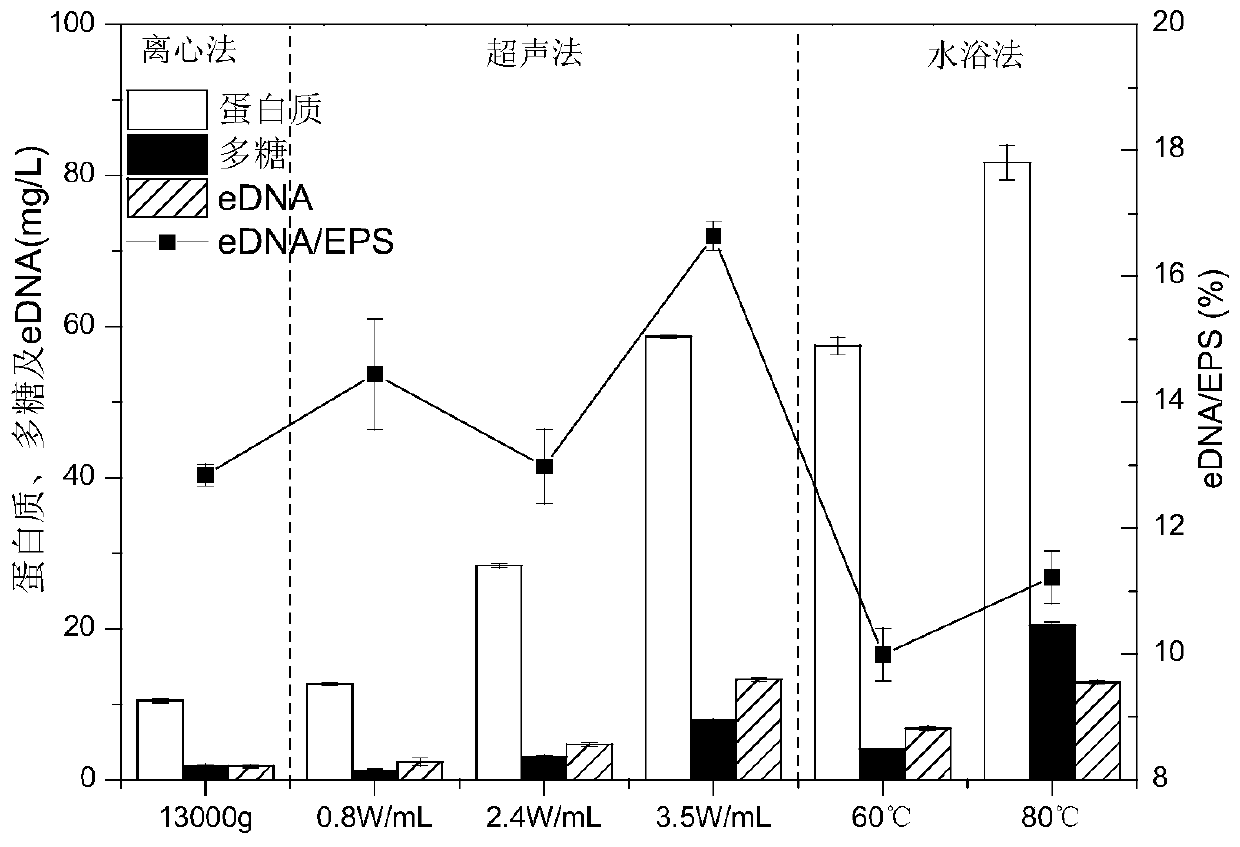
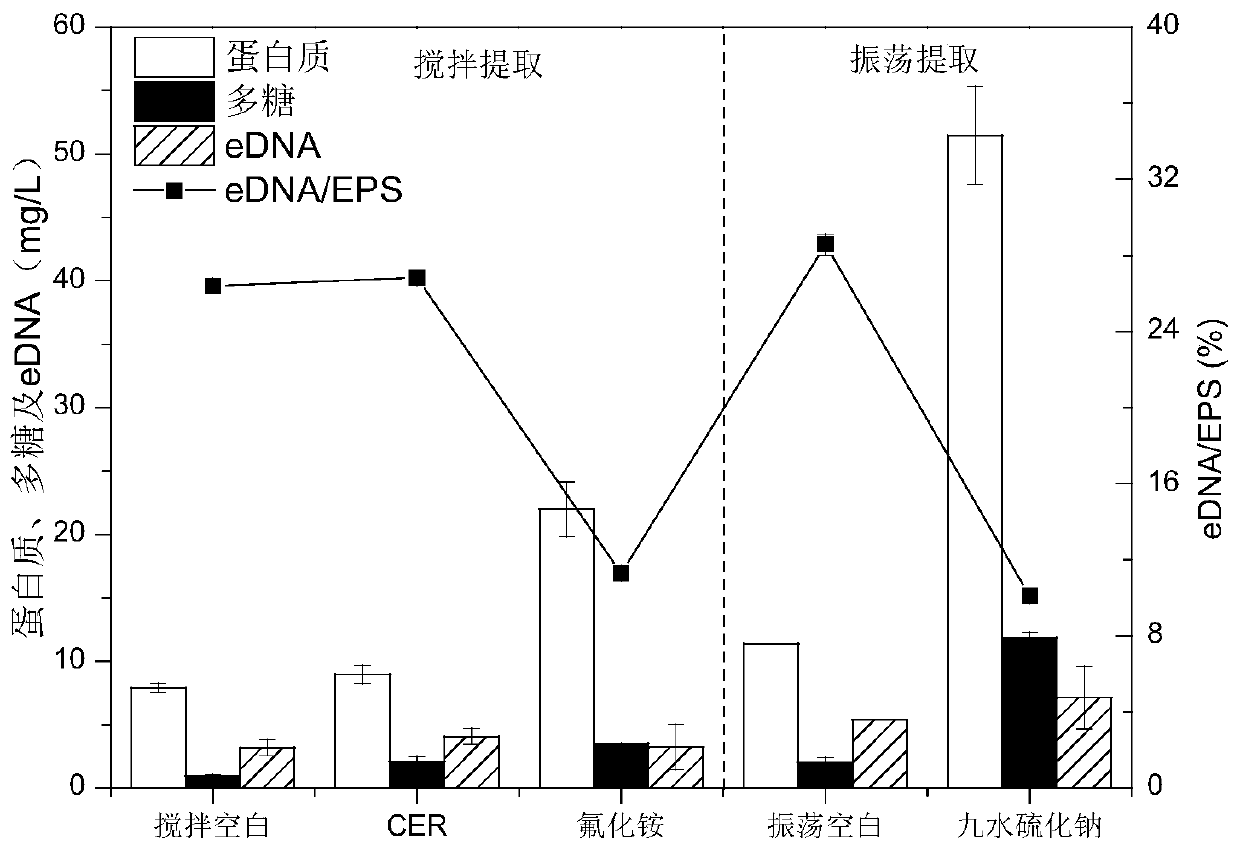
Method for extracting activated sludge extracellular polymers
A technology of extracellular polymers and activated sludge, applied in sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as low yield, incomplete coverage, and no unified extraction steps , to achieve the effect of high purity and high extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0084] A method for extracting LB-EPS of activated sludge extracellular polymers. The resuspension of the first sludge sediment is heated at 60°C or 80°C in a water bath for 5 minutes, and then the centrifugal force is 13000×g, the temperature Under the condition of 4°C, centrifuge for 15 minutes to separate the LB-EPS supernatant and the second sludge sediment.
Embodiment 2
[0089] A method for extracting ionic TB-EPS in the second sludge sediment, comprising: according to the Na 2 S·9H 2 The mass ratio of O to the second sludge sediment is 1:4, and the Na 2 S·9H 2 O was added to the resuspension of the second sludge sediment, and after being treated for 1 hour under airtight conditions with a rotation speed of 400 rpm, a temperature of 4°C, and full of nitrogen and protected from light, the NH 4 The mass ratio of F to the second sludge sediment is 1:5.9, adding the NH 4 F, under the conditions of rotation speed of 600 rpm and temperature of 4°C, the treatment was carried out for 1 hour, and the ionic TB-EPS supernatant and the third sludge sediment were separated.
Embodiment 3
[0094] A method for extracting hydrophobic TB-EPS in the third sludge sediment, comprising: adding SDS 140mg / g VSS to the third sludge sediment, stirring at 600rpm, 4°C for 45min, and then passing through 13000× g. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 minutes, and then filter the supernatant through a 0.22 μm filter membrane, which is the hydrophobic TB-EPS.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com