A method for resource utilization of epichlorohydrin waste water
A technology of epichlorohydrin and recycling, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, natural water treatment, etc. It can solve the problems of high temperature and high pressure in the wet oxidation process, the inability to recycle organic matter, and high requirements for equipment materials to achieve the treatment effect. Stable and reliable, easy for industrial implementation, and the effect of reducing COD content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
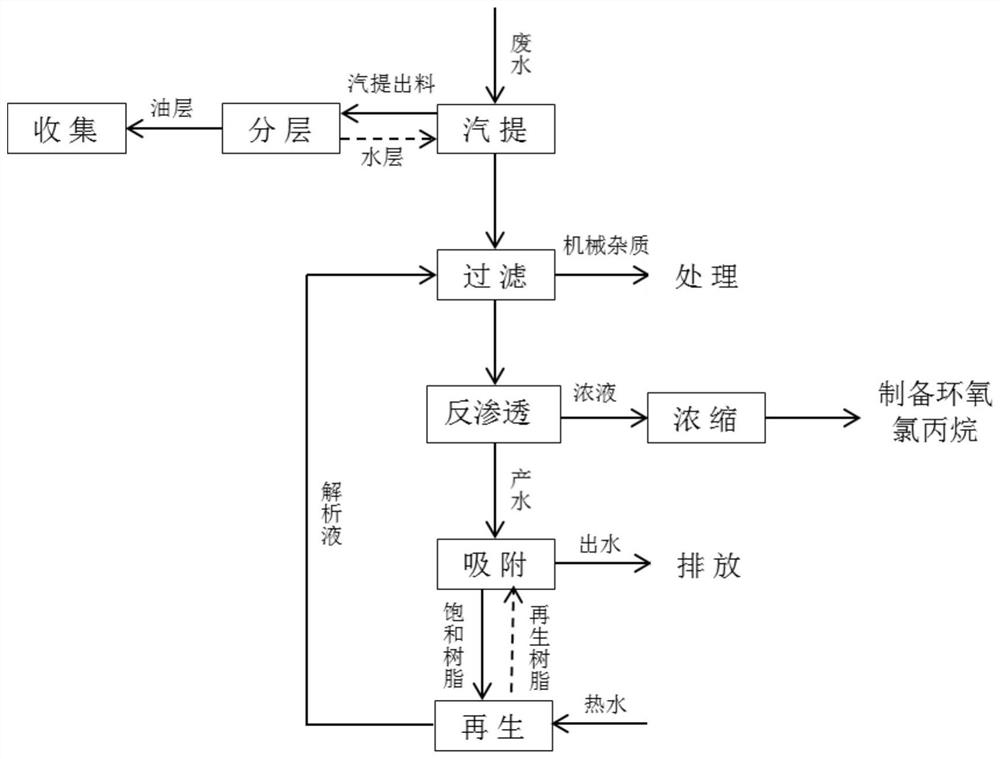
[0032] (1) Stripping
[0033] The epichlorohydrin waste water enters the stripper after preheating. Under the conditions of the operating temperature of the stripper at 95-105°C, a slight negative pressure of -0.025Mpa, and a theoretical plate number of 10, the stripped material enters the oil-water stratifier , the oil layer is recovered, the water layer is returned to the stripper kettle, and the overhead distillation amount of the stripper is under the condition of 7.0% of the inlet amount, the water COD of the stripper still kettle is 42710ppm, epichlorohydrin is not detected, and monochloropropanediol is 3.1% .
[0034] (2) reverse osmosis concentration
[0035] The water in the stripping tower is cooled to 25-35°C, and filtered through a precision filter to remove mechanical impurities. After filtration, it is sent to the reverse osmosis membrane concentration device through a booster pump. Water COD2780ppm, monochloropropanediol 0.15%, monochloropropanediol content in...
Embodiment 2
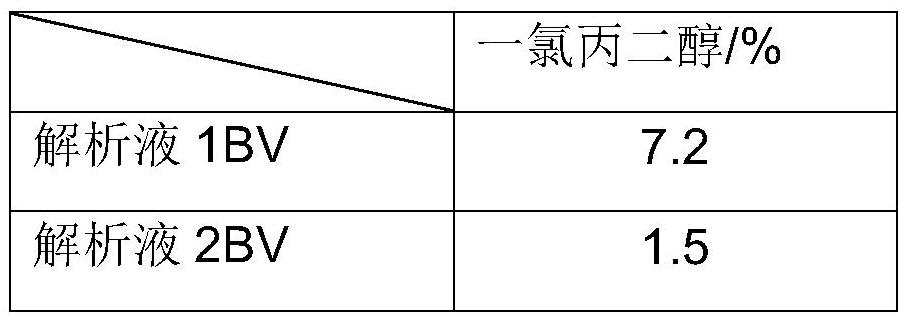
[0042] On the basis of Example 1, the pressure of the reverse osmosis concentration process is reduced to 3.0MPa, and the product water COD1765ppm, 0.09% of monochloropropanediol, and 15.0% of monochloropropanediol in the reverse osmosis membrane dope are further concentrated to more than 50% to prepare epoxy chlorine propane. The reverse osmosis product water enters the resin adsorption tower at a rate of 1BV / h, the effluent COD is 80ppm, monochloropropanediol is not detected, and pH=7.0, which meets the discharge requirements. The resin is saturated with about 100BV of water inflow, and is regenerated with hot water at 60-80°C, and the total yield of monochloropropanediol is 99.95%.
Embodiment 3
[0044] Improve reverse osmosis concentration process pressure to 5.0MPa on the basis of example 1, obtain product water COD3290ppm, monochloropropanediol 0.20%, monochloropropanediol 30.0% in reverse osmosis membrane dope, further concentrate to more than 50% to prepare epichlorohydrin . The reverse osmosis product water enters the resin adsorption tower at a rate of 1BV / h, the effluent COD is 95ppm, monochloropropanediol is not detected, and pH=7.0, which meets the discharge requirements. The resin is saturated when the influent reaches about 45BV, and it is regenerated with hot water at 60-80°C, and the total yield of monochloropropanediol is 99.93%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com