Novel cairna moschata adenovirus strain, novel cairna moschata adenovirus inactivated vaccine, and preparation method for inactivated vaccine
A virus inactivation, Muscovy duck gland technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, viruses, antiviral agents, etc., can solve problems such as economic losses in the Muscovy duck breeding industry, achieve good commercial development prospects, and reduce economic losses. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Example 1: Isolation and identification of Muscovy duck novel adenovirus GD MM strain
[0037] 1 Epidemiological survey
[0038]Since 2014, young muscovy ducks in Guangdong, Fujian, Anhui and other regions have developed infectious diseases with symptoms such as liver swelling and congestion, varying degrees of hemorrhage or necrosis on the surface, brittle texture, and liver color turning yellowish or white. . The disease usually affects Muscovy ducks under 1 month old, and the morbidity and mortality show a certain age-related correlation. At present, the prevalence of the disease is found in almost all Muscovy duck breeding areas. After clinical investigation and laboratory testing, the preliminary diagnosis was a new type of duck adenovirus. In 2018, a strain of the virus was successfully isolated from a group of 20-day-old Muscovy ducks in a Muscovy duck farm in Maoming, Guangdong.
[0039] 2 Virus isolation:
[0040] Select 50-100g of dead muscovy duck liver,...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Embodiment 2: the preparation of Muscovy duck novel adenovirus GD MM strain seed
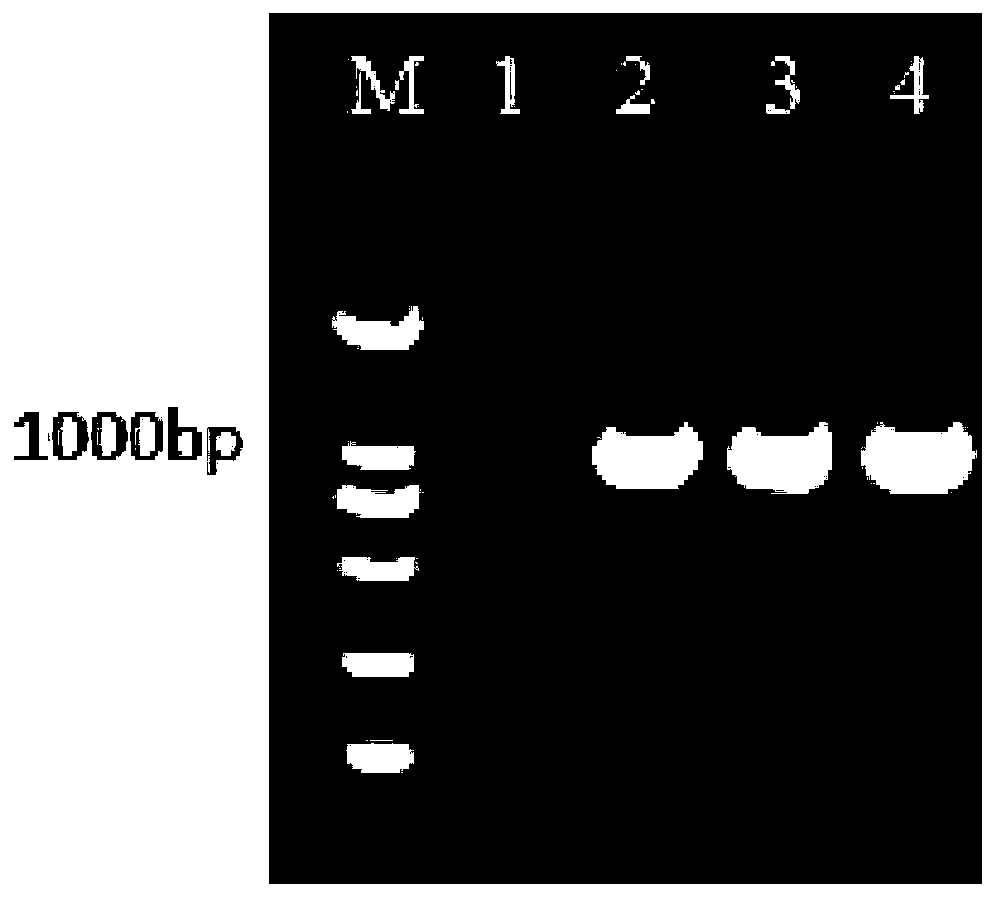
[0065] Take the third-generation embryotoxic allantoic fluid of Muscovy duck new adenovirus, filter it through a 0.22 μL filter, inoculate LMH cells growing to a single layer at a ratio of 3-5% of the culture medium, and discard the original culture medium, and adsorb for 1 hour at 37°C Discard the virus liquid, and then add bovine serum-free DMEM / F12 virus maintenance solution, 37 ° C, 5% CO 2 Under the condition of static culture for 72-96h, the virus fluid was harvested. The LMH cells were subcultured to proliferate the F5-F9 generation until more than 80% of the cells became lesioned, and the lesion time was controlled within 72-96 hours to harvest the virus liquid. Measure the virus content of this strain 5-9 generations, the results are shown in Figure 7 . Mix the sterile virus liquid tested in the same generation, quantitatively aliquot it, and store it in a -80°C refrigerator....
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3: Preparation of muscovy duck novel adenovirus GD MM strain antigen
[0067] LMH cell culture: Take LMH cells grown to a dense monolayer, discard the original culture medium, wash the cells with sterile PBS, digest with 0.25% trypsin, discard the trypsin solution, add an appropriate amount of 8% fetal bovine serum The DMEM / F12 cell culture medium was used to mix the cells, and the cells were passaged at a ratio of 1:4-1:5, at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured to a monolayer of cells.
[0068] Inoculation: Discard the original culture medium of the above-mentioned LMH cells covered with a single layer, inoculate LMH cells at a final concentration of 1‰-1%, and place at 37°C in 5% CO 2 The incubator under the condition continued to cultivate for 72-96h.
[0069] Toxic collection: After receiving the poison, observe twice a day, and record the cell lesions. Harvest the virus liquid when the cytopathy reaches more than 80%, and store it at -20°C.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com