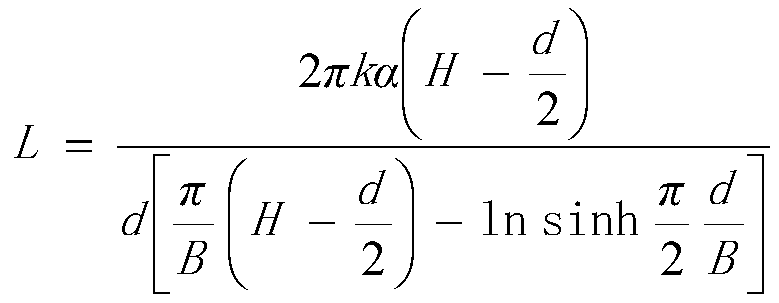Overexploitation area surface water-saving irrigation and low-pressure underground pipe network recharge exploitation supplement coupled system
An underground pipe network and coupling system technology, applied to watering devices, filtration circuits, separation methods, etc., can solve problems such as water waste, reduce filtration efficiency, and affect water flow, so as to avoid engineering volume and land occupation, and improve soil quality. Moisture content, the effect of accelerating the recharge process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
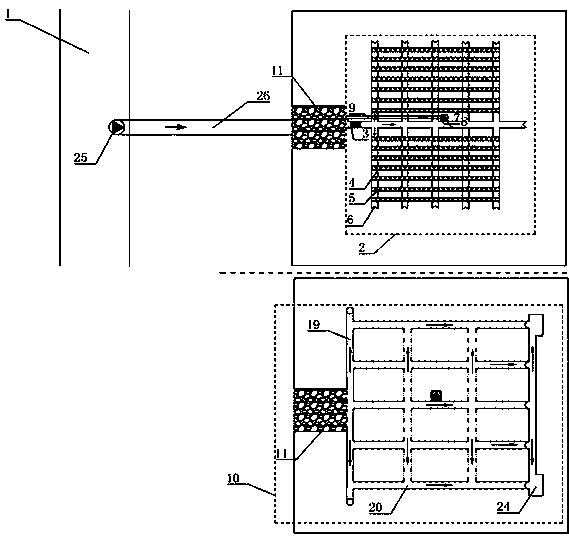
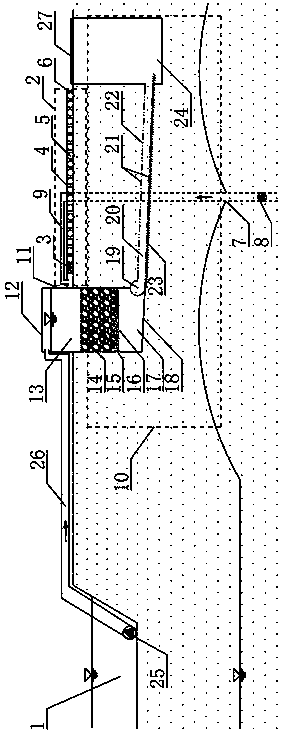
[0034] A coupling system of surface water-saving irrigation in over-exploitation areas and low-pressure underground pipe network recharge and supplementary extraction. It can get rid of the limitation of ditches and avoid the amount of work and land area caused by excavation of ditches. It uses pumping to make water intake. More convenient and flexible. It includes water source 1, filter tank 11, underground pipe network, surface drip irrigation 2 and groundwater replenishment.
[0035] The filter tank 11, the water inlet end of the filter tank 11 is connected to the water source 1 through the first centrifugal pump 25 and the first delivery pipe 26;
[0036] The underground pipe network includes a plurality of inter-connected underground water filter pipes 20 arranged in a crisscross pattern. One end of the underground water filter pipe 20 is connected to the filter tank through a water collection pipe 19, and the other end is connected to the grit tank 24;
[0037] Surface drip ir...
Embodiment 2
[0107] A coupling system of surface water-saving irrigation and low-pressure underground pipe network recharge and supplementary extraction in an over-extraction area, and its structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0108] In this embodiment, the filter tank 11 is 5m long, 5m wide, and 3m high. The water level of the buffer water distribution zone 13 is 2m, the filter material 15 is 0.4m, and the supporting layer 16 is 0.1m thick. The height of the space 17 is 0.5 m.
[0109] Its aperture d 0 = 3d 50 , Hole spacing L 0 =1.2d 0 , Where d 0 Is the diameter of the hole, L 0 Is the distance between round holes, d 50 It is the largest particle diameter when the total screening weight of rock and soil samples at the location of the underground water filter pipe is 50%. Filter material 15 particle size D 50 = 7d 50 ′, where D 50 Is the largest particle diameter of 50% of the sieved weight in the particle composition of the filter material, d 50 ′ Is the largest particle diameter ...
Embodiment 3
[0122] A coupling system of surface water-saving irrigation and low-pressure underground pipe network recharge and supplementary extraction in an over-extraction area, and its structure is the same as that of Embodiment 1.
[0123] In this embodiment, the filter tank 11 is 6m in length, 6m in width, and 3m in height, the water level of the buffer water distribution zone 13 is 2m, the height of the filter material 15 is 0.4m, and the thickness of the supporting layer 16 is 0.1m. The height of the space 17 is 0.5 m. The diameter of the circular filter hole 22 is d0=5d50, the hole spacing L0=1.5d0, where d0 is the diameter of the round hole, L0 is the hole spacing, and d50 is the cumulative sieving weight of the rock and soil sample at the location of the water filter pipe is 50% Maximum particle diameter. The particle size of the filter material 15 is D50=8d50, where D50 is the maximum particle diameter of 50% of the total sieved weight in the particle composition of the filter ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| osmotic coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com