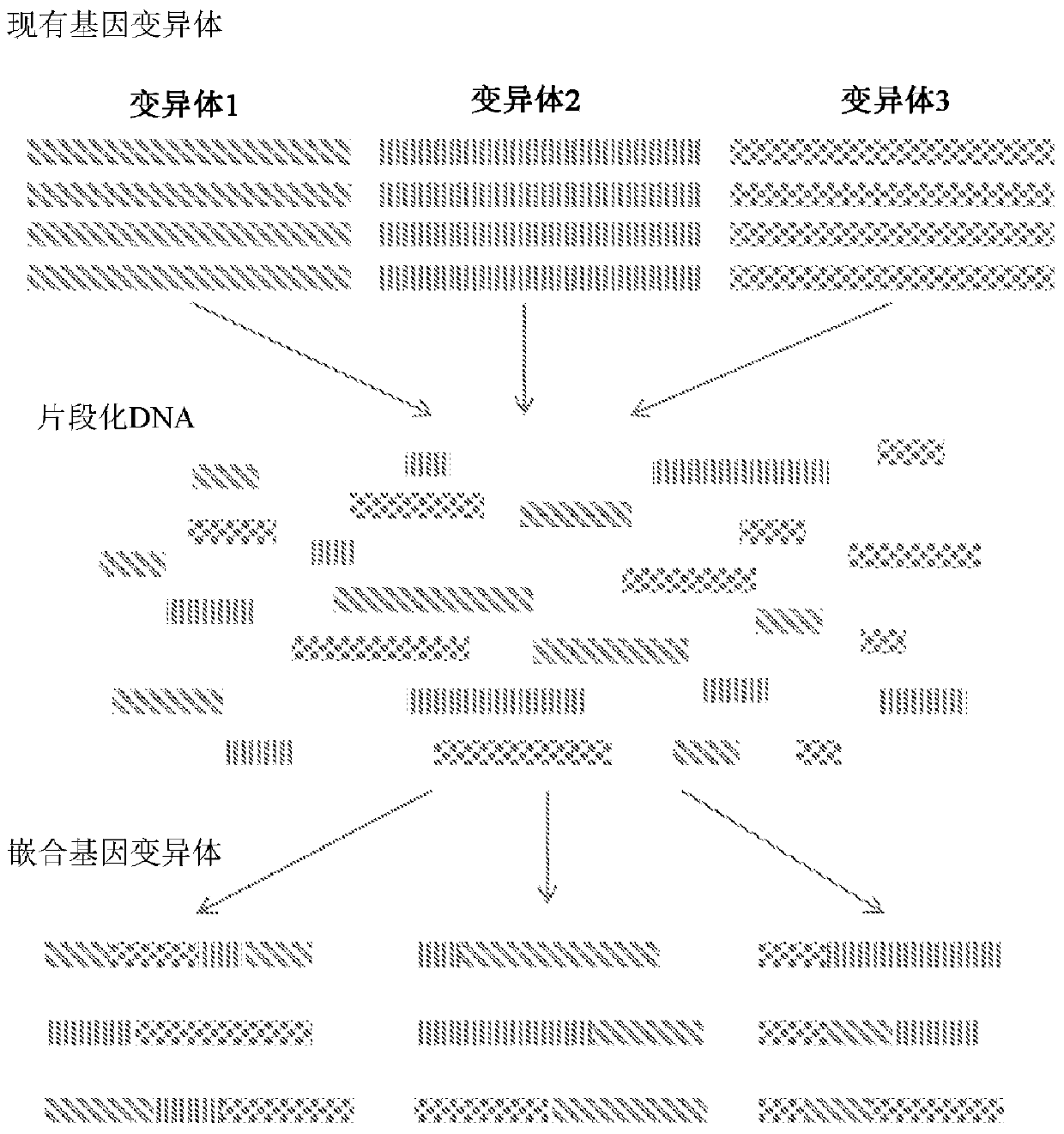
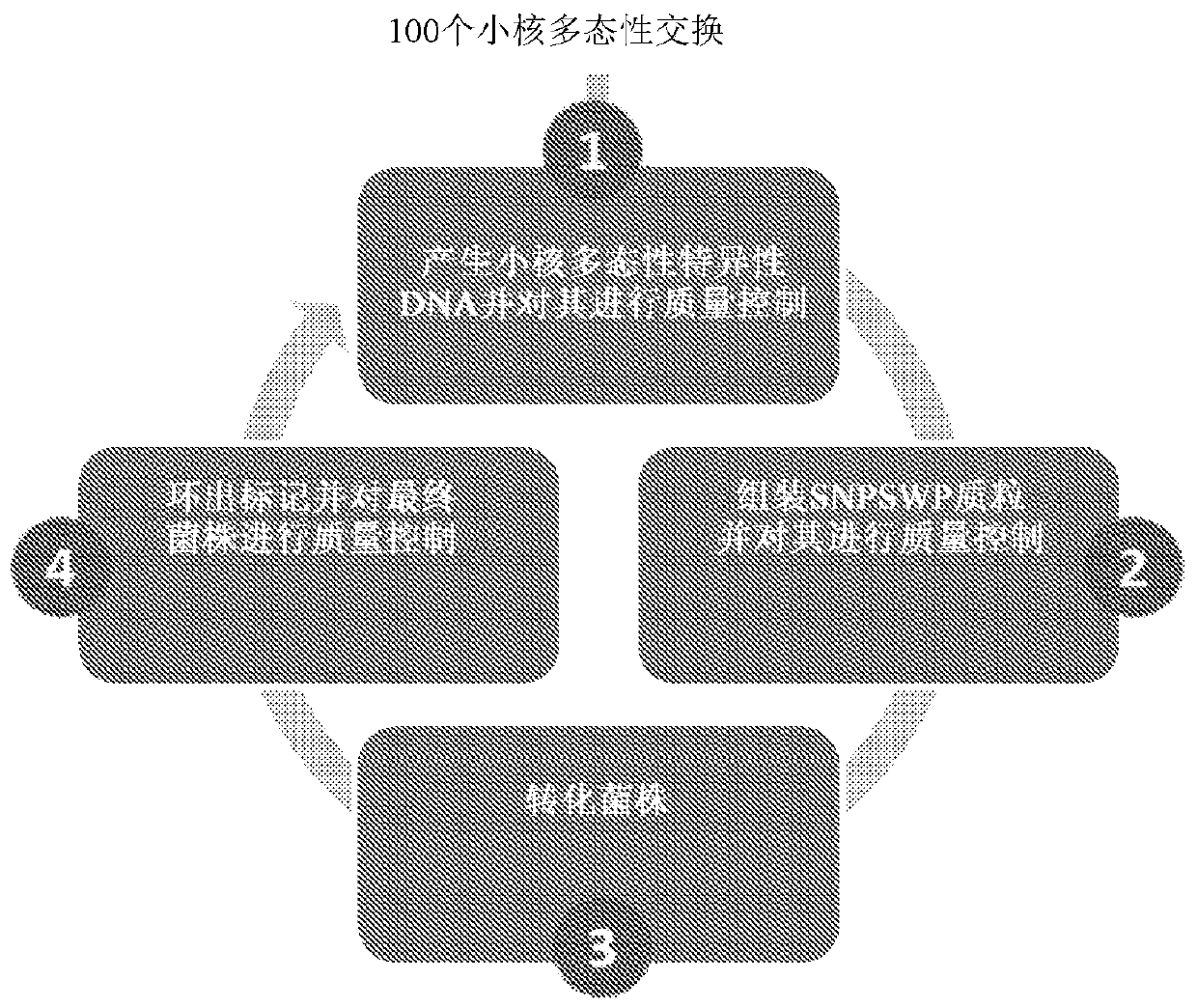
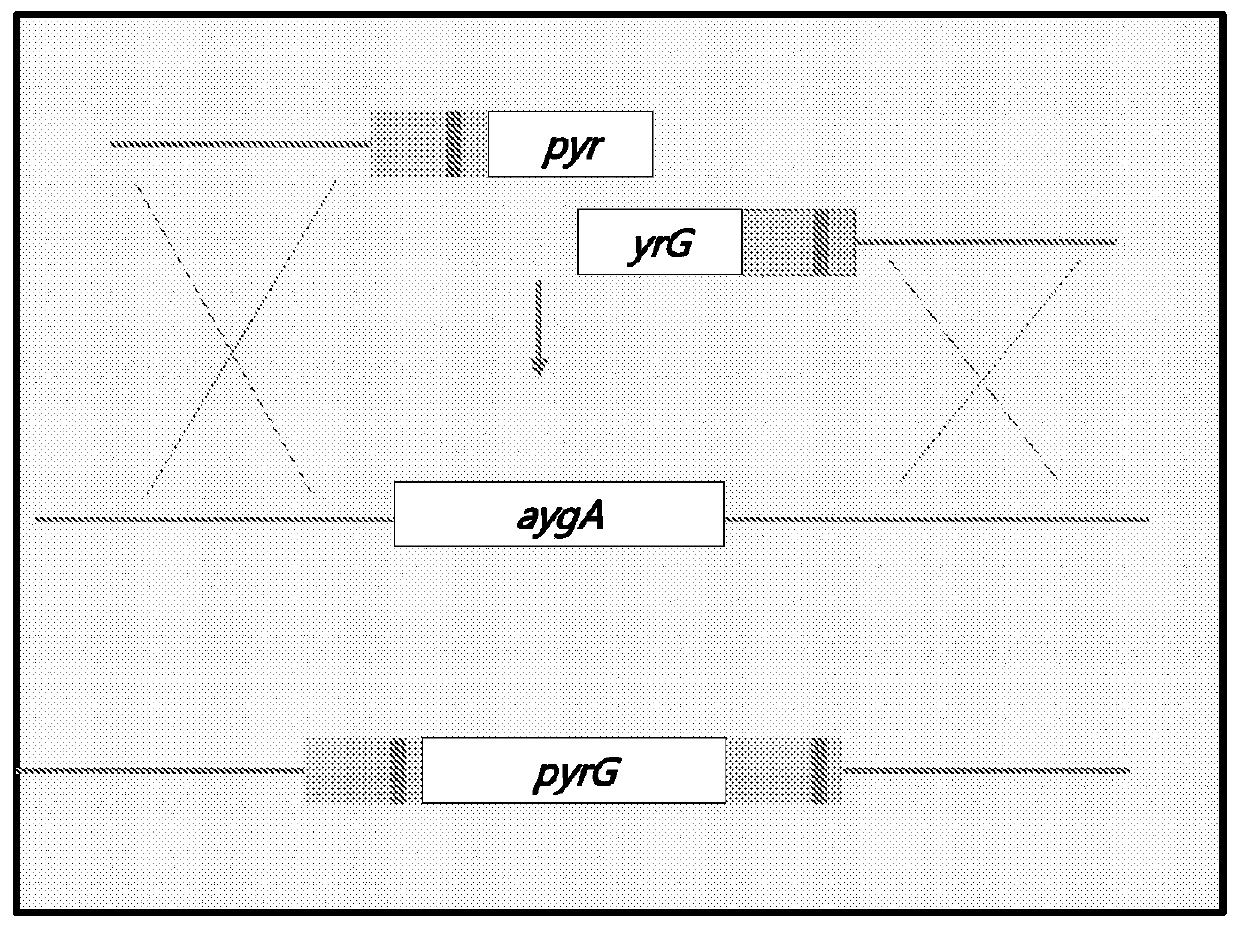
Htp genomic engineering platform for improving fungal strains
A genome and genetic technology, applied in genetic engineering, fungi, viruses/phages, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable, high viscosity, and affecting fungal growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0725] The following examples are given for the purpose of illustrating various embodiments of the invention and are not intended to limit the invention in any way. Those skilled in the art will recognize variations therein and other uses encompassed within the spirit of the invention as defined by the scope of the claims.
[0726] The following provides a brief navigation (ie Table 5) for the purpose of assisting the reader only. Nothing in this navigation is intended to limit the scope of the examples or explanations of this application. Table 5 - Navigation of the Examples Section
[0727]
example 1
[0728] Example 1: HTP genome engineering of filamentous fungi: generation and storage of filamentous fungal protoplasts
[0729] production of protoplasts
[0730] like Figure 20A As indicated in , 100 ml of complete medium was inoculated with 10 6 conidia / ml Aspergillus niger and grown overnight at 30°C at 150 rpm. After overnight growth, mycelia were harvested by filtering the culture through Miracloth. Subsequently, the mycelium was rinsed thoroughly with sterile water. For the experiments described in the Examples below, two strains of A. niger, A. niger strain 1015 and A. niger strain 11414, were used. Next, the collected and washed mycelia were subjected to enzymatic digestion by using VinoTaste Pro (VTP) enzyme mix. exist Figure 43 Characterization of each strain is depicted in .
[0731] For A. niger strain 1015, enzymatic digestion was performed by first preparing 50 ml of 60 mg / ml VTP-containing protoplast production buffer (1.2M magnesium sulfate, 50 mM pho...
example 2
[0734] Example 2: HTP Genome Engineering of Filamentous Fungi: An Alternative Approach to Protoplast Generation
[0735] like Figure 27 As indicated in , 500 ml of complete medium was inoculated with 10 6 conidia / ml Aspergillus niger and grown overnight at 30°C at 150 rpm. After overnight growth, mycelia were harvested by filtering the culture through Miracloth. Subsequently, the mycelium was rinsed thoroughly with sterile water. Next, the collected and washed mycelia were subjected to enzymatic digestion by using VinoTaste Pro (VTP) enzyme mix.
[0736] Enzymatic digestion was performed by first preparing 50 ml of 60 mg / ml VTP-containing protoplast production buffer (1.2M magnesium sulfate, 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 5). After dissolving the VTP, the buffer was placed in a clean Oakridge tube and spun at 15,000 xg for 15 minutes. The sterile solution was then filtered after centrifugation. Once made, some of the collected mycelium was added to the VTP solution, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com