Primary familial cerebral calcification pathogenic gene jam2 and its application
A gene and family technology, applied in primary familial cerebral calcification pathogenic gene JAM2 and its application field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140] Example 1: Screening of pathogenic genes in PFBC family A
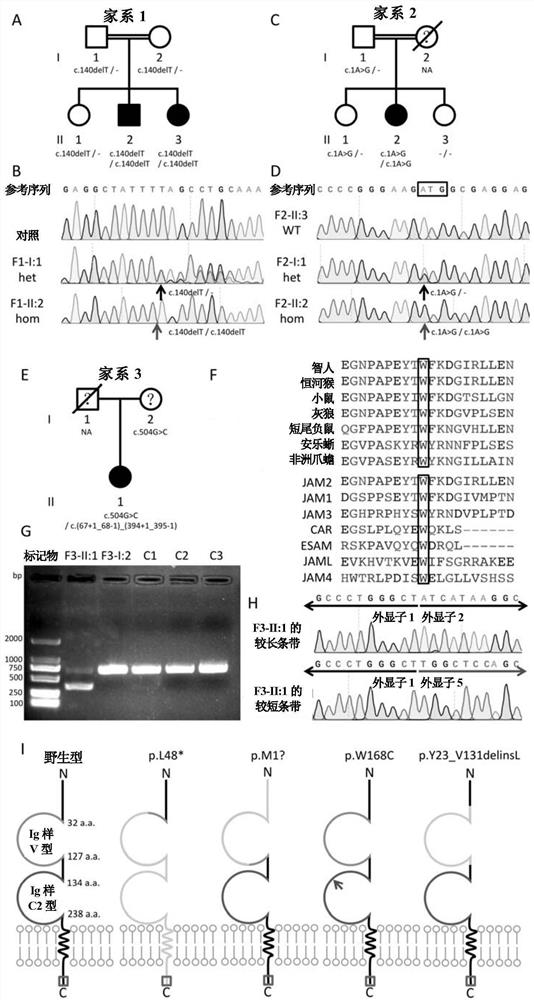
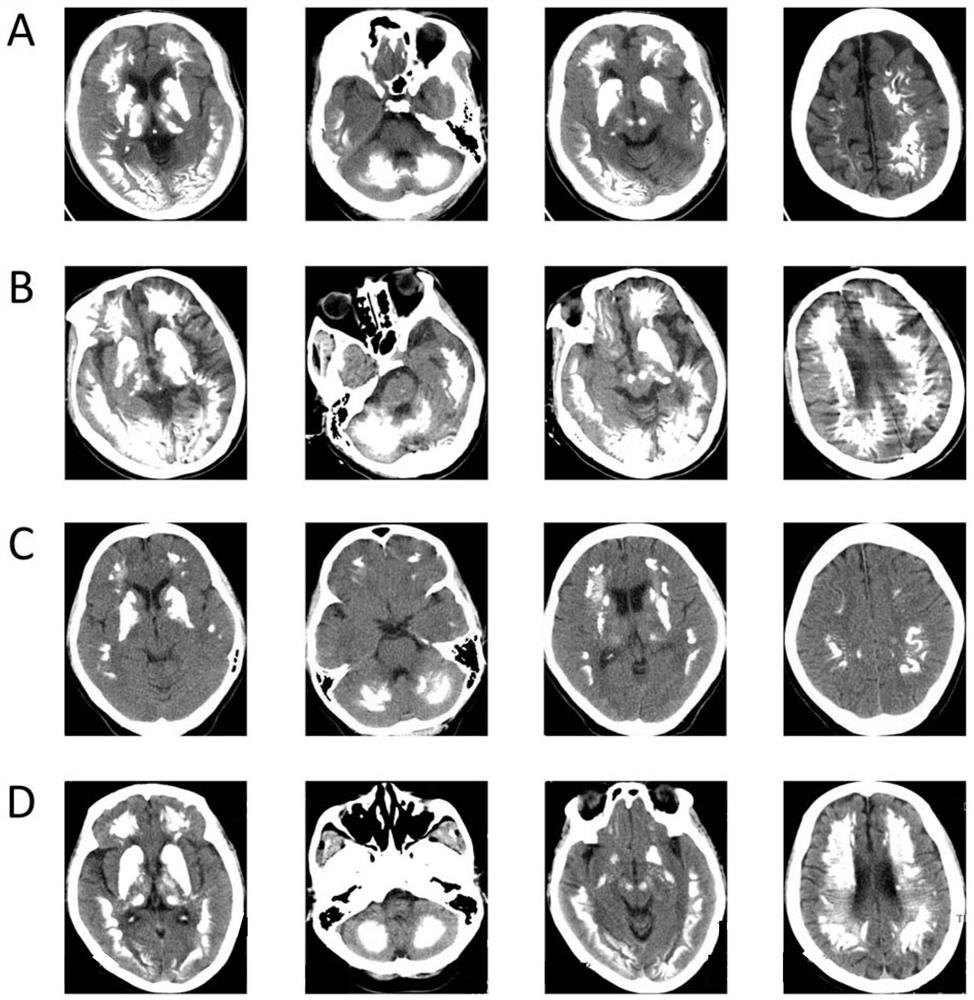
[0141] The inventor collected a PFBC family A, and judged that the family was an autosomal recessive PFBC family based on detailed family history, disease history, nervous system examination and related auxiliary examinations. The 2 PFBC patients in this family (F1-II:2, F1-II:3) both showed large areas of basal ganglia, thalamus, dentate nucleus, vermis, cerebral cortex, subcortical white matter, and midbrain Calcification, clinical manifestations of Parkinson's disease and dysarthria, his parents were consanguineous marriages, and both parents' head CT was negative.
[0142] Through the detection of related mutations in five known genes (SLC20A2, PDGFRB, PDGFB, XPR1 and MYORG), no related mutations were found, suggesting that there may be new PFBC pathogenic genes.
[0143] In this example, the family A was screened for disease-causing genes and disease-causing mutations, as follows.
[0144] 1.1 Homozygo...
Embodiment 2
[0160] Example 2: Screening for JAM2 pathogenic gene mutations in other families
[0161] Since the JAM2 gene is the only pathogenic gene analyzed in the family, in this example, the family sample verification was further expanded, and the mutation screening of the entire coding region of JAM2 was performed on the probands of 398 PFBC families.
[0162] According to the wild-type gene coding sequence SEQ ID NO:1 of JAM2, a primer pair (see Table 1) was designed to amplify the entire coding region sequence, and Sanger sequencing was performed. Table 2 shows the primer pair amplification system and conditions.
[0163] Table 1 JAM2 DNA primer sequence
[0164]
[0165]
[0166] Table 2 Primer pair amplification system and conditions
[0167] Numbering Component Amount added / μL 1 10×PCR buffer(Mg2+) 5 2 dNTP Mixture (2.5mM each) 8 3 Primer F (10μM) 0.25 4 Primer R (10μM) 0.25 5 LA Taq DNA Polymerase 0.5 6 Genomic DNA ...
Embodiment 3
[0172] Example 3: Further Screening for JAM2 Gene Mutations
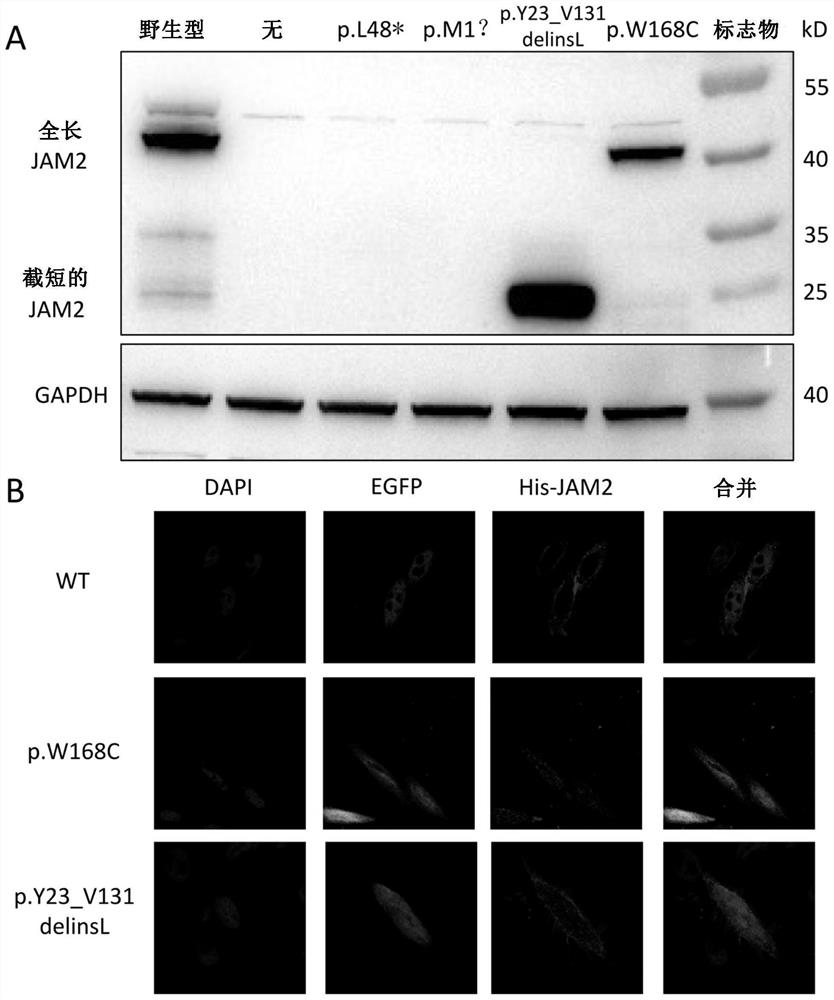
[0173] According to the study of the pathogenic mutation form and mutation function identified in the foregoing examples, it is suggested that the biallelic loss-of-function mutation is the main mutation type of JAM2 gene leading to PFBC.
[0174] Therefore, in this example, further screening of JAM2 gene mutations was carried out in the GnomAD v3 database. The screening conditions are: (i) mutations with clear loss of function (frameshift mutation, nonsense mutation, splice site mutation) and mutations that may cause loss of function (missense mutation, in-frame deletion / insertion mutation); (ii) ) There is no homozygous state in the normal population; (iii) The heterozygous carrier rate in the normal population is less than 0.01.
[0175] Finally, 15 JAM2 gene mutations with clear loss of function (Table 4) and 99 mutations that may lead to loss of JAM2 gene function (Table 4) were screened out. Among them, 15 JAM...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com