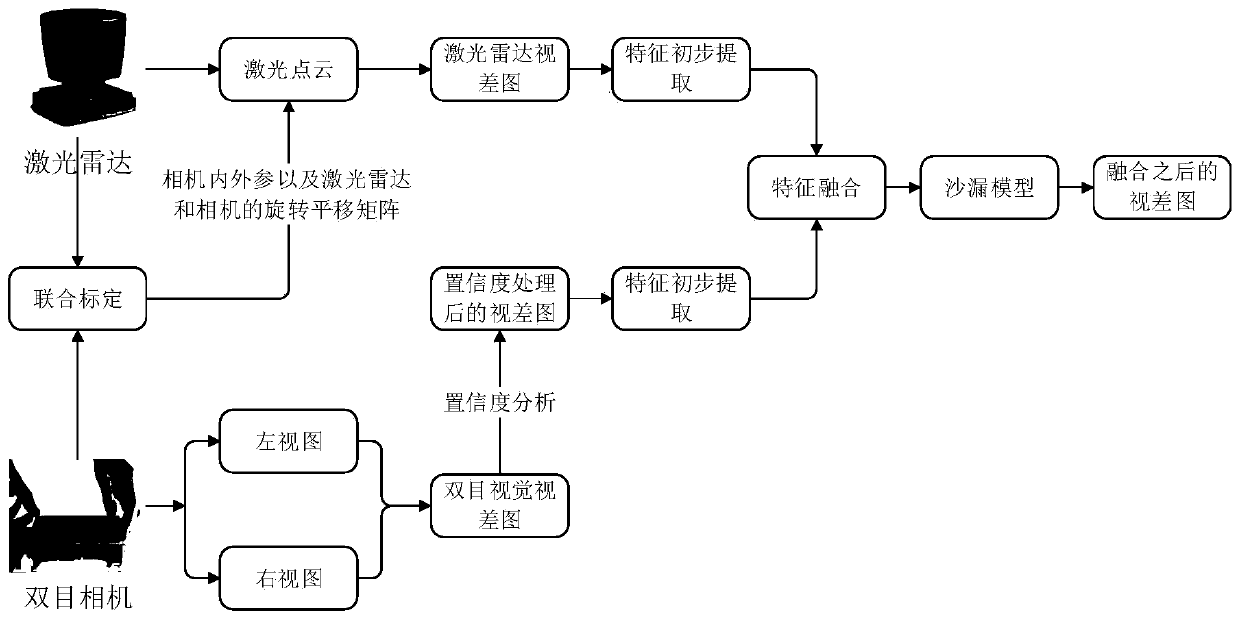
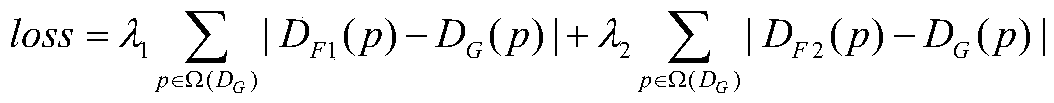Depth estimation method based on binocular vision and laser radar fusion
A technology of laser radar and binocular vision, which is applied in the field of robot and computer vision, can solve the problems of inaccurate and inaccurate recovery of depth information, achieve good fusion results, strong flexibility, and improve robustness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
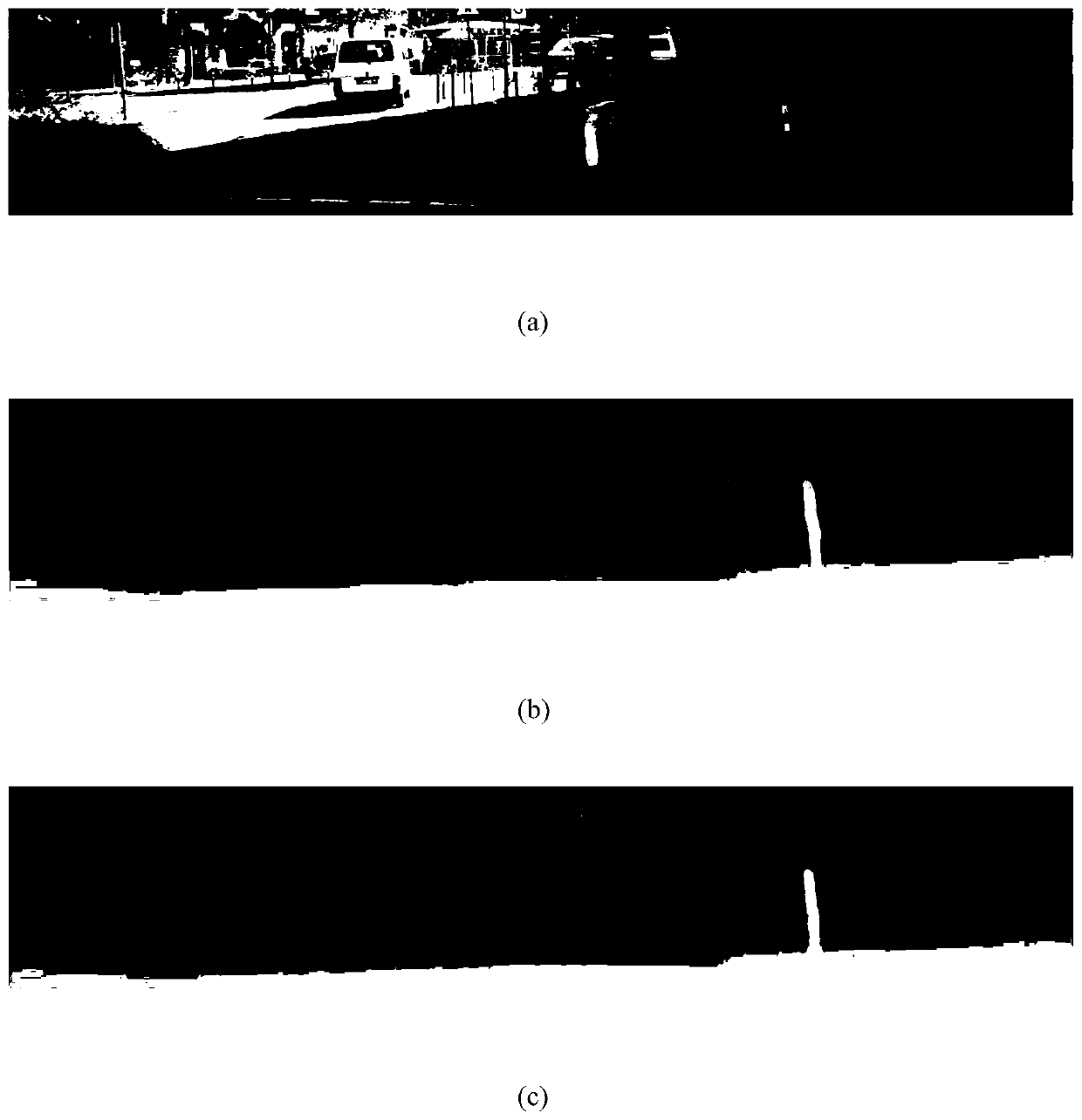
[0063] This embodiment mainly measures the pros and cons of the depth estimation quality in the road scene, mainly including the restoration of the details and the overall outline. figure 2 (a), (b), and (c) respectively represent the original graphics, the disparity map obtained by the PSMNet method and the disparity map obtained by the fusion of the method of the present invention. It can be seen from the results that, compared with the original binocular disparity map, the method of the present invention restores the contours of people and cars more accurately. At the same time, the original binocular disparity map has obvious errors in the depth estimation of distant poles, and there is a gap in the middle of them, but the method of the present invention estimates the depth information of the entire pole well.
Embodiment 2
[0065] This embodiment evaluates the method of the present invention through the Kitti2015 dataset. The Kitti2015 dataset consists of 200 sets of data, including left and right views and the corresponding ground truth. The corresponding lidar data can be obtained from the original data of Kitti. The data set compares the disparity map with the ground truth and calculates the error rate to evaluate the quality of the depth estimation. The lower the error rate, the better the quality of the depth estimation. The error rate is defined as the proportion of the number of pixels whose disparity value differs from the ground truth by more than 3 or more than 5% among all pixels. The specific results are shown in Table 1:
[0066] Table 1. Performance of each method on Kitti2015
[0067]
[0068] As can be seen from the table, the PSMNet method we used has an error rate of 3.98% on the Kitti2015 dataset. Afterwards, the result map obtained by PSMNet is fused, and the error rate ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com