Field-free geometric calibration method and system for satellite-borne laser altimeter
A laser altimeter and geometric calibration technology, which is applied in the field of aerospace photogrammetry, can solve the problems of limitations and the large difference in the accuracy of laser geometric pointing and calibration, and achieve the effect of solving the inaccurate initial pointing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
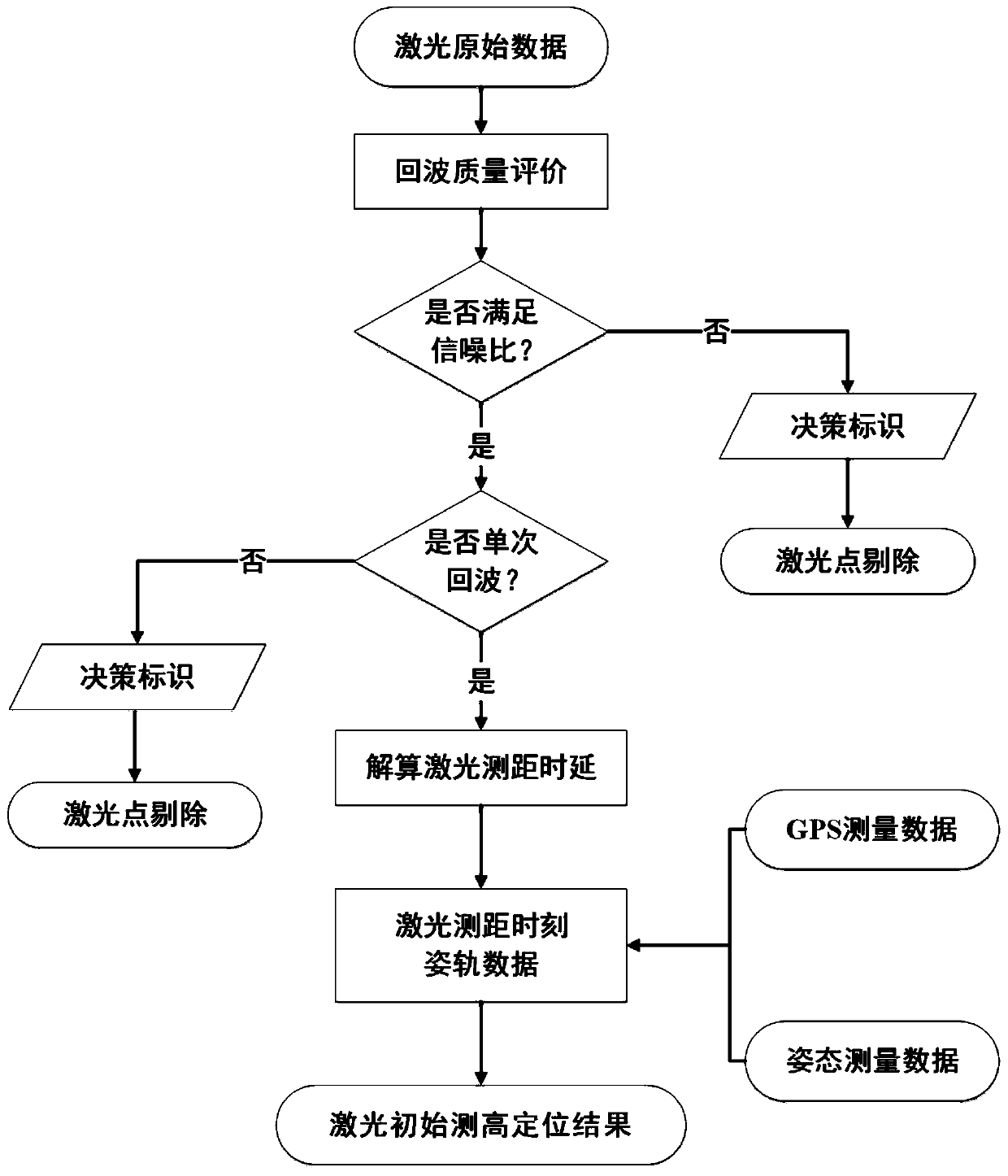
[0073] This embodiment will provide a geometric positioning method for spaceborne laser altimetry. For the process, see figure 1 .
[0074] The basic principles of spaceborne laser geometric positioning are as follows:
[0075] The position coordinates of the laser are denoted by S, the coordinates of the center of the earth are R, and the distance from the center of the earth is RS. It emits a laser signal to reach point A on the surface of the earth. The measured distance value is ρ. The distance from the laser measurement point A to the center of the earth is RA.
[0076] From this, the strict geometric positioning model of spaceborne laser altimetry is obtained, that is, the distance equation, and its object space form can be described as the following formula:
[0077]
[0078] in, Represents the position of the satellite in the earth-centered Cartesian coordinate system, R(t) is the rotation matrix from the body coordinate system to the earth-centered Cartesian co...
Embodiment 2
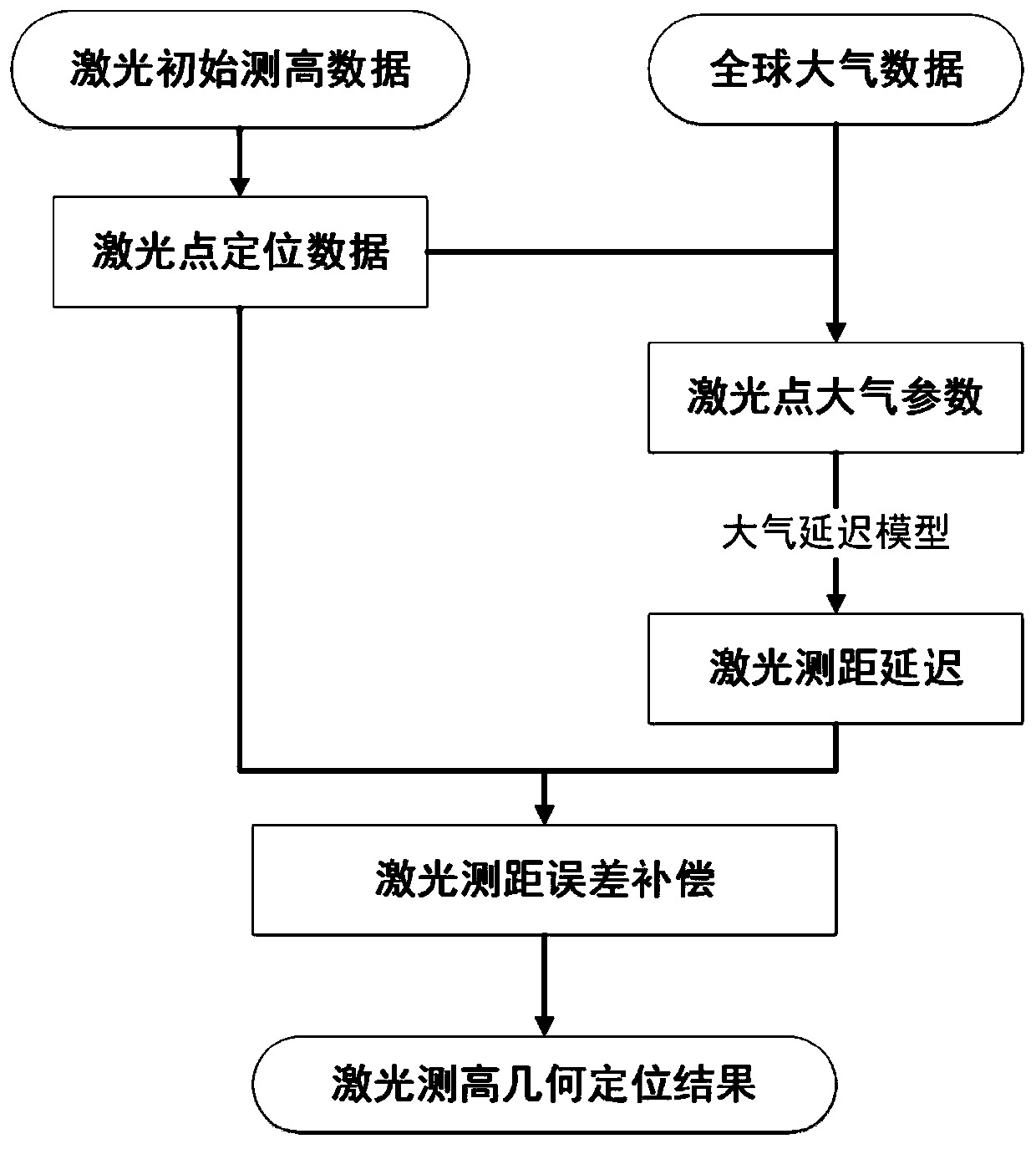
[0086] This embodiment provides a method for correcting atmospheric delay in spaceborne laser ranging, see attached figure 2 .
[0087] The path of laser propagation in the atmosphere is different from the straight-line propagation in vacuum. The influence of the atmosphere on laser ranging mainly includes atmospheric delay and atmospheric refraction, and the most important factor affecting laser ranging is atmospheric delay. During the propagation of laser in the atmosphere, the observation accuracy of the laser altimetry system is greatly limited due to the influence of atmospheric refraction. Therefore, the atmospheric delay error of laser ranging must be corrected before on-orbit calibration of the laser.
[0088] Atmospheric delay correction is mainly to eliminate the ranging delay error caused by the refraction of the atmosphere when the laser passes through the troposphere. Assuming that the propagation speed v of the electromagnetic wave signal in the atmosphere, the...
Embodiment 3
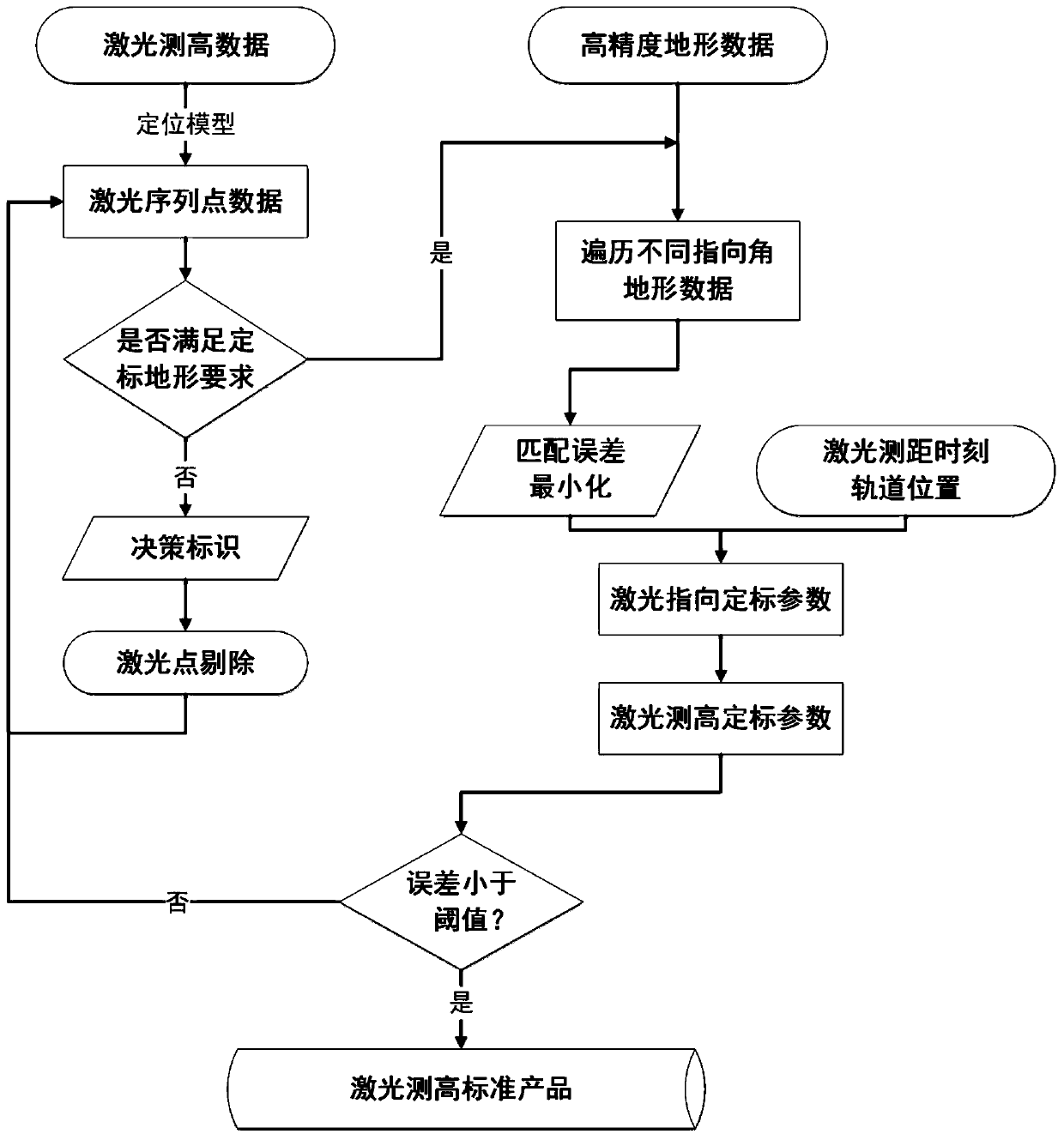
[0108] This embodiment provides a spaceborne laser geometric calibration method based on terrain constraints, see attached image 3 .
[0109] The basic principle of geometric calibration of the laser altimeter is as follows: Assume that the position of the satellite laser is S, the laser emits a signal to point A on the surface, and SA is the actual pointing and distance of the laser ranging. The laser calculation path becomes SA', which will cause the model error Δh in the direction of laser ranging, which will cause errors in the elevation of footprints obtained by the laser altimetry positioning model.
[0110] Then, based on the rigorous geometric positioning model of the spaceborne laser, the geometric calibration model of laser altimetry can be constructed, as follows:
[0111]
[0112] In formula (13), t is the error compensation amount of the laser ranging time, R(φ,ω) is the offset matrix related to the laser beam exit angle (φ,ω), where φ,ω represent the laser...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com