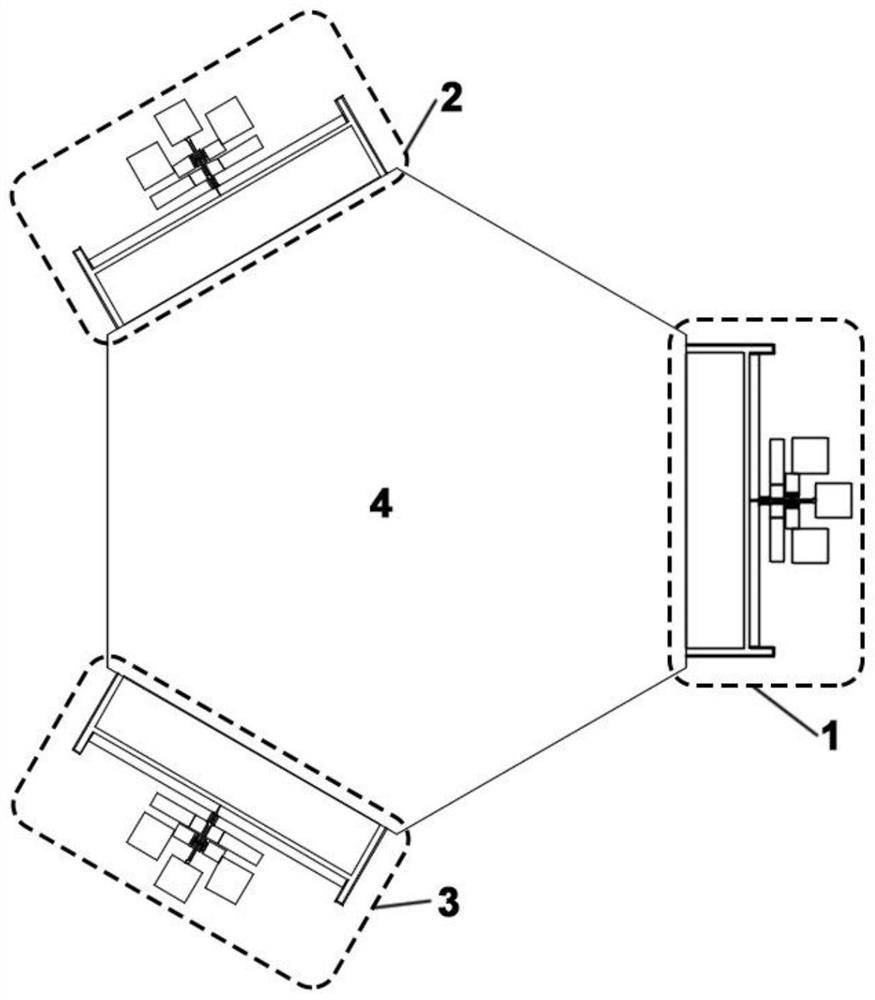
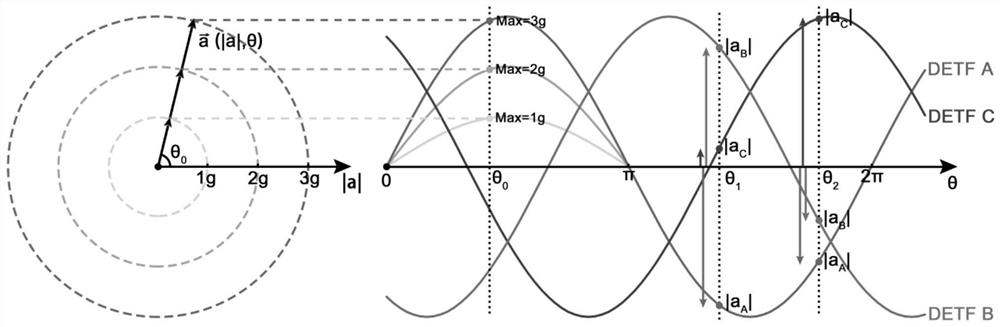
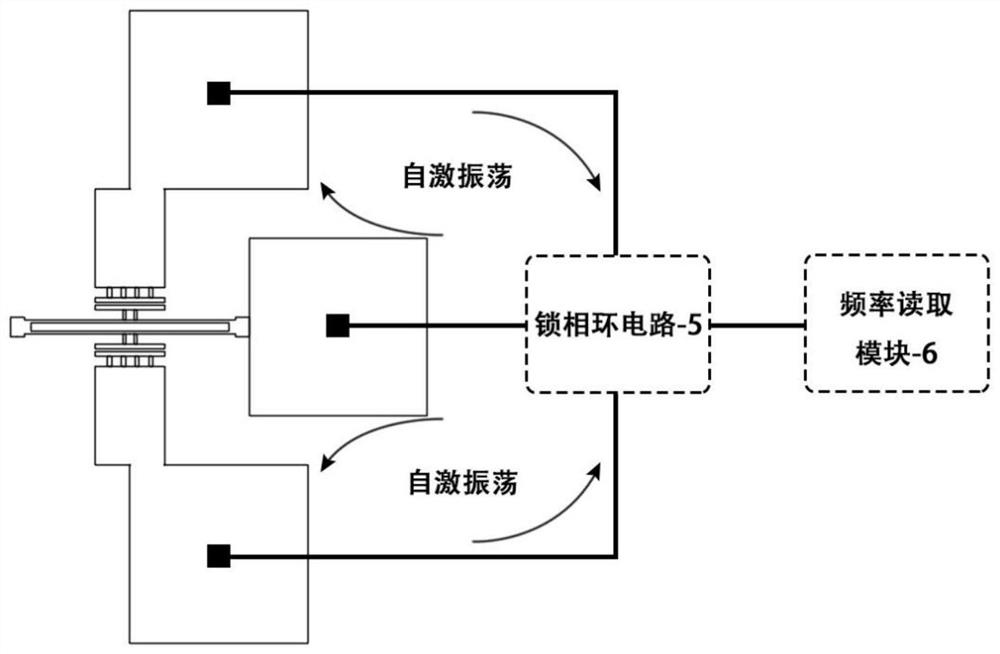
A temperature self-compensating in-plane biaxial acceleration sensor and temperature compensation method
A biaxial acceleration and temperature compensation technology, which is applied in the direction of speed/acceleration/shock measurement, measurement of acceleration, and test/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement equipment, which can solve high power consumption, large system size, and unsatisfactory results etc. to eliminate the influence of temperature coefficient, reduce random error and eliminate dead zone
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] In describing the present invention, it should be understood that the terms "center", "longitudinal", "transverse", "upper", "lower", "front", "rear", "left", "right", " The orientation or positional relationship indicated by "vertical", "horizontal", "top", "bottom", "inner", "outer", "side", "end", "side" etc. is based on the Orientation or positional relationship is only for the convenience of describing the present invention and simplifying the description, and does not indicate or imply that the referred device or element must have a specific orientation, be constructed and operated in a specific orientation, and thus should not be construed as a limitation of the present invention. In addition, the terms "first" and "second" are used for descriptive purposes only, and cannot be interpreted as indicating or implying relative importance or implicitly specifying the quantity of indicated technical features. Thus, a feature defined as "first" and "second" may explicit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com