A low-latency and high-reliability polar code fast decoding method and decoder
A fast decoding and polar code technology, applied in the field of communications, can solve the problems of reduced decoding delay, large decoding delay, etc., to reduce the number of memory blocks, reduce resource consumption, and reduce decoding time delayed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
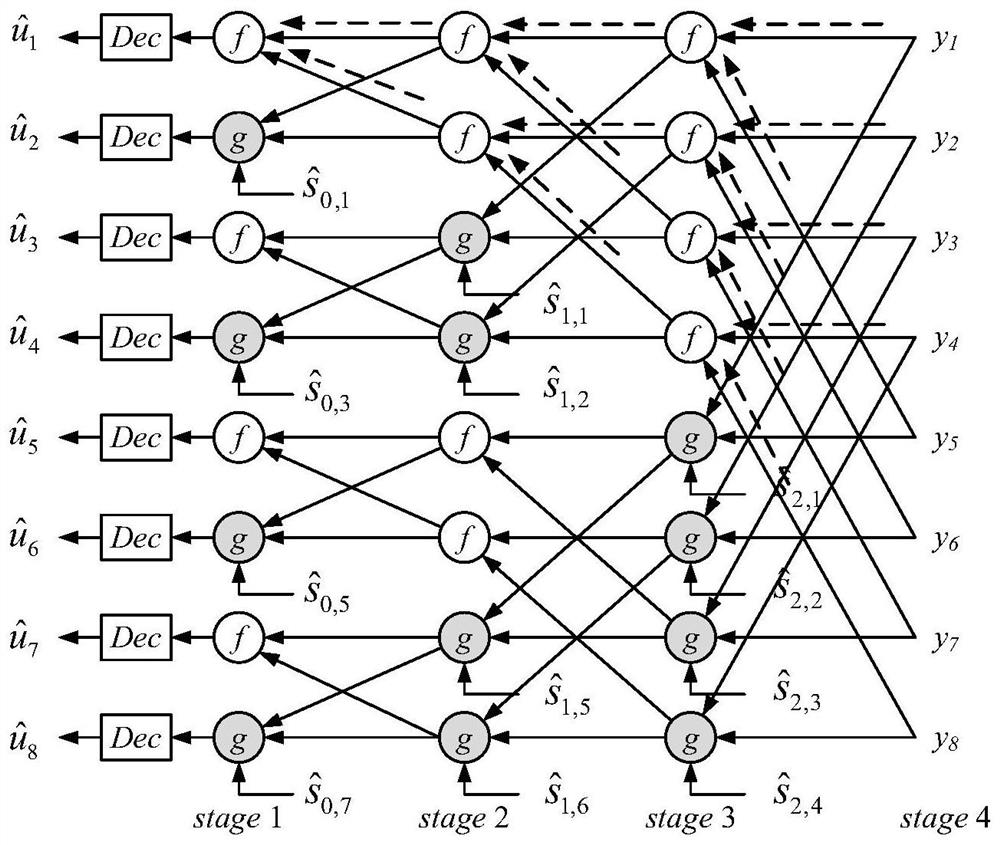
[0047] Embodiment 1: First, taking a polar code with code length N=16 and information bit length K=10 as an example, the implementation method of the improved core code word grouping of the fast multi-node SCL algorithm is described. When M=2, such as Figure 9a , 9b As shown, white circles represent frozen bits, and black circles represent information bits. Figure 9a Represents the codeword grouping result of the original multi-node SCL algorithm, Figure 9b Indicates the code word grouping result of a low-delay and high-reliability polar code fast decoding method proposed by the present invention. According to our previous explanation of the Rate-1 node, Figure 9b S in 6 That is, a Rate-1 node with a length of 4.
[0048] Down Figure 10a , 10b The comparison of polar code frame error and bit error performance under different code rates and different list numbers is given respectively. Taking 1024 code length as an example, 1 / 2( Figure 10a ), 2 / 3( Figure 10b ) tw...
Embodiment 2
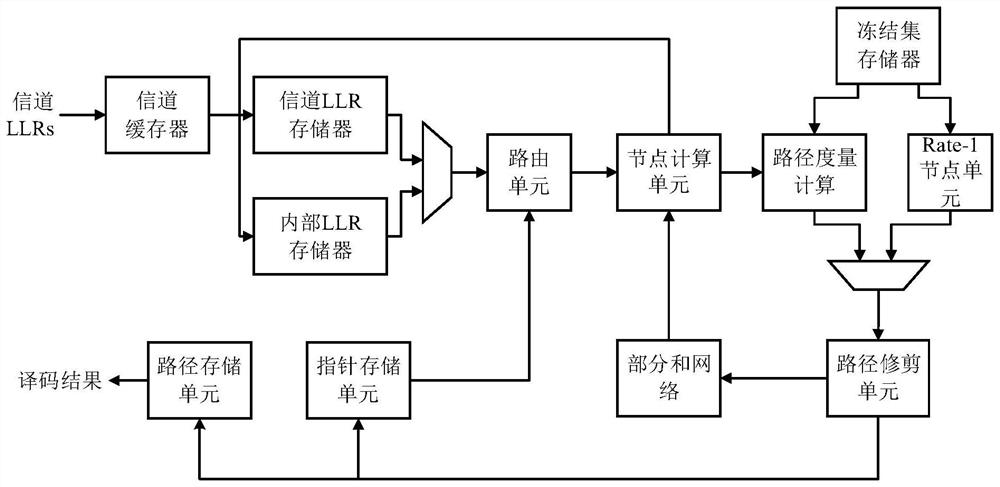
[0049] Example 2: figure 2 The overall architecture diagram of the decoder is given, which mainly consists of storage unit (including channel buffer, channel LLR memory, internal LLR memory, frozen set information storage, path information storage unit), node computing unit, routing unit, Rate-1 node A processing unit, a path extension and metric calculation unit, a path pruning unit, a part and network, and a pointer storage unit are formed. The log-likelihood ratio information (LLR) received through the channel is first stored in the channel buffer (Channel Buffer), and then stored in the channel LLR memory according to the designed storage address. The routing unit (RouteUnit) is used to select from which The read data in the LLR memory is sent to the calculation module. After the node calculation is completed, the node type is judged according to the frozen set information, and then enters the path expansion and measurement value calculation module, and the path is delete...
Embodiment 3
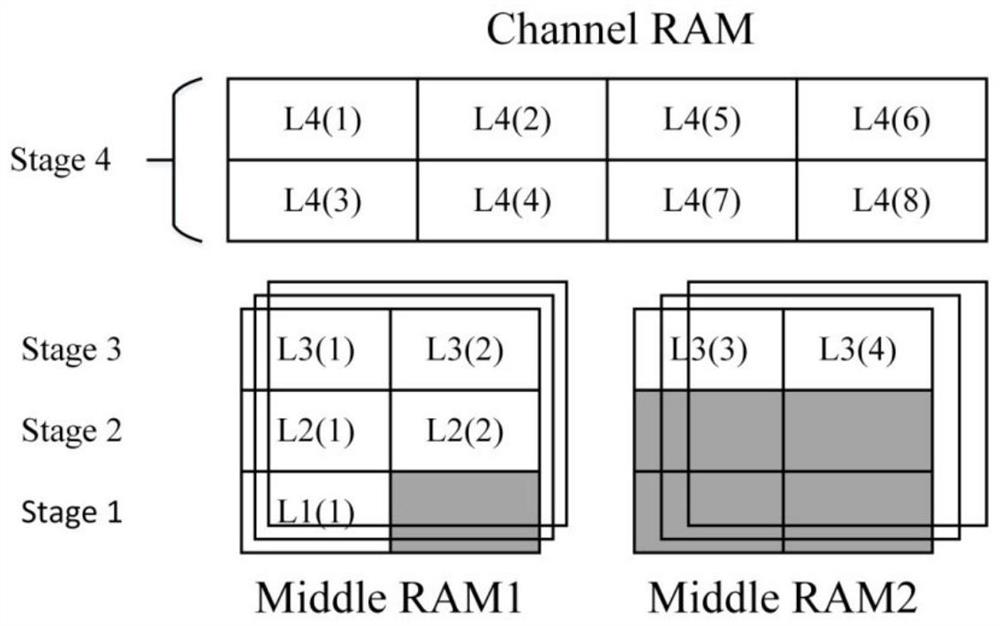
[0057] For scenarios with low resource consumption and high performance requirements, the present invention designs another batch processing optimization architecture based on SC network serial-parallel combination, which is a polar code fast decoder based on SC network serial-parallel combination, such as Figure 6a , the architecture includes SC computing network, sorting network (to complete the expansion and pruning of paths), parts and computing units; as Figure 6b , wherein the SC computing network includes an LLR information storage module, a node computing unit, and a routing unit; further, the LLR information storage module includes a channel LLR memory and an internal LLR memory. The logarithmic likelihood ratio information (LLR) received by the decoder from the channel is first stored in the channel LLR memory, the node calculation unit completes the LLR calculation of the internal node, and the result is stored in the internal LLR memory, and the routing unit is us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com