Concurrent access control method in distributed database system
An access control and database technology, applied in the information field, can solve the problems of system scalability bottleneck, cannot be serialized, destroy database consistency requirements, etc., to avoid excessive rollback and write skew problems, high practical significance, The effect of great practical significance and value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
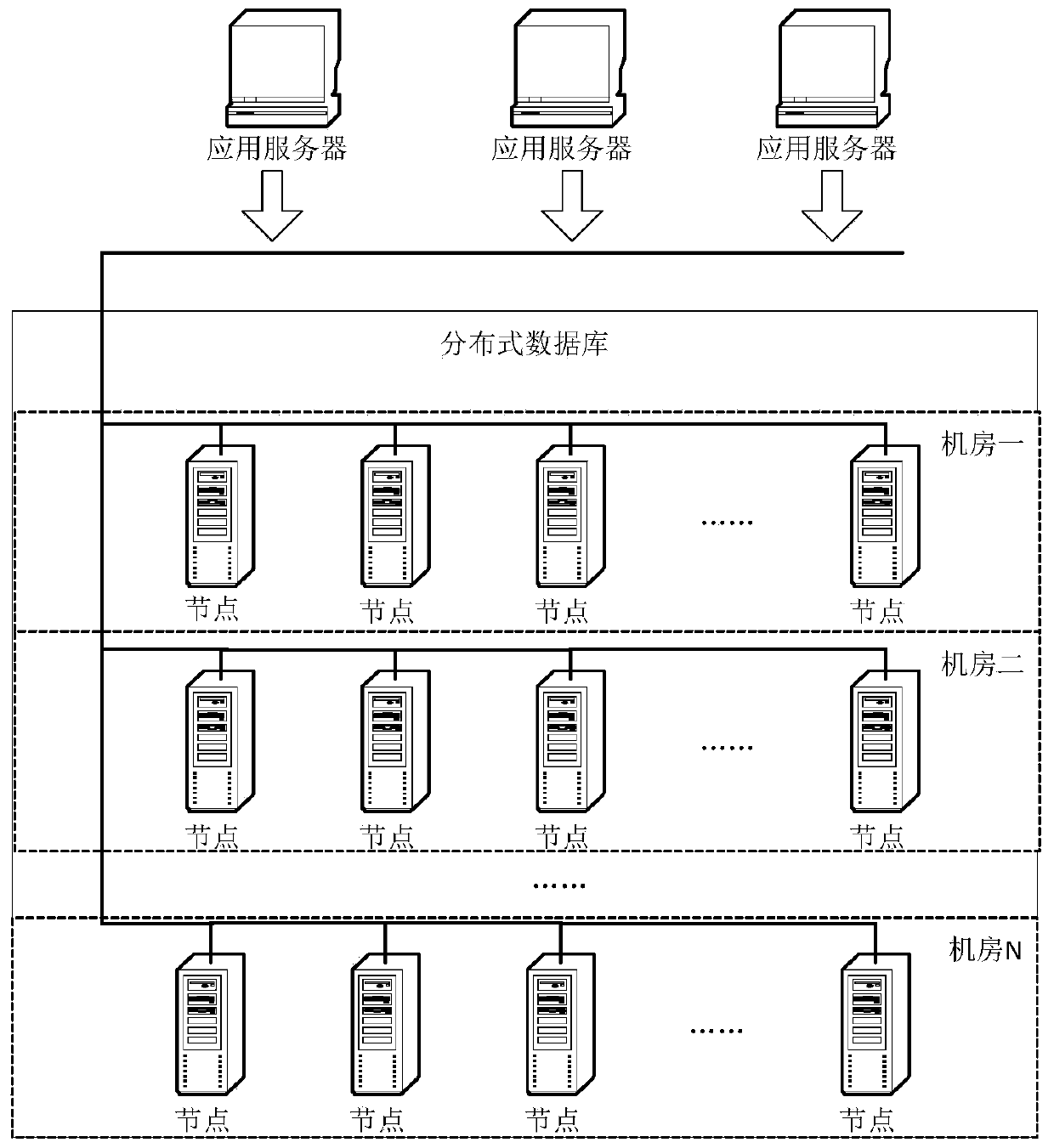
[0029] figure 1 A schematic diagram of the application environment of this method is given. In the modern information environment, a distributed database may often be established on hundreds or thousands of computers in several geographically separated computer rooms, and provide unified database services to the outside world. Computer nodes in a distributed database usually include routing nodes, management nodes, and data nodes, and each node implements part of the overall functions. Replication technology is often used in data nodes to improve data availability and reliability. The present invention does not relate to these related infrastructures and technologies, but only focuses on how to realize data concurrent access control among various data nodes.
[0030] When an application accesses a distributed database, it connects to the database system through the network and initiates a read or update request to the database. figure 1 Shown in is a typical architecture wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com