Automatic addressing laser scanning electrode structure, control method and manufacturing method
A technology of laser scanning and automatic addressing, applied in the field of microelectronics and optics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Example 1:
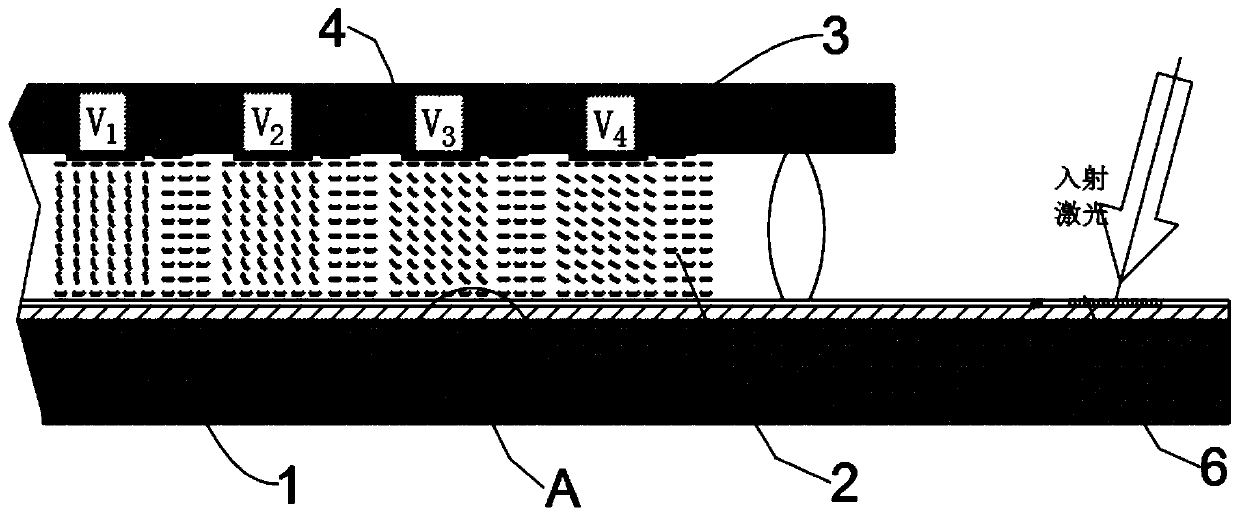
[0088] Such as figure 1 As shown, a self-addressing laser scanning electrode structure includes a conductive substrate 1 with a waveguide structure, a liquid crystal layer 2 is arranged above the conductive substrate, an electrode control array panel 3 is arranged above the liquid crystal layer, and the electrode control Several transparent and conductive driving electrodes 4 are arranged on the array panel, so that the switching state and applied voltage of each driving electrode can be independently controlled, and the driving electrodes are respectively connected to a master controller.
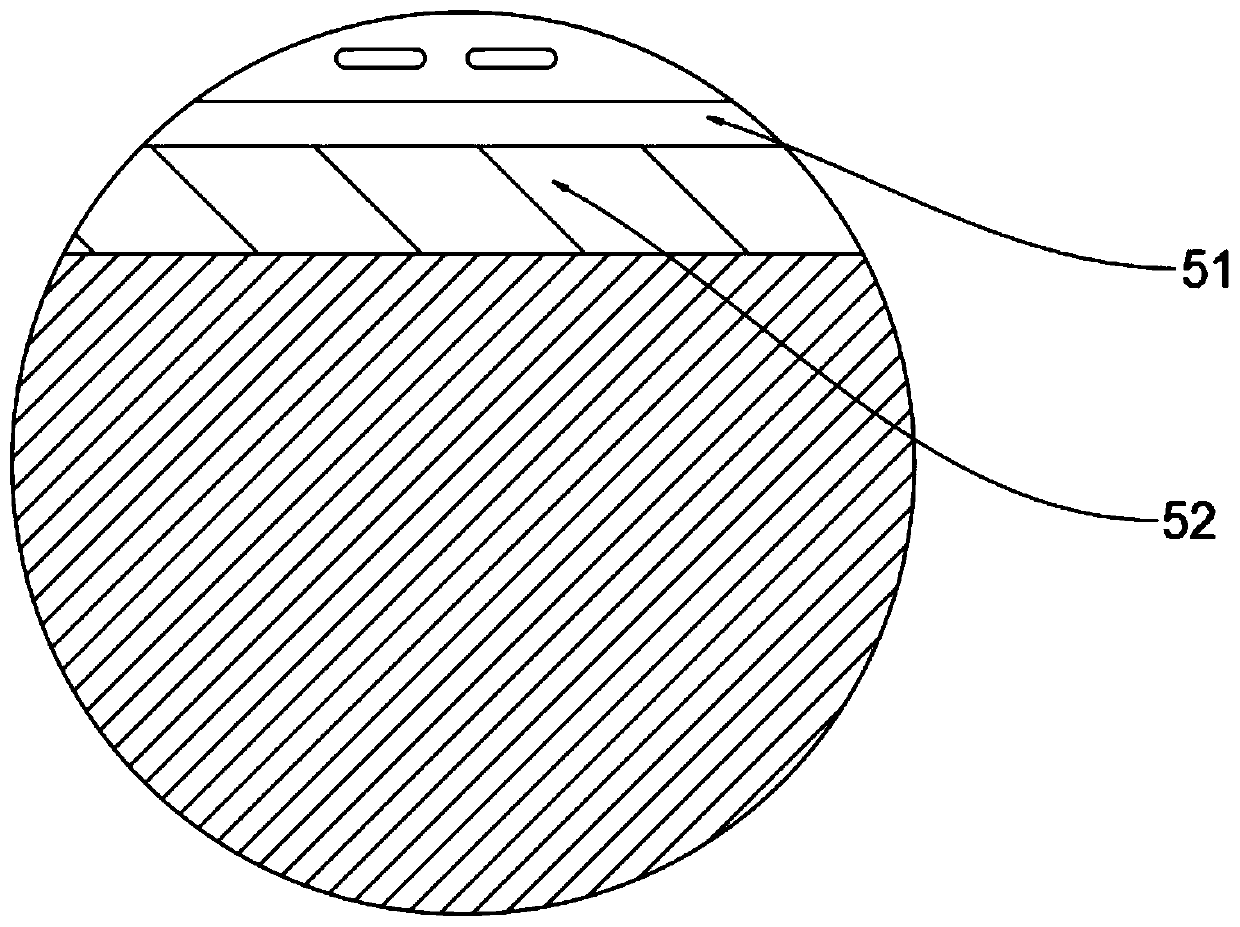
[0089] It includes a light guiding layer 5, the light guiding layer includes a first layer structure 51 and a second layer structure 52, the refractive index of the first layer structure is higher than the refractive index of the second layer structure.
[0090] Preferably, a grating film coupling device 6 is arranged on the light guiding layer 5, and the incident lase...
Embodiment 2
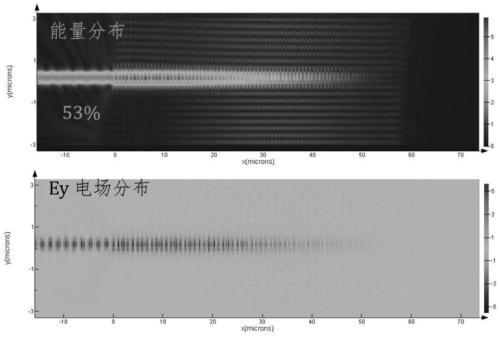
[0097] Such as Figure 4 , based on the device in embodiment 1, we provide a kind of automatic addressing laser scanning electrode control method in embodiment 2, comprising the following steps:
[0098] (1) Determine the preset propagation trajectory of the laser;
[0099] (2) Determine the coordinates of the driving electrodes that need to be driven according to the preset propagation trajectory of the laser;
[0100] (3) Controlling the voltage of the driving electrodes so that the laser light entering the liquid crystal layer is deflected according to a preset propagation track.
[0101] Preferably, the following steps are also included:
[0102] (4) Control the coordinates and directions of the driving electrodes according to the preset laser scanning requirement range, and then realize the laser scanning in the preset angle range.
[0103] Preferably, in said step (1), the following steps are included:
[0104] (11) Equivalent the laser preset propagation trajectory ...
Embodiment 3
[0125] Through the method in this embodiment 2, we provide a kind of embodiment 3, to specifically regulate the laser deflection direction:
[0126] In step (2), a combination of several micro-biasing units of the same shape is used to control the laser deflection according to a preset trajectory, including the following steps:
[0127] Set the angle between the incident straight side and the outgoing straight side for each micro-bias unit
[0128] Set to use the same voltage to control the micro-bias control unit;
[0129] According to the set voltage value and angle Calculate the angle at which each micro-bias unit can adjust the laser deflection, so as to determine the number N of micro-bias units required to achieve laser deflection;
[0130] The center of the circumscribed circle of the triangle formed by the incident side and the outgoing side of each micro-deflection unit is equidistantly set on the equivalent circular arc of the preset laser deflection track, so a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com