Method for improving wear resistance of high-chromium cast-iron alloy by adopting microalloying engineering
A technology of micro-alloying and high-chromium cast iron, which is applied in the field of metallurgical casting to achieve the effects of improving product yield, solving the problem of high brittleness of castings, and reducing the cost of charge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
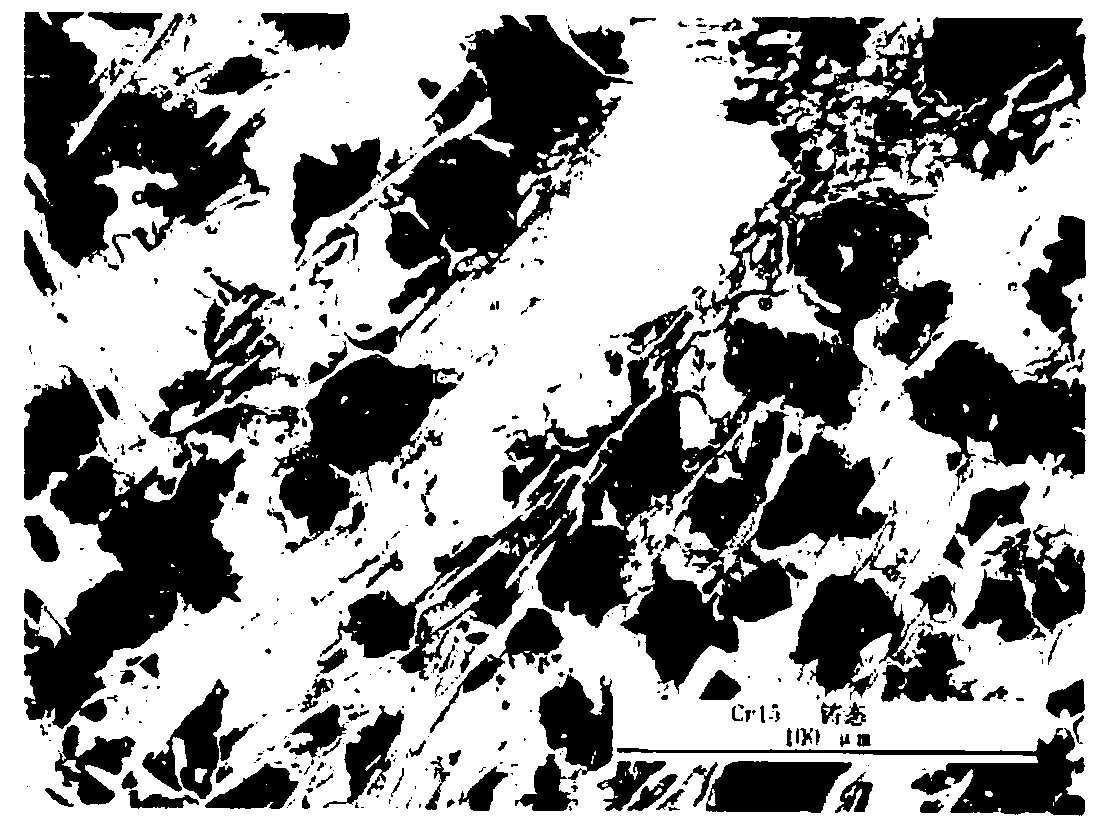
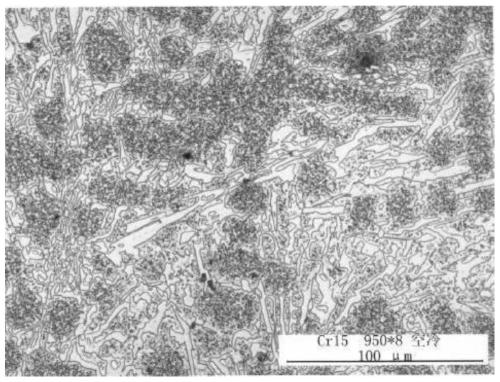
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Utilize micro-alloying engineering to improve the method for BTMCr15Mn3Cu1 (GX15) alloy wear resistance, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) According to the following components 2.7-2.9wt%C, 0.4-0.7wt%Si, 2.4-3.0wt%Mn, 15-18wt%Cr, 0.9~1.1wt%Cu, <0.06wt%S, <0.10wt% %P, 0.07wt%B, and the balance is Fe. Weigh the raw materials and place them in an induction furnace, heat up until the raw materials are completely melted, remove impurities, and obtain molten iron;
[0040] (2) Taking molten iron as the measurement basis, 0.2wt% aluminum, 1.0wt% zinc-copper alloy (copper 87wt%, zinc 13wt%) and 0.3wt% YBTW-4 refining, 0.2wt% No. 2 rare earth ferrosilicon alloy mixed as a modifier;
[0041] (3) After adding the modificator in the step (2) into the ladle, pour the molten iron in the step (1) into the ladle, stir, remove slag, and pour at 1380-1410° C.;
[0042] (4) After pouring, the casting is kept at 650°C for 5 hours, then raised to 920°C for 2 hours, and finally ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] On the basis of Example 1, Example 2 is carried out in order to further improve the morphology of eutectic carbides and increase the hardness of GX15. The steps are as follows:
[0050] (1) Melting qualified molten iron to form GX15;
[0051] (2) Add composite modificator 0.2% Al+0.1% copper-zinc alloy+0.13wt% YBTW-2 alloy in step (1) to carry out pre-furnace treatment, pour guard plate;
[0052] (3) Carry out the pretreatment of the protective plate prepared in step (2) at 650° C. for 5.0 hours;
[0053] (4) The guard plate treated in step (3) is subjected to a microalloying-austenitizing treatment at 920° C. for 2 hours → 950° C. for 8 hours, and air-cooled after being taken out of the furnace.
[0054] The guard plate obtained after the above treatment, the produced GX15 material guard plate, the macro hardness (HRC) of factory inspection: 66.8, 64.7, 62.6, compared with the hardness of 59.4HRC of the factory inspection guard plate produced in Example 1, at least i...
Embodiment 3
[0058] The GX15 material that the method for embodiment 1 is produced is carried out abrasion test on abrasion testing machine:
[0059] Abrasion test model: MSH-120;
[0060] Number of rotations: 2790 rpm;
[0061] Abrasion sample: Standard abrasion testing machine abrasion disc;
[0062] Medium: quartz sand, particle size 20-40, mixing ratio 40% (2kg sand: 3kg water);
[0063] Abrasion test time: 8h.
[0064] The test results are shown in Table 1.
[0065] Table 1 Comparison of abrasion test results between GX15 and A05
[0066]
[0067] It can be seen from Table 1 that the abrasive rate of GX15 is 0.605%, which is lower than that of A05, which is 0.678%, and its abrasive rate coefficient is 0.89. Since the smaller the coefficient of abrasion rate, the higher the abrasion resistance, the abrasion resistance of GX15 material is higher than that of A05 material.
[0068] The GX15 material prepared by the method in Example 1 is used to make the impeller and rear guard ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Macro hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com