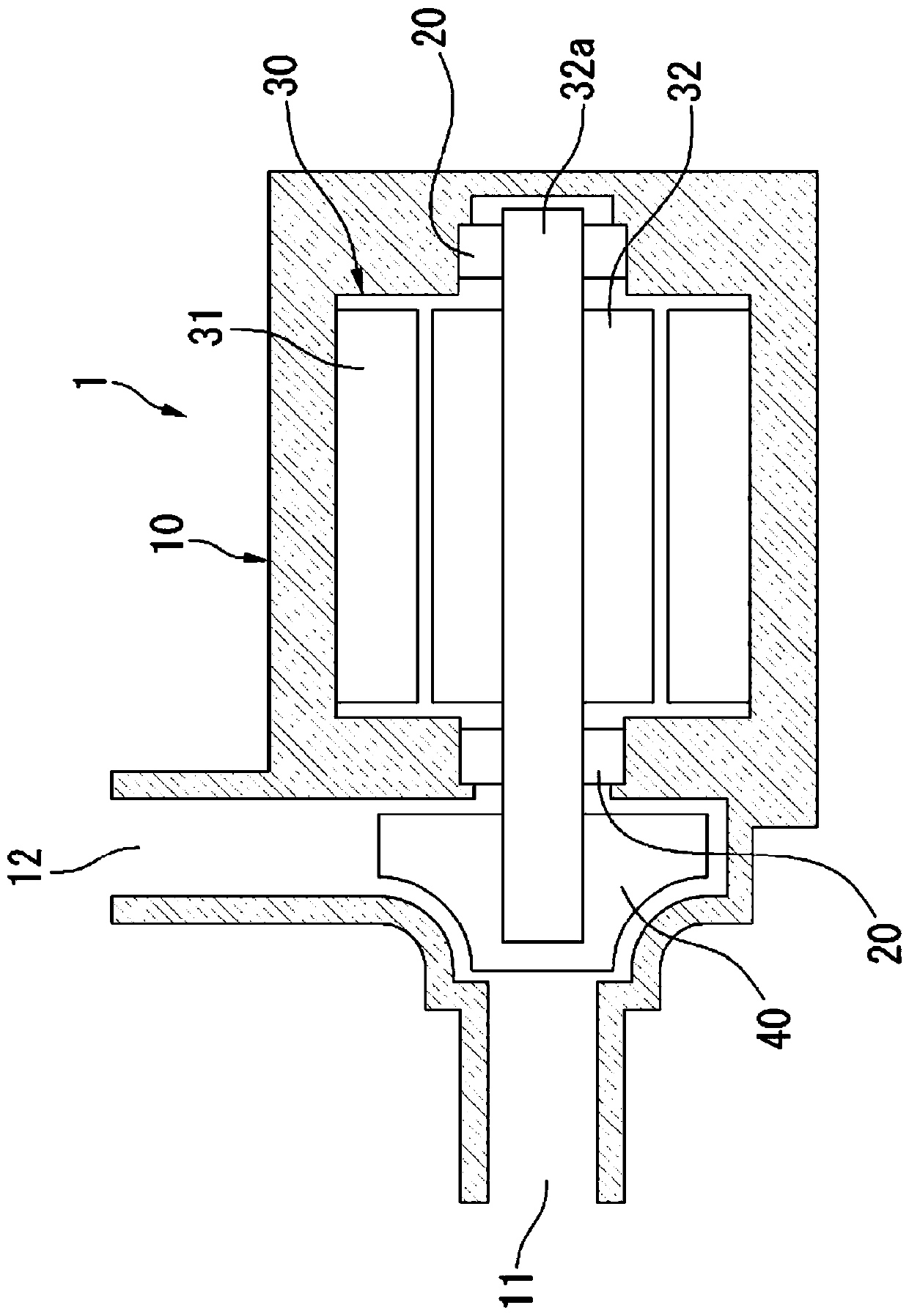
Sintered bearing and method for producing sintered bearing
A technology for sintered bearings and manufacturing methods, applied in the direction of bearings, bearing components, shafts and bearings, etc., can solve the problems of sintered bearings such as low water resistance/corrosion resistance, insufficient sliding properties, and unsuitability, so as to reduce frictional resistance and improve Lubricity, lubricating effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 4
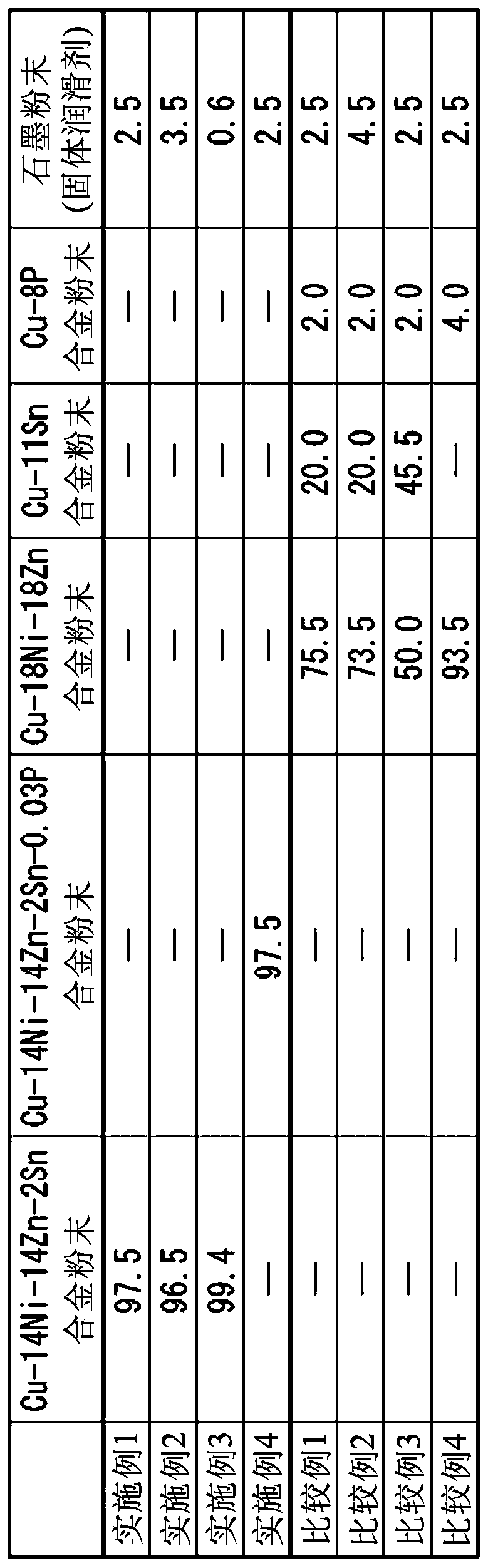
[0224] The raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Example 4 was produced from Cu-14Ni-14Zn-2Sn-0.03P alloy powder and graphite powder (solid lubricant).
[0225] On the other hand, the raw material powders of the sintered bearings of Comparative Examples 1 to 3 were produced from Cu-18Ni-18Zn alloy powder, Cu-11Sn alloy powder, Cu-8P alloy powder, and graphite powder (solid lubricant).
[0226] In addition, the raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Comparative Example 4 was produced from Cu-18Ni-18Zn alloy powder, Cu-8P alloy powder, and graphite powder (solid lubricant).
[0227] Specifically, as image 3 As shown, the raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Example 1 is calculated by stirring and mixing 97.5 mass % Cu-14Ni-14Zn-2Sn alloy powder and 2.5 mass % produced from graphite powder.
Embodiment 2
[0228] The raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Example 2 was obtained by stirring and mixing 96.5% by mass of Cu-14Ni-14Zn-2Sn alloy powder and 3.5% by mass of graphite powder in a mass ratio relative to the total mass of the raw material powder (sintered compact). And generated.
Embodiment 3
[0229] The raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Example 3 was obtained by stirring and mixing 99.4% by mass of Cu-14Ni-14Zn-2Sn alloy powder and 0.6% by mass of graphite powder in a mass ratio relative to the total mass of the raw material powder (sintered compact). And generated.
[0230] The raw material powder of the sintered bearing of Example 4 was obtained by stirring and mixing 97.5 mass % Cu-14Ni-14Zn-2Sn-0.03P alloy powder and 2.5 mass % produced from graphite powder.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com