Efficient simulation algorithm for influence of terrain occlusion on GNSS interference source action area
An area of action and interference source technology, applied in the field of GNSS interference source optimization deployment, can solve the problems of long calculation time and large amount of calculation, and achieve the effect of avoiding interpolation calculation, reducing calculation time, and reducing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] In order to make the technical solutions and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
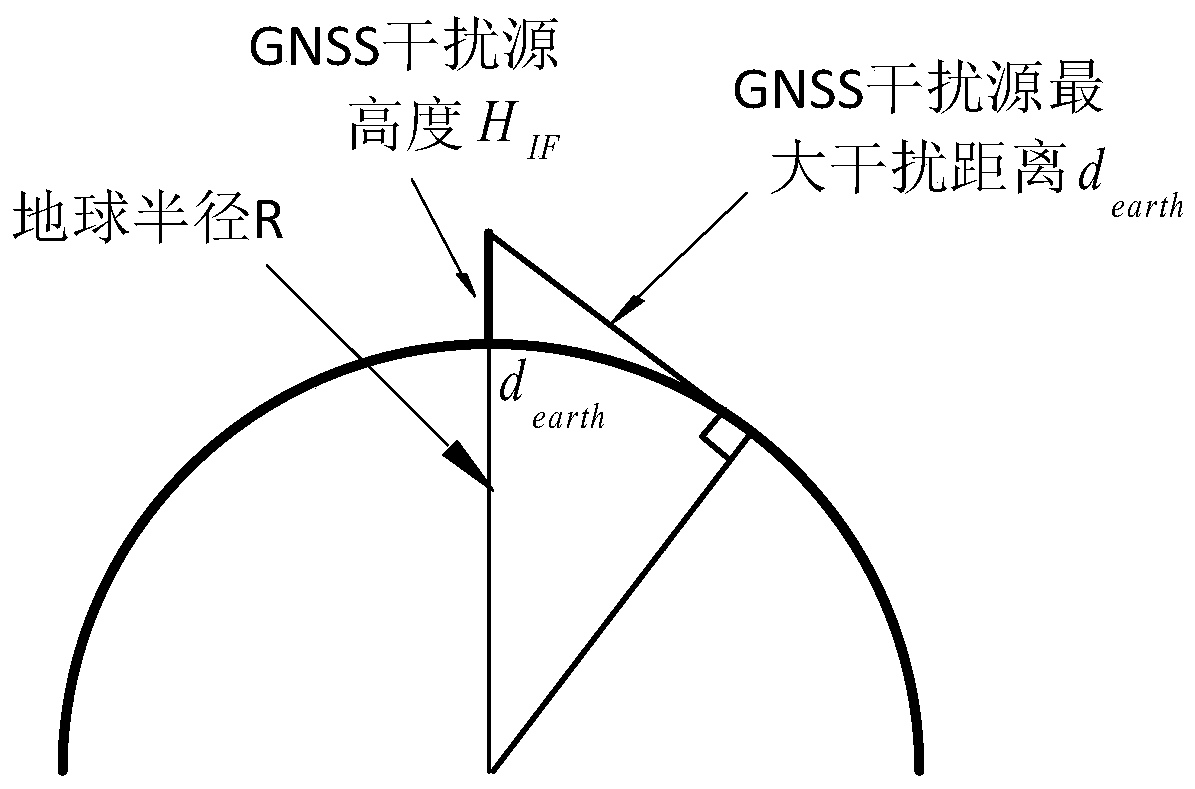
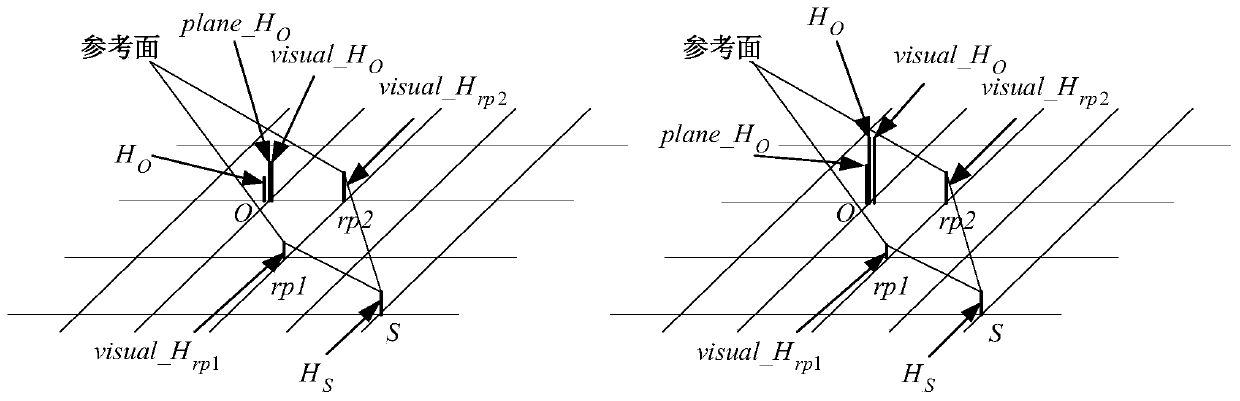
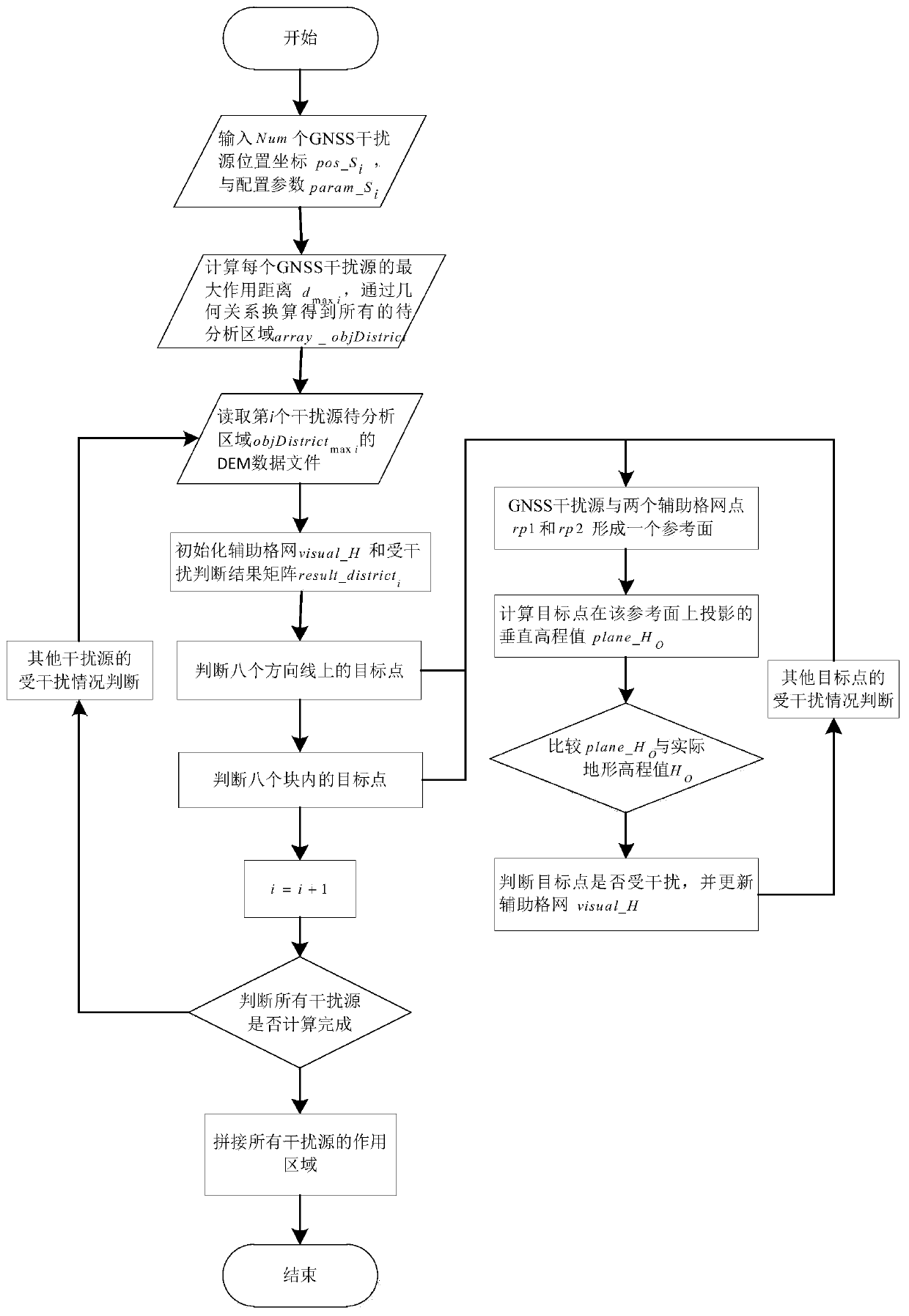
[0044] There are three main factors affecting the action area of GNSS interference sources: free space propagation loss, earth curvature, and terrain occlusion. The present invention comprehensively considers these three factors, and proposes a new GNSS interference source action area calculation method affected by terrain occlusion, which is a GNSS interference source action area calculation method based on the reference plane visible domain analysis.
[0045] Assuming that the GNSS interference source propagates in free space, and does not consider the influence of terrain and earth curvature, the pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com