Automatic calibration method for discrete element hertz contact parameters during geotechnical material simulation
A geotechnical material, automatic calibration technology, used in the analysis of materials, the use of applied stable tension/pressure to test the strength of materials, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problem that the convergence efficiency and convergence accuracy cannot be guaranteed, and the model cannot achieve the best convergence. Efficiency, lack of mathematical foundation and other problems, to achieve the effect of clear implementation process, promotion of analysis and research, and good convergence of calibration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
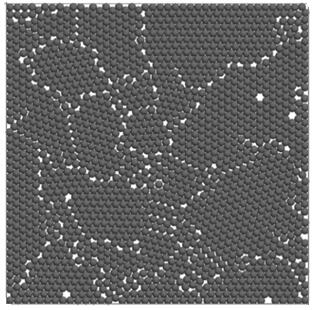
[0170] Apply the method of the present invention to a two-dimensional single-size random particle sample (such as figure 2 ), the test parameters are as follows:
[0171]
[0172] Table 1 Parameters of the two-dimensional single particle random arrangement particle model
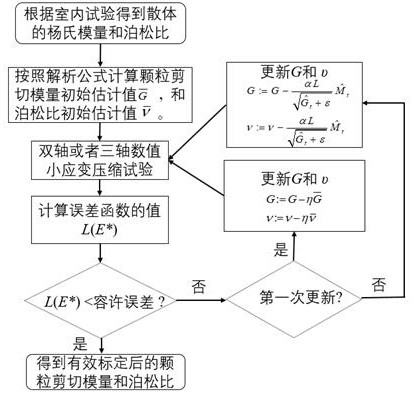
[0173] The calibration steps are as follows:
[0174] Step (1): Determine the macroscopic parameters of rock and soil materials through laboratory tests. In this example, the small strain Young's modulus 10Gpa, Poisson's ratio 0.2 is the calibration target.
[0175] Step (2): Enter the target macroscopic parameters into the following formula, in the case of 2D simulation, the initial estimates of particle contact shear modulus and Poisson's ratio and
[0176] 2D discrete element model:
[0177]
[0178]
[0179] Among them, φ is the porosity in the sample; is the average coordination number of the particle sample; when the sample has a single particle size distribution, r is the parti...
Embodiment approach 2
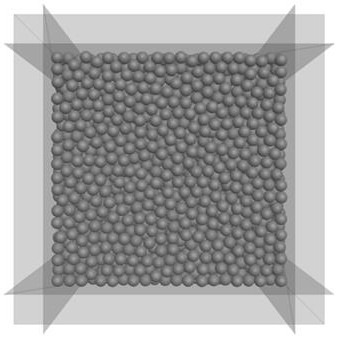
[0207] Apply the method of the present invention to three-dimensional single-size random particle samples (such as image 3 ), the test parameters are as follows:
[0208]
[0209] Table 3 Parameters of the three-dimensional single particle random arrangement particle model
[0210] The calibration steps are as follows:
[0211] Step (1): Determine the macroscopic parameters of rock and soil materials through laboratory tests. In this example, the small strain Young's modulus 10Gpa, Poisson's ratio 0.2 is the calibration target.
[0212] Step (2): Enter the target macroscopic parameters into the following formula, in the case of 2D simulation, the initial estimates of particle contact shear modulus and Poisson's ratio and
[0213] 3D discrete element model:
[0214]
[0215]
[0216] Among them, φ is the porosity in the sample; is the average coordination number of the particle sample; when the sample has a single particle size distribution, r is the par...
Embodiment approach 3
[0226] Apply the method of the present invention to three-dimensional multi-size random particle samples (such as Figure 4 ), the test parameters are as follows:
[0227]
[0228] Table 5 Parameters of three-dimensional multi-size random arrangement particle model
[0229] The calibration steps are as follows:
[0230] Step (1): Determine the macroscopic parameters of rock and soil materials through laboratory tests. In this example, the small strain Young's modulus 10Gpa, Poisson's ratio 0.2 is the calibration target.
[0231] Step (2): Enter the target macroscopic parameters into the following formula, in the case of 2D simulation, the initial estimates of particle contact shear modulus and Poisson's ratio and
[0232] 3D discrete element model:
[0233]
[0234]
[0235] Among them, φ is the porosity in the sample; is the average coordination number of the particle sample; when the sample has a single particle size distribution, r is the particle rad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com