Robot autonomous mapping method in strange environment
A robot and environmental technology, applied in the direction of instruments, electromagnetic wave re-radiation, navigation, etc., can solve the problems of consuming more and more computing resources and low exploration efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing the amount of data processing, improving the speed and improving the efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
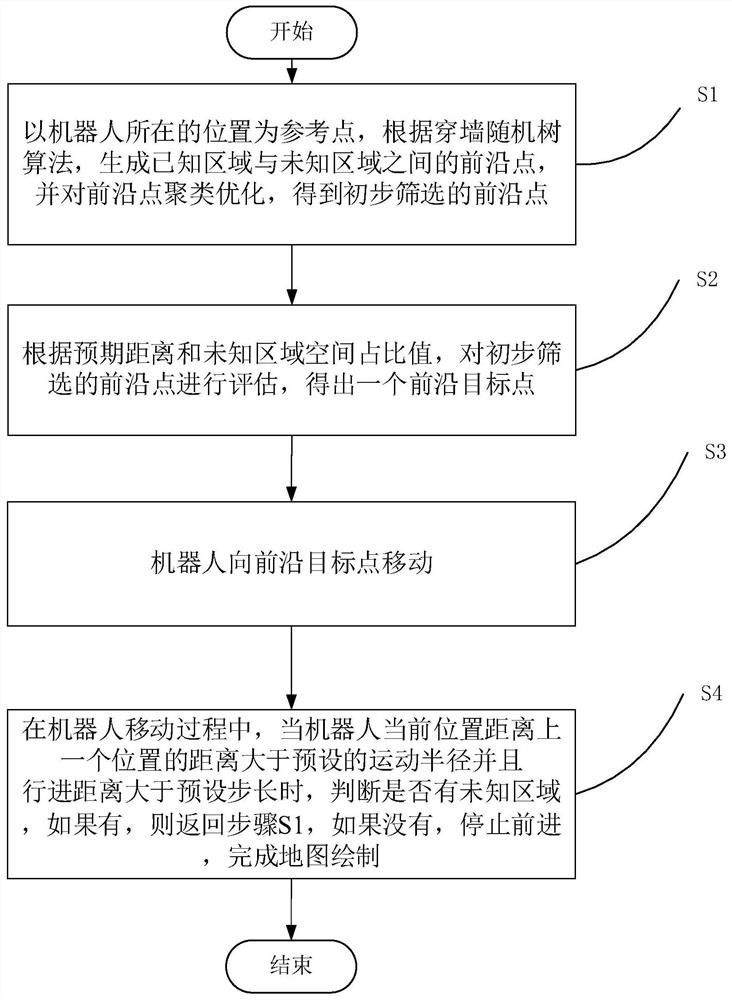
[0041] The flow chart of a method for robot autonomous mapping in an unfamiliar environment is shown in figure 1 As shown, the steps include:
[0042] S1, taking the position of the robot as the reference point, according to the random tree algorithm through the wall, generate all the frontier points between the known area and the unknown area.
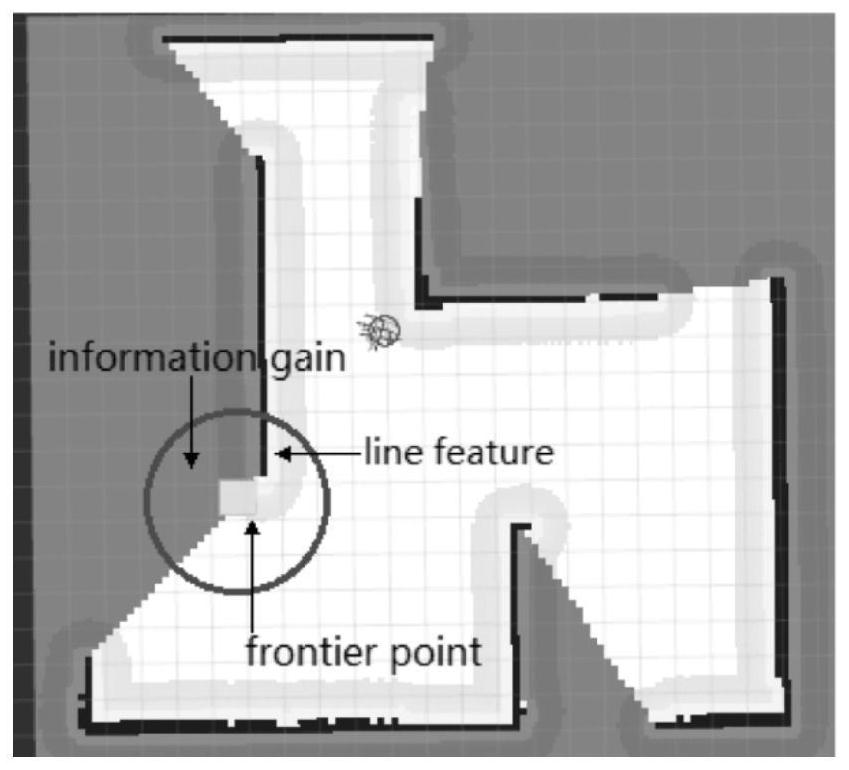
[0043] This method uses the open source SLAM algorithm Gmapping based on the filtering SLAM framework to construct a 2D grid map, and the known area and the unknown area are divided according to the 2D grid map. In a raster map, a raster cell has three states: free, occupied (i.e. obstacles are present) and unknown. The frontier point in the grid map is defined as the boundary between free and unknown grids, and the present invention subsequently uses the wall-through random tree algorithm to generate frontier points on the map, which is also realized based on the grid map. For closed environments, the wall-penetrating random tree a...
Embodiment 2
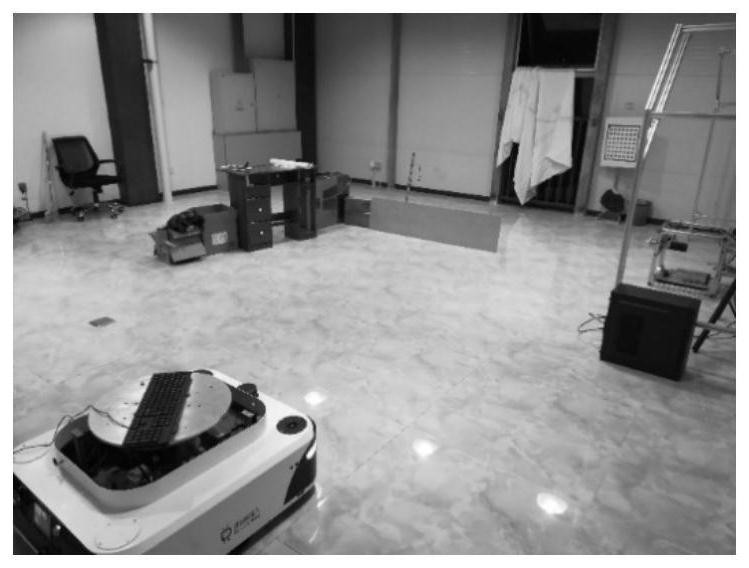
[0065] By adopting the method of the invention, the construction of the map of the unknown area by the robot has been realized. The experimental site is in a free space of 8m×8m, which is simply arranged in cardboard boxes as follows: image 3 venue shown. The robot used in the experiment is a two-wheel differential robot with a size of 85cm×75cm. The experimental robot is shown in the figure Figure 4 . It is equipped with Leishen lidar, the angle is 180 degrees, and the measurement radius is 8m. The picture of the lidar is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0066] The lidar uses USB to serial port to transfer data to the mini-PC, and runs the underlying driver "leishen_lidar_node" node of the lidar to realize the reading and correction of the original data of the lidar, and convert the corrected lidar data into a standard LaserScan format under ROS and issued as a Topic named / uestc003 / scan. Then subscribe and build the map through the / uestc003 / slam_gmapping node, and the / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com