Method for preparing acrylic acid
一种丙烯酸、丙烯的技术,应用在羧酸盐制备、有机化合物的制备、碳基化合物制备等方向,能够解决没有公开丙烯醛等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0013] The production of acrylic acid further comprises contacting the acrolein mixture obtained by the method of the present invention described above with a mixture of oxidation catalysts (the first mixed metal oxide catalyst and the second mixed metal oxide catalyst described above) to produce a mixture containing acrylic acid. Suitable second mixed metal oxide catalysts are known in the art, for example, as described in U.S. Patent No. 4,892,856 and U.S. Patent No. 6,762,148, and include, for example, one of molybdenum, vanadium, tungsten, copper, and antimony or more. In certain embodiments, the second mixed metal oxide catalyst comprises primary and minor components. In certain embodiments, the primary component includes one or more of molybdenum and vanadium. In certain embodiments, the secondary component includes one or more of tungsten, copper, and antimony.
[0014] In certain embodiments, the inventive method step of contacting a reactant gas to form a mixture c...
example 1
[0018] Characterization of Thermal Oxidation Constraints in Exemplary and Comparative Processes
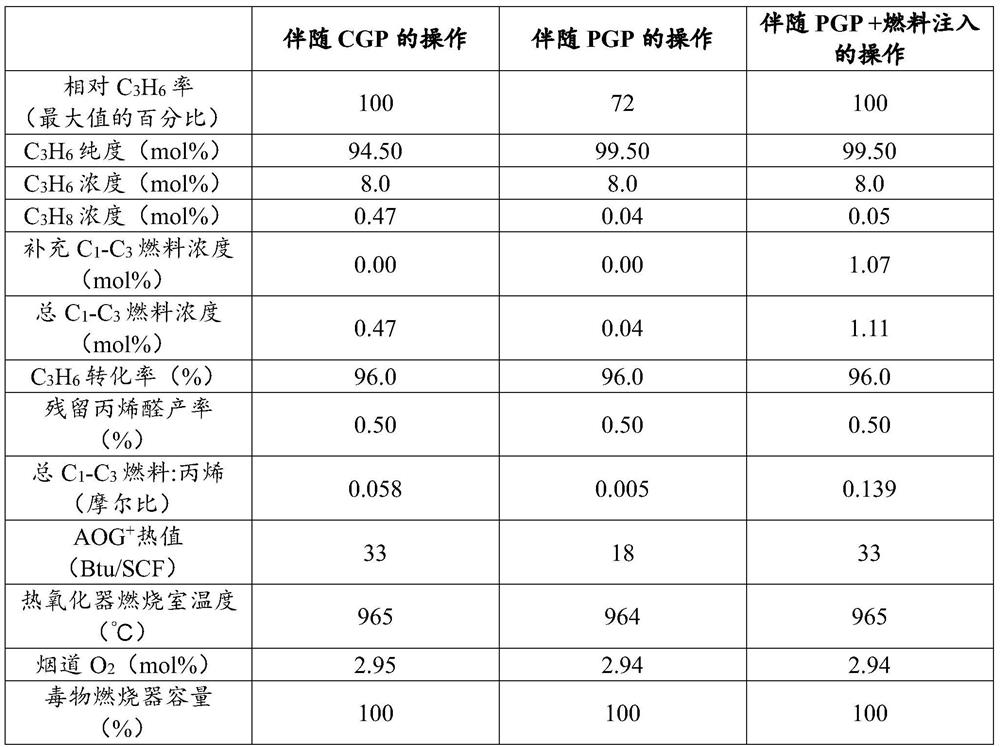
[0019] As shown in Table 1, a conventional two-stage single-pass acrylic acid process operates at typical conditions based on chemical grade propylene ("CGP"), polymer grade propylene ("PGP") and PGP with supplemental fuel.
[0020] Table 1. Thermal Oxidation Constraints in Exemplary and Comparative Processes
[0021]
[0022] + "AOG" means absorber off-gas
[0023] The results show that the process is limited by the energy input to the thermal oxidizer. Operating under the above conditions produces a vapor waste stream containing 30% to 40% of the energy input to the thermal oxidizer. As the purity of the propylene feed increases, the energy content of the vapor waste stream decreases. In the extreme case where the propylene content of the polymer grade propylene feed is at least 99.5%, the energy content in the vapor waste stream is 50% of that in the case of CGP. Witho...
example 2
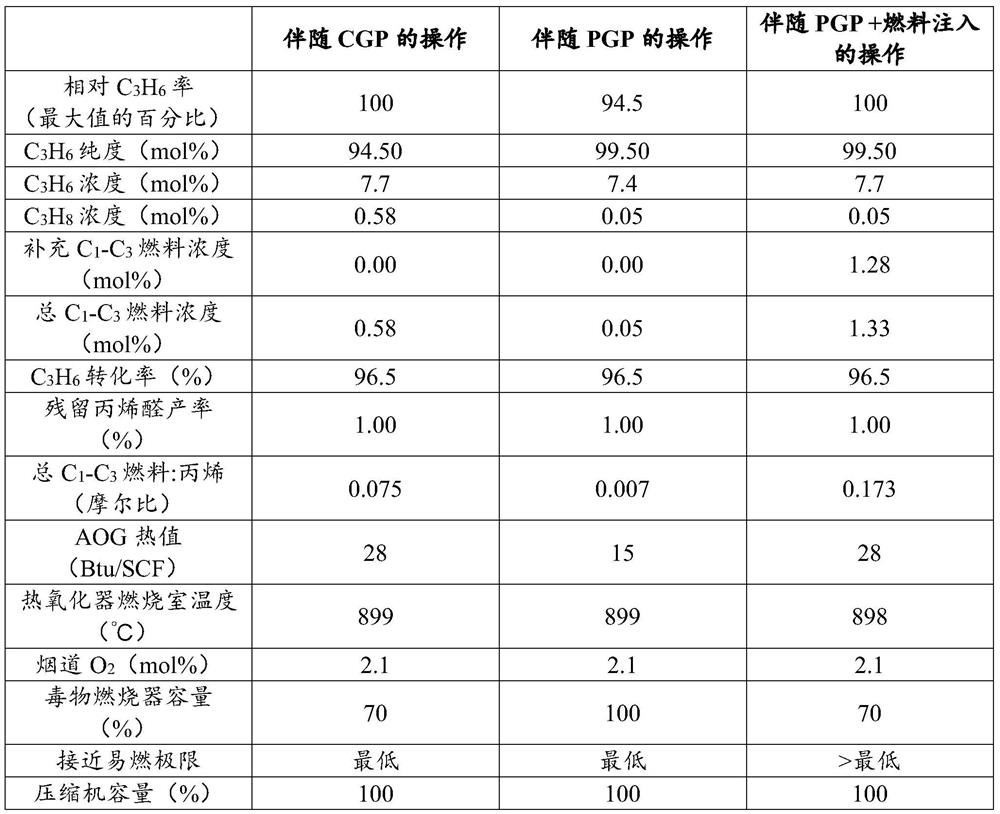
[0026] Characterization of flammability constraints during exemplary and comparative procedures
[0027] One hazard inherent in propylene oxidation is the management of hazards related to the flammability of propylene. This hazard can be controlled by operating with the reactor feed composition outside the flammable zone within some safe margin. The distance between the operating point and the flammable area is defined as approaching the flammable limit. Certain safety margins exist to cover errors in flammability boundary correlations, errors in reactor feed composition determination, and to prevent reactor trips associated with reactor feed flow perturbations. The reactor feed is controlled so that the feed composition moves above the upper flammability limit without passing through the flammable region. When the feed composition exceeds the flammability limit, increasing the fuel content tends to increase the oxygen required to produce a flammable mixture (more fuel incre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com