Method for treating spent catalyst by utilizing magnetite in sintering process
A technology of invalid catalyst and sintering process, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems caused by sintering, and achieve the effect of avoiding quality deterioration and solving the problem of low-temperature reduction and differentiation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] The invention proposes a method for treating spent catalysts in a sintering process by utilizing magnetite, which can properly solve the resource utilization problem of spent catalysts. The sinter produced by this method can meet the various metallurgical performance indicators of the sinter required by the blast furnace. At the same time, it can also use metal elements such as V, W, and Ti in the spent catalyst, which has a positive effect on the protection of the blast furnace lining and the optimization of the quality of molten iron. It provides a new treatment method for the efficient utilization of spent catalysts.
[0039] Concrete experimental steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0040] Step 1: Raw material pretreatment
[0041] (1) Treatment and crushing of spent catalyst: Take the spent SCR catalyst used in the industrial field, treat and break the spent catalyst: remove the blockage in the pores of the catalyst, and then use strong wind to remove ...
Embodiment 2
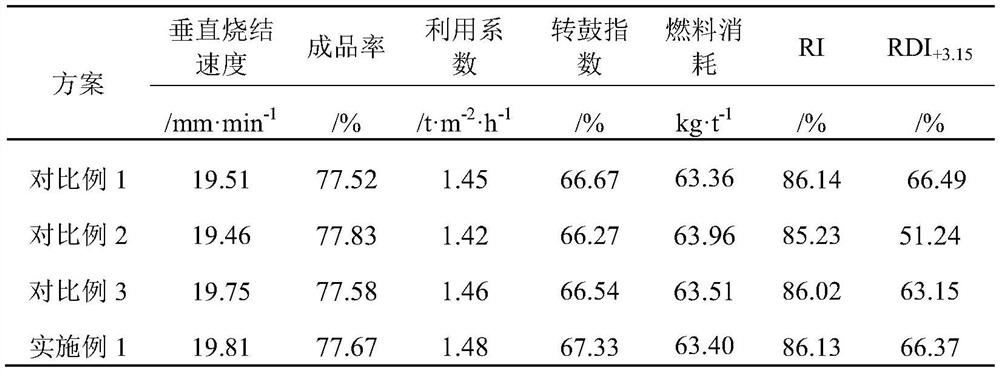
[0085] The basic process of the new method of using the sintering procedure to process the spent catalyst of the present embodiment is the same as that of Example 1, the difference is that the spent catalyst add-on of the present embodiment accounts for 1% of the weight percentage a of the total raw material for sintering, and the sintered magnetite add-on Accounting for sintering total raw material weight percentage b is 4.08%, therefore, the mass percent of each component of the dry material of sintering mixture is: card powder: 10.66%, Brazilian mixed powder: 4.52%, wool tower powder: 3.09%, Pb powder: 15.63%, Newman powder: 3.13%, Yangdi powder: 11.15%, dirty ore: 0.55%, sintered magnetite powder: 5.94%, returned ore: 24.38%, limestone: 3.98%, dolomite: 4.38%, quicklime: 3.13%, fuel: 4.38%, pre-granulated pellets containing spent catalyst: 5.08%, sinter production quality indicators and sinter metallurgical properties are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
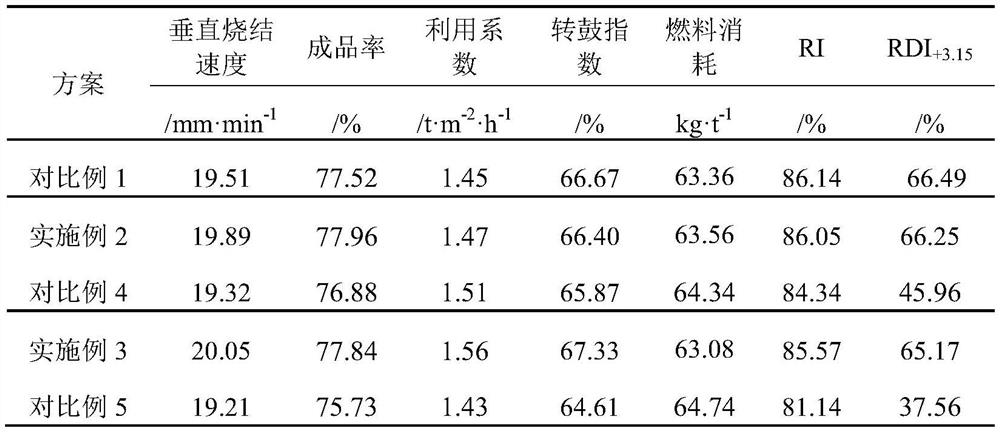
[0089] The basic process of the new method of using the sintering process to process the spent catalyst in this embodiment is the same as in Example 1, the difference is that the amount of spent catalyst used for pre-granulation accounts for 2% of the weight percentage a of the total raw material for sintering in this embodiment. The amount of sintered magnetite added in the pre-granulation accounted for 8.16% of the weight percentage b of the total raw material for sintering. Therefore, the mass percentages of each component of the dry material of the sintered mixture are: card powder: 10.55%, Brazil mixed powder: 4.47%, Raw tower powder: 3.06%, Pb powder: 15.47%, Newman powder: 3.10%, Yangdi powder: 11.04%, dirty ore: 0.54%, sintered magnetite powder: 1.76%, returned ore: 24.13%, limestone: 3.94 %, dolomite: 4.33%, quicklime: 3.10%, fuel: 4.33%, pre-granulated pellets containing spent catalyst: 10.16%, sintering production quality indicators and sintering metallurgical proper...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com