Novel structure cable, photoelectric composite cable, composite optical cable and shell
A new type of structure and housing technology, applied in the direction of insulating cables, communication cables, fiber mechanical structures, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, not compact enough structure, poor heat dissipation effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
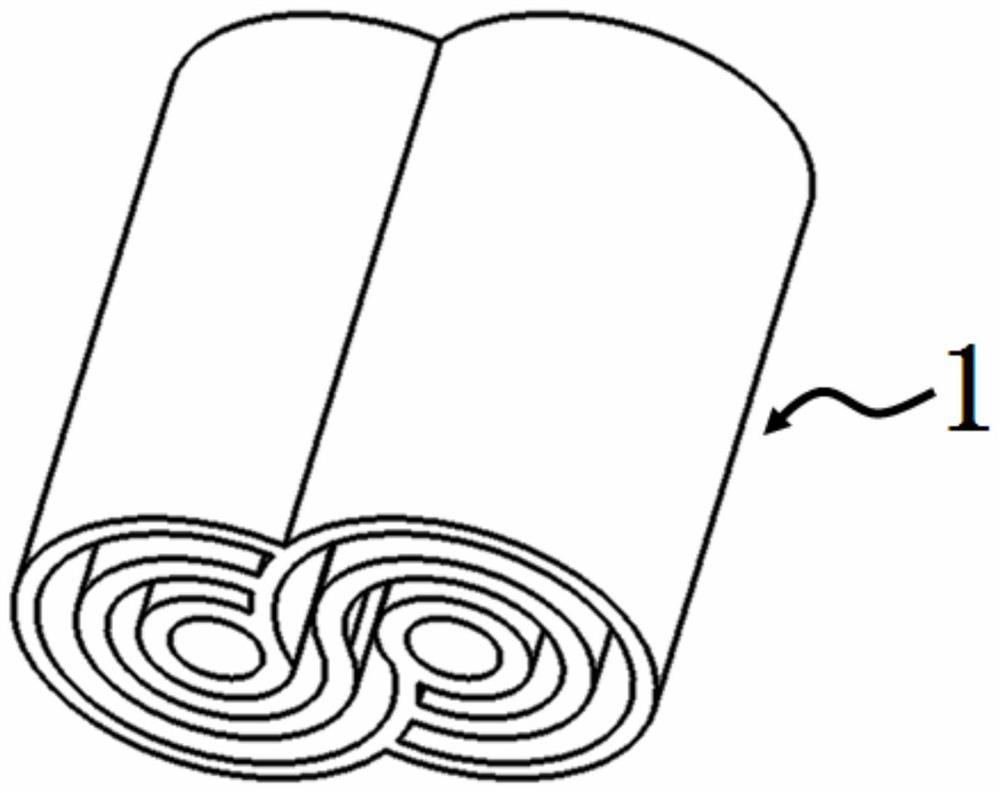
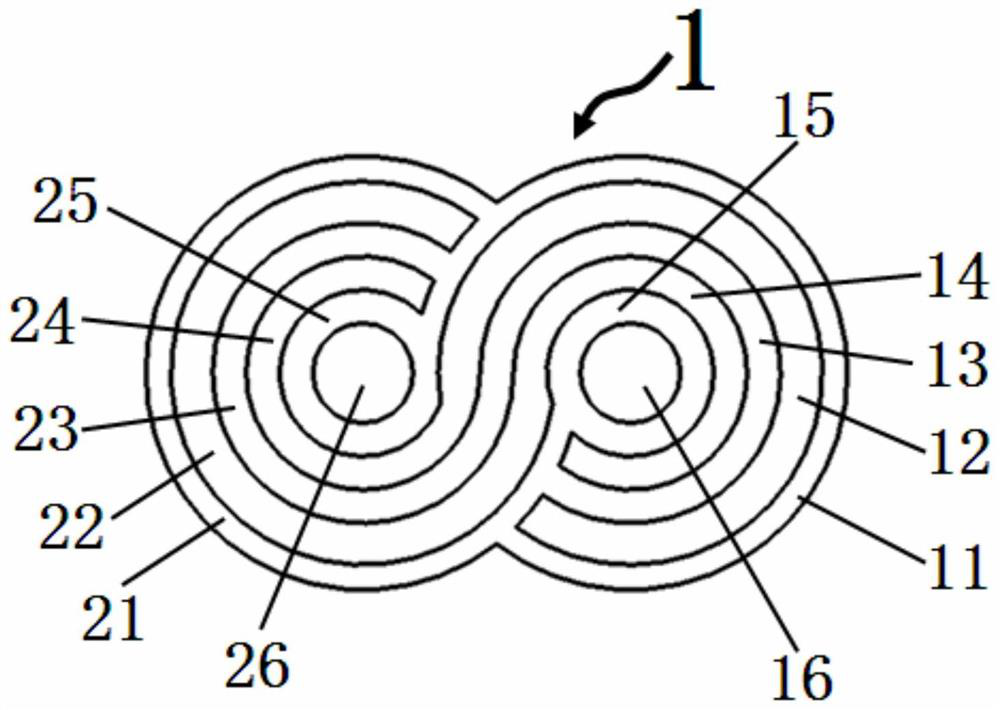
[0068] please see Figure 1 to Figure 3 , a new type of structural cable, with a housing 1, a first power transmission unit 32, a second power transmission unit 34, a third power transmission unit 36, a fourth power transmission unit 42, a fifth power transmission unit 44, a sixth power transmission unit 46, a third power transmission unit The power transmission unit 36 is composed of a first electric conductor 361 and a first insulator 362 covering the first electric conductor, and the sixth power transmission unit 46 is composed of a second electric conductor 461 and a second insulator 462 covering the second electric conductor constitute;
[0069] It is characterized in that: the housing 1 is an integral structure, the housing 1 is composed of a first protection body and a second protection body, and the first protection body is composed of a first insulating layer 11 and a first cavity distributed sequentially from outside to inside. body 12, second insulating layer 13,...
Embodiment 2
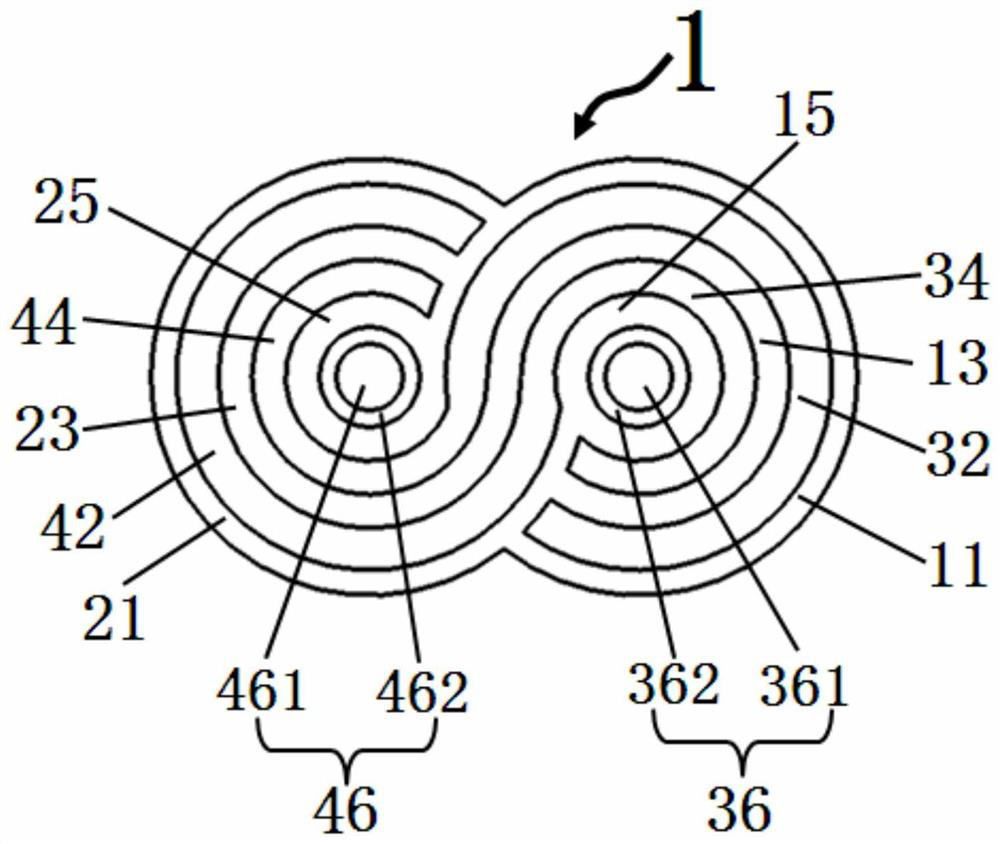
[0091] please see Figure 4 , and refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , a new structure photoelectric composite cable, with a housing 1, a first power transmission unit 32, a second power transmission unit 34, a first light transmission unit 56, a fourth power transmission unit 42, a fifth power transmission unit 44, a second light transmission unit 66, the first light transmission unit 56 is composed of the first photoconductor 561 and the first sleeve 562 located outside the first photoconductor 561, and the second light transmission unit 66 is composed of the second photoconductor 661 and the second photoconductor located The second casing 662 other than 661 constitutes;
[0092]It is characterized in that: the housing 1 is an integral structure, the housing 1 is composed of a first protection body and a second protection body, and the first protection body is composed of a first insulating layer 11 and a first cavity distributed sequentially from outside to inside. body 12, s...
Embodiment 3
[0109] please see Figure 5 , and refer to Figure 1 to Figure 4 , a new structure photoelectric composite cable, has a housing 1, a plurality of first power transmission units 32, a plurality of second power transmission units 34, a first light transmission unit 56, a plurality of fourth power transmission units 42, a plurality of fifth power transmission units Unit 44, the second light transmission unit 66, the first light transmission unit 56 is composed of the first light conductor 561 and the first sleeve 562 outside the first light conductor 561, the second light transmission unit 66 is composed of the second light conductor 661 and the second sleeve 662 outside the second photoconductor 661;
[0110] It is characterized in that: the housing 1 is an integral structure, the housing 1 is composed of a first protection body and a second protection body, and the first protection body is composed of a first insulating layer 11 and a first cavity distributed sequentially from...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com