Preparation method of ultralow-friction rubber material
A rubber material and ultra-low friction technology, applied in the field of friction materials, can solve problems such as poor retention, complicated process, and high production costs, and achieve the effects of reducing friction coefficient and wear rate, simple operation, and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
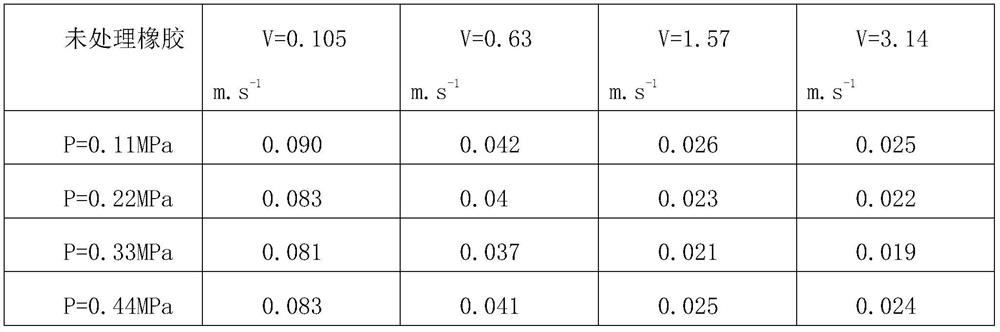
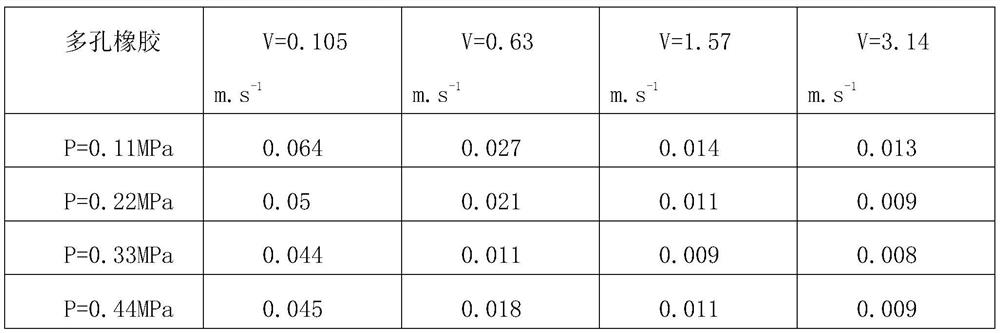
[0020] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an ultra-low friction rubber material, which includes 6 parts by weight of rubber and 0.5-2 parts by weight of a pore-forming agent. In this embodiment, the number of parts by weight of the pore-forming agent is 1 part.
[0021] The rubber is an existing and commonly used rubber, which is not specifically limited, and can be nitrile rubber, natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, butadiene rubber, or isoprene rubber, etc.; in this embodiment, nitrile rubber is selected.
[0022] The pore-forming agent is non-toxic and water-soluble particles, which can be sodium chloride or potassium chloride. In this embodiment, low-cost and easily available sodium chloride is selected. The particle size of the pore-forming agent is 140-200 μm, and as a further preference, the particle size of the pore-forming agent is 164±15 μm.
[0023] The specific preparation steps include fully blending the rubber and the pore-forming agent, follow...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The difference between this embodiment and Example 1 is only that the parts by weight of the pore-forming agent are 0.5 parts, the selected rubber is natural rubber, the pore-forming agent is potassium chloride, and the particle size of the pore-forming agent is 140 μm. The number of times of refining in the machine is 20 times, the pressure of vulcanization treatment is 9.5MPa, the temperature is 160°C, and the time is 25min.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The difference between this example and Example 1 is that the weight parts of the pore-forming agent is 2 parts, the rubber used is isoprene rubber, the particle size of the pore-forming agent is 200 μm, and the number of refining times in the open rubber mixer is 35 times, the pressure of vulcanization treatment is 10.5MPa, the temperature is 180°C, and the time is 35min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com