Pathogenic gene locus database and establishment method thereof
A disease-causing gene and method establishment technology, applied in genomics, instrumentation, proteomics, etc., can solve problems such as unknown significance, neglected sites, and large amounts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
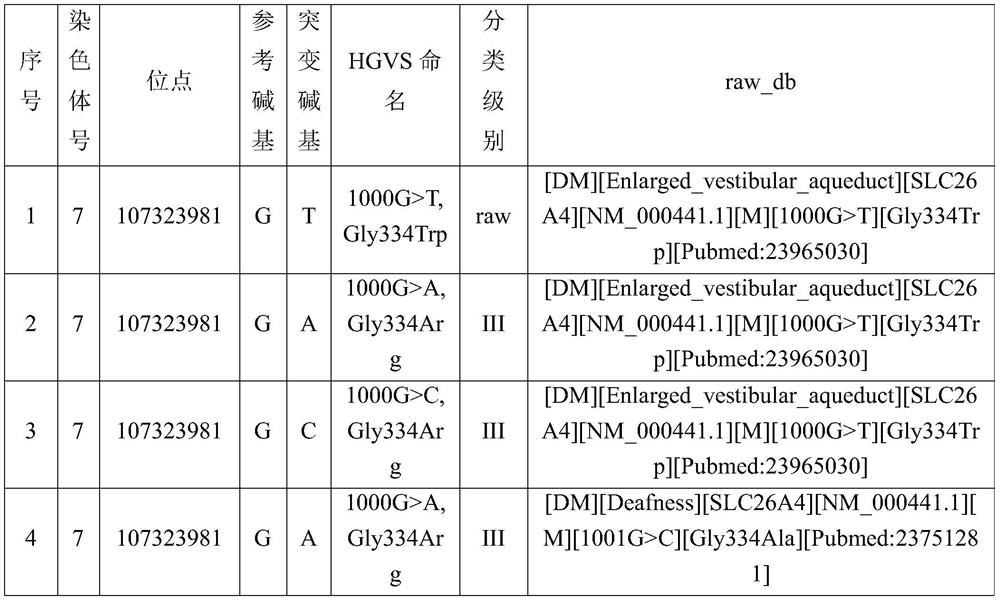
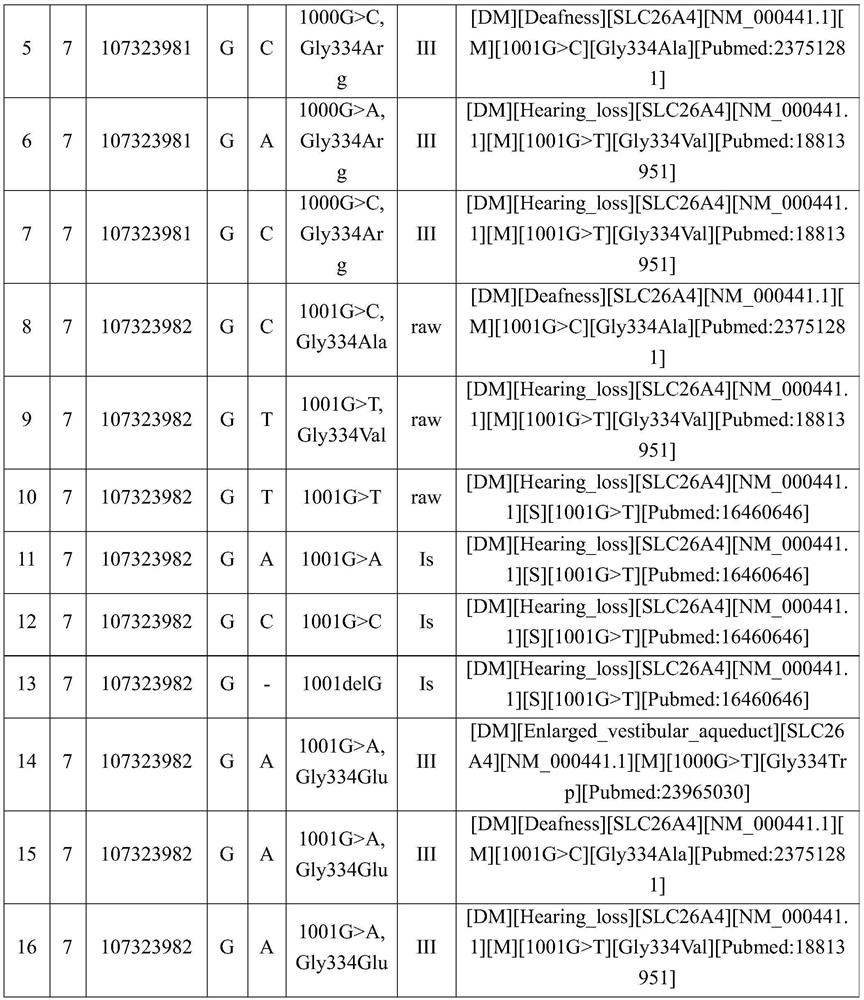
[0042] A disease-causing gene locus database is established by the following methods:
[0043] 1. Obtain reference data.
[0044] Obtain clinically verified disease-causing gene locus data information as reference data.
[0045]For example, clinically verified disease-causing gene locus data information can be obtained from databases that include pathogenic loci, such as HGMD, ClinVar, etc. In this embodiment, the HGMD database is used as the basis for expansion.
[0046] 2. Expand to obtain mutation site data.
[0047] Amino acid changes caused by base mutations are the most common type of mutations recorded in the disease-causing site database. There are often many types of base mutations that cause a certain amino acid change. Some require mutations to specific amino acids to cause disease, and some require mutations. Mutations to stop codons cause disease, and some only require amino acid changes to cause disease, but only sites with published research results are includ...
example 1
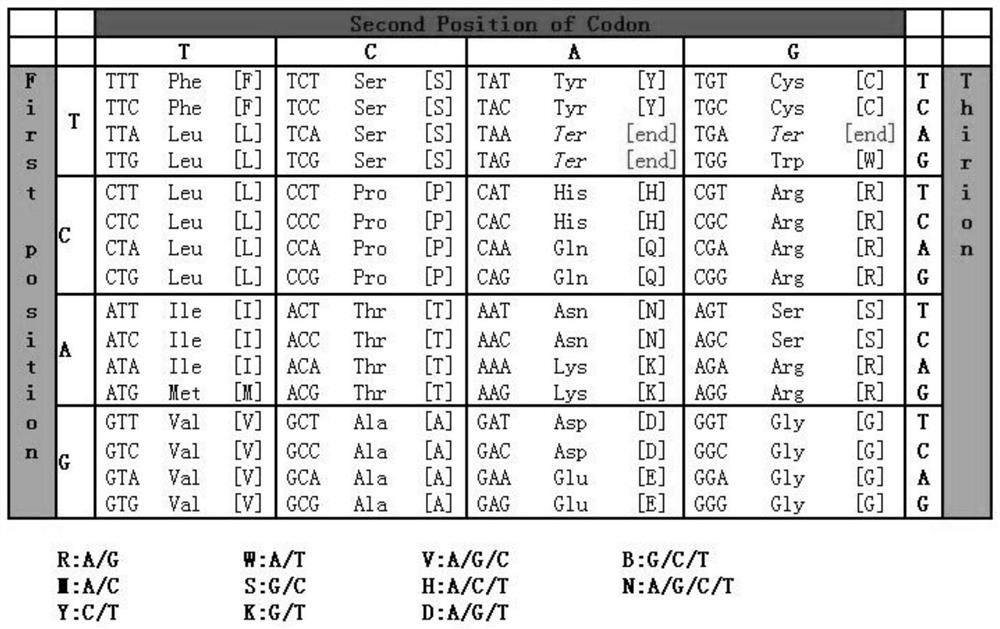
[0056] For example, the 268th amino acid of the DMD gene is Leu, and the codon is TTA, and there is only one record in the database, namely [c.804A>C; p.Leu268Phe]. After checking the codon table, there may be 9 single-base mutations at this codon, which are as follows:
[0057] 1) Two are termination mutations: [c.803T>A; p.Leu268Term], [c.803T>G; p.Leu268Term];
[0058] 2) Five missense mutations: [c.804A>C; p.Leu268Phe], [c.804A>T; p.Leu268Phe], [c.803T>C; p.Leu268Ser], [c.802T> A; p.Leu268Ile], [c.802T>G; p.Leu268Val];
[0059] 3) There are two synonymous mutations: [c.804A>G; p.Leu268Leu], [c.802T>C; p.Leu268Leu];
[0060] After comparing with the reference data of pathogenic mutation sites [c.804A>C; p.Leu268Phe] in the HGMD database, [c.804A>T; p.Leu268Phe] can be expanded to class I; [c.803T >A; p.Leu268Term], [c.803T>G; p.Leu268Term] can be extended to type II; [c.803T>C; p.Leu268Ser], [c.802T>A; p.Leu268Ile], [ c.802T>G; p.Leu268Val] can be extended to category Ⅲ...
example 2
[0062] The 333rd amino acid of DMD gene is Ser, the codon is TCA, and there is only one record in the database, namely [c.998C>A; p.Ser333Term]. After checking the amino acid codon table, there are 9 single-base mutations at this codon, which are as follows:
[0063] 1) There are two termination mutations: [c.998C>A, p.Ser333Term], [c.998C>G, p.Ser333Term];
[0064] 2) There are 4 missense mutations: [c.998C>T, p.Ser333Leu], [c.997T>C, p.Ser333Pro], [c.997T>A, p.Ser333Thr], [c.997T >G,p.Ser333Ala];
[0065] 3) There are three synonymous mutations: [c.999A>T, p.Ser333Ser], [c.999A>C, p.Ser333Ser], [c.999A>G, p.Ser333Ser];
[0066] After comparing with the reference data [c.998C>A; p.Ser333Term] of the pathogenic mutation site in the HGMD database, it can be concluded that [c.998C>G, p.Ser333Term] can be extended to class I, and can also be extended to Class II, because class I overlaps with class II, that is to say, the mutation in the original database is a termination muta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com