Culture material and culture method for cultivating agaricus bisporus by utilizing dry-wet separated cow dung
A technology of dry-wet separation and cow dung, which is applied in cultivation, plant cultivation, mushroom cultivation, etc., to achieve the effects of high mushroom density, increased utilization value, and high yield per unit area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
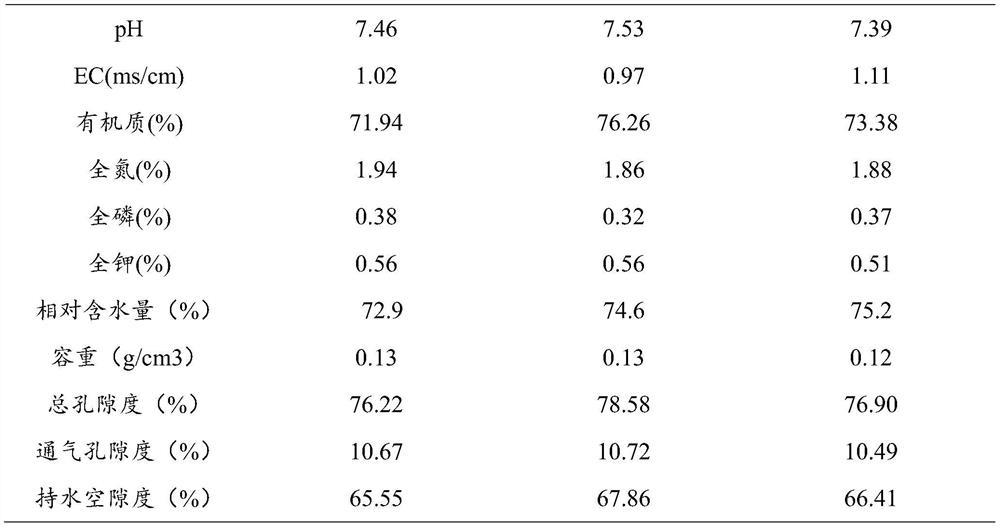
[0027] A compost for planting Agaricus bisporus using dry-wet separation of cow dung, the nutrient is made of the following raw materials in parts by weight:
[0028] 54 parts of Pleurotus eryngii mushroom residue, 42 parts of dry-wet separated cow manure, 0.8 part of superphosphate, 0.2 part of compound fertilizer, 0.5 part of wheat bran, 1.5 part of lime, and 1 part of gypsum; the quality of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in compound fertilizer The ratio is 1:1:1.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Agaricus bisporus culture
[0040] The strain of Agaricus bisporus tested was "W192", which was quoted from the Institute of Edible Fungi, Fujian Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Dry-wet separation of dairy cow dung comes from the Animal Husbandry Research Institute of Huanggang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and Pleurotus eryngii mushroom residue comes from Wuhan Tiantian Edible Fungi Co., Ltd.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com