In-vitro efficient preparation method and application of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human inducible pluripotent stem cells
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, applied in the field of high-efficiency preparation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro, can solve the problems of long differentiation cycle, low efficiency and complicated differentiation operation of mesenchymal stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
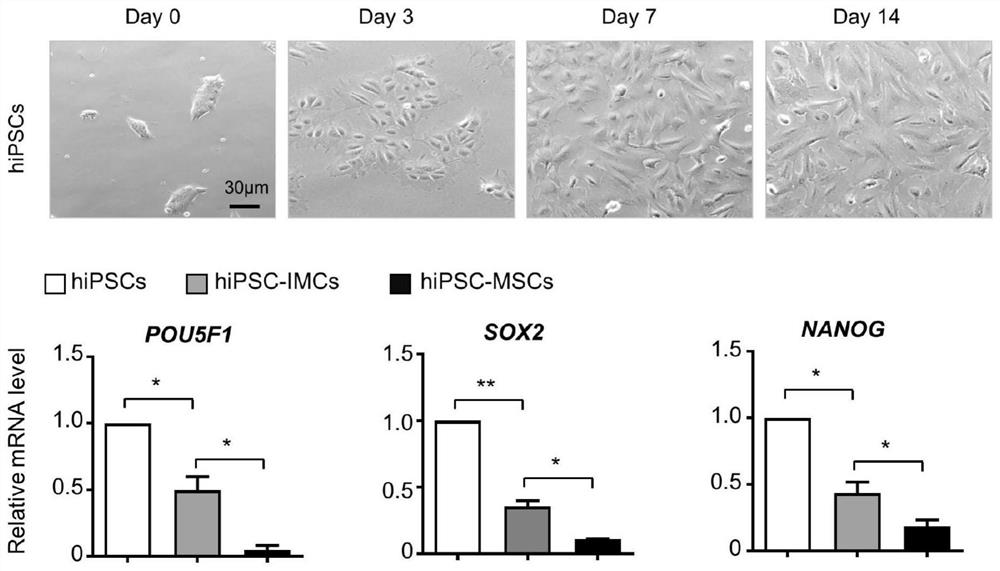
[0028] Example 1: Culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells.
[0029] 1. GFR matrigel plating: according to the GFR matrigel (Corning) instruction manual, after diluting with DMEM-F12 medium, transfer to a six-well cell culture plate (1mL / well) with a pipette, and transfer to 37°C cell culture box incubate for 1 hour for later use;
[0030] 2. Digestion of human induced pluripotent stem cells: According to the Dispase enzyme product manual (StemCell Technology), human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) were digested at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate and digest in a cell incubator for 5 minutes to single cells, resuspend in 5 mL of DMEM-F12 medium and pipette to single cells with a 10 mL pipette, then centrifuge (at room temperature, 300g for 5 minutes), then maintain with 3 mL of human pluripotent stem cells The above hiPSCs were resuspended in medium (Gibco E8 medium, with a final concentration of 10 nM Y-27632 added) and counted for later use.
[0031] Inoculation of hu...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into mesenchymal stem cells.
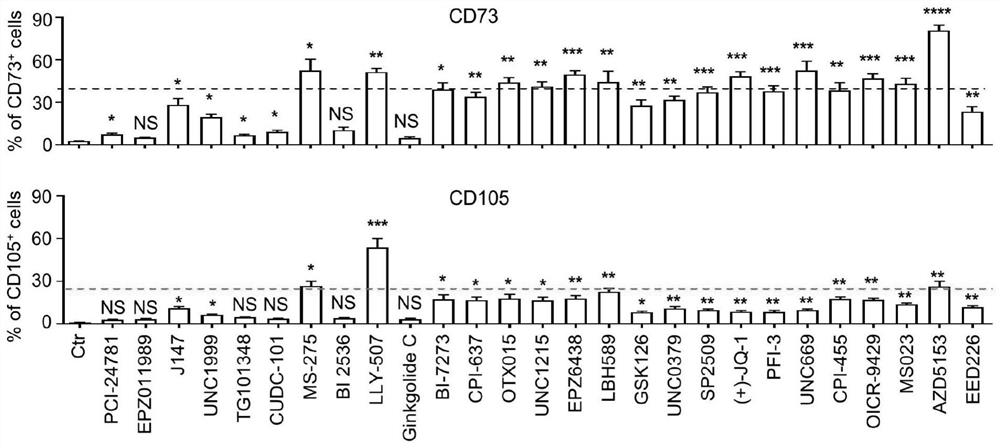
[0033] 1. Preparation of hiPSCs-to-MSCs-inducing differentiation medium: prepare in advance the induction-differentiation basal medium (3% fetal bovine serum, DMEM-F12 medium, 5nM Y-27632), in which the experimental group adds corresponding small chemical molecules (PCI- 24781, EPZ011989, J147, UNC1999, TG101348, CUDC-101, MS-275, BI 2536, LLY-507, Ginkgolide C, BI-7273, CPI-637, OTX015, UNC1215, EPZ6438, LBH589, GSK126, UNC0379, SP2 (+)-JQ-1, PFI-3, UNC669, CPI-455, OICR-9429, MS023, AZD5153, EED226), the final concentration was 10nM / mL, and the control group was the basal medium for inducing differentiation (without adding chemical small molecular).
[0034] 2. Cell treatment: Observe the morphology and density of hiPSCs under a microscope. When the cells grow into small clones, add the original old human pluripotent stem cell maintenance medium (Gibco E8 medium, and add...
Embodiment 3
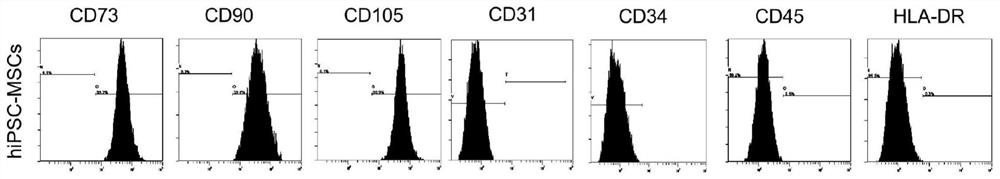
[0040] Example 3: In vitro functional identification of mesenchymal stem cells (hiPSC-MSCs) produced by differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells.
[0041] 1. Adipogenic, osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of hiPSC-MSCs in vitro: according to 6×10 4 Cells / well were seeded in six-well cell-adherent culture plates (Corning), and when hiPSC-MSCs grew adherently until the cell confluence reached 70%-80%, the hiPSC-MSCs maintenance medium was discarded and the in vitro directional induction and differentiation were performed as follows.
[0042] (1) In vitro induced adipogenic differentiation culture system: After discarding the mesenchymal stem cell maintenance medium (DMEM-F12 medium, adding 10% fetal bovine serum, 10ng / ml bFGF, 4ng / ml EGF), replace Stem Cell company The MensenCult adipogenic differentiation medium was replaced with a fresh above-mentioned adipogenic differentiation medium every 3.5 days, and the culture continued until the 18th day. The d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com