Method for estimating breeding value by fitting genome with non-additive effect
A technology of additive effect and breeding value, applied in the fields of genomics, proteomics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of complex genetic composition, and achieve the effect of good flexibility, improved prediction accuracy, and improved estimation accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
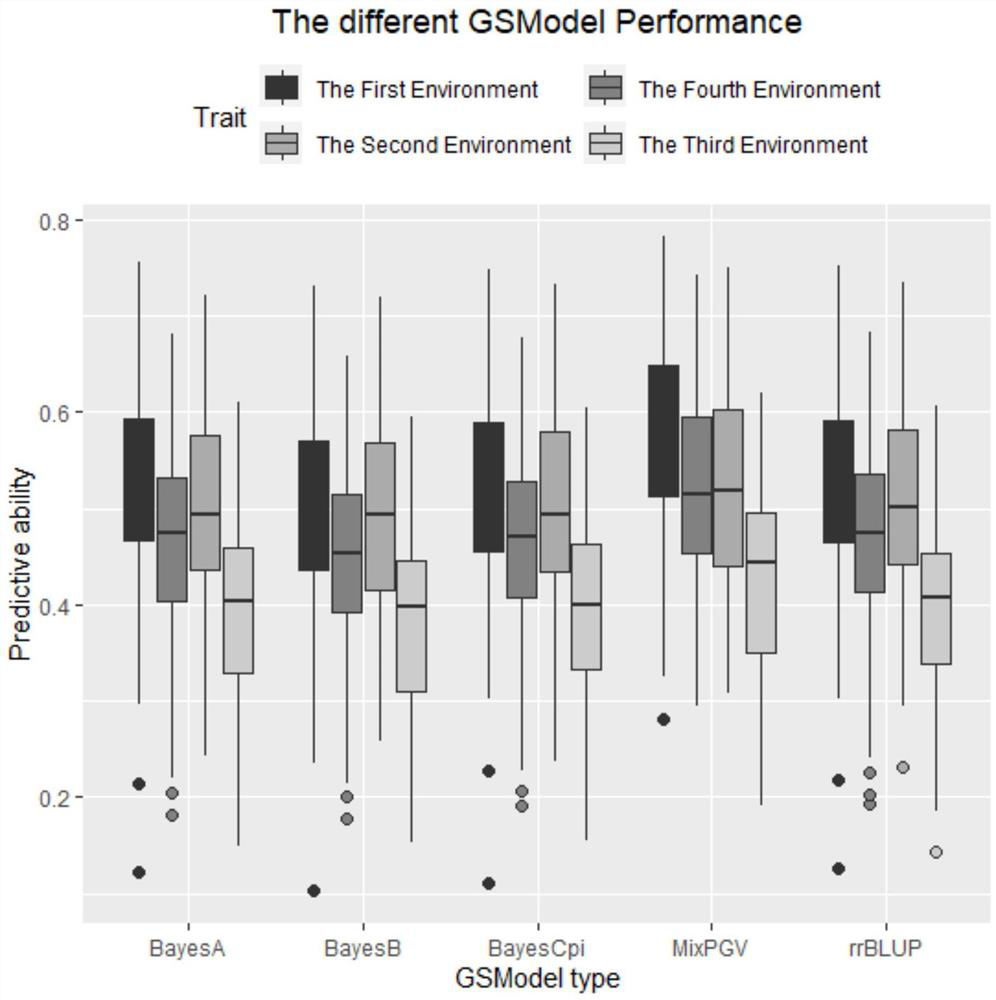
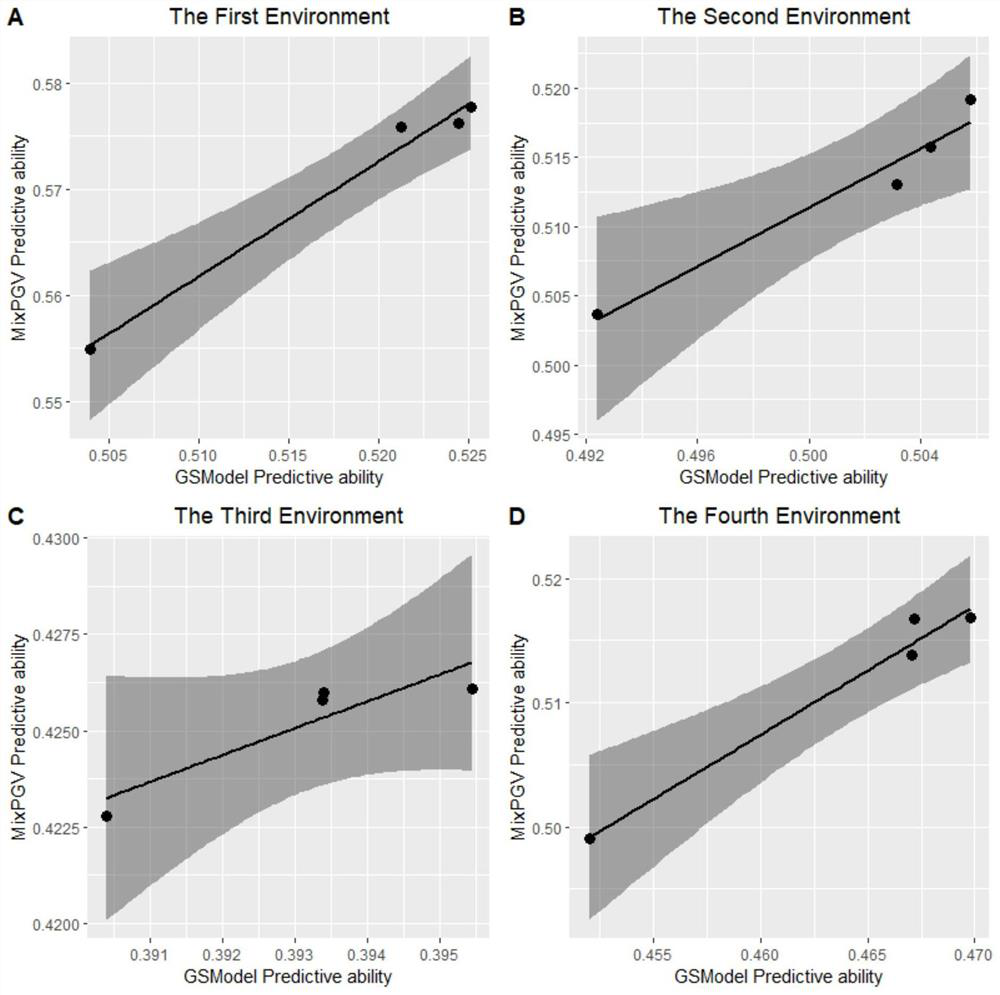
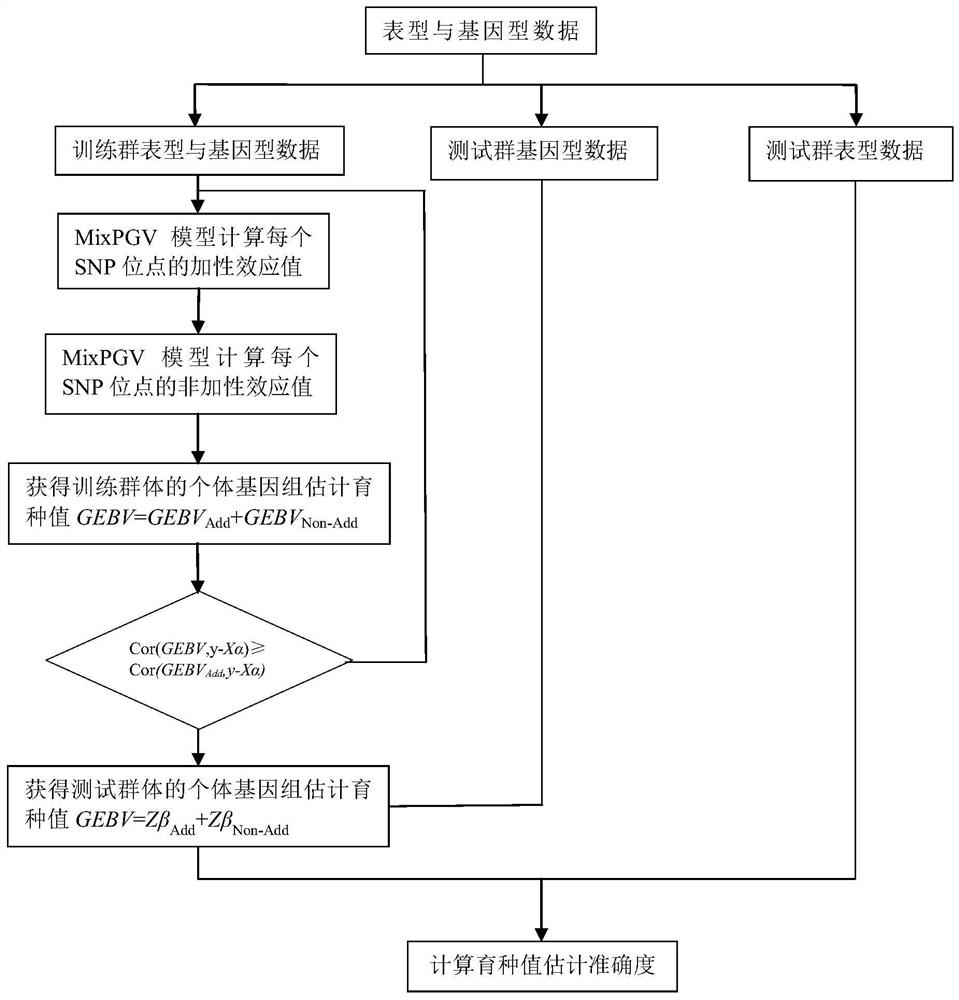
[0047] The experimental data is the wheat data set provided by CIMMYT Global Wheat Project, which contains 599 wheat lines. The wheat dataset includes the average yield of wheat in four environments, and the dataset has four objects: wheat.Y, wheat.A, wheat.X, and wheat.set. wheat.Y is the two-year average yield of wheat lines; wheat.A is the molecular relationship matrix of the same family; wheat.X is the DArT marker genotype, and the data comes from pure breeds. For the DArT marker, an allele is coded by 1 or 0, indicating its presence or absence, respectively. The wheat set represents 10 sets of observations that are disjoint from each other.
[0048] The specific method of calculating the genome estimated breeding value for wheat in each observation set is as follows:
[0049] 1) Data collection: sampling the wheat individuals to be judged, and measuring the phenotype value and genotype data of each individual;
[0050] 2) data grouping: the wheat individuals in step 1)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com