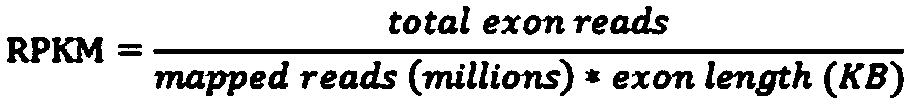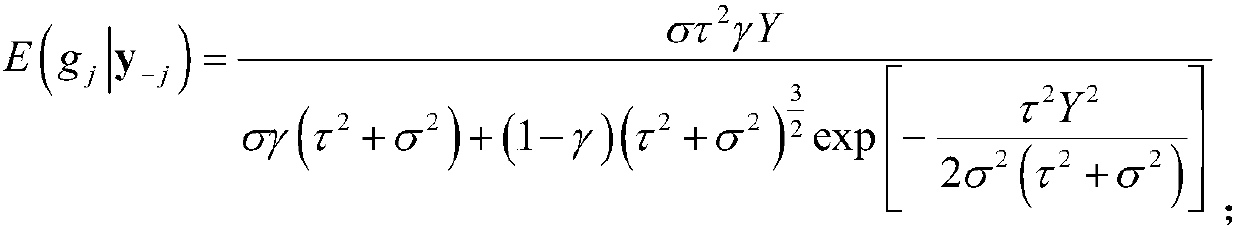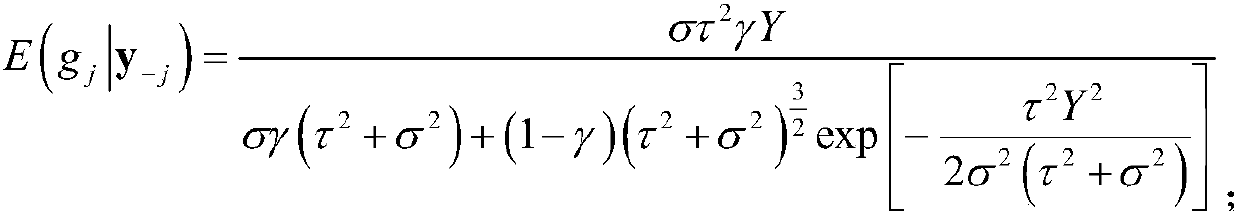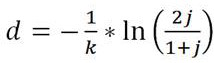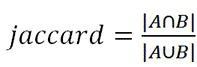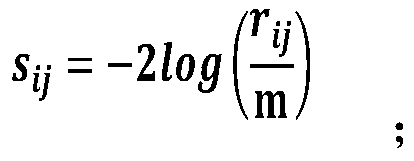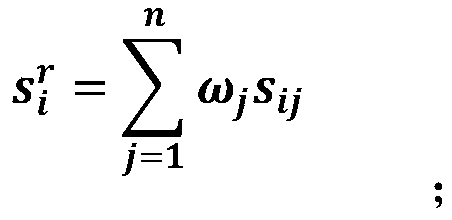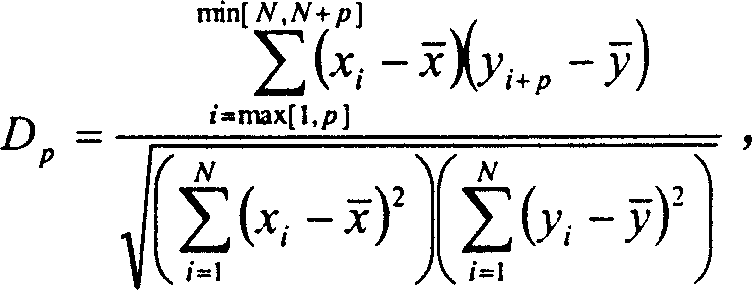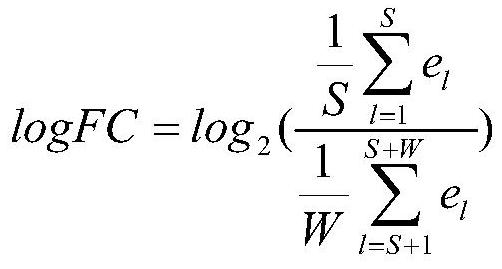Patents
Literature
62 results about "Computational gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
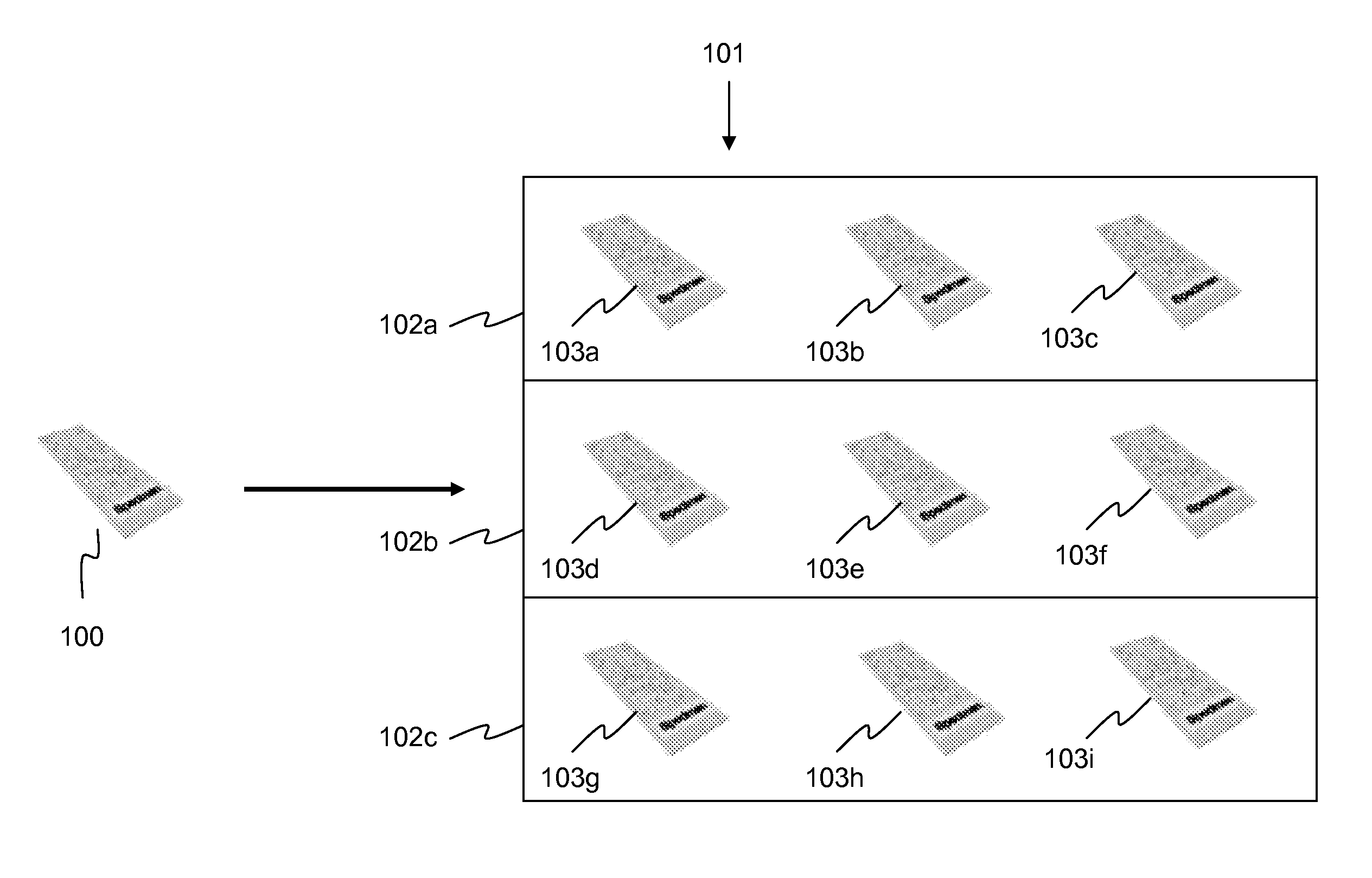
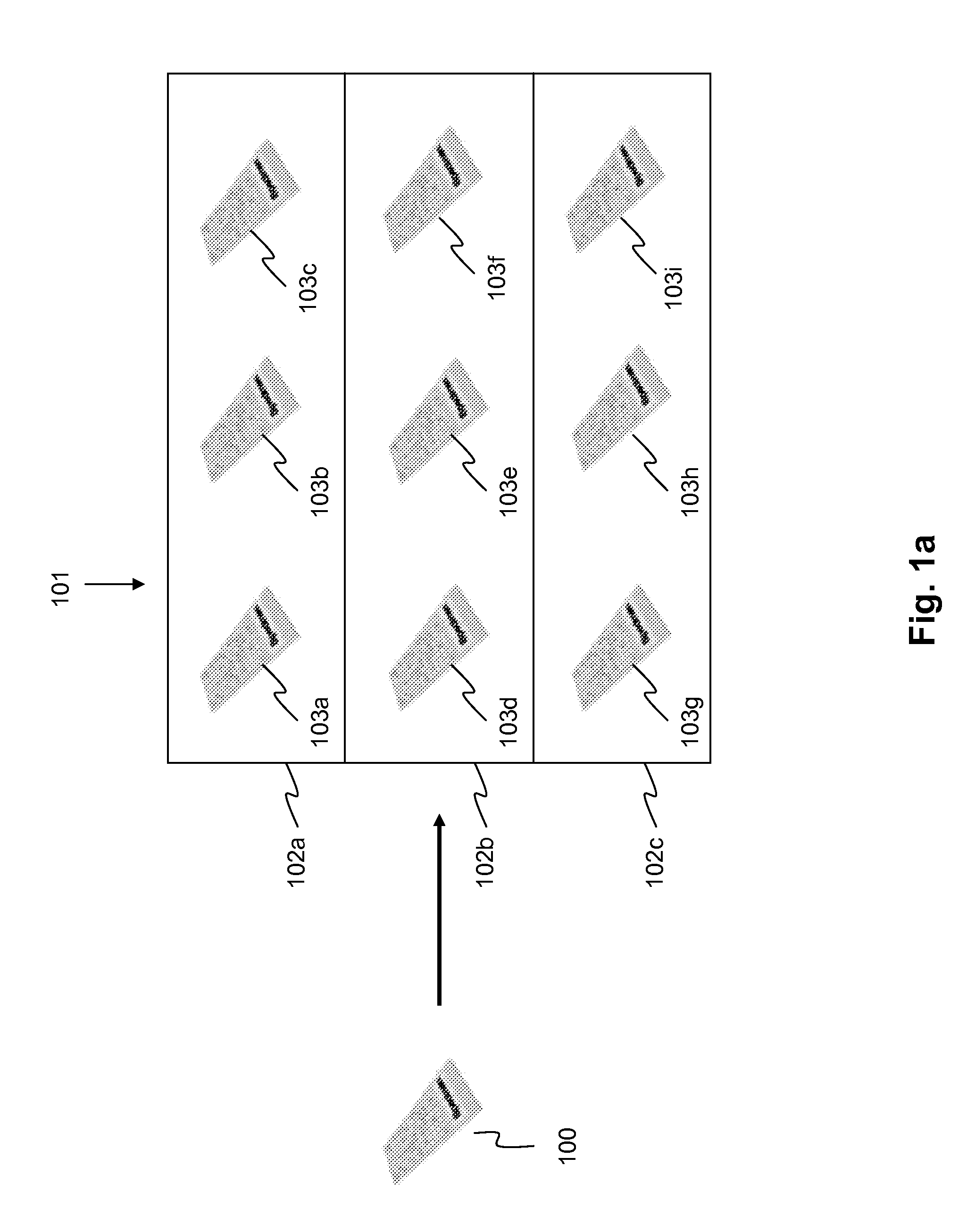
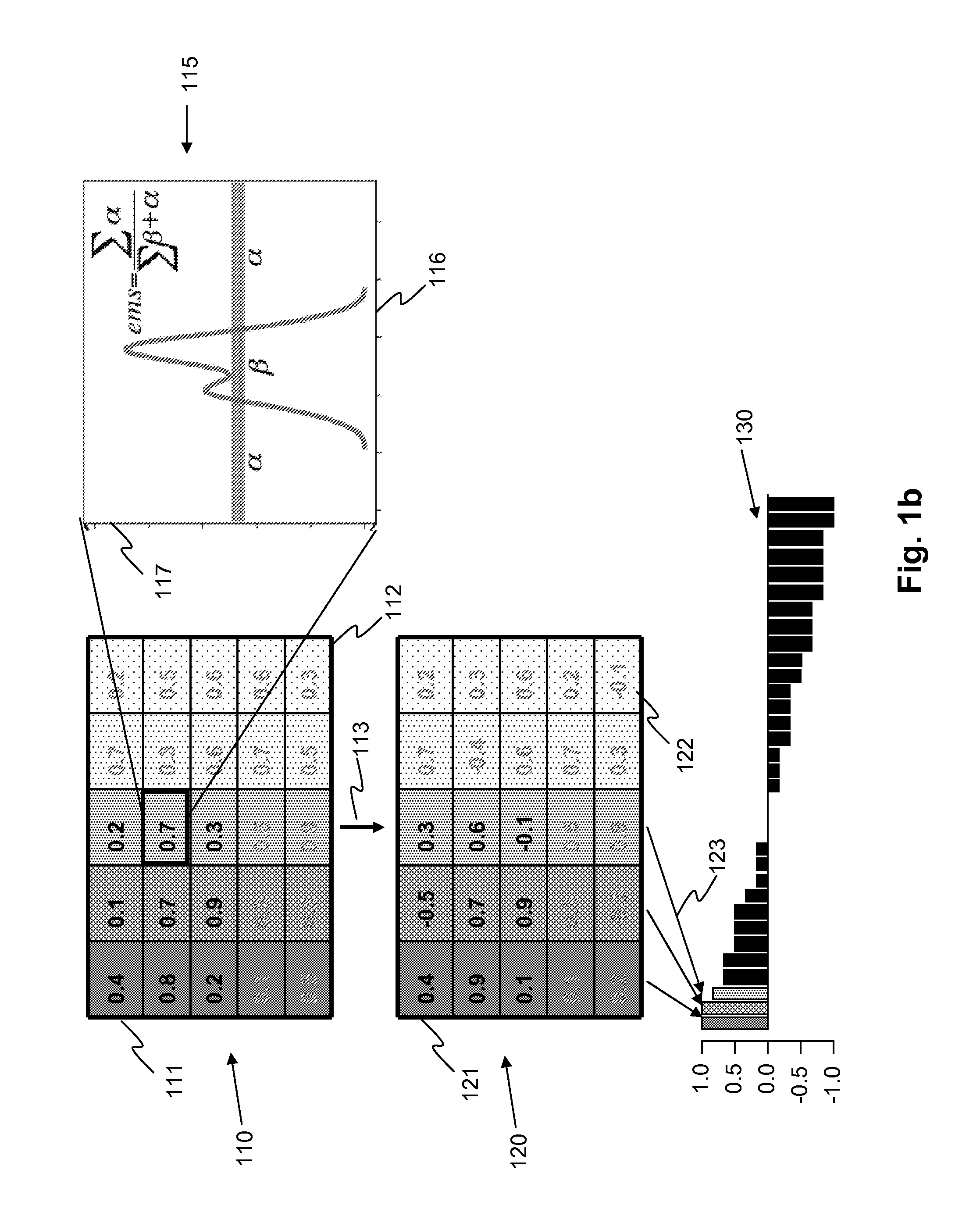
A computational gene is a molecular automaton consisting of a structural part and a functional part; and its design is such that it might work in a cellular environment. The structural part is a naturally occurring gene, which is used as a skeleton to encode the input and the transitions of the automaton (Fig. 1A). The conserved features of a structural gene (e.g., DNA polymerase binding site, start and stop codons, and splicing sites) serve as constants of the computational gene, while the coding regions, the number of exons and introns, the position of start and stop codon, and the automata theoretical variables (symbols, states, and transitions) are the design parameters of the computational gene. The constants and the design parameters are linked by several logical and biochemical constraints (e.g., encoded automata theoretic variables must not be recognized as splicing junctions). The input of the automaton are molecular markers given by single stranded DNA (ssDNA) molecules. These markers are signalling aberrant (e.g., carcinogenic) molecular phenotype and turn on the self-assembly of the functional gene. If the input is accepted, the output encodes a double stranded DNA (dsDNA) molecule, a functional gene which should be successfully integrated into the cellular transcription and translation machinery producing a wild type protein or an anti-drug (Fig. 1B). Otherwise, a rejected input will assemble into a partially dsDNA molecule which cannot be translated.
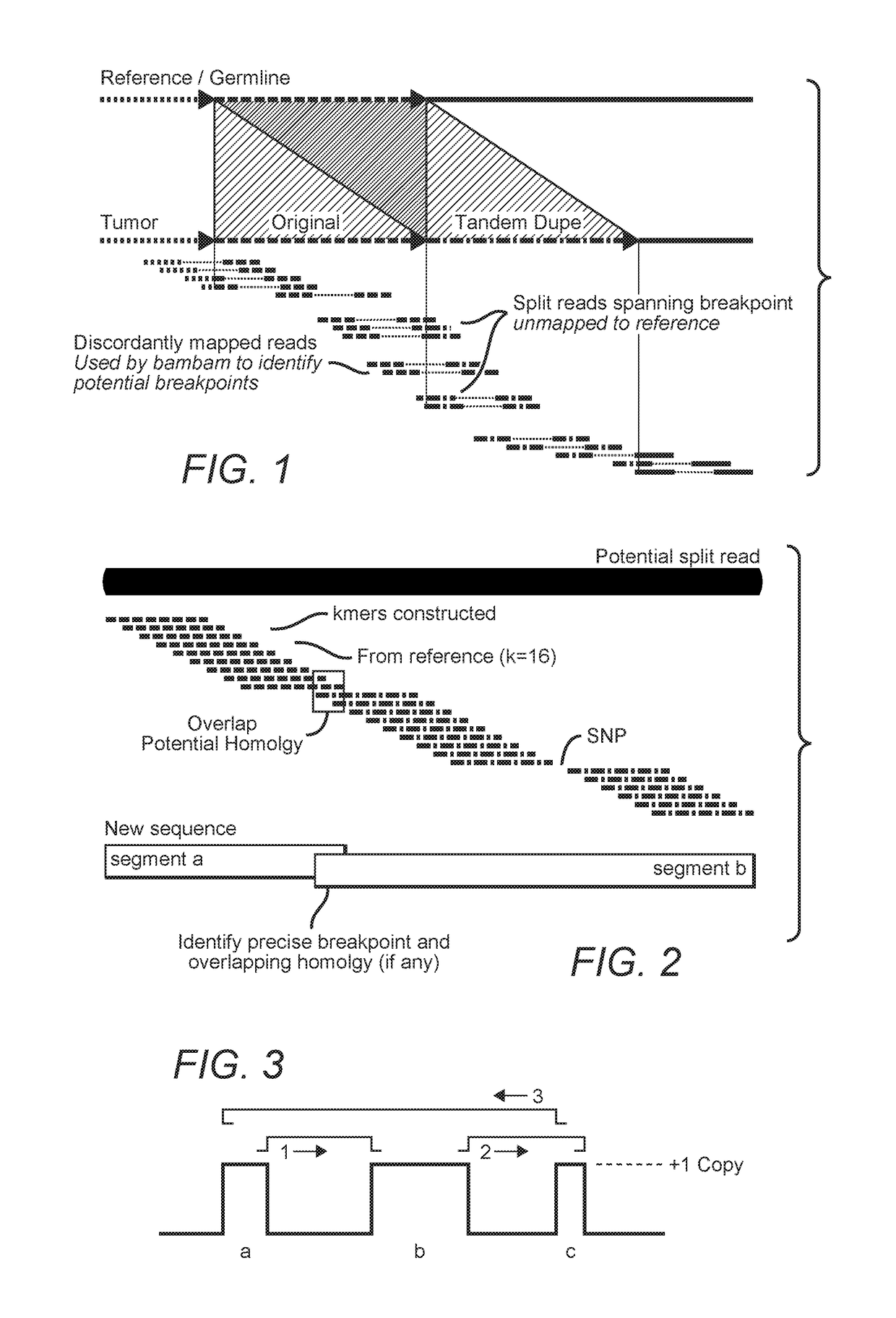
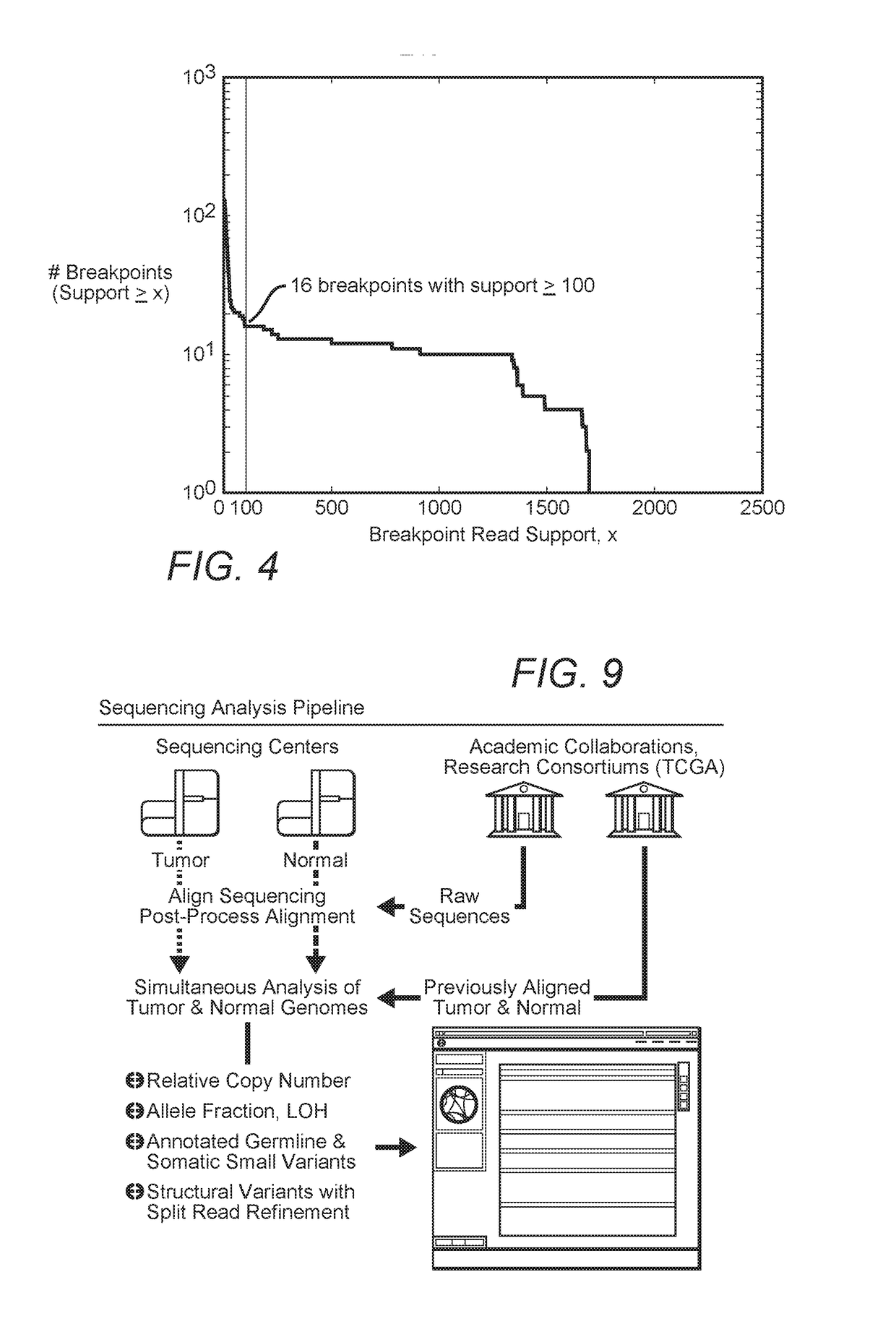
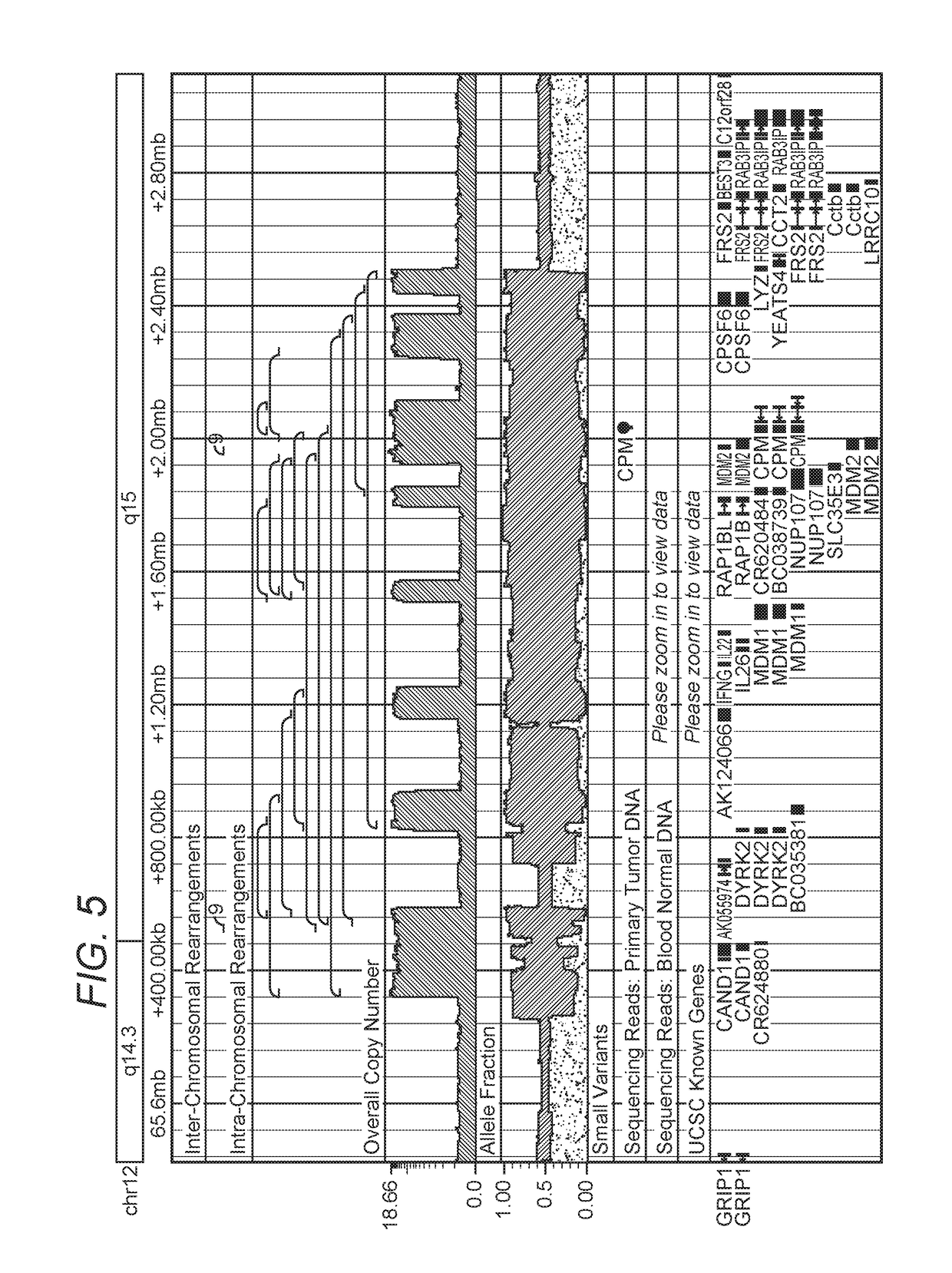
MDM2-Containing Double Minute Chromosomes And Methods Therefore
InactiveUS20140350130A1Rapid identificationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisMdm2 Protein
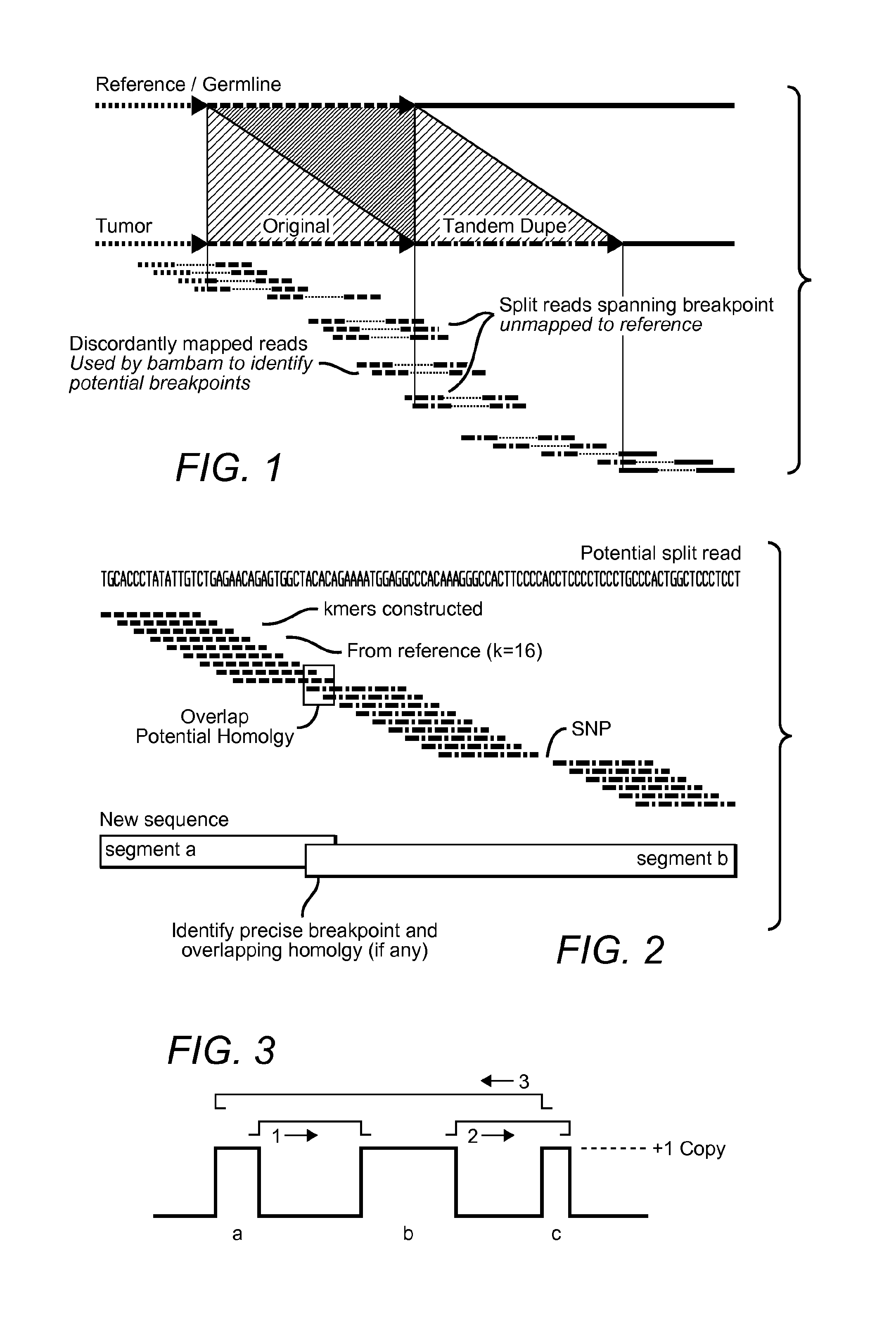
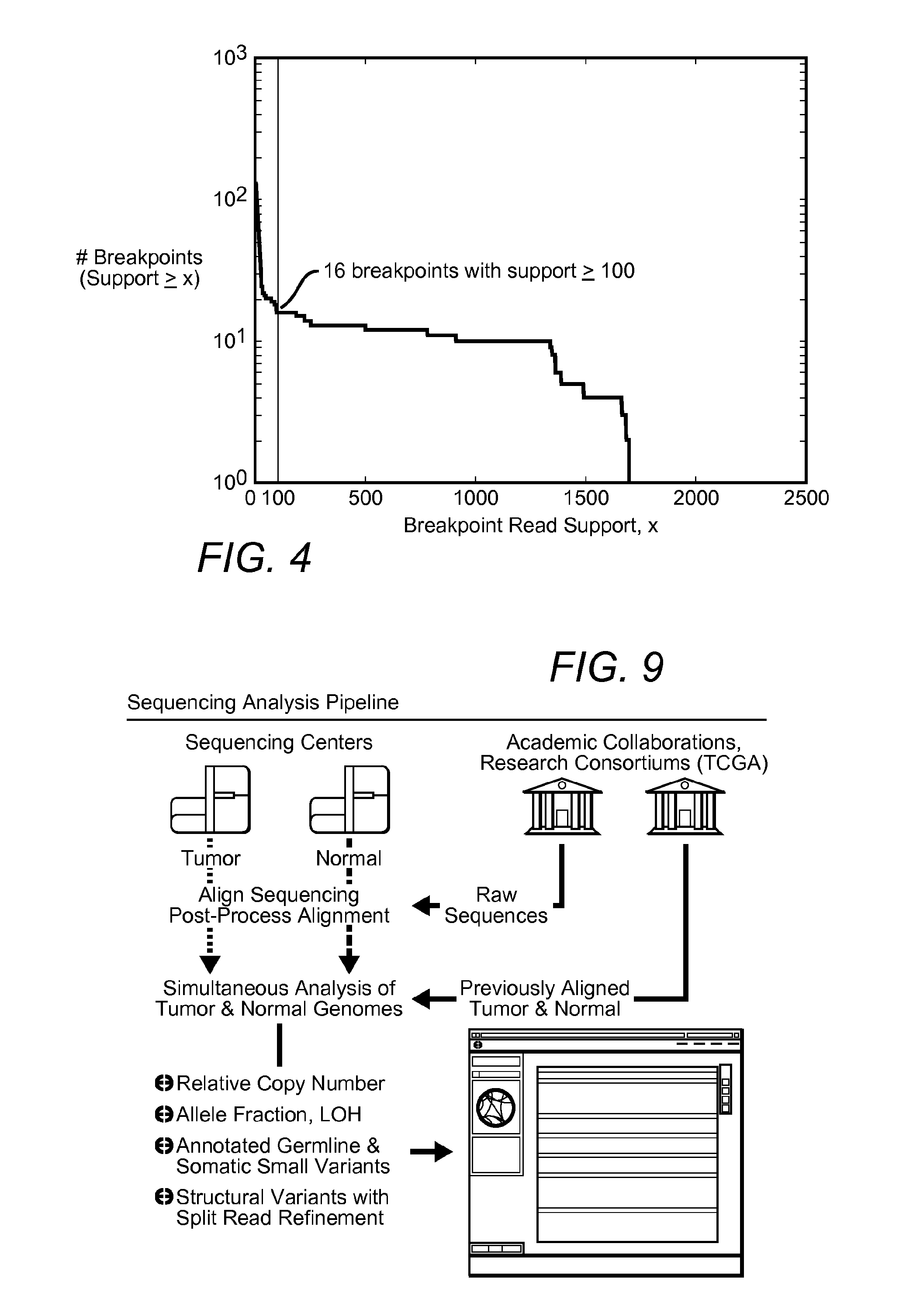
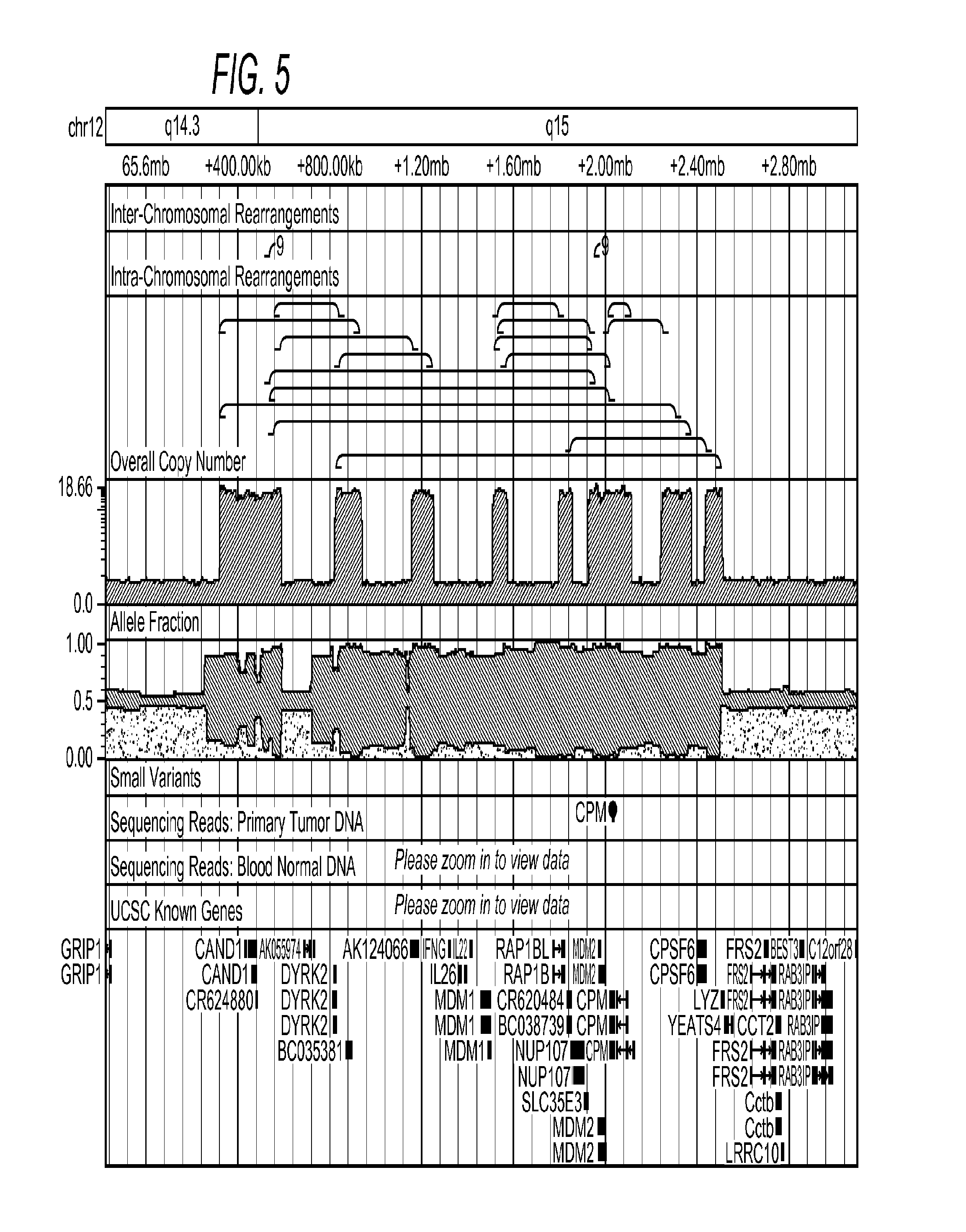
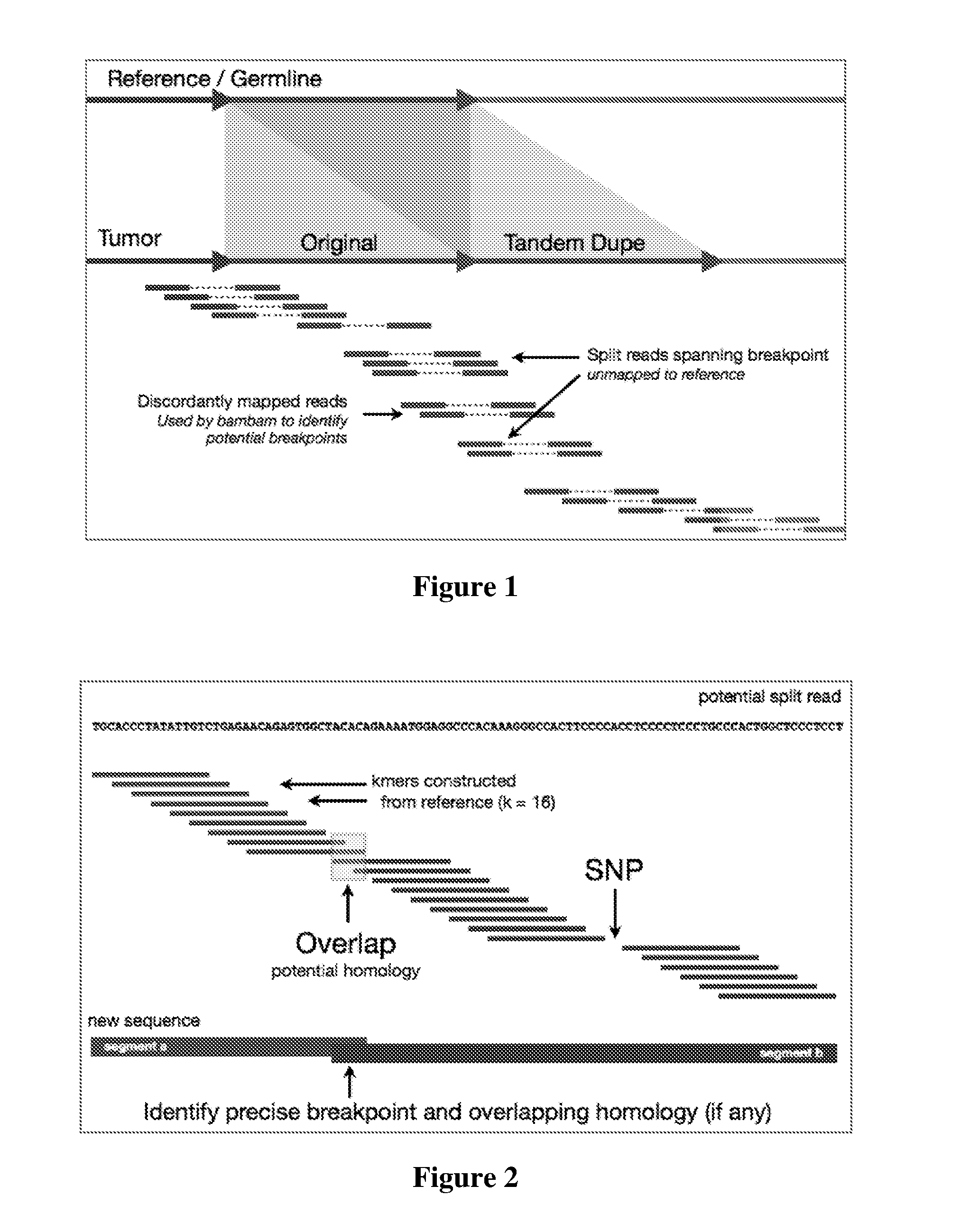
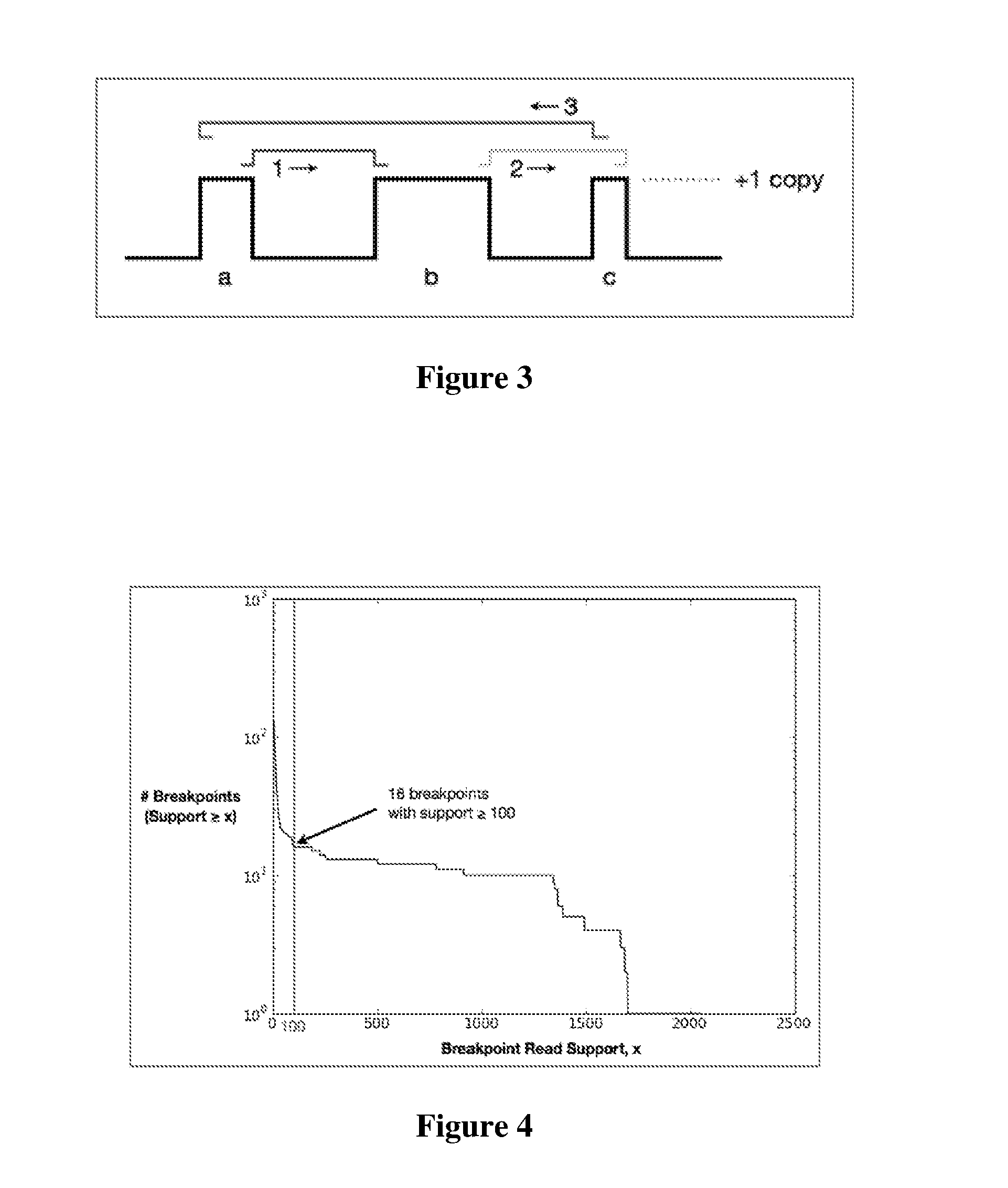
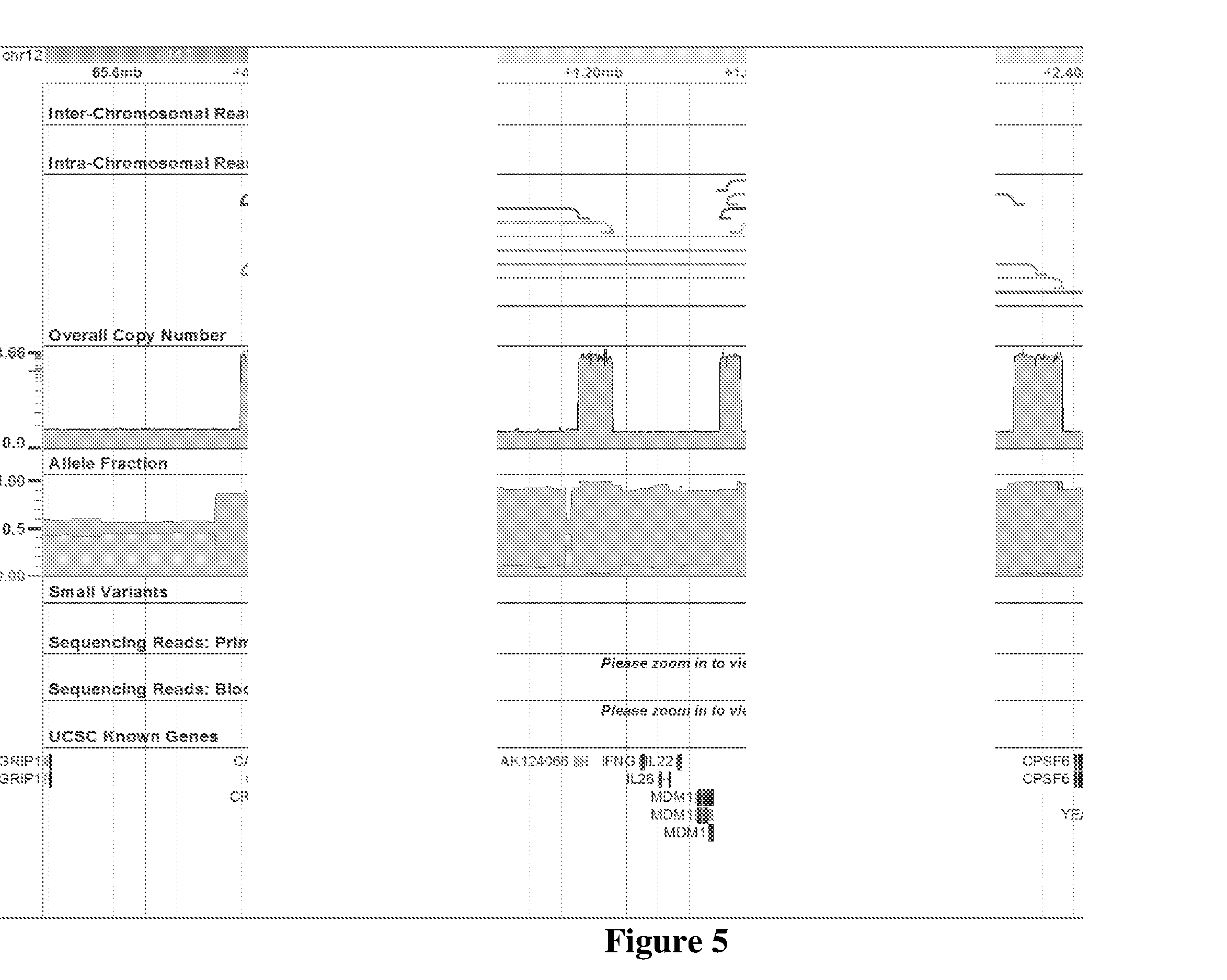
Contemplated systems and methods allow for computational genomic analysis using paired-end sequence analysis and split read refinement to thereby identify high-confidence breakpoints associated with high copy numbers and orientation of rearrangements, which is then the basis for full reconstruction of double minutes (DM). In especially preferred aspects, the DM will also include an oncogene or tumor suppressor gene, and / or may be found in blood or blood derived fluids.
Owner:FIVE3 GENOMICS
Transcriptome-based tumor neoantigen identification method
ActiveCN108491689AImprove accuracyComprehensive identificationSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsSample sequenceTumor-specific antigen
The invention discloses a transcriptome-based tumor antigen identification method. The method comprises four steps of: obtaining an RNA sample of a patient tumor tissue, and carrying out library construction and amplification on the RNA sample to obtain an RNA sample sequencing result of the tumor tissue; aligning short read segments of the RNA sample sequencing result to a human reference genometo obtain an RNA alignment result; calculating gene expression quantity according to the RNA alignment result, and carrying out mutation detection and prediction of fusion gene events according to theRNA alignment result; and predicting transcriptome HLA typing according to the alignment result, wherein calculation of the gene expression quantity, mutation detection and prediction of the fusion gene events are carried out according to a specified order or simultaneously carried out; and using the gene expression quantity of a transcriptome sample, depth of transcriptome mutation sites in a whole-exon sequencing sample and binding force of neonatal short peptides and the patient HLA typing as an analysis result to submit the same to a downstream analyst. The invention provides the method capable of identifying a tumor-specific antigen of an individual sample from tumor patient transcriptome NGS data.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Method for gene copy number variation analysis
InactiveCN106055923AHigh-resolutionImprove accuracyHybridisationSpecial data processing applicationsHuman DNA sequencingComputational gene
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
New fast Bayes method estimating genomic estimated breeding value
InactiveCN107590364ACalculation speedImprove stabilitySpecial data processing applicationsGenomic sequencingGenotype
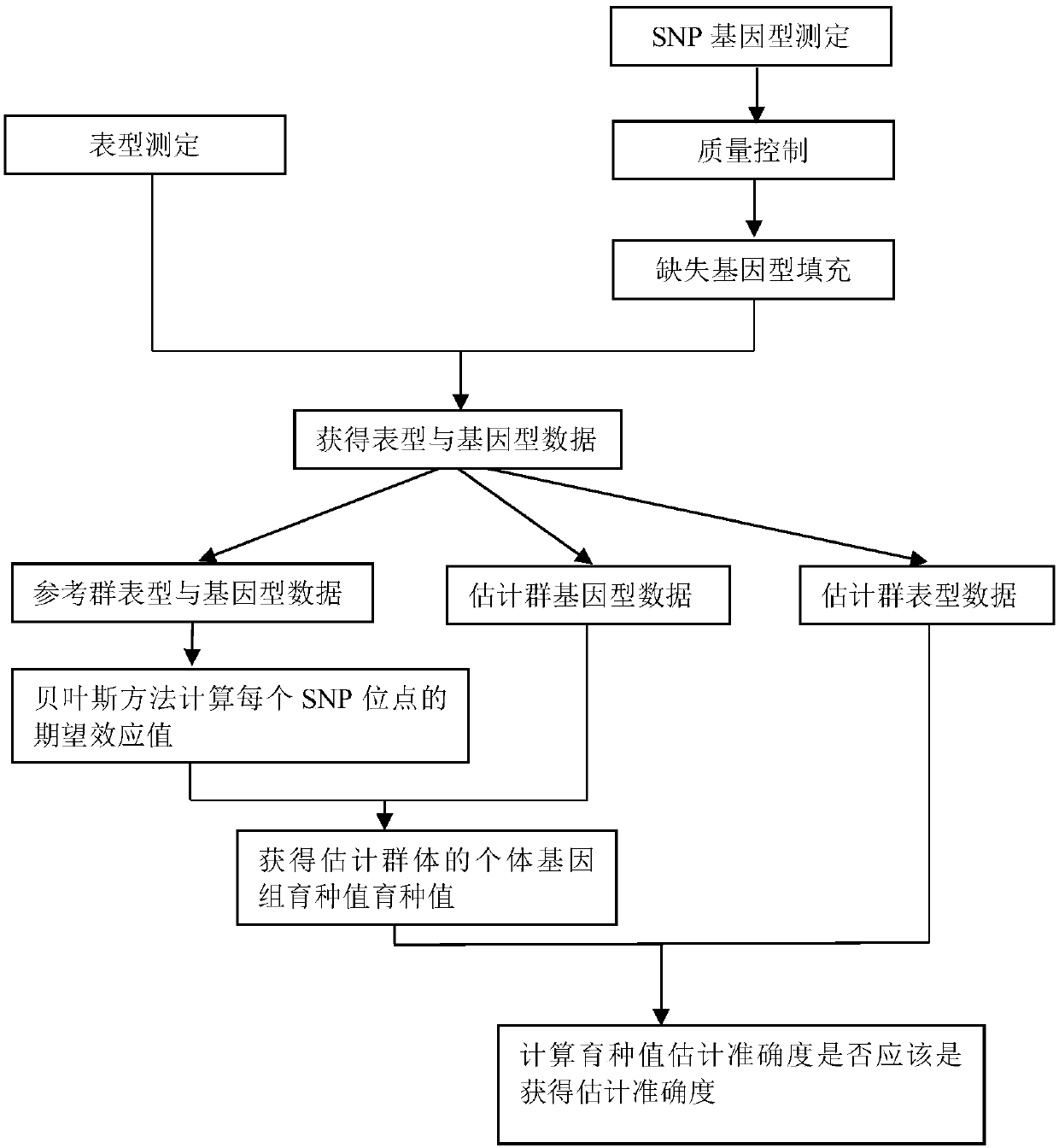
The invention discloses a new fast Bayes method estimating a genomic estimated breeding value. The method comprises the steps of performing productivity phenotype test and genome sequencing on all individuals, and acquiring SNP sites of a genome; screening out qualified SNP sites, and supplementing missing genotypes; dividing all individuals into a reference group and an estimation group randomly;calculating an expected effect value of each SNP site in a Bayes model of the reference group according to a phenotype value of the reference group and an iterative conditional expectation algorithm;accumulating expected effect values of all SNP sites so as to obtain a genomic estimated breeding value (GEBV) of the estimation group; and calculating a related coefficient of the GEBV and the phenotype value or a true breeding value so as to acquire estimation accuracy. The method has the characteristics of being fast in calculation speed and high in stability, and maintaining the estimation accuracy of the breeding value.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
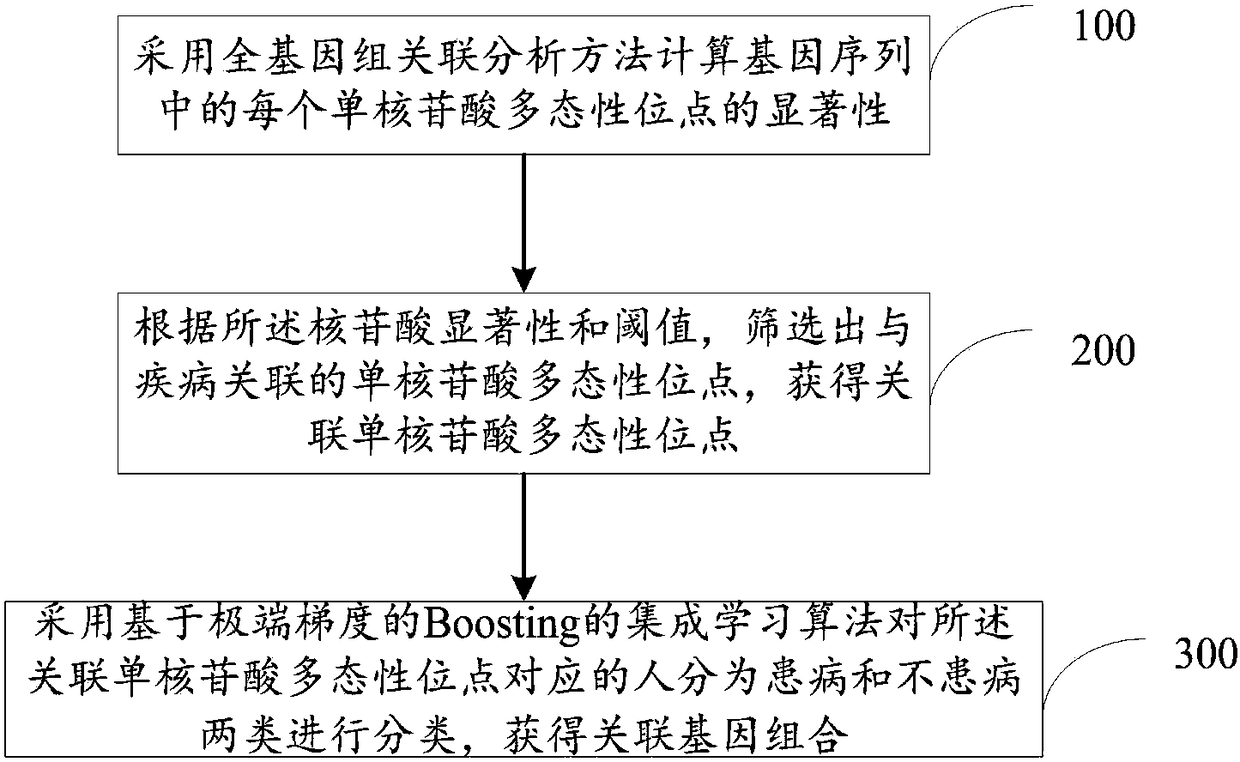
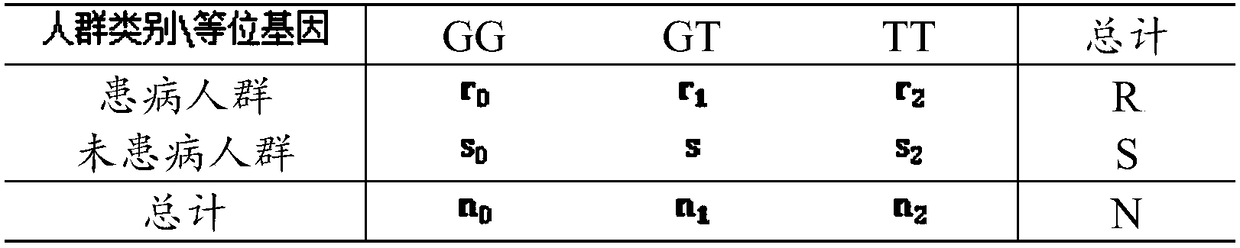
Disease-associated gene combination counting method and system
InactiveCN108256293AImprove accuracyHealth-index calculationBiostatisticsDiseaseDegree of association
The invention discloses a disease-associated gene combination counting method and system. The method comprises computing the significance of every mononucleotide polymorphic site in a gene sequence through a genome-wide association analysis method, wherein the significance presents the degree of association between the mononucleotide polymorphic site and diseases, acquiring the significance of themononucleotide polymorphic sites; according to the significance and a threshold value, screening out the mononucleotide polymorphic sites associated with the diseases to acquire the associated mononucleotide polymorphic sites; through an extreme gradient-based Boosting ensemble learning method, categorizing people corresponding to the associated mononucleotide polymorphic sites into affected onesand non-affected ones and further acquiring associated gene combinations. By combining the genome-wide association analysis method and the gradient-based Boosting ensemble learning method to categorize people corresponding to the associated mononucleotide polymorphic sites into the affected ones and the non-affected ones and further to acquire the associated gene combinations, the disease-associated gene combination counting method can improve the accuracy of acquired disease-associated gene combination results.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
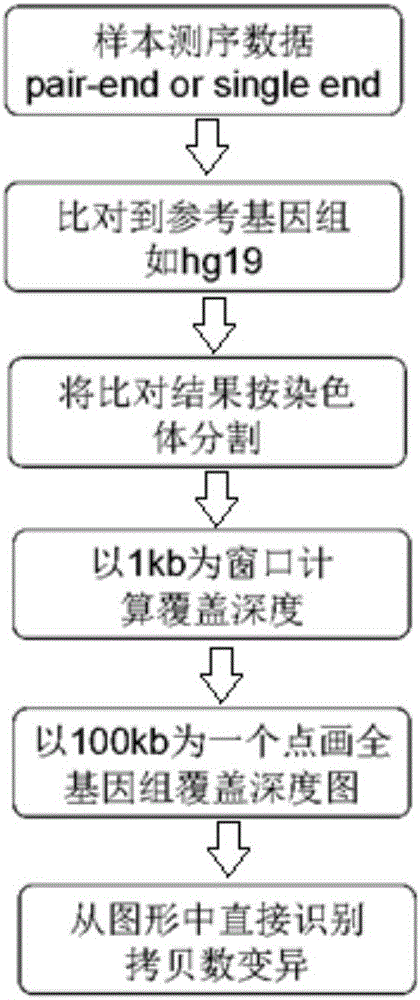
Analysis system for gene copy number variation
InactiveCN106055926AHigh-resolutionImprove accuracySequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsHuman DNA sequencingComputational gene
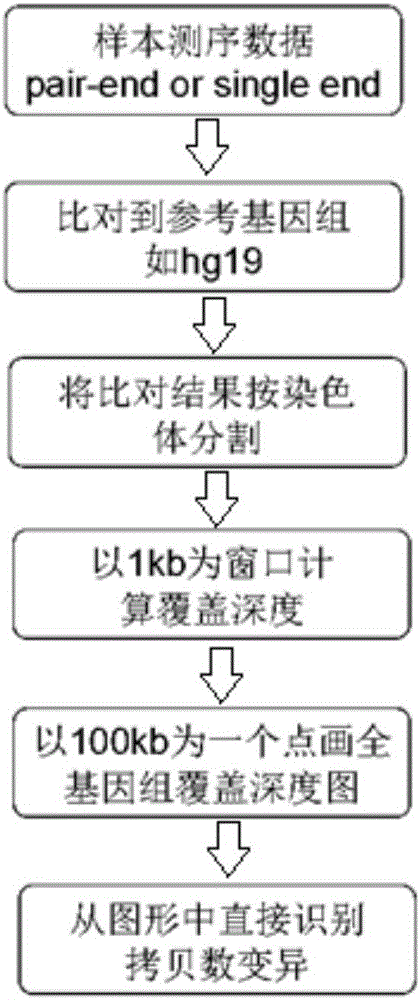
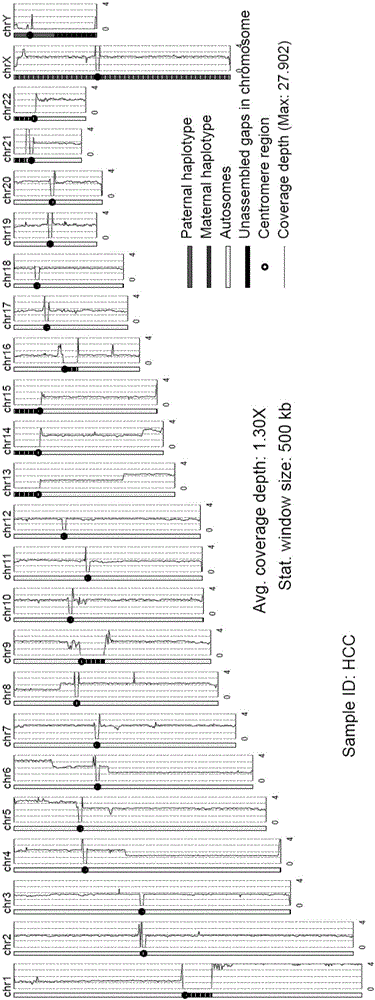
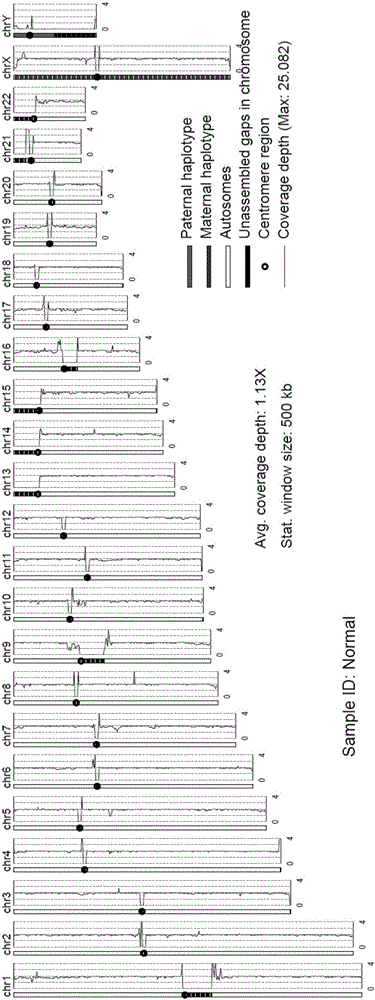
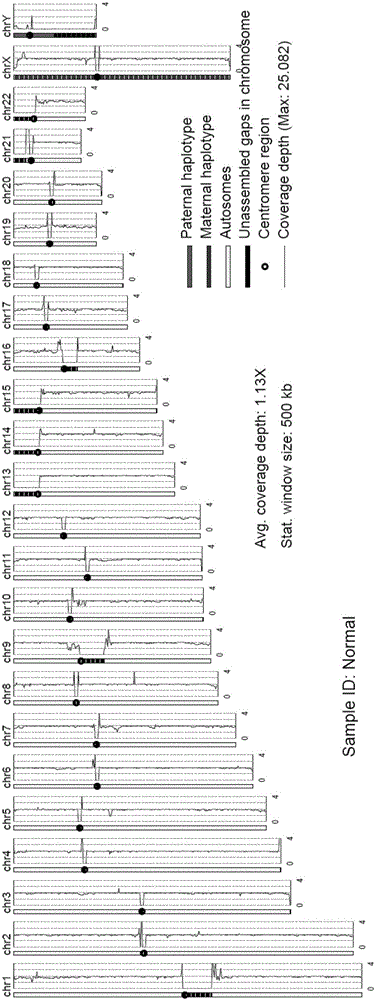
The invention provides an analysis system for gene copy number variation. The system comprises an analysis module, a division module, a statistics module, a window computing module and a picture module, wherein the analysis module is used to read in an index document and a reference genome of data, and make comparison; the division module is used to divide a sam document of a comparison result of the whole genome according to chromosomes; the statistics module is used for statistics of a comparison result of comparison sequencing data; the window computing module is used to compute an average covering depth of each window on the genome with 1KB as the window, and results are given in the form of a list; the picture module is used to draw a chromosome covering depth picture according to computing results; and the analysis module is a major module which successively calls other modules to complete each part of analysis work. The system provided by the invention has the advantages that the copy number variation on a human genome level can be accurately analyzed by high-throughput sequencing data, and high-resolution pictures can be displayed; and the statistics can be carried out to data comparison information, so that data assessment becomes convenient.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
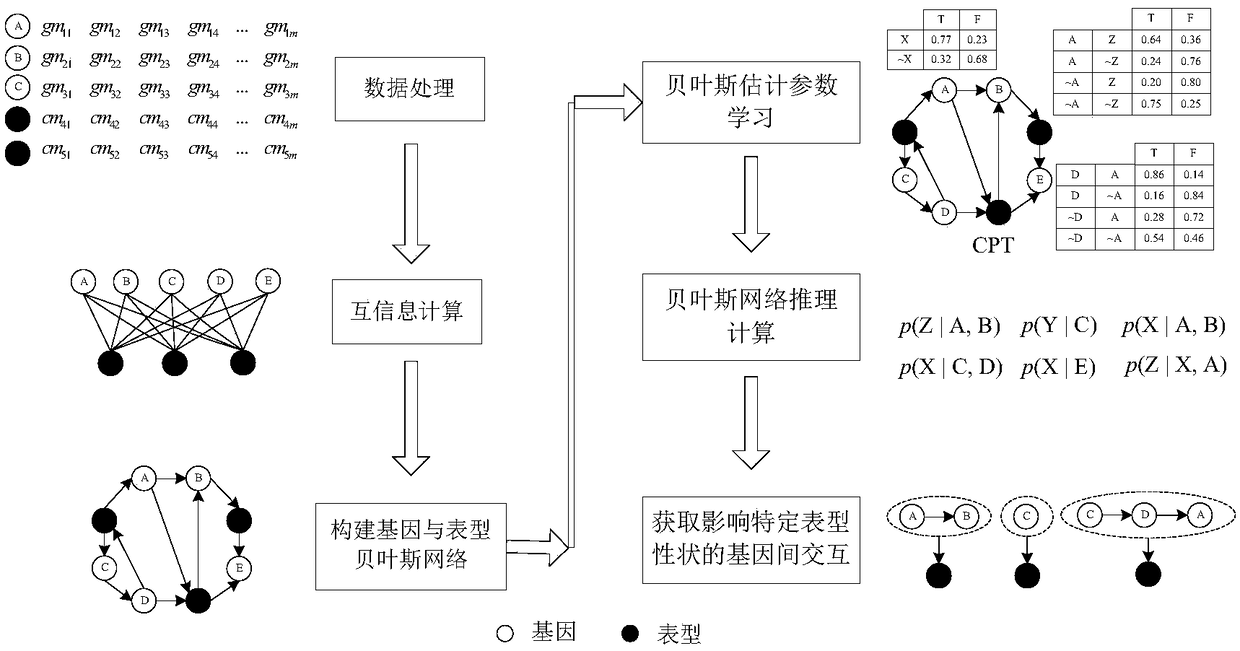
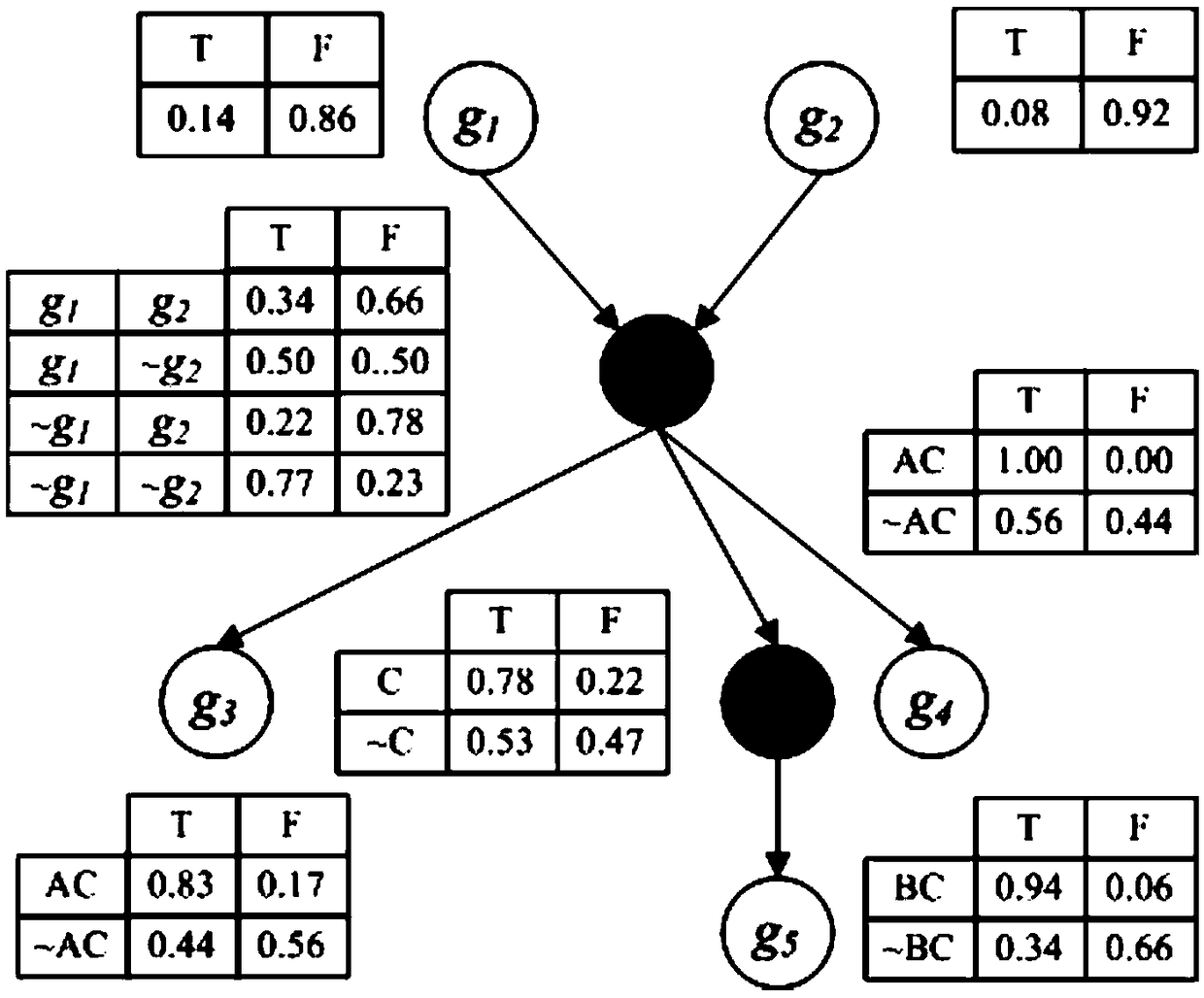
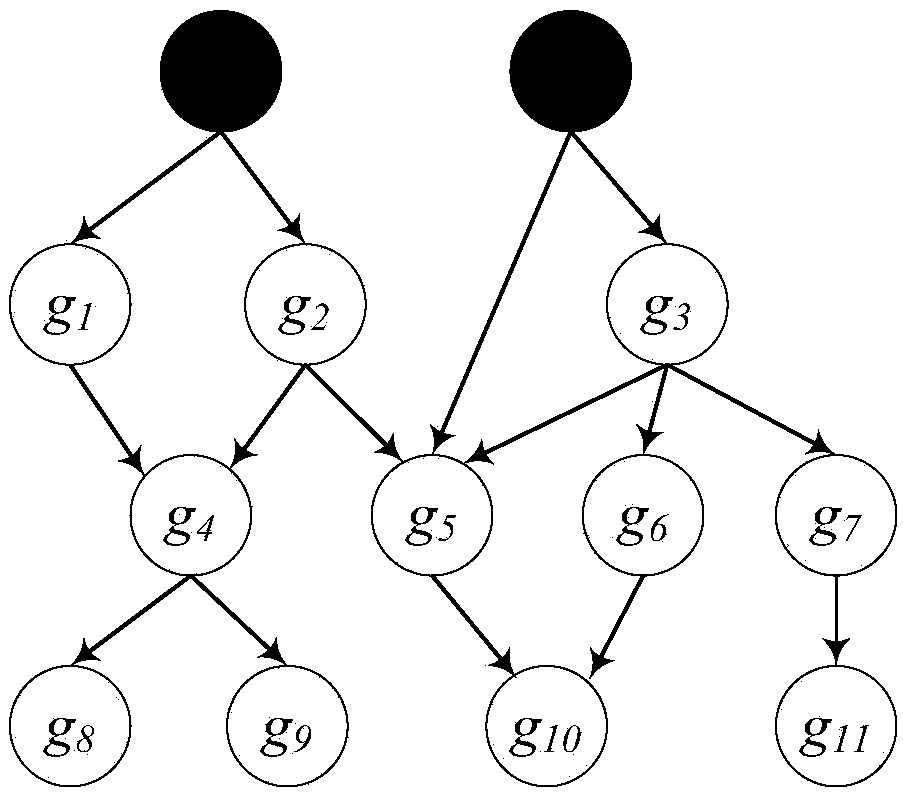
Intergenic interaction relation excavation method based on Bayesian network reasoning
The present invention provides an intergenic interaction relation excavation method based on Bayesian network reasoning. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, employing a method of estimation of entropy by employing a Gaussian kernel probability density estimation quantity to calculate interaction information between genes, between genes and phenotypic characters and between phenotypes and the phenotypic characters; 2, employing a three-stage dependence analysis Bayesian network structure learning method to construct a Bayesian network including genes and phenotypic character nodes;3, employing the Bayesian estimation parameter learning method to perform parameter learning to obtain a contingent probability form between nodes; and 4, employing a Gibbs sampling Bayesian network approximate reasoning method to calculate the contingent probabilities of genes with different quantities and the phenotypic characters, and obtaining an intergenic interaction relation influencing thespecial phenotypic characters according to the calculation result. The intergenic interaction relation excavation method based on Bayesian network reasoning can help biology researchers of obtainingof epistasis genetic locuses influencing the special phenotypic characters to assist in gene function excavation and provide reference for hereditary basis analysis of complex quantitative charactersof different species.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
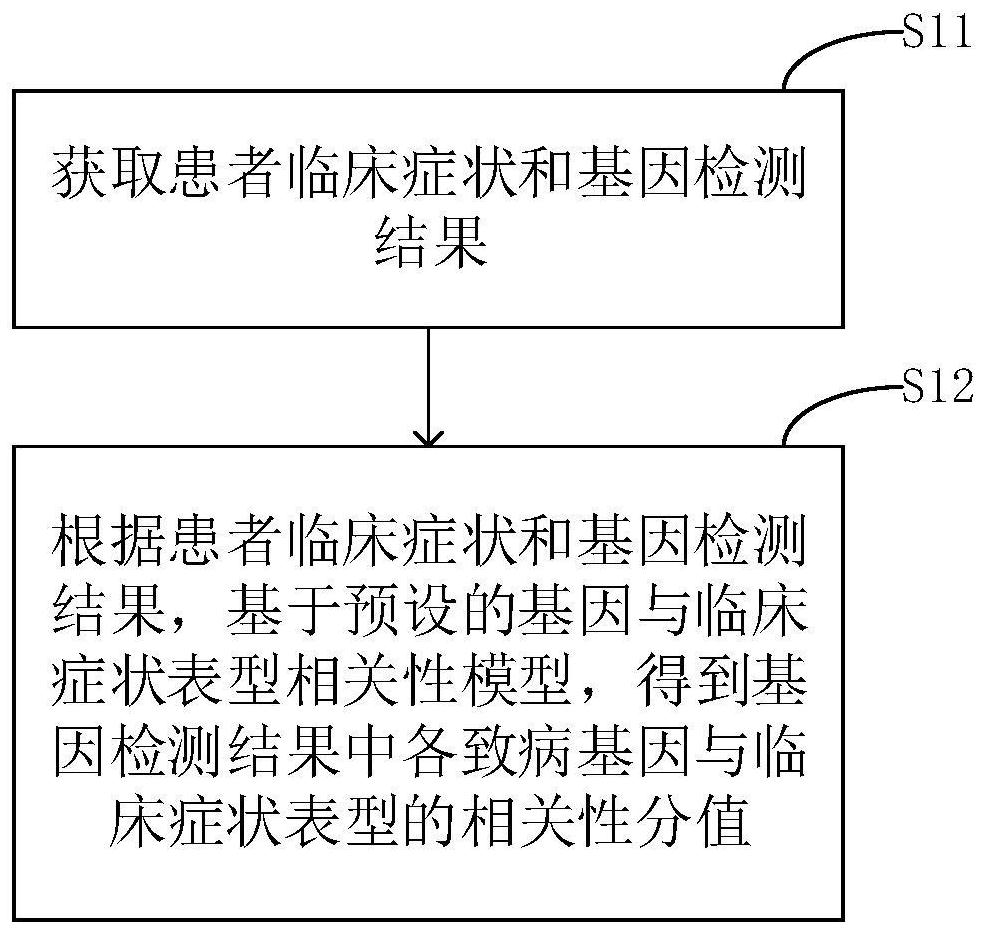
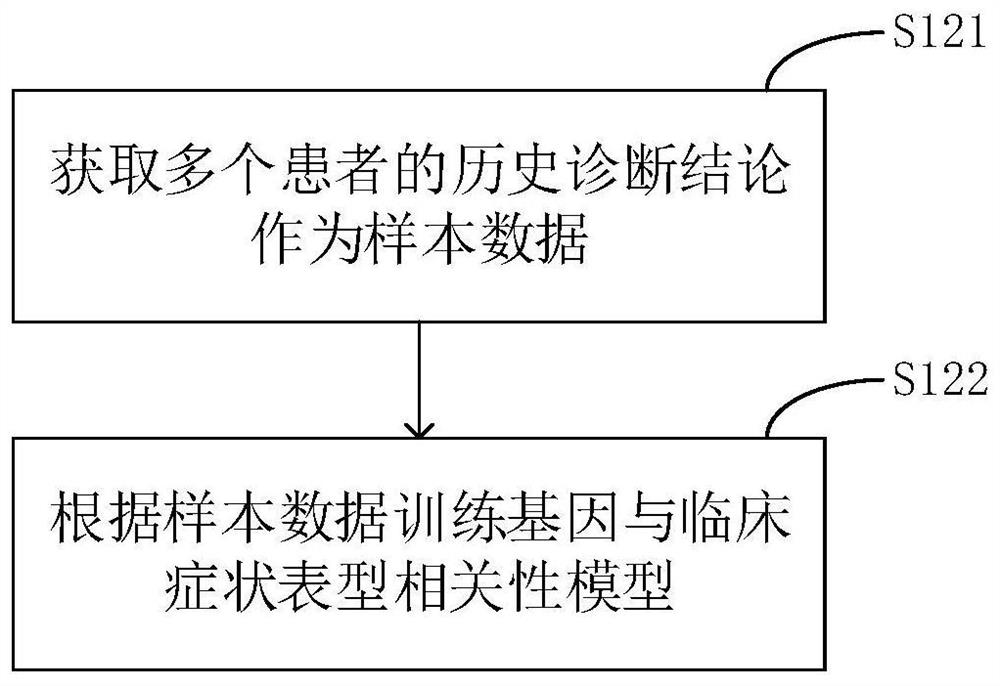
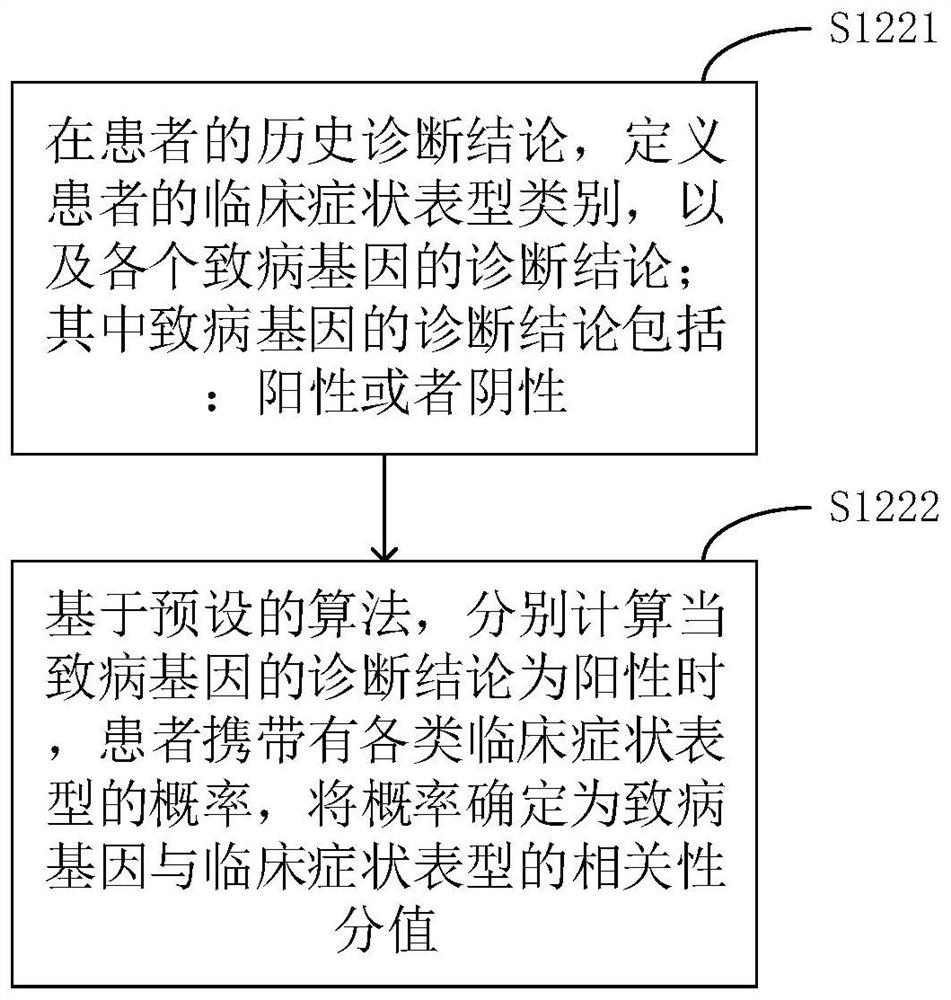
Phenotype-based pathogenic gene quantitative measurement and calculation method and equipment
The invention relates to a phenotype-based pathogenic gene quantitative measurement and calculation method, which comprises the following steps: obtaining clinical symptoms and gene detection resultsof a patient, and obtaining correlation scores of pathogenic genes and clinical symptom phenotypes in the gene detection results based on a preset gene and clinical symptom phenotype correlation modelaccording to the clinical symptoms and the gene detection results of the patient. According to the invention, due to the fact that a gene cannot necessarily and completely cause certain clinical symptom phenotype, a quantitative index is required to describe the possibility, and according to clinical symptoms shown when a patient sees a doctor and gene detection results obtained through gene sequencing, correlation scores of all pathogenic genes in the gene detection results and clinical symptom phenotypes are calculated, and the higher the correlation scores of the pathogenic genes and a certain clinical symptom phenotype are, the more easily the clinical symptom phenotype is caused by the pathogenic genes, so that a genetic counselor can conveniently evaluate the pathogenic gene causingthe disease symptoms of the patient.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
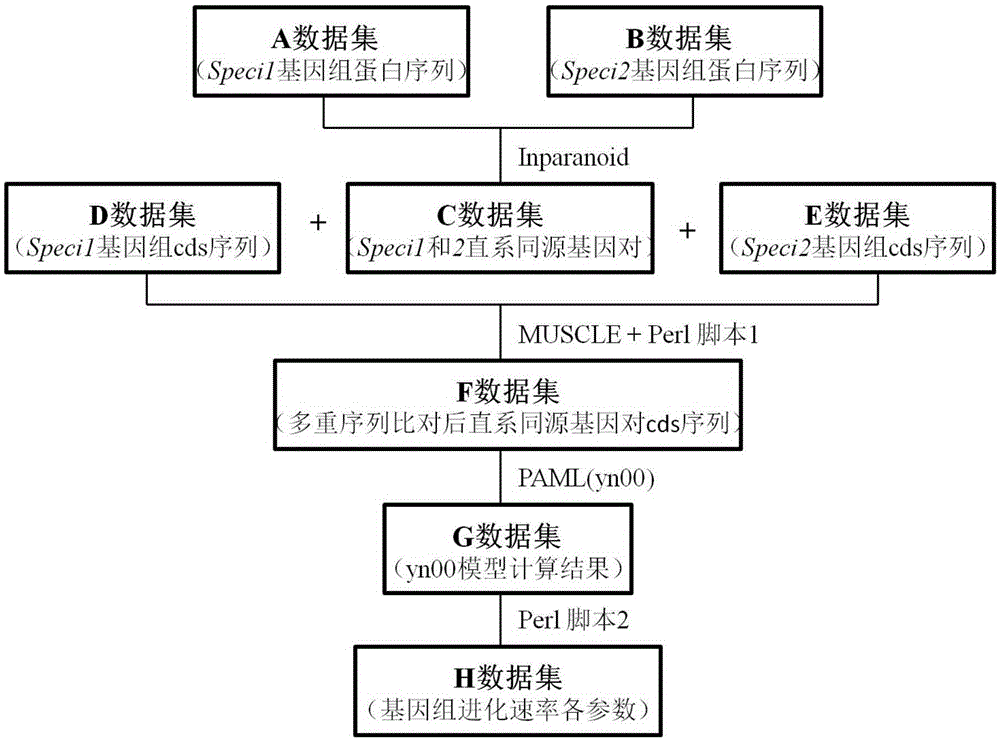
Method for batch computing of evolutionary rate of orthologous genes of genome
ActiveCN105426700ASmooth connectionGood effectBiostatisticsSpecial data processing applicationsOrthologous GeneComputational gene
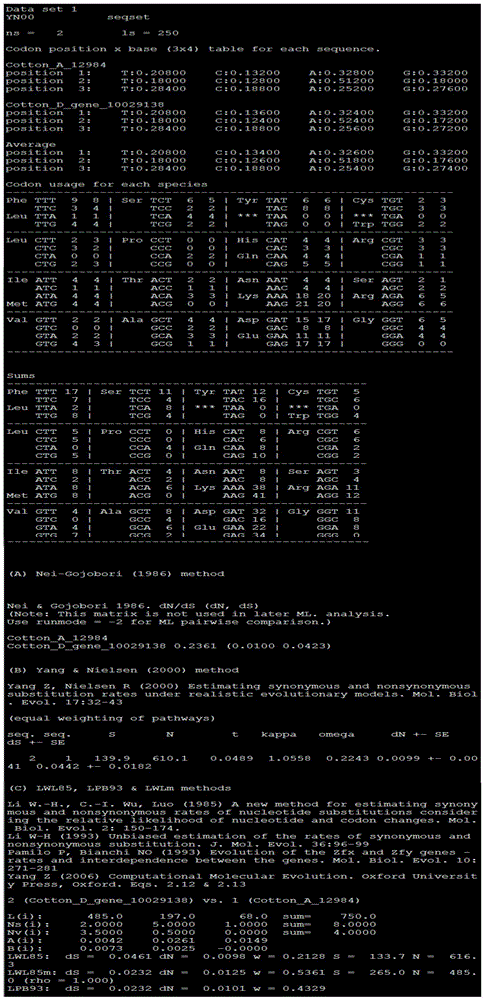
The invention discloses a method for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of orthologous genes of a genome. According to the method for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome, an InParanoid program for clustering searching of orthologous genes after a paired comparing result is obtained based on Blast, an MUSCLE program based on multi-sequence comparative analysis and a PAML software package yn00 program for evaluating the synonymous and non-synonymous substitution ratio based on comparison between coding protein DNA sequences are comprehensively used, and the methods such as Perl scripting language programming are combined. It is proved through experiments that a method comparing system for batch computing of the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome is good in repeat effect on various parameter values for detecting the genome and computing the evolutionary rate of the orthologous genes of the genome, high in speed and capable of easily achieving batch computing, automation and processing.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Survival prediction method and system based on image genomics
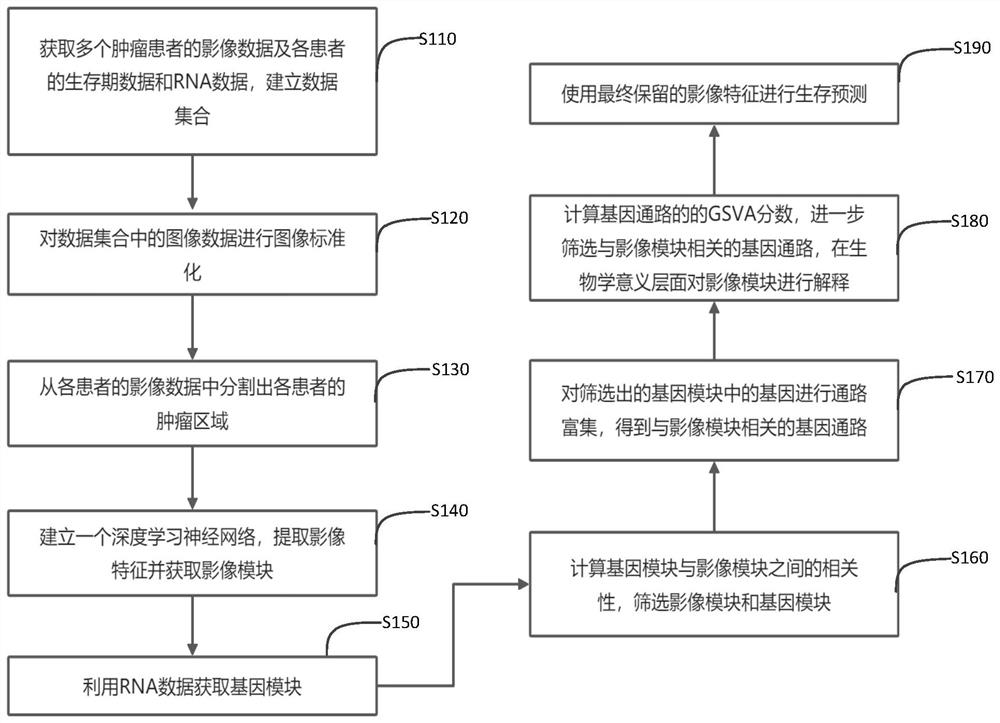
ActiveCN112907555AImprove generalization abilityImprove interpretabilityImage enhancementImage analysisData setComputational gene
The invention discloses a survival prediction method and system based on image genomics. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring image data of tumor patients and lifetime data and RNA data of each patient, and establishing a data set; segmenting a tumor area of each patient from the image data; inputting the image data of each patient into a neural network to extract image features and cluster the image features to obtain a plurality of image modules; obtaining a gene module of each patient by using the RNA data; performing screening according to the correlation between the gene modules and the image modules, and selecting a plurality of gene modules and image modules which are strongly correlated; performing pathway enrichment on genes in the selected gene module to obtain a gene pathway related to the image module; calculating a gene set variation analysis score of the gene pathway, and retaining the gene pathway having strong correlation with the image module; and carrying out survival prediction by using the retained image features. According to the invention, the biological interpretability in the aspect of survival prediction can be improved, and the generalization ability of deep learning can be improved at the same time.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-scale biological data clustering method and system based on spanning tree
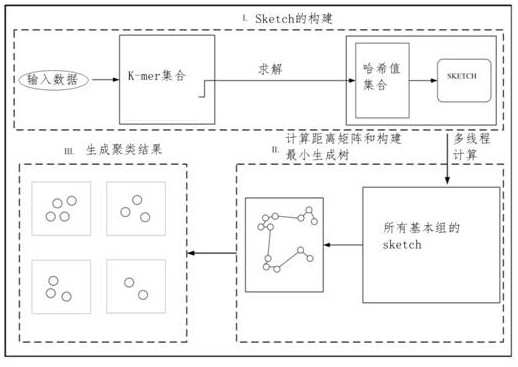
ActiveCN114420215ASmall calculation timeSmall footprintBiostatisticsSequence analysisDistance matrixOriginal data
The invention provides a large-scale biological data clustering method and system based on a spanning tree, belongs to the technical field of data processing of large-scale genome data, and solves the problem of low calculation efficiency at present. Streaming a distance matrix between the genomic sequences and constructing a minimum spanning tree based on the similarity between the estimated genomic sequences, generating the minimum spanning tree by dividing the distance matrix into sub-graphs and constructing sub-minimum spanning trees; and cutting off edges exceeding a given threshold length in the minimum spanning tree to generate a clustering result. According to the method, the sketch algorithm is adopted to estimate the similarity between the sequences, and the dimension of a k-mer set in sketch is far smaller than that of an original sequence, so that the calculation time and space occupation of sequence similarity analysis by adopting the sketch algorithm are far smaller than those of direct accurate comparison of original data.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method, an arrangement and a computer program product for analysing a biological or medical sample
InactiveUS20130066860A1Reduce the numberData processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementReference databaseOutput device
An aspect of the present invention is a computer executable method for characterizing, e.g. for diagnostic purposes, utilizing a reference database, a query sample tissue based on the gene expression data of the tissue. The method is characterized in that it comprises the steps of calculating an expression match score (EM-score) indicating the likelihood of having the gene expression level observed in the query sample in each of the tissue categories of the reference database, calculating for the genes of the sample tissue, using e.g. the EM-score, tissue specificity score (TS-score), that expresses how uniquely a gene identifies the query sample as belonging to a certain tissue category, calculating, utilizing e.g. the TS-score, overall similarity of the sample tissue in relation to a tissue category of the reference database, and storing at least some resulting characterization data to a memory device or outputting the data to an output device of a computer. An arrangement and a computer program product are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDISAPIENS OY
Biomarker selecting method based on meta-analysis, and system
ActiveCN110246544AResolve System DifferencesBiostatisticsSequence analysisSample TypeBiological macromolecule
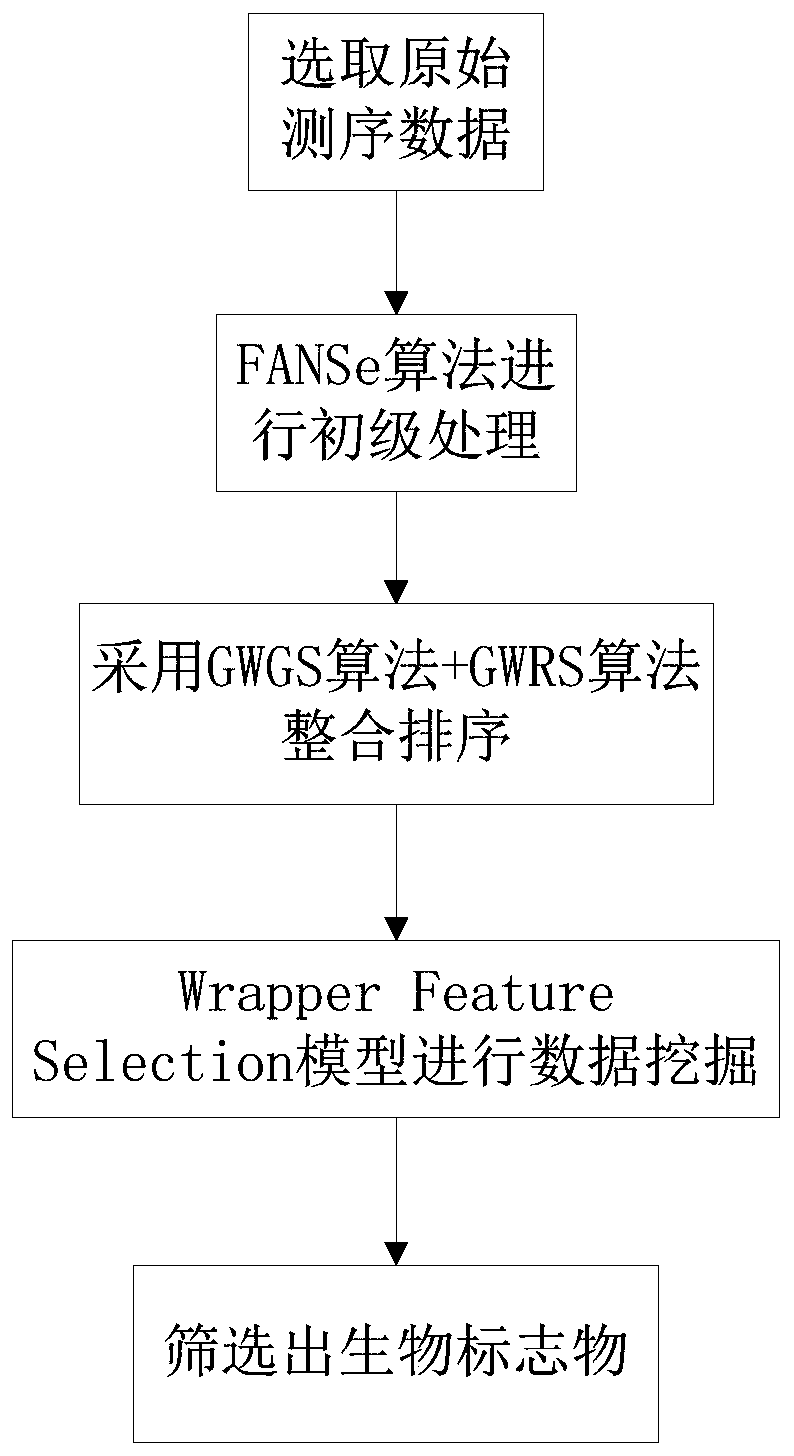
The invention discloses a biomarker selecting method based on meta-analysis, and a system. The method comprises the following steps of selecting original sequencing data; performing mapping analysis on the original sequencing data by means of an FANSe algorithm, obtaining gene quantification information and setting a gene original group; calculating an importance sequence of the gene in the original group according to a GWGS algorithm, integrating the importance of each group of genes according to a GWRS algorithm, obtaining an integrated gene importance arrangement list, sequencing the genes according to the importance from highest to lowest; performing data mining by means of a Wrapper Feature Selection model based on the SVM, differentiating a data sample type, and screening the biomarker from the gene with high importance. According to the method, multi-center original sequencing data are integrated according to the characteristic of the sequencing data, and system differences in platform, sample and experiment designing are settled; an integrating analysis algorithm with high robustness is used for performing deep data mining, thereby mining common, specific and key biomacromolecules.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Microbial species and functional composition analysis method for metagenome sequencing data
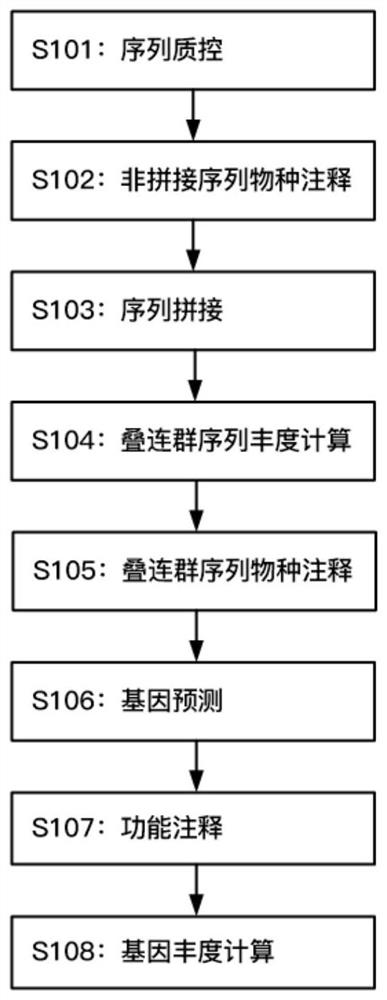
PendingCN112599198AHigh false positiveHigh sensitivitySequence analysisInstrumentsGenomic sequencingMicroorganism
The invention discloses a microbial species and functional composition analysis method for metagenome sequencing data, which comprises the following steps: 1) cutting off a linker sequence fragment and a low-quality fragment in original data, and filtering out an over-short sequence and a sequence containing fuzzy bases; (2) performing species annotation by using the obtained data; (3) splicing the sequences without the non-target species; (4) performing similarity clustering on the contiguous group sequences; (5)using a blastn algorithm; (6) predicting gene regions in the non-redundant contiguous group sequences; (7) comparing a non-redundant protein sequence set with various protein annotation databases; and (8) calculating the gene sequence abundance. According to the method, further analysis of the contiguous group sequence generated by splicing is met, and the problems that the result is high in false positive, depends on construction of a special database and is narrow in application range are avoided; the sensitivity is high and the accuracy is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI PASSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
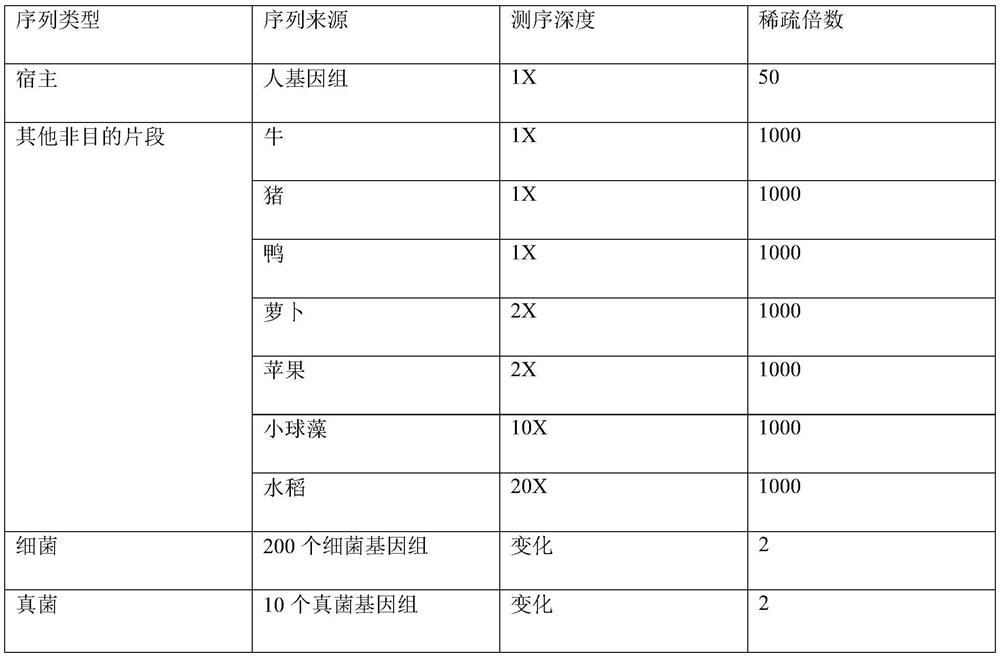
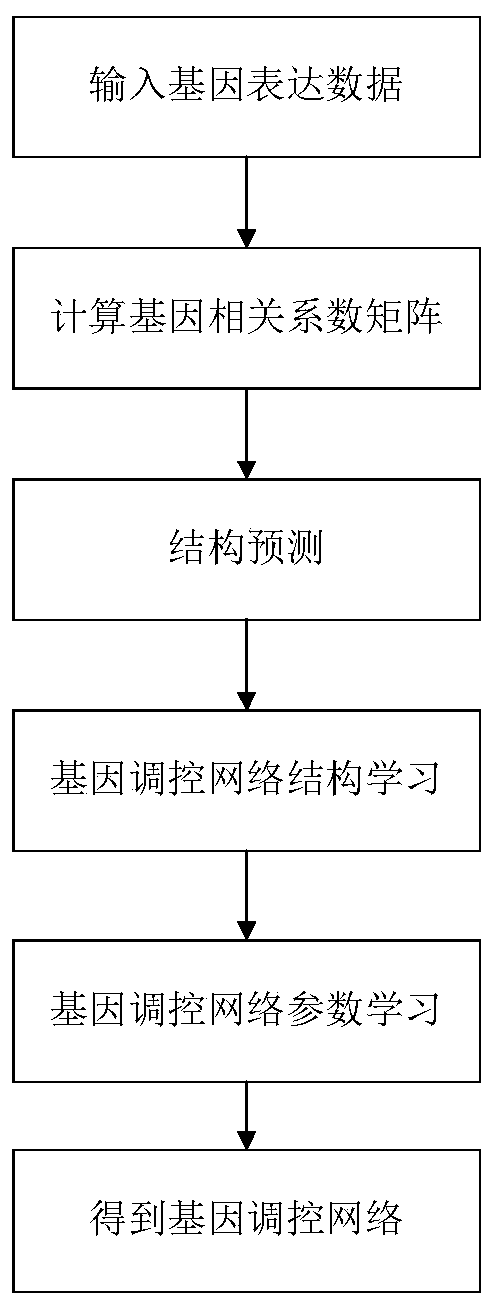
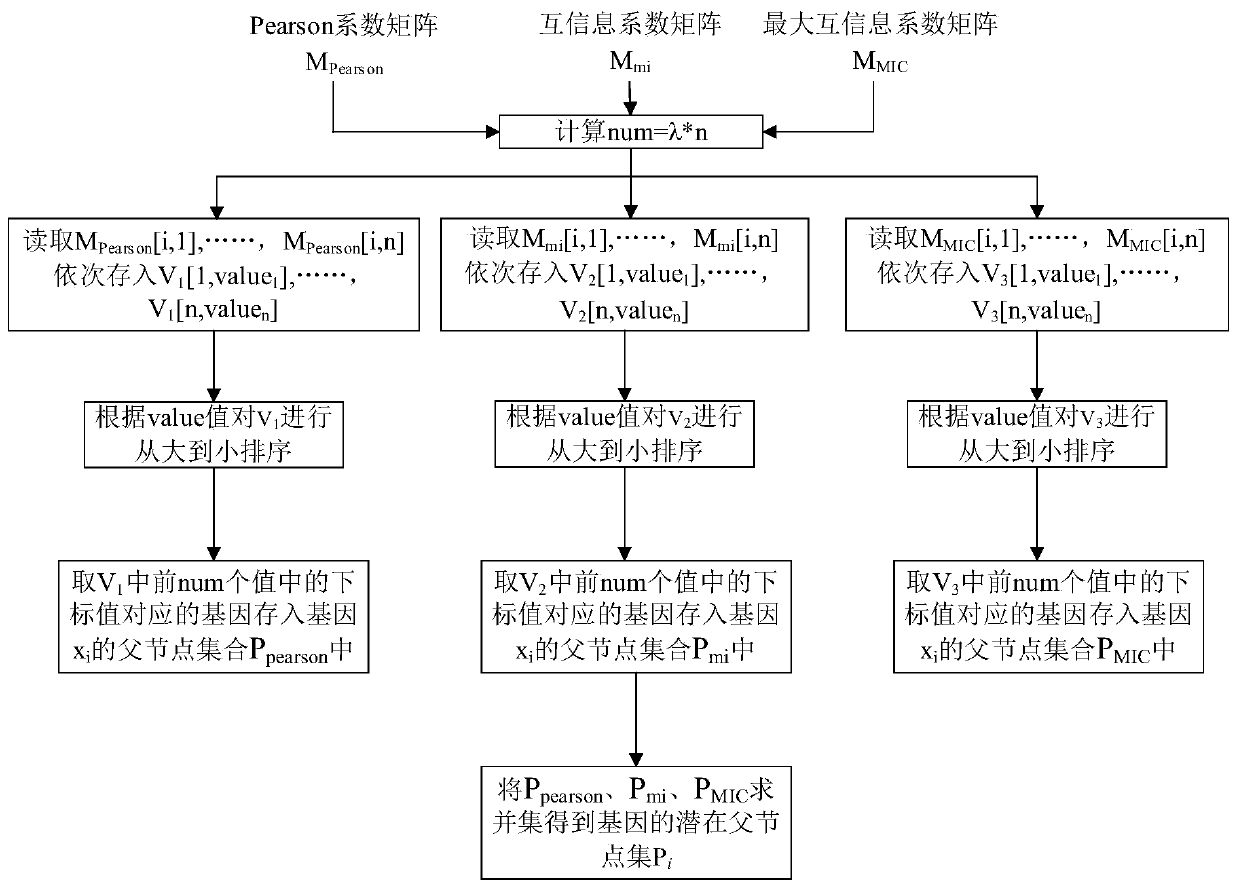
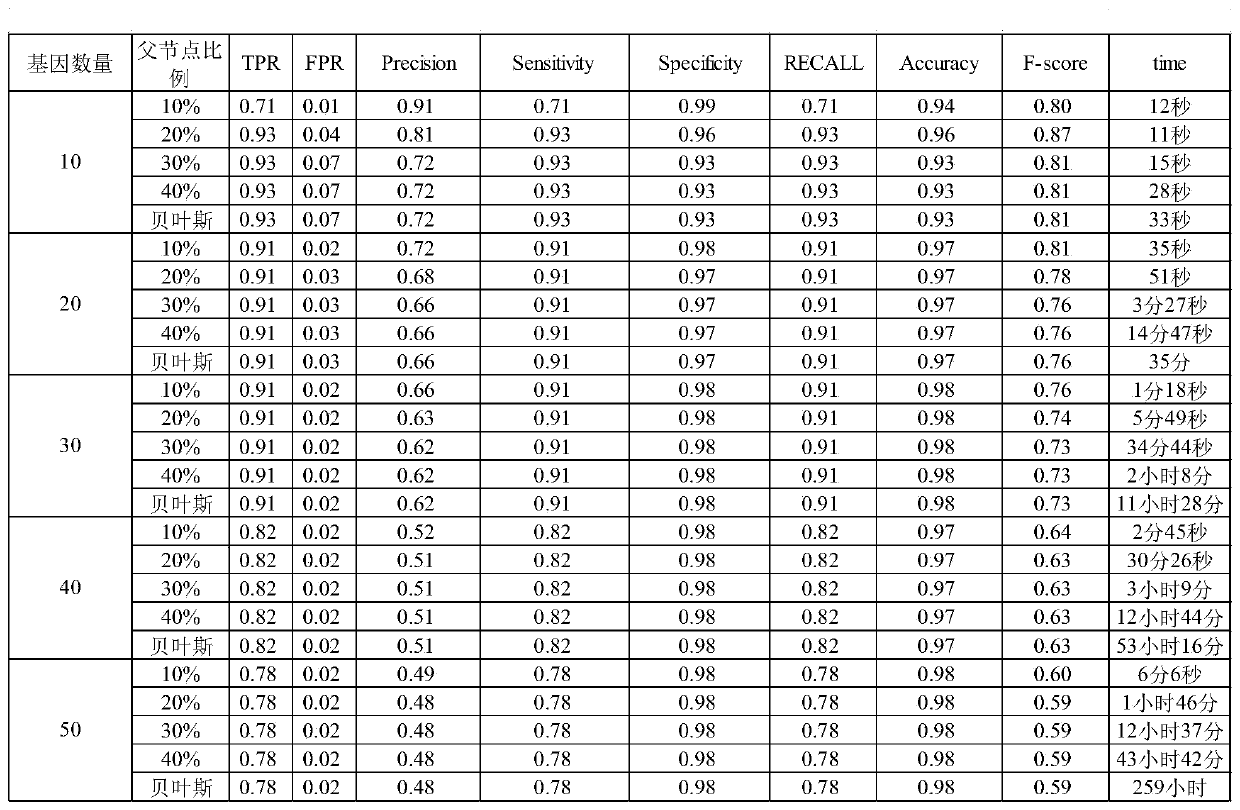
Method for constructing gene regulatory network based on structural prediction
ActiveCN110675912AReduce build timeQuick buildHybridisationSystems biologyStructure learningData mining
The invention provides a method for constructing a gene regulatory network based on structural prediction. The method includes the following steps: first calculating a coefficient matrix, determiningthe correlation between genes, by calculating the Peason coefficient, the mutual information, and the maximum mutual information between the genes, as a basis for screening potential parent node sets;then, performing structural prediction, using an obtained coefficient matrix between genes as the basis for determining the potential parent node sets of the genes, and selecting a potential parent node set for each gene; finally, performing the structural learning and parameter learning of the gene regulatory network. The method predicts the potential parent node sets of the genes by a method based on of the combination of the Person coefficient, the mutual information, and the maximum mutual information, narrows the search range of structure learning, shortens the construction time of the gene regulatory network to a certain extent, improves computing performance, can build a large-scale gene regulatory network quickly and accurately, and further understands the gene regulatory mechanism of organisms.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Genetic reference material for gene detection of alpha-thalassemia and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111893178AEasy to countEasy to calculateFungiHaemoglobins/myoglobinsHereditary MutationThalassemia
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly discloses a genetic reference material for gene detection of alpha-thalassemia and a preparation method thereof. The genetic reference material of the invention is to insert yeast cells of a genetic reference material gene required for gene detection of the alpha-thalassemia into a URA3 gene. The invention selects the yeastcells as the background and carriers of genetic mutation, utilizes the advantages that the yeast cells are convenient to storage and culture, simple in genetic operation, high in homologous recombination efficiency, convenient to count and the genome DNA copy number is convenient to calculate and the like, and combines a CRISPR / Cas9 technology to target the URA3 gene to prepare the genetic reference material for gene detection of the alpha-thalassemia, and consistency with human cell sample treatment operations can be achieved through protoplast formation.
Owner:重庆市人口和计划生育科学技术研究院 +1
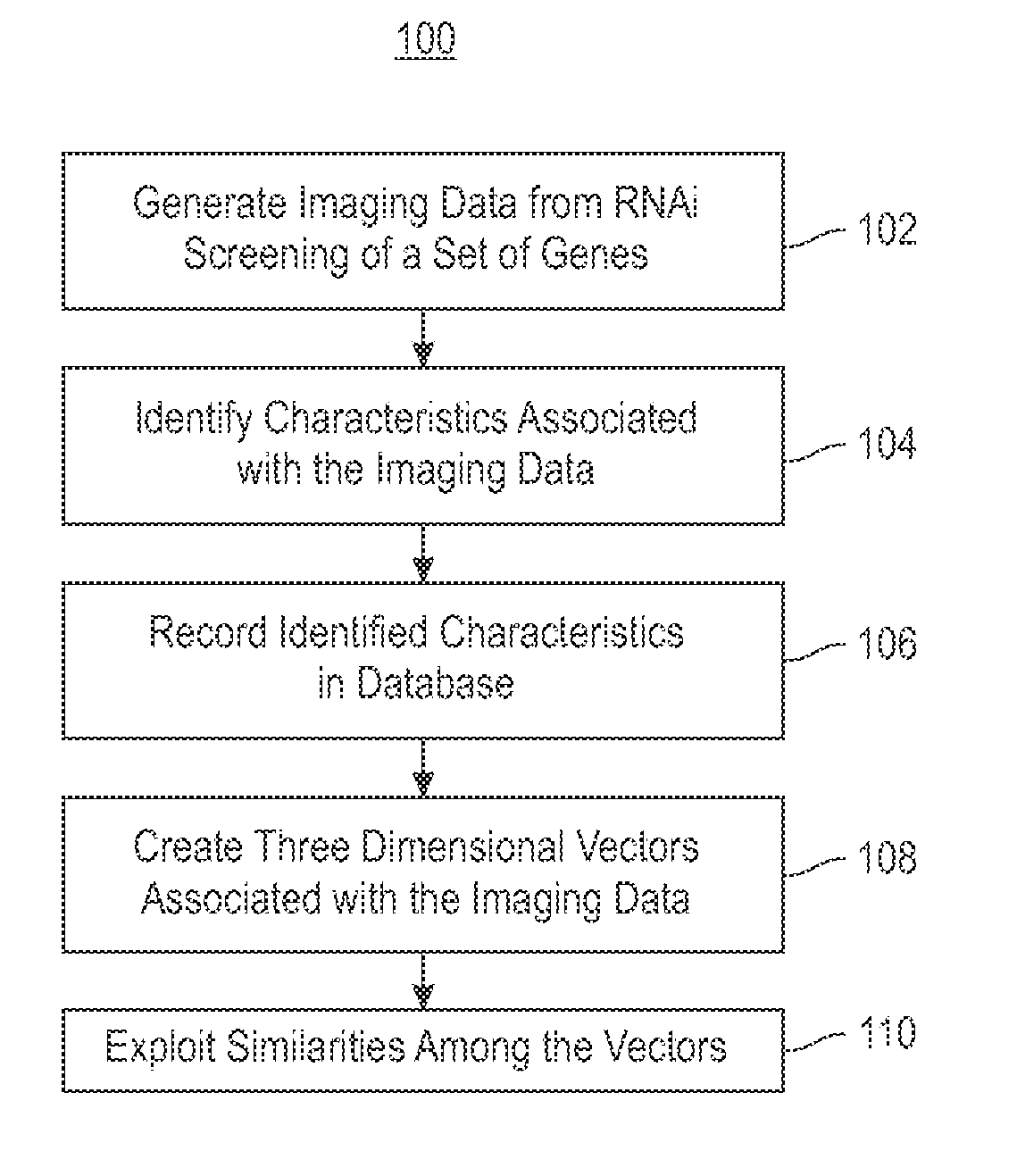
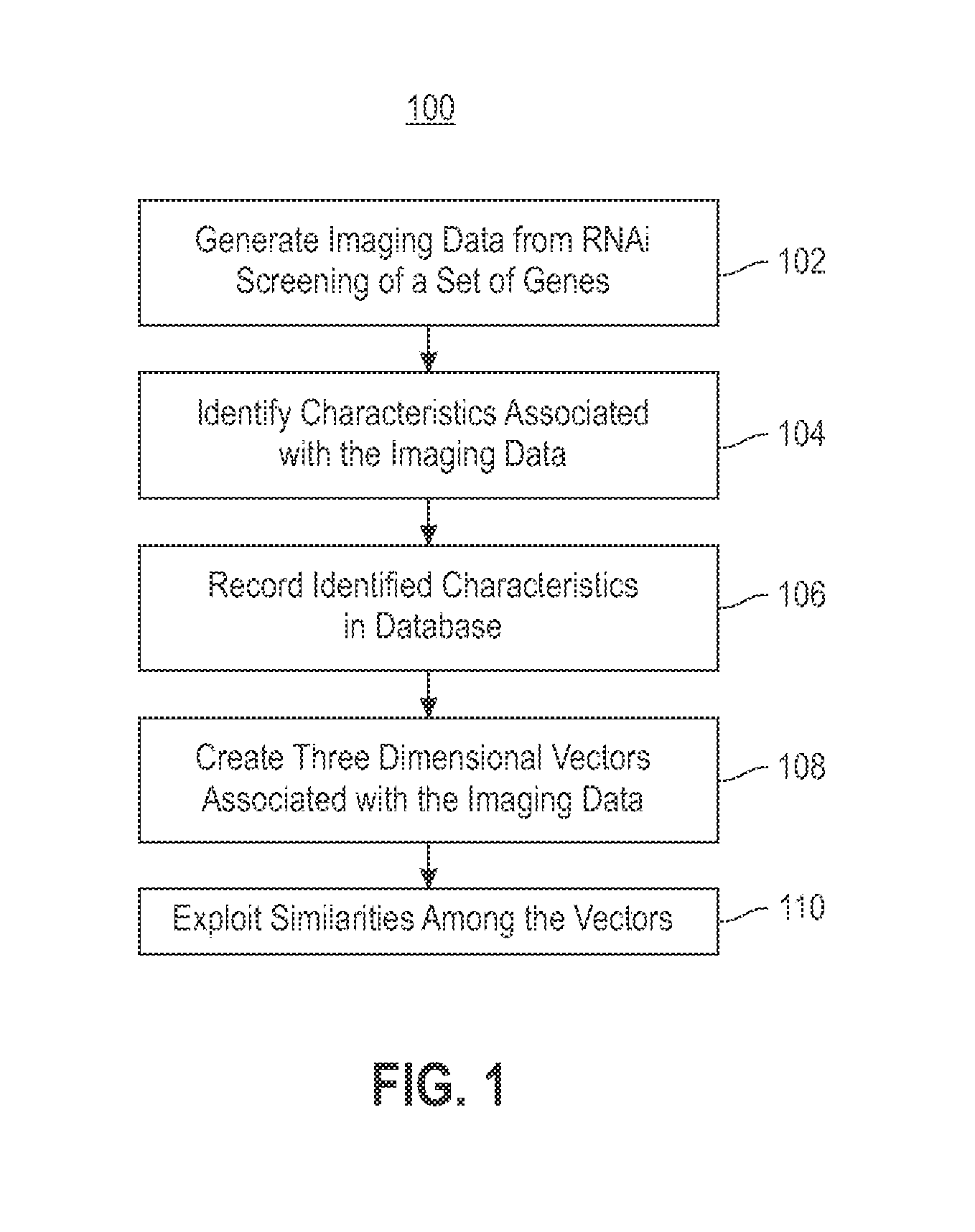
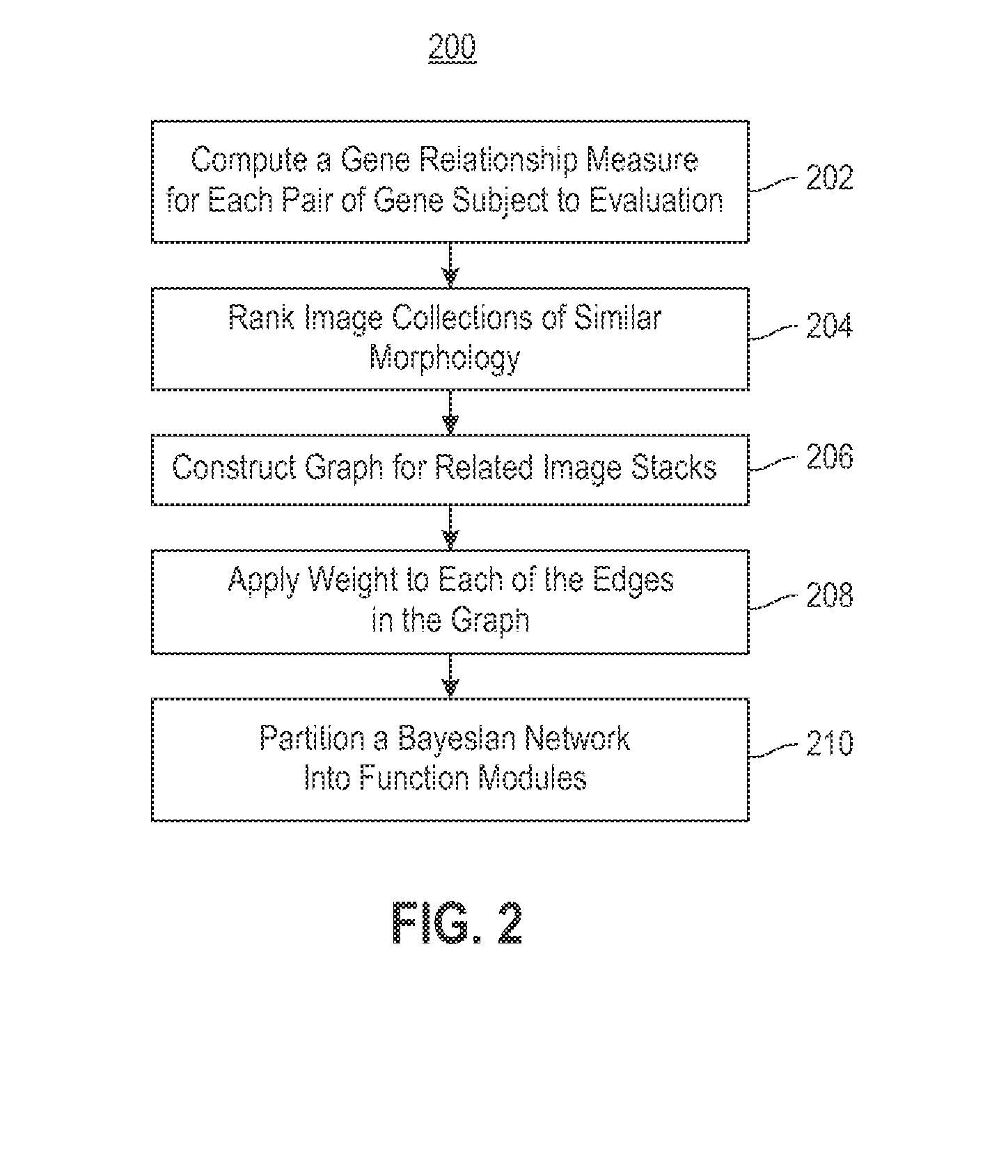
Using RNAi Imaging Data For Gene Interaction Network Construction
Embodiments of the invention relate to a constructing a gene interaction network. Tools are provided to compute a gene relationship measure based upon cellular images, and to rank image collections having a similar morphology. The ranking is based upon capturing similarity within the ranked collection by modeling a three dimensional shape of a cellular image stack. The graph is constructed for related images stacks. Nodes in the graph represent genes, and edges drawn between the nodes represent corresponding image stacks in a commonly ranked list. Accordingly, the graphical representation mathematically and visually connects respective genes.
Owner:IBM CORP
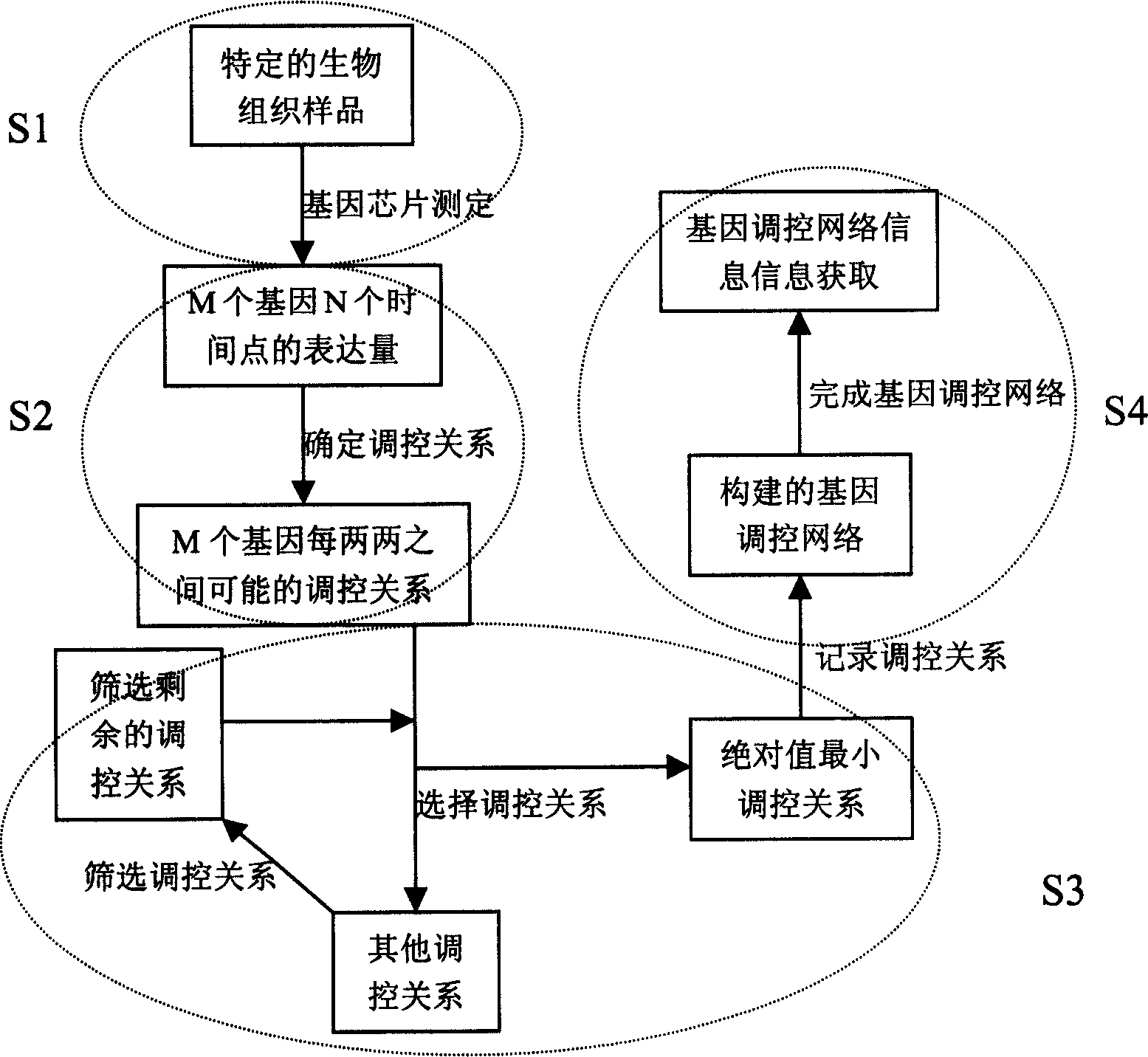
Process of constructing gene regulation network by continuous gene expression spectrum
InactiveCN1560271AAvoid the limitations of extracting gene regulatory networksMicrobiological testing/measurementPhase differenceChips gene expression
The invention relates to a biochip gene expression spectrum system, especially a method of constructing gene regulation and control network by continuous gene expression spectrum. It considers the size, direction and time phase difference of gene regulation and control. By large-scale gene chip continuous expression spectrum data, it considers the change condition of expression quantity with the time, calculates the distance of regulation and control relationship between genes, makes clustering analysis on the distance to construct a large-scale gene regulation and control network. The steps: a), obtaining several continuous expression spectrum gene chip data at time points of several genes; b), determining the distance of regulation and control relation between all the genes; c) selecting specific distances to construct gene regulation and control network.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
CRISPR/Cas9 system for knocking out dmrt1 gene at double gRNA sites in yellow catfish and application
ActiveCN110923229AHigh knockout efficiencyReduce identification costsMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
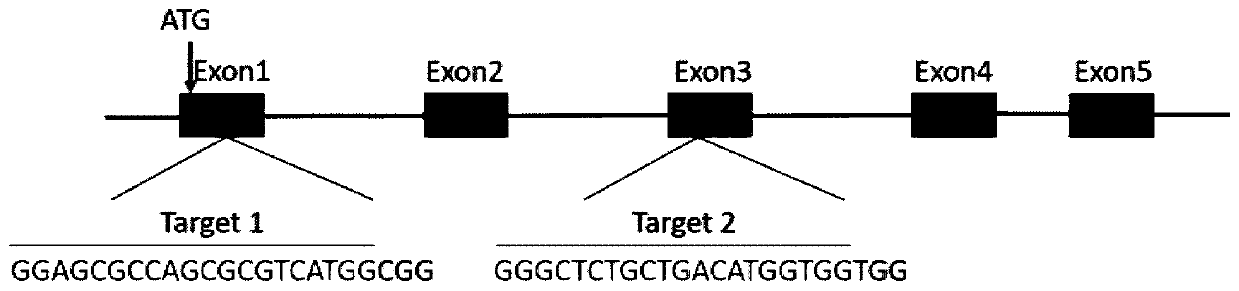
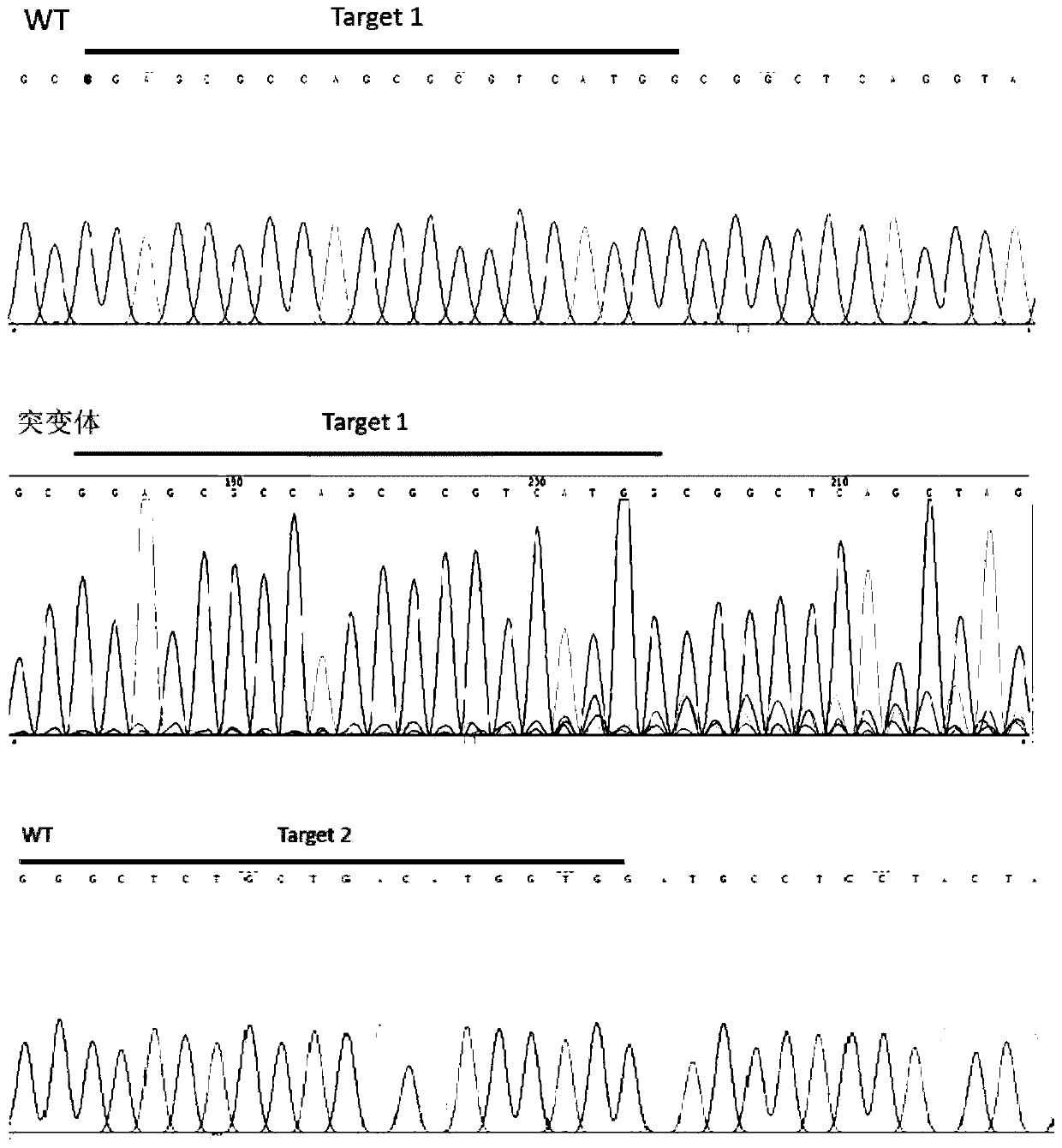
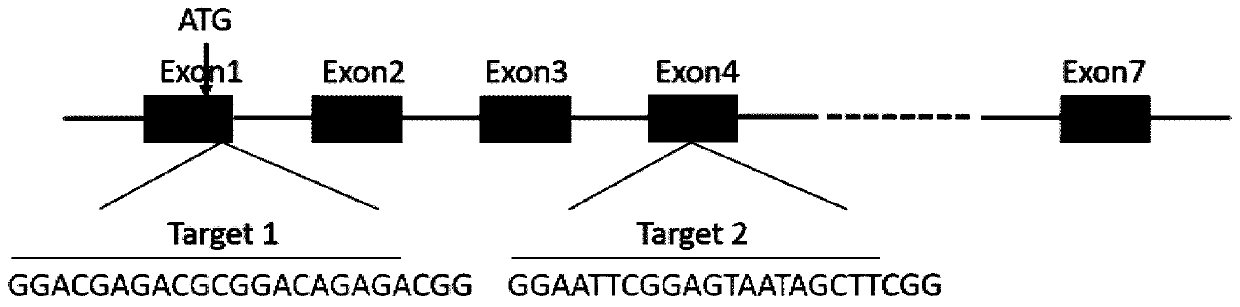
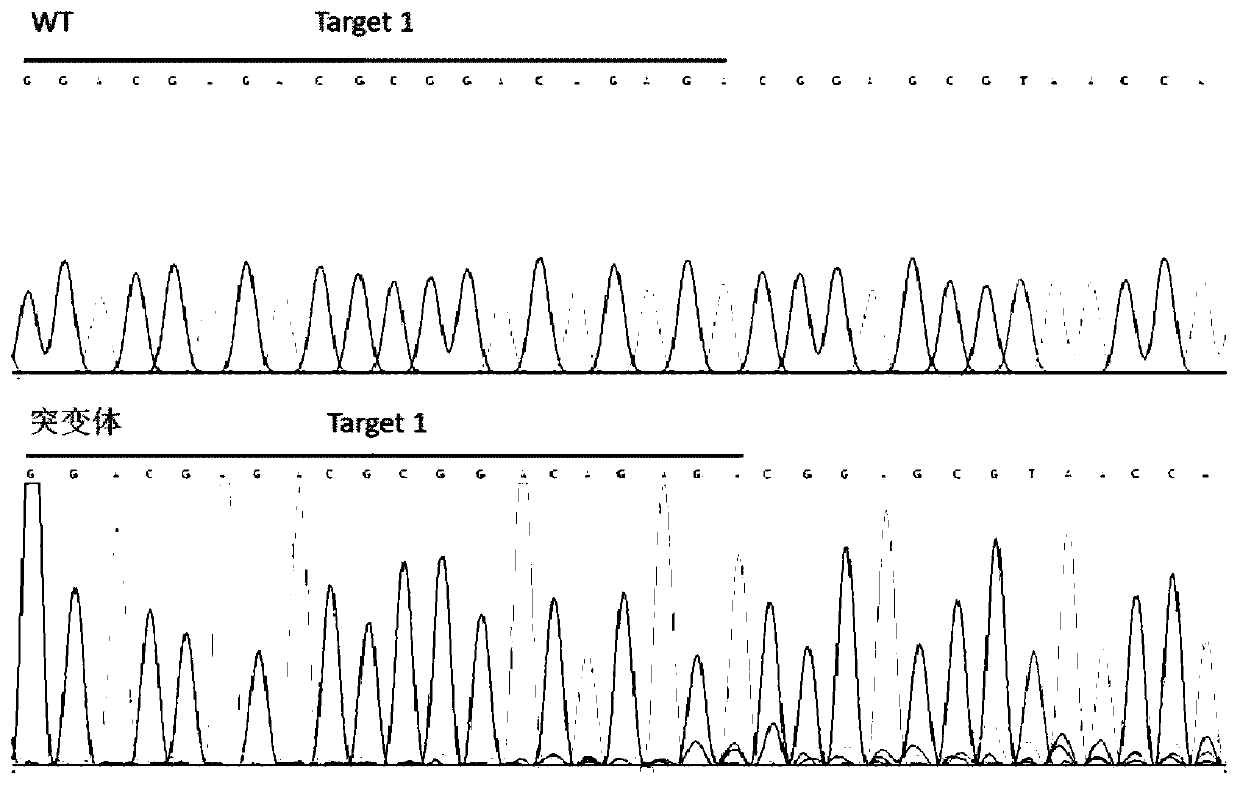
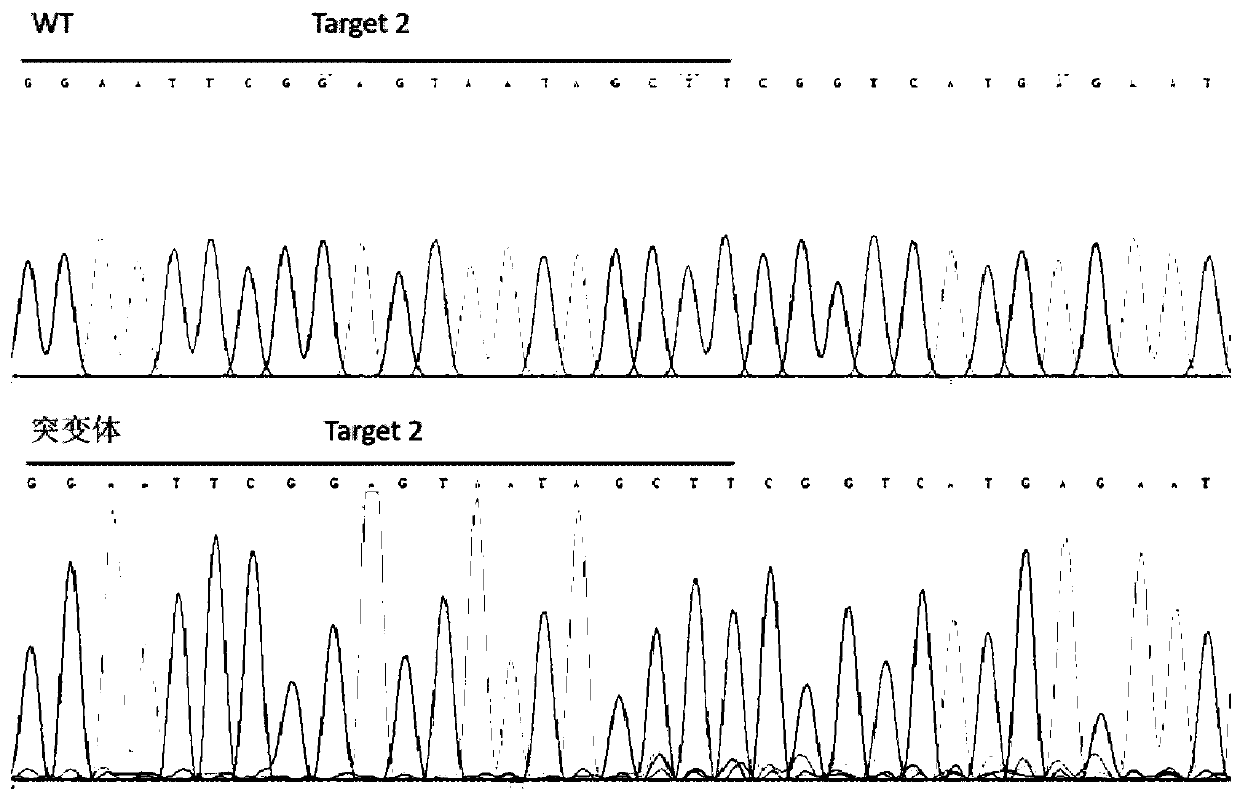
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system for knocking out a dmrt1 gene at double gRNA sites in yellow catfish. The CRISPR / Cas9 system comprises the following steps: (1) designing a target site 1 on a first exon of the dmrt1 gene of the yellow catfish, and designing a target site 2 on a third exon; (2) designing a primer according to a target site sequence in the step (1) to detect the accuracyof the target sites in parent fishes, amplifying the target site 1 and nearby sequences by using dmrt1 E1 F and dmrt1 E1 R, and amplifying the target site 2 and nearby sequences by using dmrt1 E3 F and dmrt1 E3 R; (3) performing PCR amplification on a gRNA1 fragment by using dmrt1 E1 gRNA F and gRNA R by taking pUC19-gRNA-scaffold plasmid as a template, performing PCR amplification on a gRNA2 fragment by using dmrt1 E3 gRNA F and gRNA R, and performing in-vitro transcription and purification by taking the PCR product as a template to obtain gRNA; (4) performing in-vitro transcription synthesis on Cas9 mRNA by taking pXT7-hCas9 linearized plasmid as a template; (5) performing microinjection on the Cas9 mRNA and the two gRNAs into a cell-stage embryo of the yellow catfish; and (6) detectingthe mutation type, and calculating the gene editing rate.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
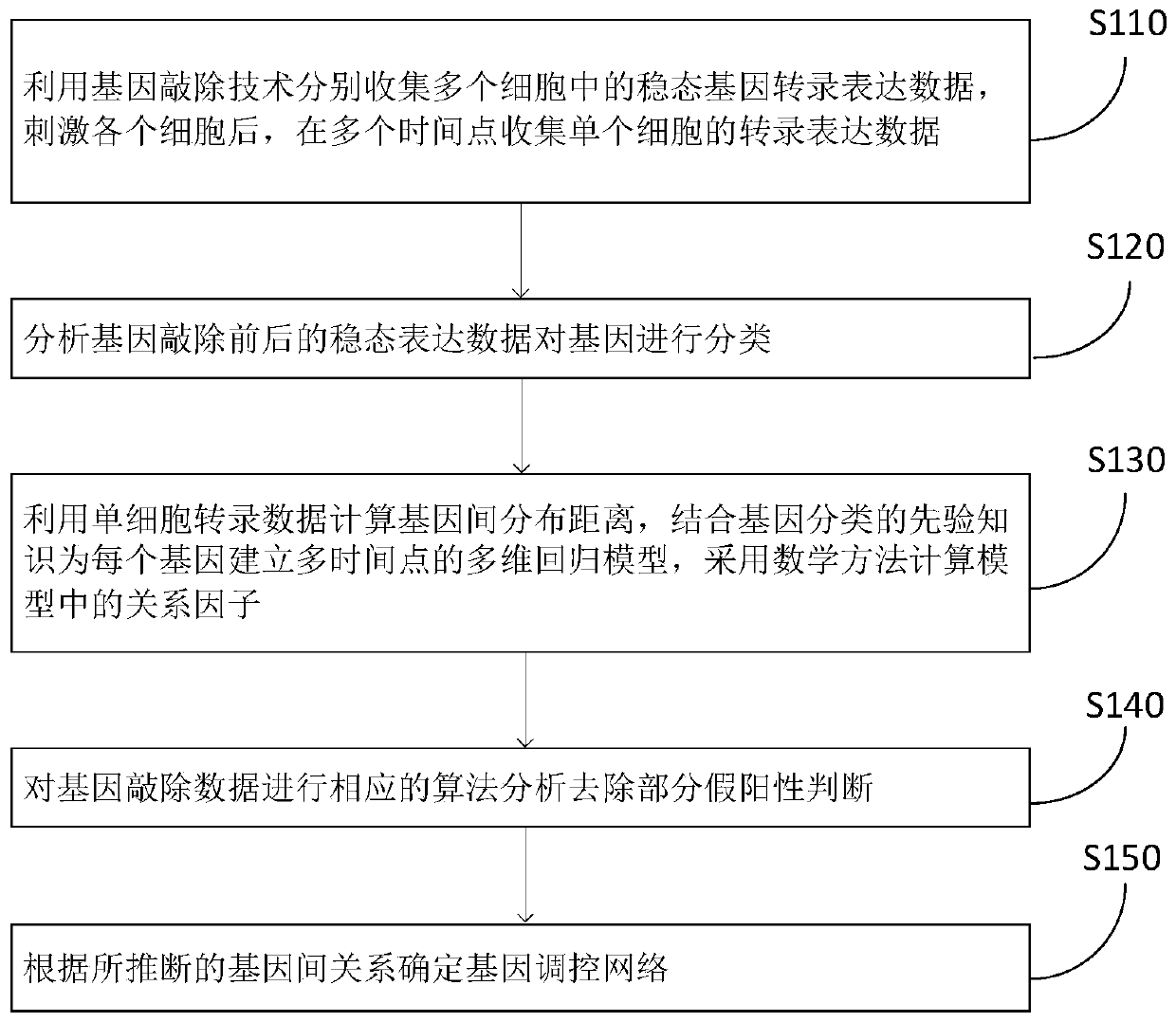
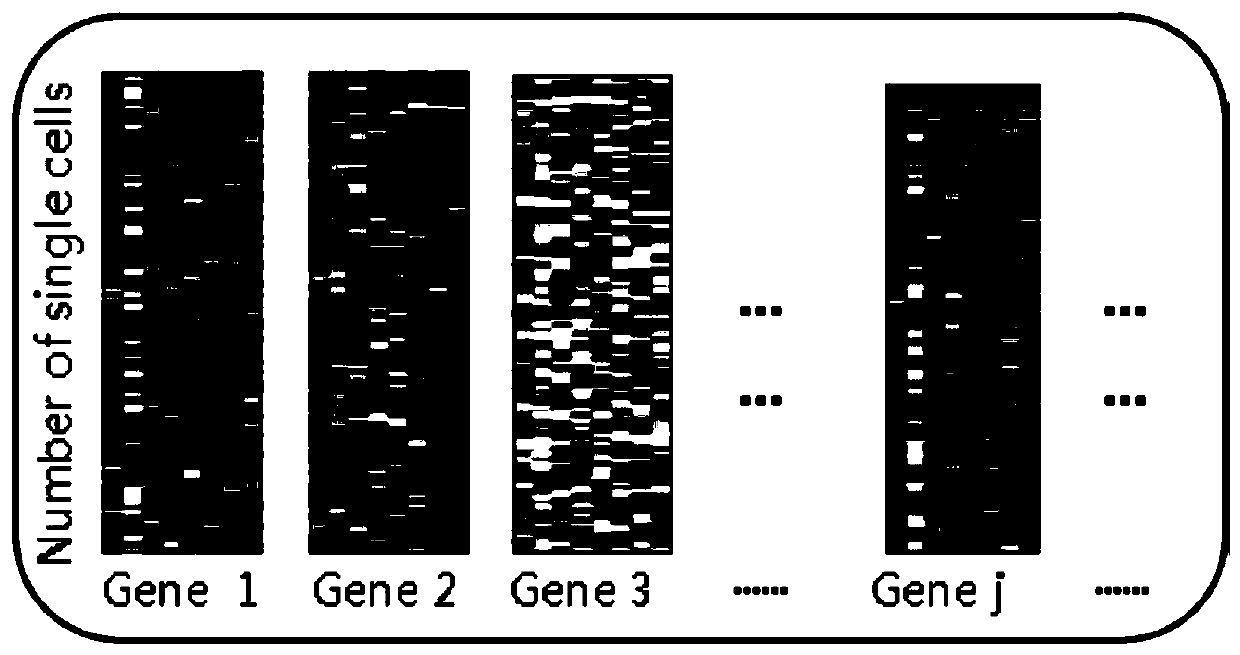
Method for deducing gene regulation network by using single cell transcription and gene knockout data
ActiveCN110517724AImprove accuracySolve problems with high computational complexityBiostatisticsSystems biologyComputation complexityMulti dimensional
The invention discloses a method for deducing a gene regulation network by using single cellular transcription and gene knockout data, which comprises the following steps of: classifying genes by analyzing steady-state expression data before and after gene knockout to serve as priori knowledge so as to reduce the space-time complexity and improve the deduction accuracy; calculating an inter-gene distribution distance by utilizing single cell transcription data, establishing a multi-time-point multi-dimensional regression model for each gene according to the gene classification result, and calculating a relation factor in the model by adopting a mathematical method; performing corresponding algorithm analysis on the gene knockout data to remove part of false positive judgment, and making upfor the defect of analyzing dynamic data. According to the method, the problem of high computation complexity in analyzing the time sequence single-cell data is effectively solved, and the accuracy of deducing the gene regulation network is improved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for estimating breeding value by fitting genome with non-additive effect
PendingCN111883206AIncrease flexibilityImprove stabilityProteomicsGenomicsCorrelation coefficientAlgorithm
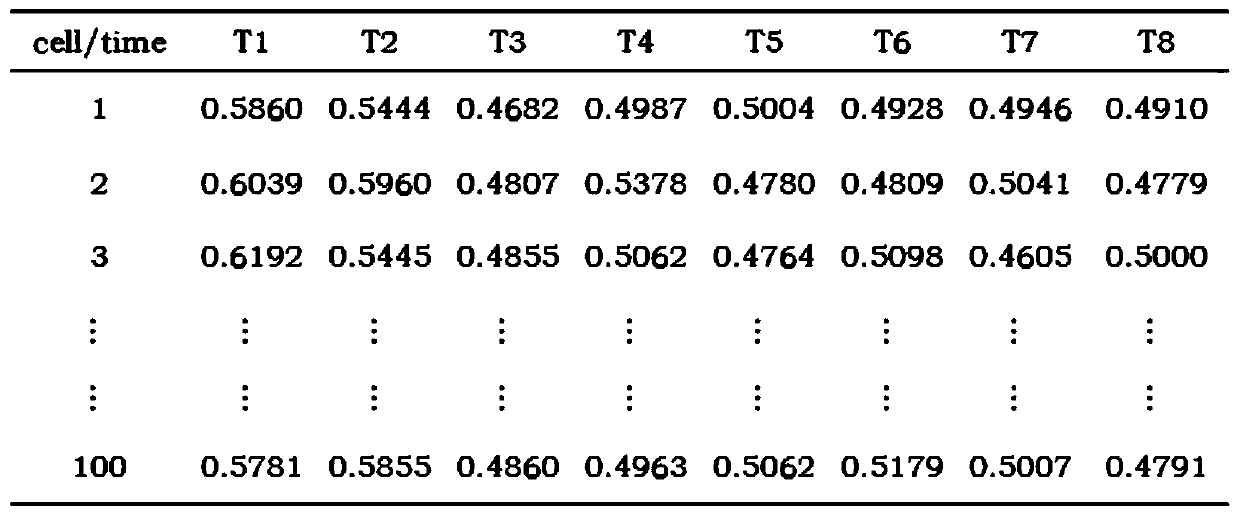
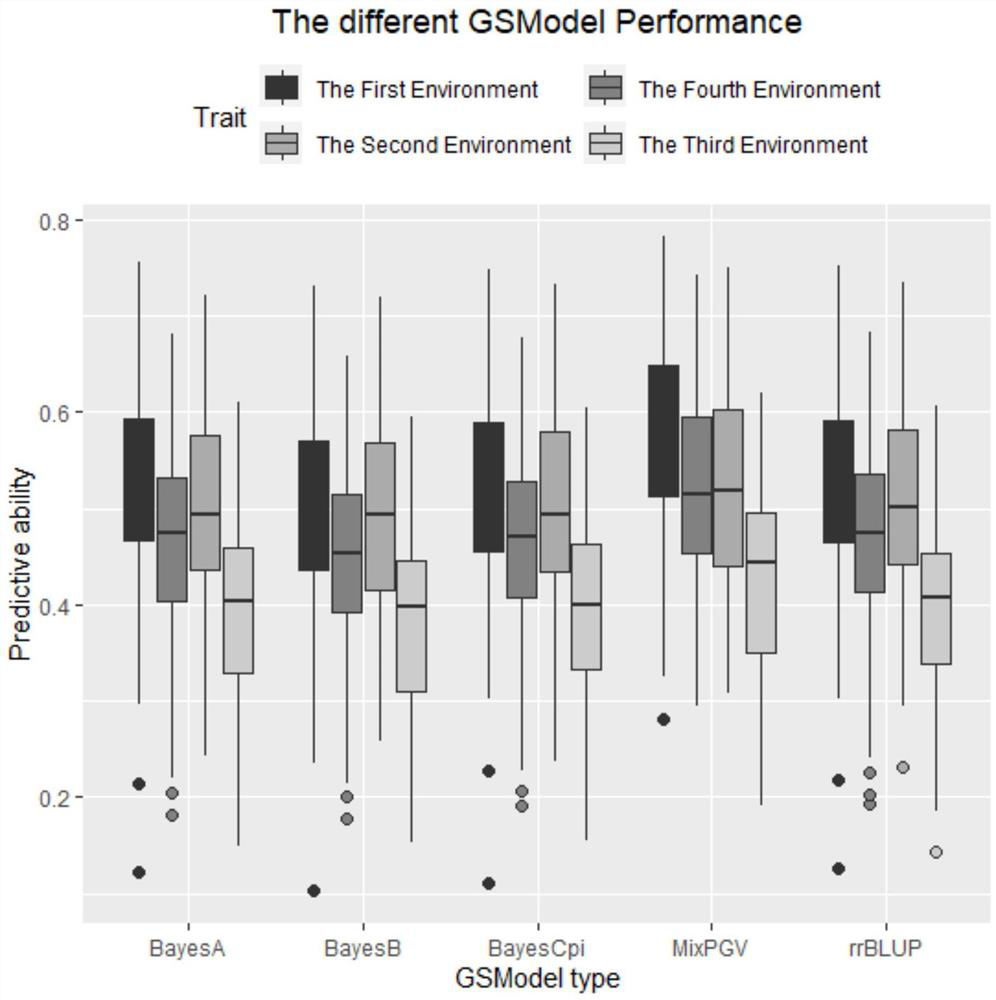
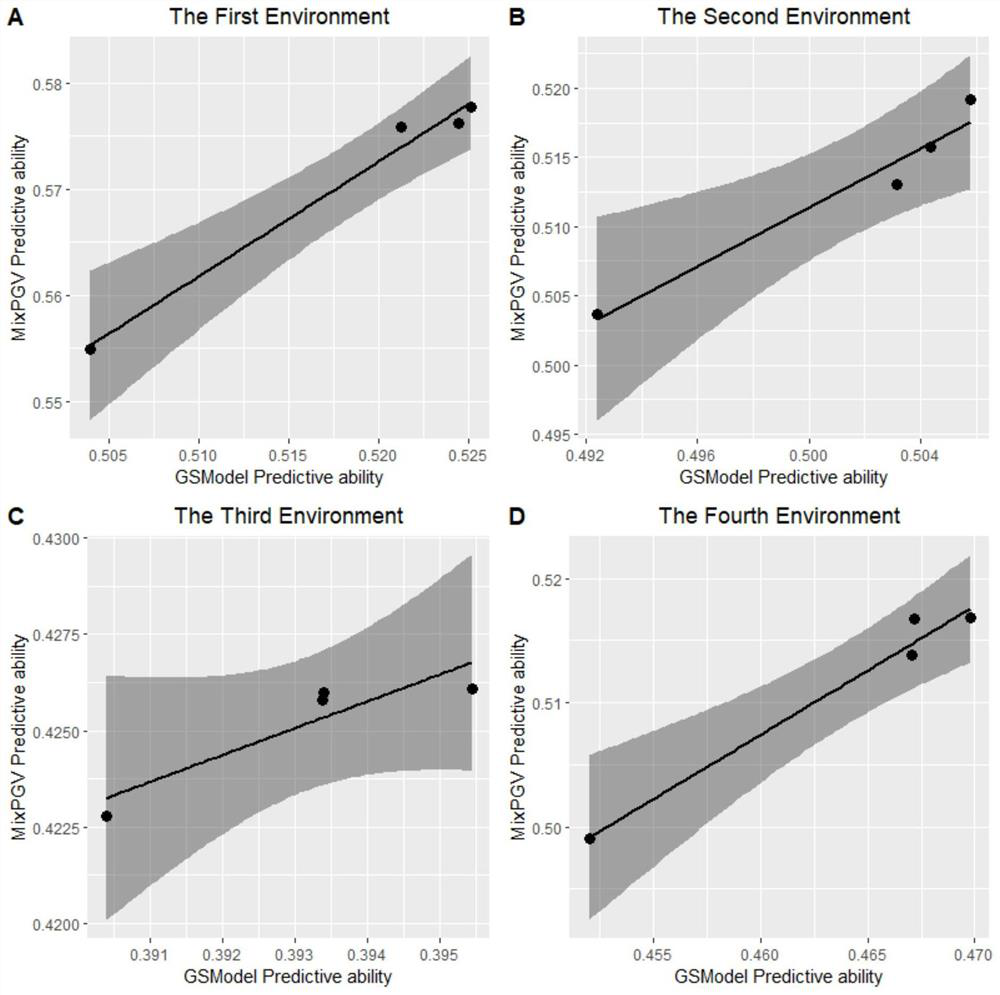
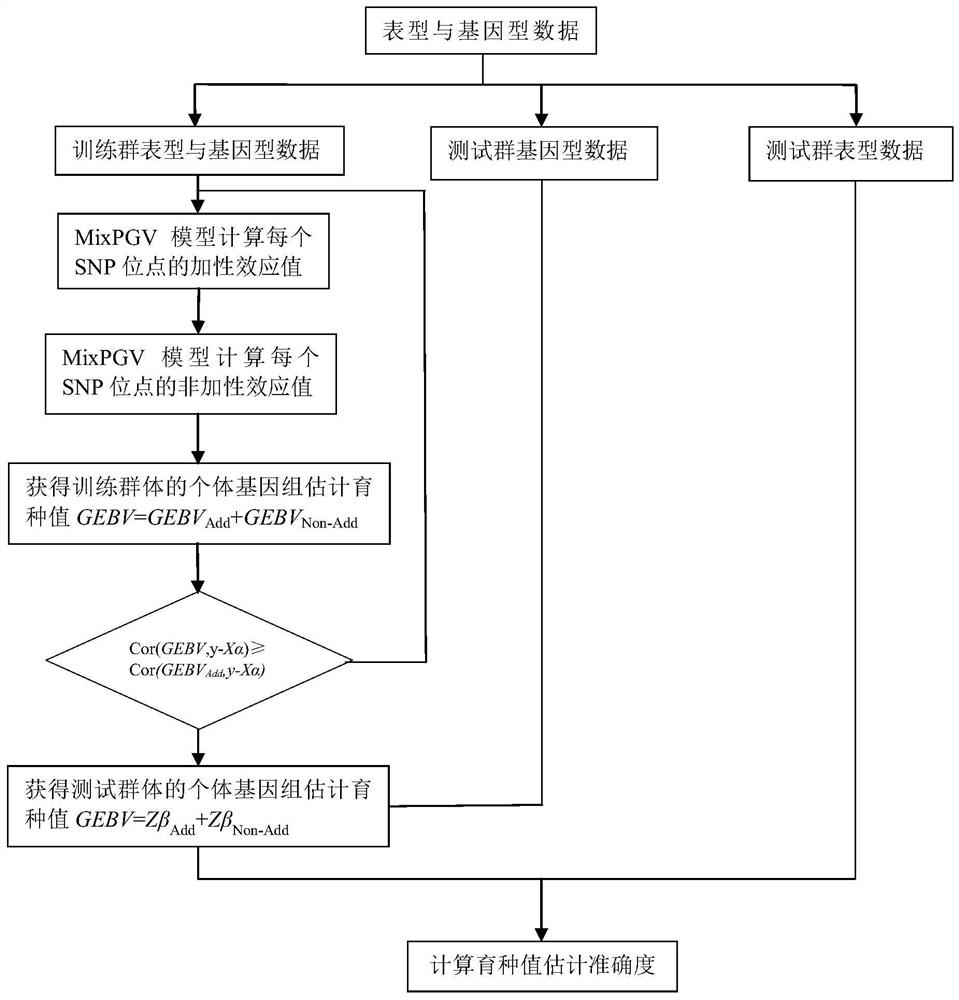
The invention discloses a new method for estimating breeding value by fitting genome with non-additive effect. According to the method, an additive effect prediction model and a non-additive effect prediction model in genome selection are combined into a meta-algorithm of a prediction model,. Compared with a prediction model only fitting an additive effect, the method disclosed by the invention can generally obtain a better prediction effect. The method comprises the following specific steps of acquiring complete genotype information and phenotype information of a single group; randomly dividing a training group and a test group, and performing iterative training on the training group through a hybrid algorithm MixPGV; obtaining an expected additive effect value and an expected non-additive effect value of each SNP site, and performing accumulating to obtain an additive genome estimated breeding value GEBVAdd and a non-additive genome estimated breeding value GEBVNon-Add of an MixPGV prediction model; and accumulating the additive genome estimated breeding value GEBVAdd and the non-additive genome estimated breeding value GEBVNon-Add to obtain a genome estimated breeding value GEBVof the group, and finally calculating a correlation coefficient of the genome estimated breeding value GEBV and a real breeding value to obtain estimation accuracy.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Methods of creating trait prediction models and methods of predicting traits
To provide methods of creating trait prediction models for predicting phenotypes of traits from single nucleotide polymorphism data and methods of predicting traits with which traits can be predicted with a high accuracy.This is a method of creating a trait prediction model for predicting a phenotype of a multifactorial trait using data of a plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to a trait for each of a plurality of individuals of an organism: representing each of the plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms as a matrix; classifying the plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms into a plurality of categories based on their genetic architectures; calculating, for each of the categories, a genomic similarity matrix using the represented matrix and the number of the single nucleotide polymorphisms belonging to the category; and applying the genomic similarity matrix and a parameter of the genetic architecture to a linear mixed model.
Owner:IWATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
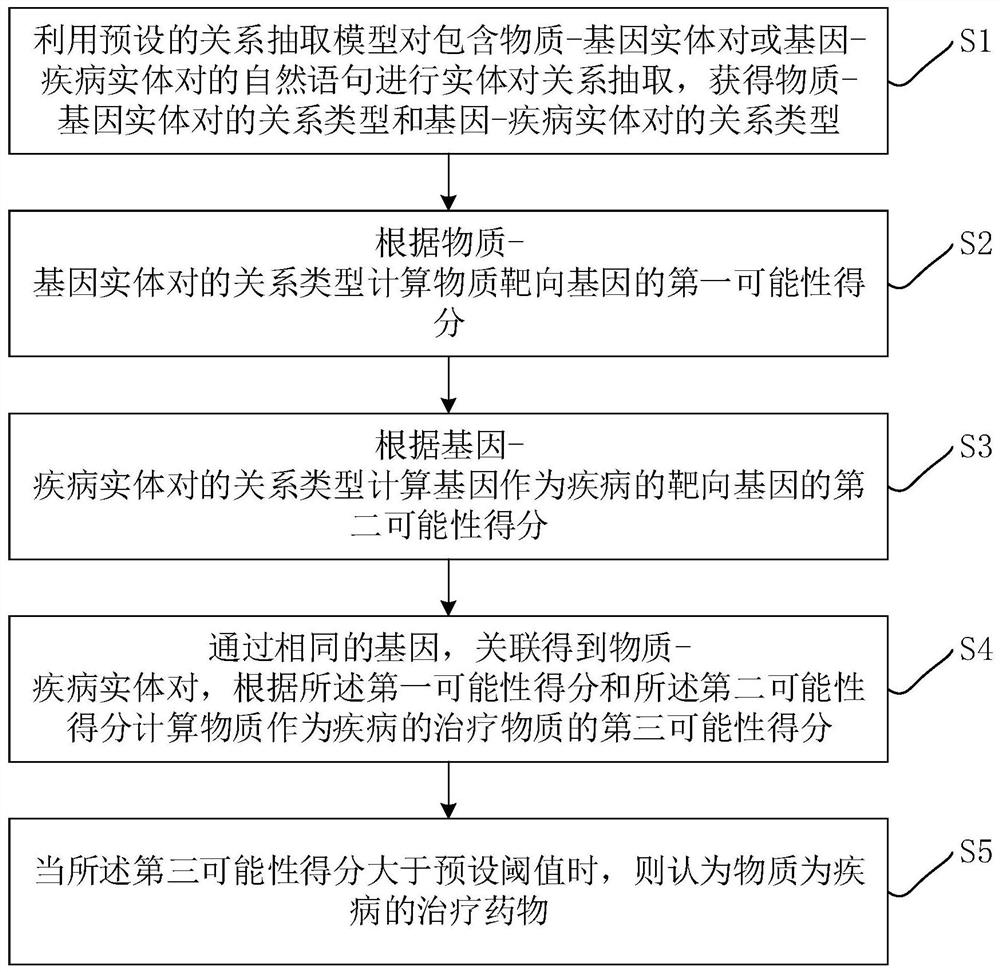
Drug discovery method and device based on relationship extraction and knowledge reasoning and computer equipment
PendingCN112017735ALow costReduced recallsNatural language data processingChemical machine learningDisease entityTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to artificial intelligence, and discloses a drug discovery method and device based on relationship extraction and knowledge reasoning and computer equipment. The method comprisesthe steps of obtaining a relation type of a substance-gene entity pair and a gene-disease entity pair through a relation extraction model, and calculating a first possibility score of a substance targeting gene according to the relation type of the substance-gene entity pair; calculating a second likelihood score of the gene as a target gene of the disease according to the relationship type of the gene-disease entity pair; calculating a third likelihood score of the substance as a therapeutic substance for the disease. The relationship extraction model may be stored in a blockchain. Accordingto the method, substance-gene and gene-disease relationship types are automatically extracted from massive medical literatures, and knowledge is utilized to reasoning substances with treatment effects or potential treatment effects of the drugs, so that high cost and low recall of a scheme based on structural property similarity of the compounds are avoided, and more substances with potential curative effects can be obtained.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
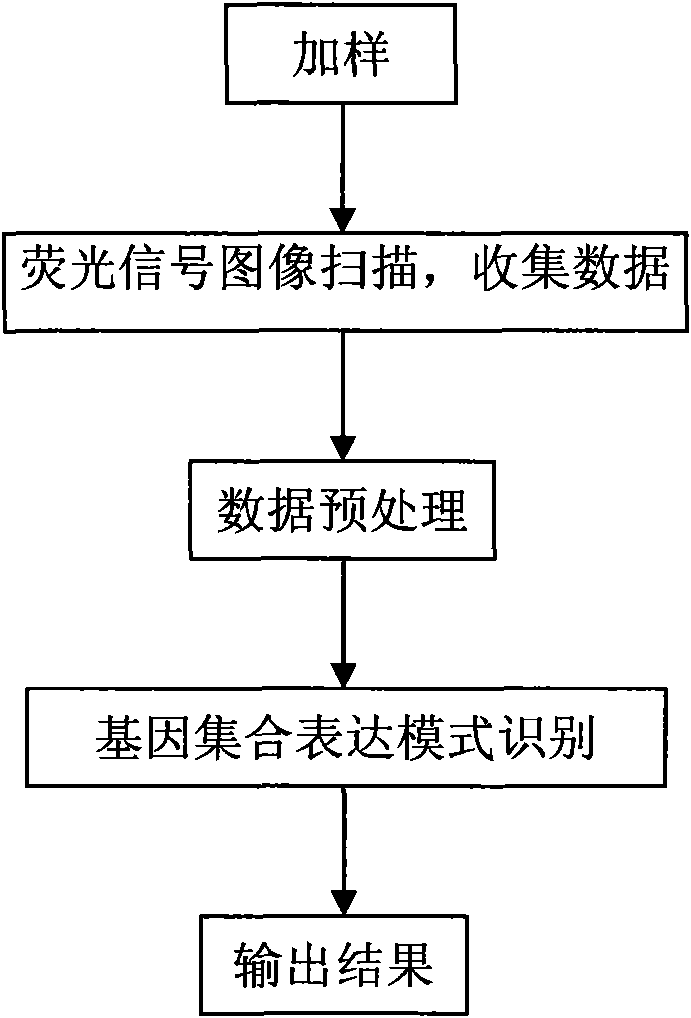
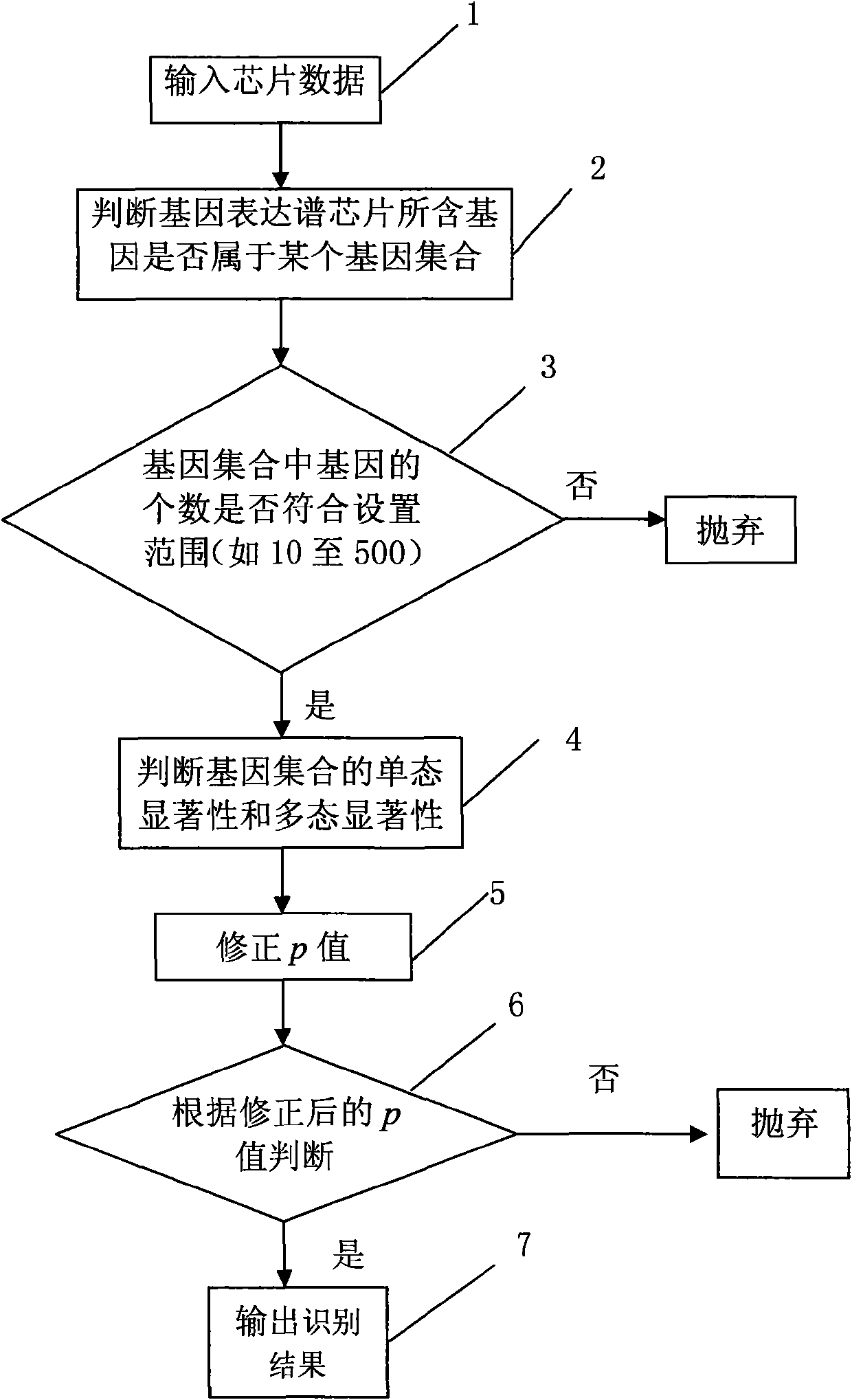
Method for extracting characteristic expression patterns of multiple gene sets
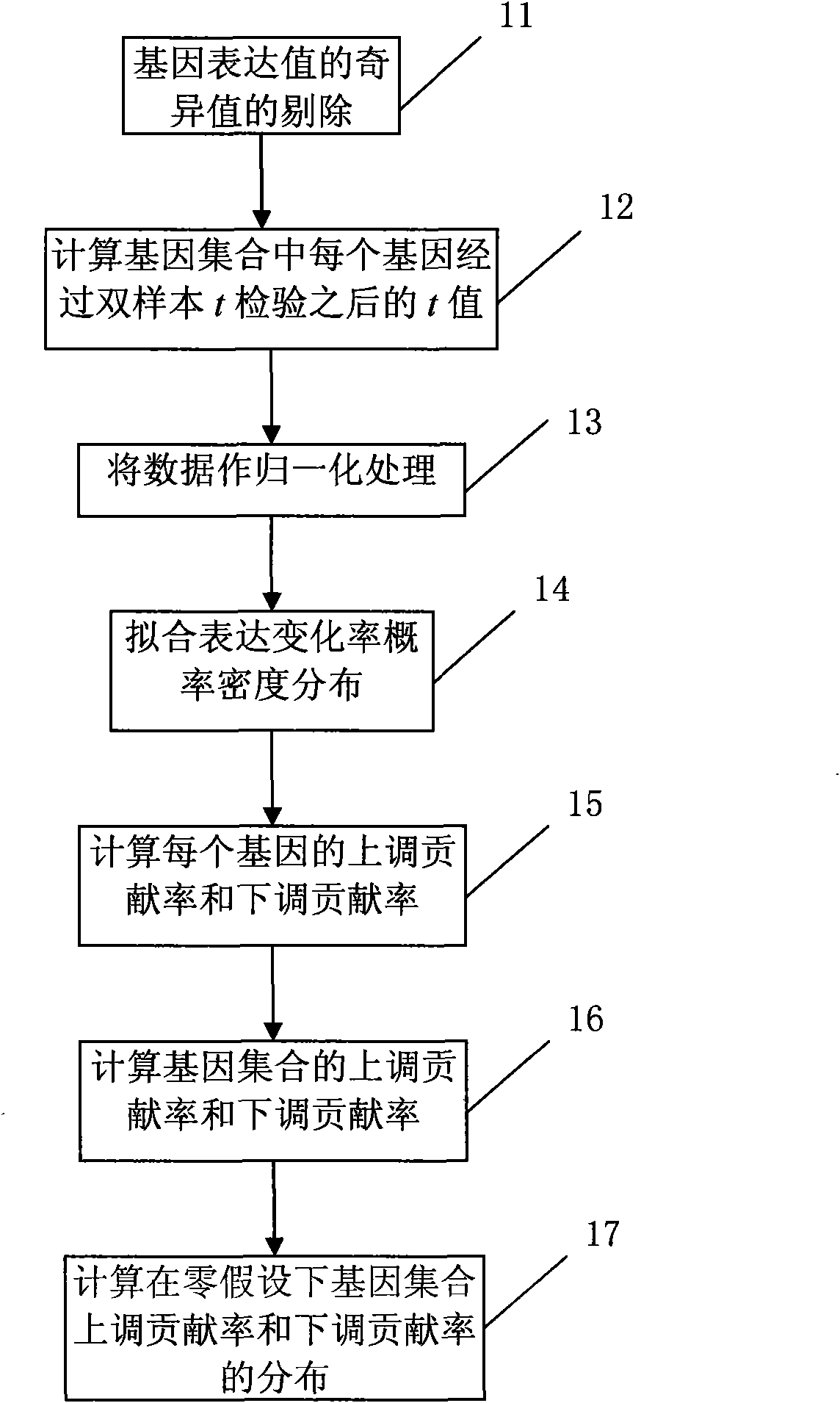
InactiveCN101565747AEfficient identificationIncrease valueMicrobiological testing/measurementComputational geneGene expression profiling
The invention discloses a method for extracting characteristic expression patterns of multiple gene sets, which comprises the following steps: inputting chip data; judging a gene set of genes contained in a gene expression spectrum chip; judging whether the number of the genes in each gene set is in the range of the capacity size of the gene set, and if no, abandoning the gene set, otherwise, performing the next step; calculating the monomorphism significance and the polymorphism significance of the gene sets; correcting an original p value; and judging whether the monomorphism significance and the polymorphism significance of the gene sets accord with a threshold value requirement, if no, abandoning the result, and if so, outputting the recognition result. The method can effectively recognize multiple characteristic expression patterns, discriminate ineffective interference noises, and greatly improves the value of gene expression spectrums in practical application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Dual-gRNA site amh gene knockout method in pelteobagrus fulvidraco and application
ActiveCN110684767AHigh knockout efficiencyReduce identification costsMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyPUC19
The invention discloses a dual-gRNA site amh gene knockout method in pelteobagrus fulvidraco. The method comprises the following steps of (1) designing a target site 1 on the first exon of a pelteobagrus fulvidraco amh gene, and designing a target site 2 on the fourth exon; (2) according to a target site point sequence design primer in the step (1), detecting the accuracy of the target site in parent fish, amplifying the target site 1 and a near sequence by using amh E1 F and amh E1 R, and amplifying the target site 2 and the near sequence by using amh E4 F and amh E4 R; (3) using a pUC19-gRNA-scaffold plasmid as a template, performing PCR amplification on a gRNA1 fragment by using amh E1 gRNA F and gRNA R, and performing PCR amplification on a gRNA2 fragment by using amh E4 gRNA F and gRNA R, wherein the PCR products are used as the template, in vitro transcription is performed, and purification is performed, so that gRNA is obtained; (4) using a pXT7-hCas9 linearization plasmid as atemplate, and performing in vitro transcription to synthetize Cas9 mRNA; (5) performing microinjection on Cas9 mRNA and two gRNA into a cell stage embryo of pelteobagrus fulvidraco; and (6) detectingthe mutation type, and calculating the gene editing rate. The invention further discloses an application of the method.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
MDM2-Containing Double Minute Chromosomes And Methods Therefore
Contemplated systems and methods allow for computational genomic analysis using paired-end sequence analysis and split read refinement to thereby identify high-confidence breakpoints associated with high copy numbers and orientation of rearrangements, which is then the basis for full reconstruction of double minutes (DM). In especially preferred aspects, the DM will also include an oncogene or tumor suppressor gene, and / or may be found in blood or blood derived fluids.
Owner:FIVE3 GENOMICS
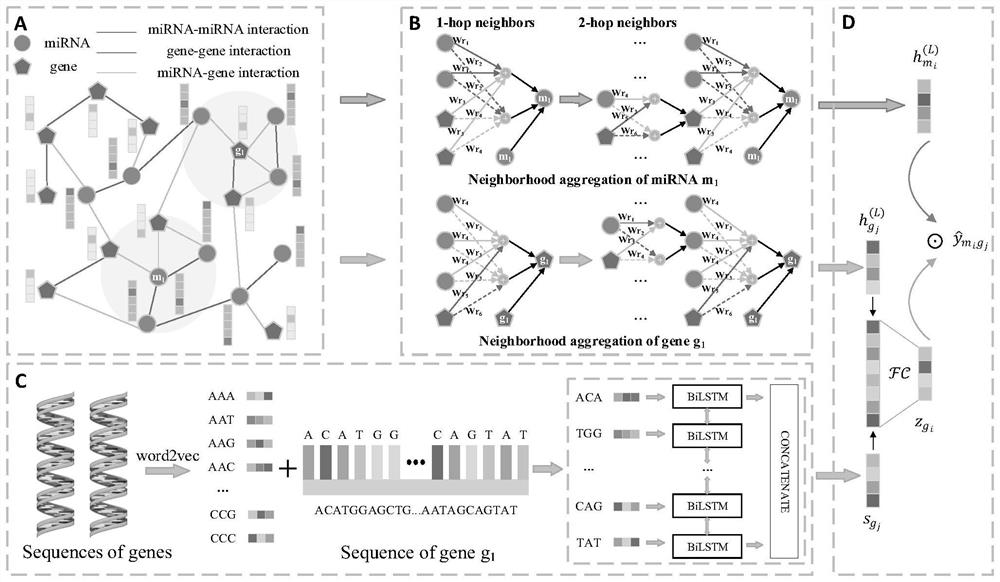
Method and system for predicting interaction between miRNA and gene based on multi-relational graph convolutional network
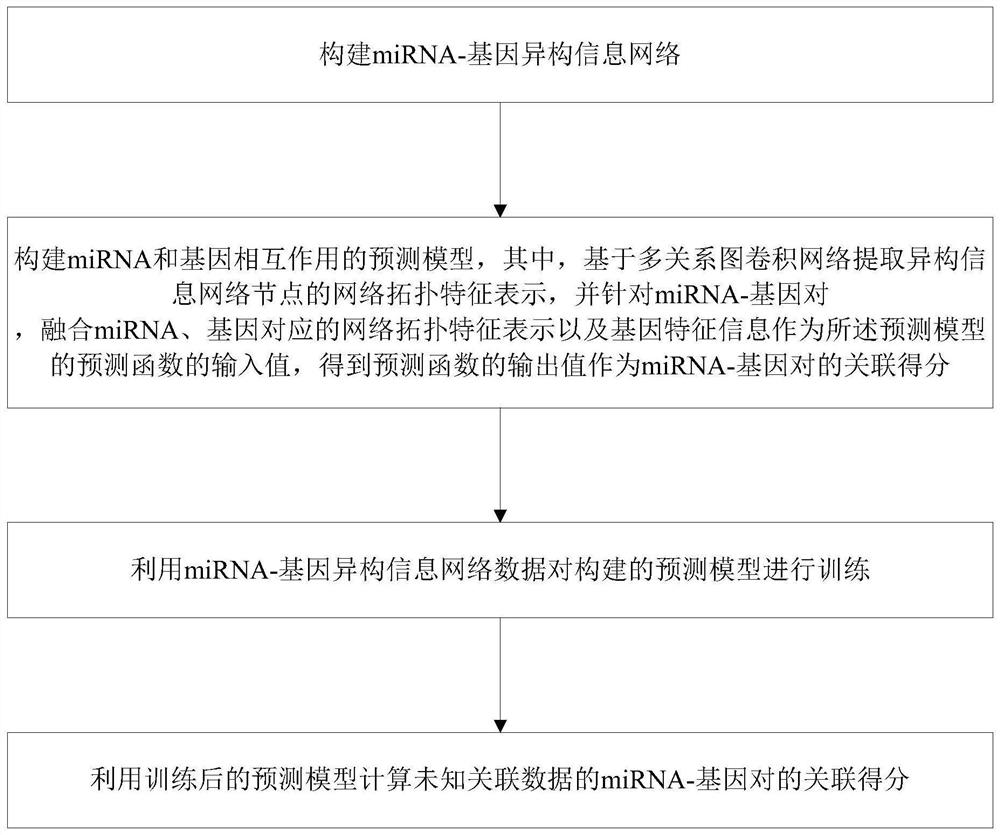
PendingCN114093422ARich forecasting meansFully capture the structureNeural architecturesSequence analysisInformation networksHeterogeneous network
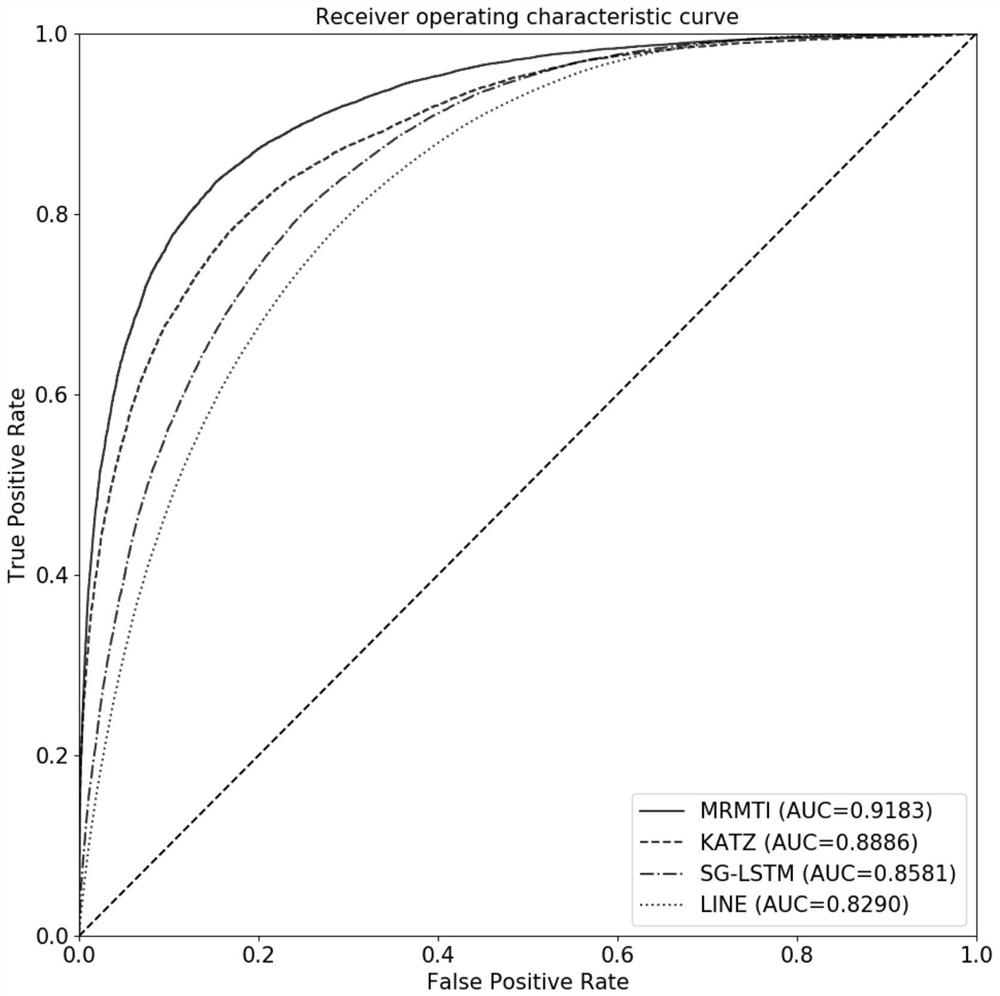
The invention discloses a method and a system for predicting interaction between miRNA and a gene based on a multi-relational graph convolutional network. The method comprises: constructing a heterogeneous information network of miRNA and genes, and learning network topology features of nodes by using a multi-relational graph convolutional network based on the heterogeneous network; meanwhile, capturing effective characteristics of the gene sequence by using a recurrent neural network; and finally, combining network topology characteristics with sequence characteristics, and calculating an association prediction score of the miRNA-gene pair by using the obtained miRNA and gene embedding. According to the method, manual feature construction is not needed in the implementation process, representation learning is combined, the advantages of the multi-relation graph convolutional network are fully utilized, effective gene sequence information is mined, and feature representation of miRNA and gene nodes is better captured. Experimental results show that the MRMTI is superior to other comparison methods in the aspect of association prediction of miRNA and genes, and has good prediction performance.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Drug relocation method based on differential expression data
ActiveCN111785319ACollection is reliableAccurate Forecast AccuracyBiostatisticsDrug referencesDiseasePharmaceutical drug
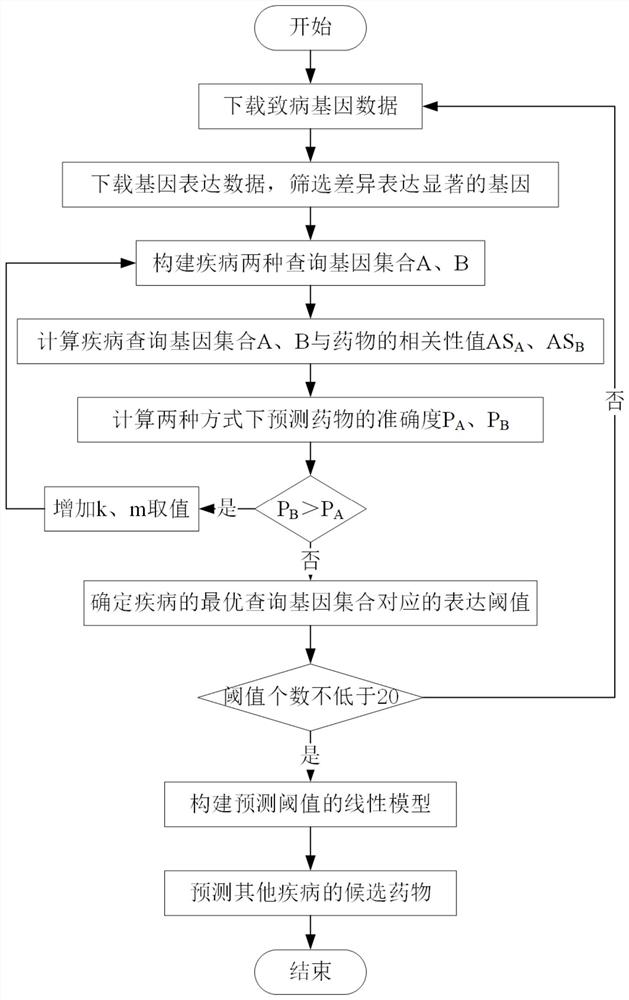
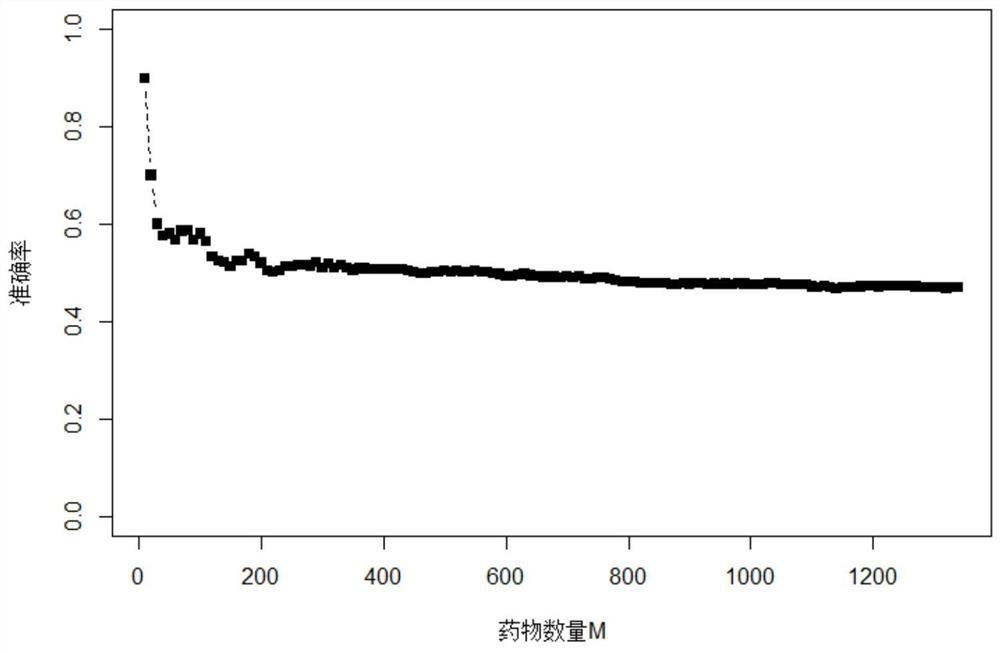
The invention provides a drug relocation method based on differential expression data, and mainly solves the problems of no screening of differential genes and low drug prediction accuracy in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring gene data, calculating a gene expression change value and a significant value thereof, and screening out a gene set with significant differential expression; constructing two query gene sets of the disease by utilizing the gene set and the pathogenic gene; obtaining correlation values of the two gene sets and drugs and drug prediction accuracy corresponding to the correlation values; comparing the predicted drug accuracy of the two gene sets; calculating a difference value between the screened gene set and standard normal distribution,and constructing a prediction model of the optimal disease query gene set according to the difference value and the calculated expression threshold; using the model for predicting gene sets of otherdiseases and calculating the accuracy of predicted drugs, and screening out candidate drugs with potential treatment effects. The method is high in prediction accuracy and can be used for predicting candidate drugs with potential treatment effects on diseases.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
MDM2-Containing Double Minute Chromosomes And Methods Therefore
Contemplated systems and methods allow for computational genomic analysis using paired-end sequence analysis and split read refinement to thereby identify high-confidence breakpoints associated with high copy numbers and orientation of rearrangements, which is then the basis for full reconstruction of double minutes (DM). In especially preferred aspects, the DM will also include an oncogene or tumor suppressor gene, and / or may be found in blood or blood derived fluids.
Owner:FIVE3 GENOMICS
Clustering method of gene microarray containing missing values based on joint training
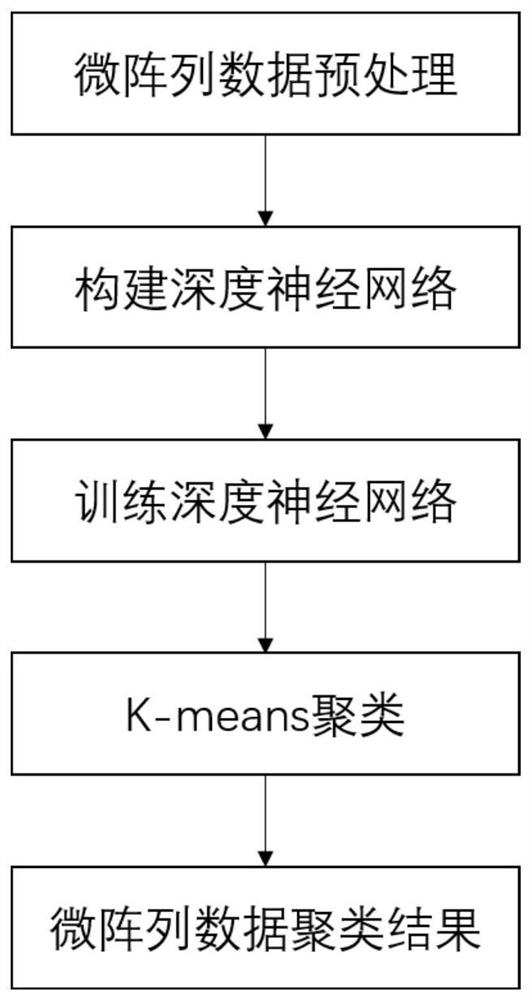
ActiveCN112712855AHigh precisionGood clustering performanceBiostatisticsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputational geneTest set
The invention discloses a clustering method for gene microarrays containing missing values based on joint training; the method comprises the following steps: calculating the missing rate of gene microarray data, removing gene points with the missing rate exceeding 10%, and then dividing the gene microarray data into a training set and a test set; constructing a deep neural network, including a Sequence-To-Sequence encoding-decoding network and an adversarial learning module, and training the constructed deep neural network by using the training set to determine parameters of the deep neural network; inputting the test set into a deep neural network to obtain deep feature representation containing missing value gene microarray data in the test set; and finally, applying a K-means clustering algorithm to the deep feature representation to obtain a clustering result of the gene microarray containing the missing values. According to the method, an end-to-end framework can be provided for gene expression data clustering, and the difficulty that a proper filling method and a clustering method need to be selected to be combined in a traditional method is solved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com