Microbial species and functional composition analysis method for metagenome sequencing data
A technology of sequencing data and metagenomics, which is applied in the field of microbial gene analysis, can solve problems such as limited application range, limited application area, and low sensitivity, and achieve the effects of avoiding high false positive results, improving accuracy, and high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
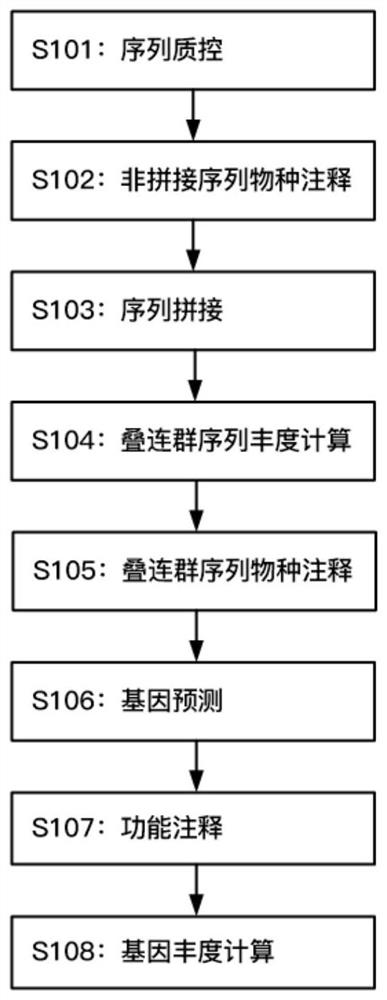
[0073] A microbial species and functional composition analysis method for metagenomic sequencing data, comprising the following steps:
[0074] 1) Cut off the linker sequence fragments and low-quality fragments in the original data, filter out short sequences and ambiguous base sequences; if the host genome is known, delete the host sequence;
[0075] 2) Use the data obtained above for species annotation, and count the number of species sequences as the abundance, and then eliminate the sequences annotated to non-target species based on the annotation results;
[0076] 3) splicing the sequence after removing the non-order species to obtain the contig sequence;
[0077] 4) Perform similarity clustering on the contig sequences, and calculate the non-redundant contig sequence abundance of each sample, and remove the sequences whose total abundance is zero;
[0078] 5) Use the blastn algorithm to compare the non-redundant contig sequences to the nucleic acid database, and use the...
Embodiment 2
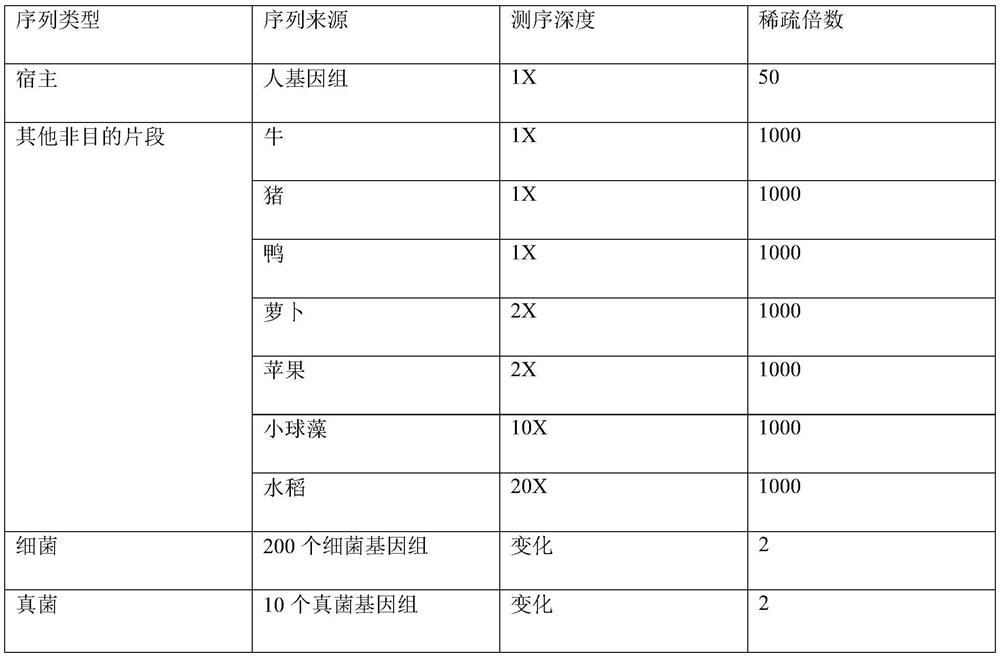
[0091] In the embodiment of the present invention, the simulated metagenomic data is used for analysis, and the species composition of the simulated data is shown in Attached Table 1, wherein the known host genome is the human genome.
[0092] In step S101, first use FastQC to check the sequencing quality of the original data; use Cutadapt to identify potential adapter sequences at the 3' end, and truncate at the identified adapters. here. It is required that the matching length with the linker sequence (R1: AGATCGGAAGAGCACACGTCTGAACTCCAGTCA; R2: AGATCGGAAGAGCGTCGTGTAGGGAAAGAGTGT) be at least 3 bp, and a base mismatch rate of up to 20% is allowed. Then use the fastp software to cut the low-quality fragments. Specifically, the sliding window method is used to perform quality screening on the sequence: the window size is 5 bp, and it starts to move from the first base position at the 5' end, and the average quality of the bases in the window is required. Greater than or equal t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com