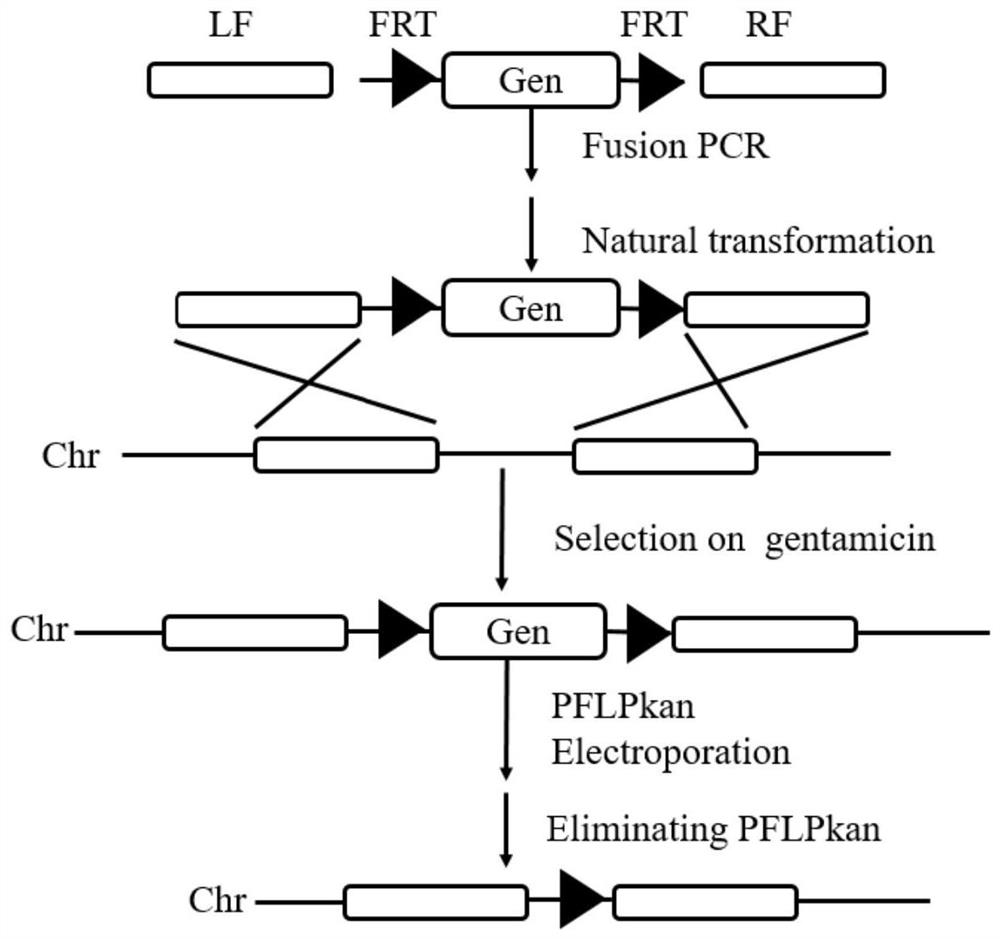
Method for traceless knockout of ralstonia solanacearum gene and application thereof
A technology of traceless knockout and R. solanacearum, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of inconvenient operation and knockout failure, and achieve the effect of simple operation, less operation steps and high resistance screening efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 The traceless knockout of R. solanacearum gene phcA
[0038]Ralstonia solanacearum has a variety of virulence factors, including exopolysaccharide (EPS), cell wall degrading enzyme (CWDE), secretion system and so on. Existing studies (Genin et al., 2012) have elucidated the complex regulatory mechanism of R. solanacearum. Among them, PhcA, the product of the gene phcA, is located in the center of the complex regulatory network and is a transcriptional regulator of the LysR family, which directly or indirectly regulates the production of EPS, CWDE and other virulence factors in a population density-dependent manner.
[0039] The gene accession number of the phcA gene of Ralstonia solanacearum is AC251_03705, its length is 1044bp, and it encodes a key regulatory factor of the phc QS system. Previous studies have shown (Wang Dechen, 2016) that the deletion of the R. solanacearum gene phcA will reduce its exopolysaccharide, which is a relatively intuitive phenoty...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Example 2 The traceless knockout of R. solanacearum EP1 gene epsB
[0094] The present invention adopts the same method to knock out the R. solanacearum exopolysaccharide gene epsB (the gene accession number is AC251_23630).
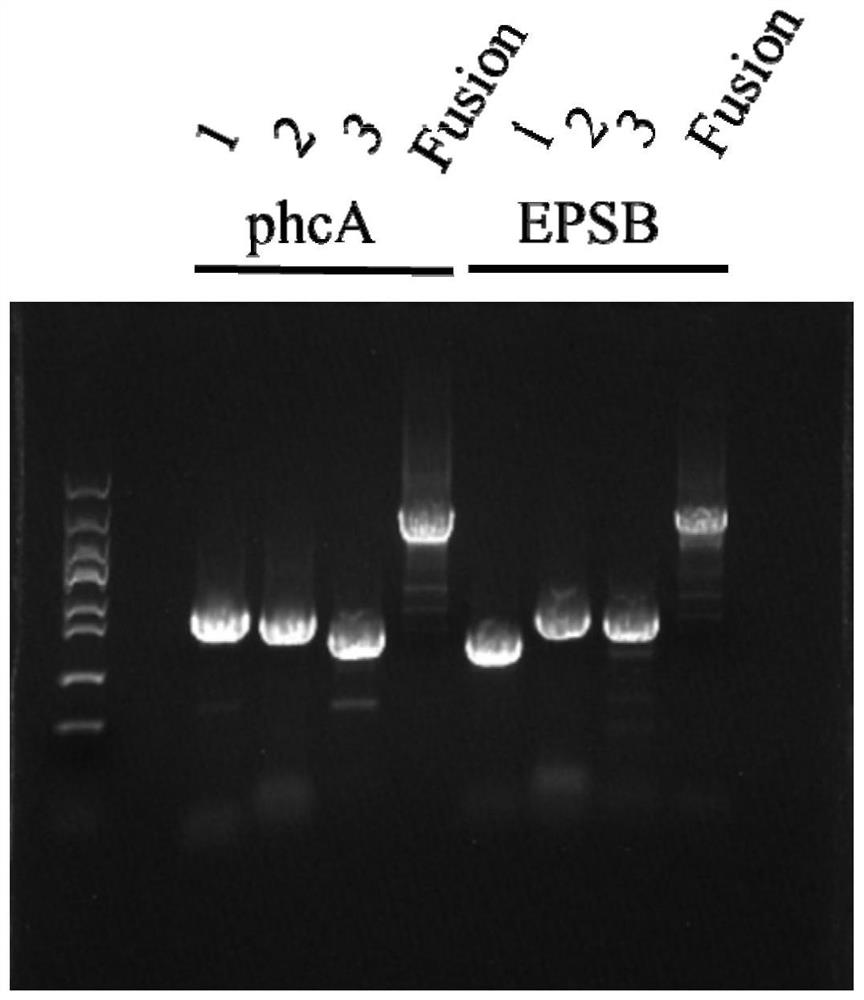
[0095] According to the sequence of the epsB gene, the primers for amplification of the upstream and downstream homology arms, the fragments of the upstream and downstream homology arms of R. solanacearum gene epsB, the gentamycin resistance gene fragment and the electrophoresis results of the fusion fragment of the three are as follows figure 2 As shown, 1 is the upstream homology arm fragment of epsB, 2 is the gentamicin resistance gene fragment with FRT sites at both ends, and 3 is the upstream homology arm and downstream homology arm fragment of epsB, composed of figure 2 It can be seen that the fusion fragment of the gene epsB was successfully obtained. The screening results of epsB gene knockout mutants with FRT sites and gentamicin resis...
Embodiment 3
[0098] The knockout of the Ralstonia solanacearum gene of embodiment 3 different hosts
[0099] In addition, the present invention adopts the method for seamlessly knocking out R. solanacearum genes described in Example 1 to carry out seamless knockout of different genes in R. solanacearum of different plant hosts, and detects the obtained scarless knockout mutants colony morphology. The present invention respectively knocks out the phcA gene in the R. solanacearum EP1 strain whose host is eggplant, the phcB gene in the R. solanacearum GMI1000 strain whose host is tomato, and the phcB gene in the R. solanacearum NS25 strain whose host is casuarina, The colony surface morphology of the three knockout mutants obtained is as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the left is the mutant obtained by knockout by the traditional method, and the right is the knockout mutant obtained by the scarless knockout method of the present invention. Depend on Figure 8 As can be seen, the mutant strai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com