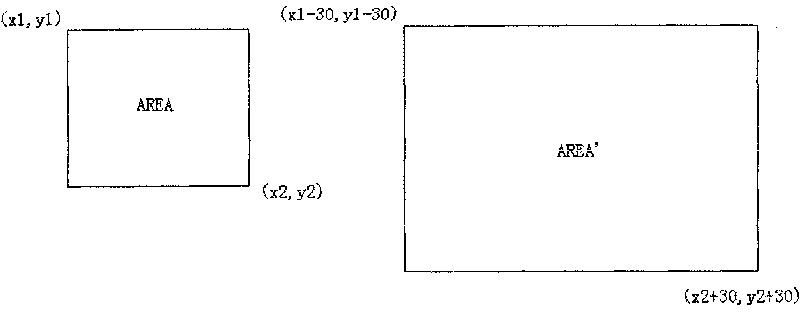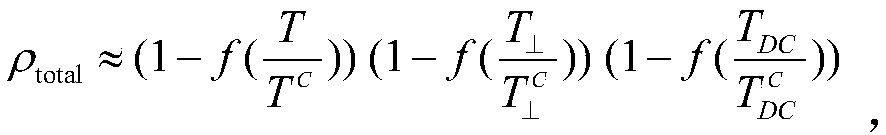Patents
Literature
185 results about "Image stack" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
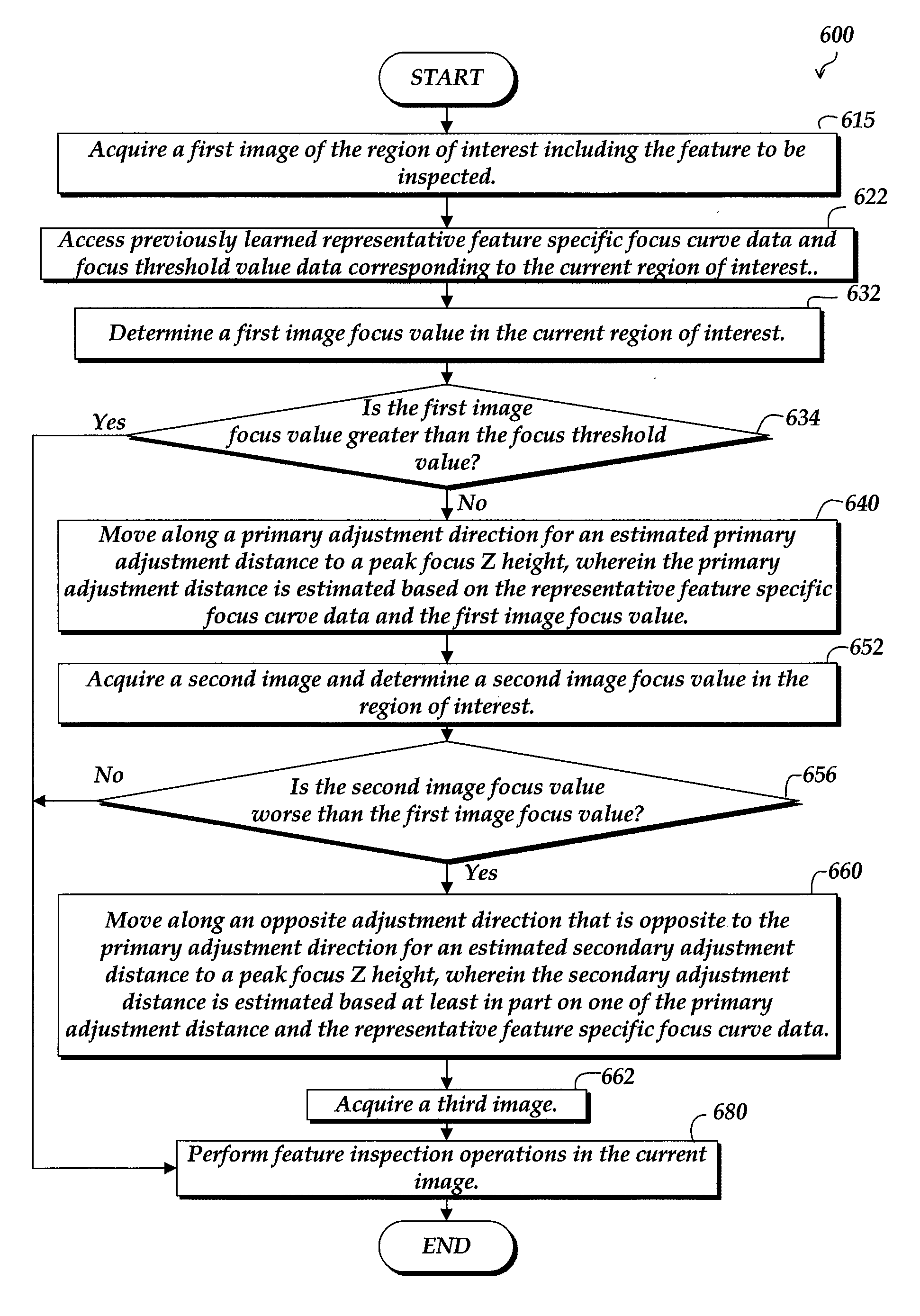
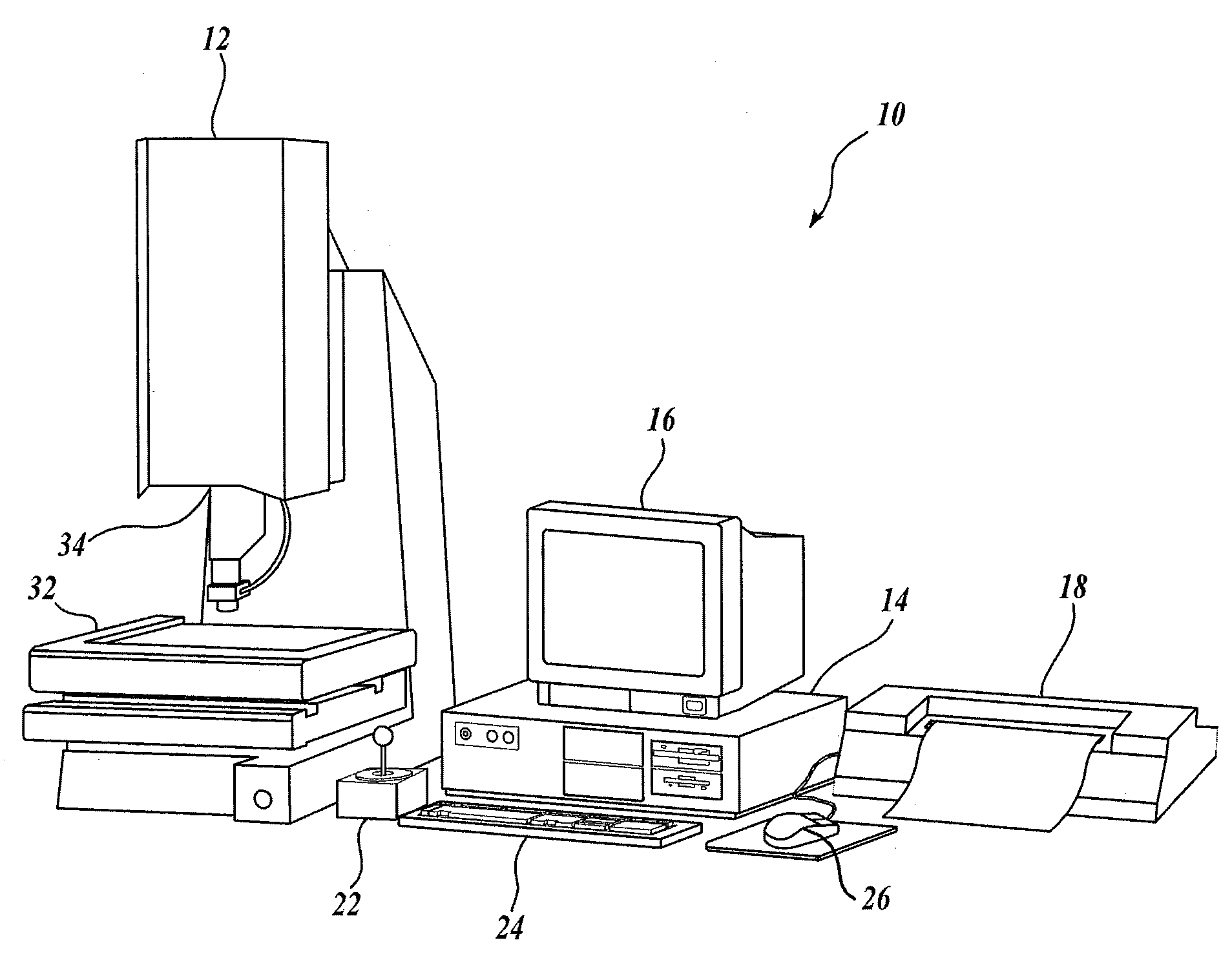
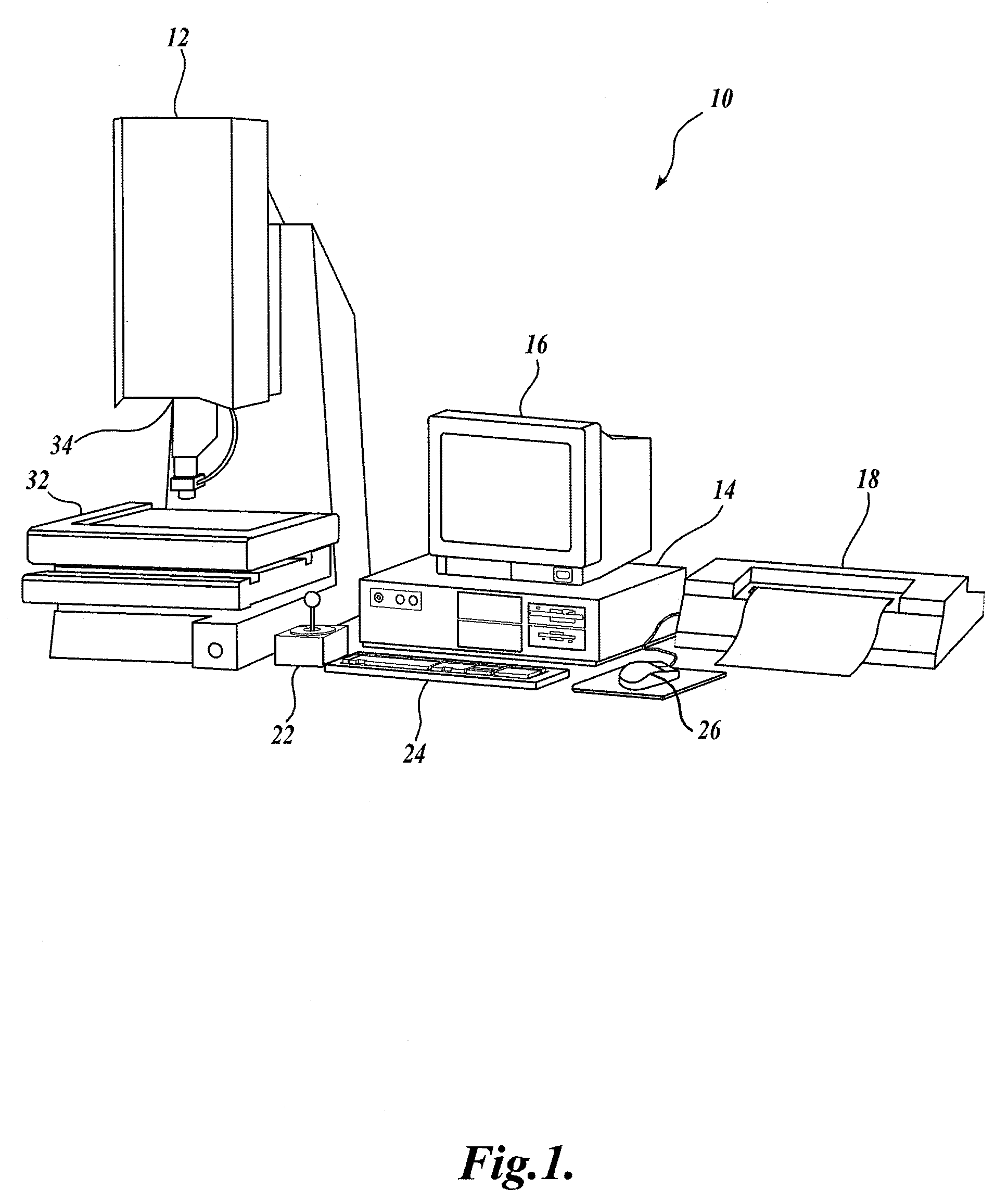
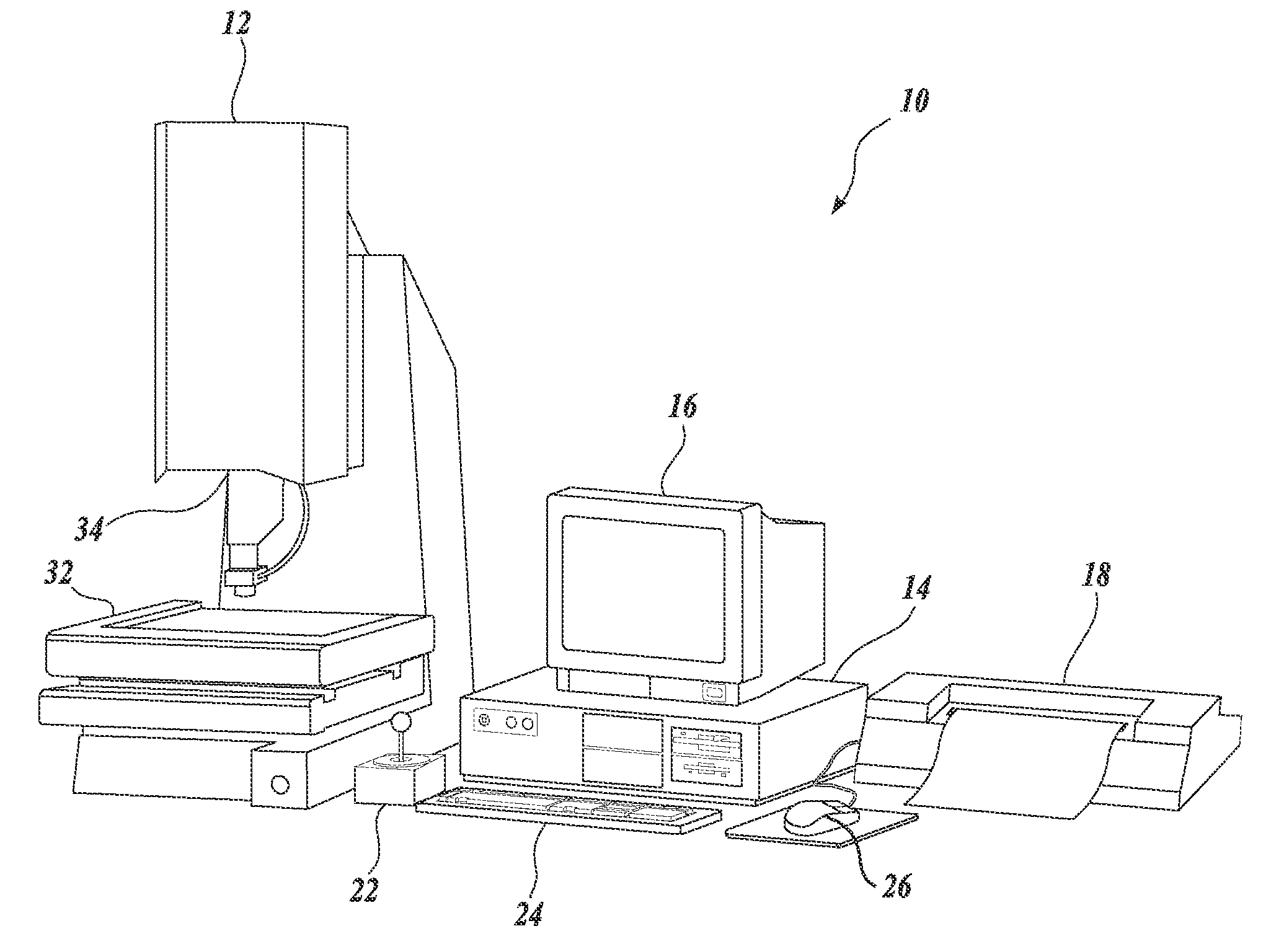
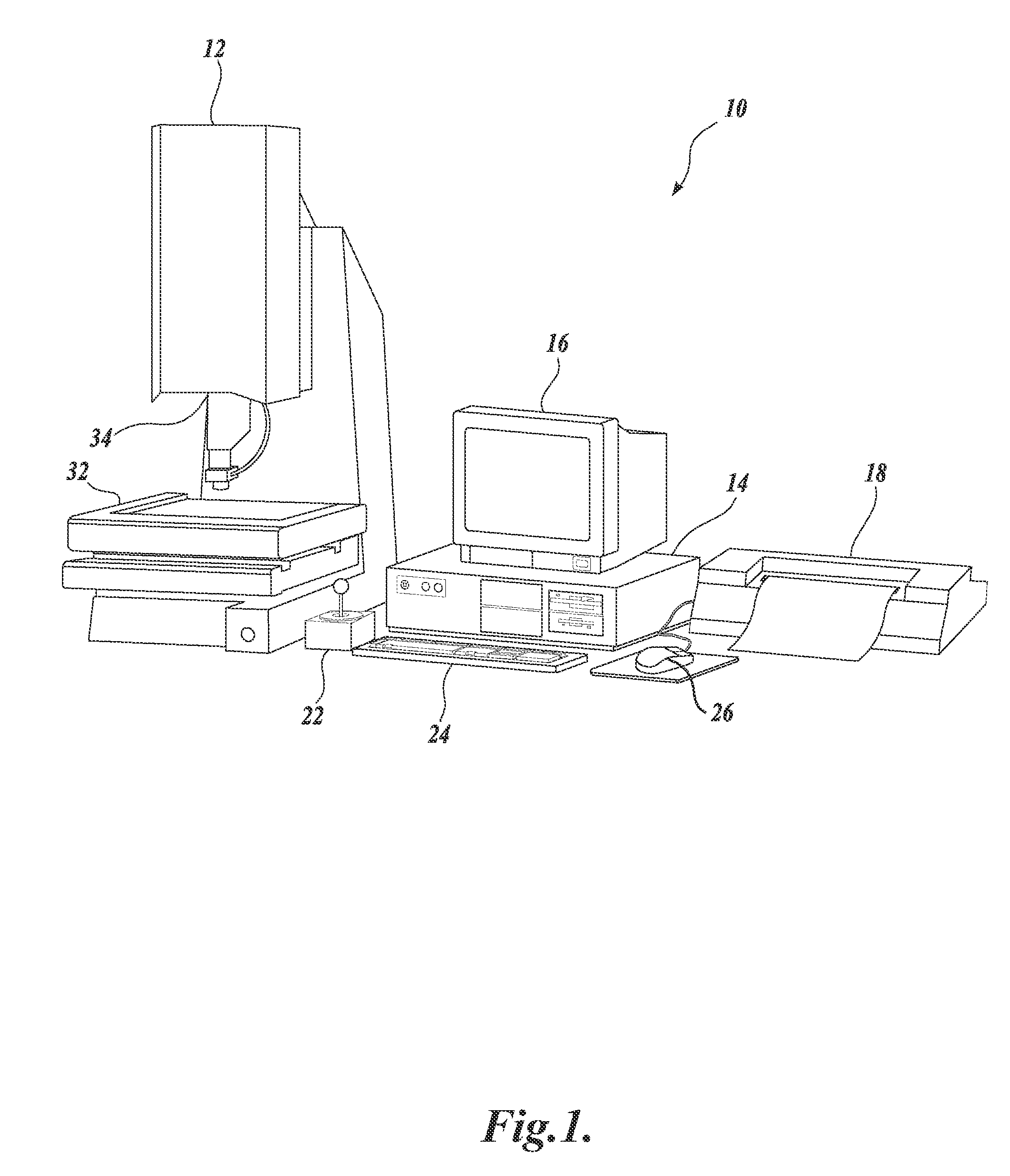
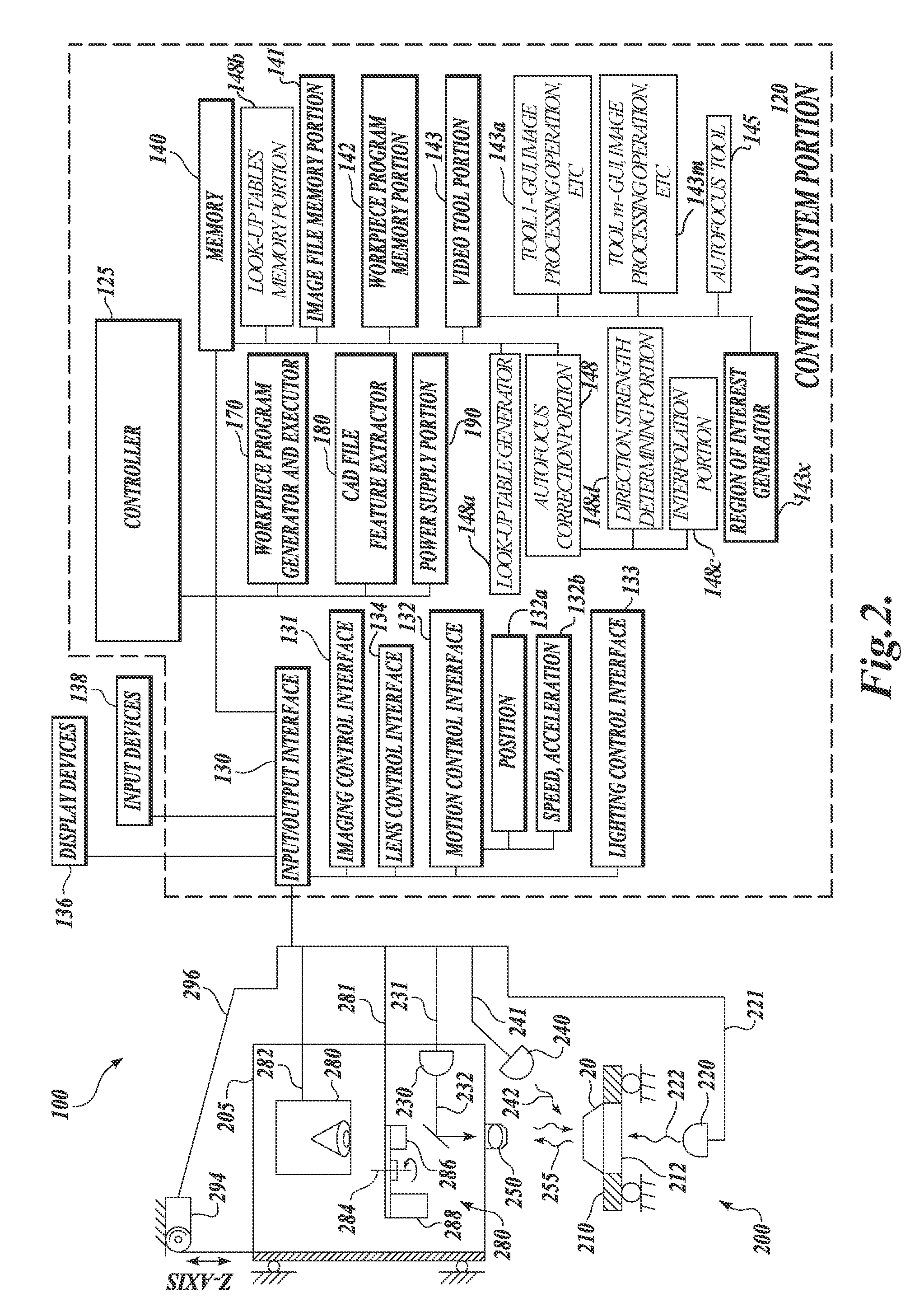
System and method for fast approximate focus
ActiveUS8111938B2Improve throughputQuick focusTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Engineering
Fast approximate focus operations providing an approximately focused image that is sufficiently focused to support certain subsequent inspection operations. The operations are particularly advantageous when used to provide images for successive inspection operations that predominate when inspecting planar workpieces. Improved inspection throughput is provided because, in contrast to conventional autofocus operations, the fast approximate focus operations do not acquire an image stack during a run mode as a basis for determining a best focused image. Rather, during learn mode, a representative feature-specific focus curve and a focus threshold value are determined and used during run mode to provide an approximately focused image that reliably supports certain inspection operations. In one embodiment, an acceptable approximately focused inspection image is provided within a limit of two focus adjustment moves that provide two corresponding images. The adjustment moves are based on the representative feature-specific focus curve provided in learn mode.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
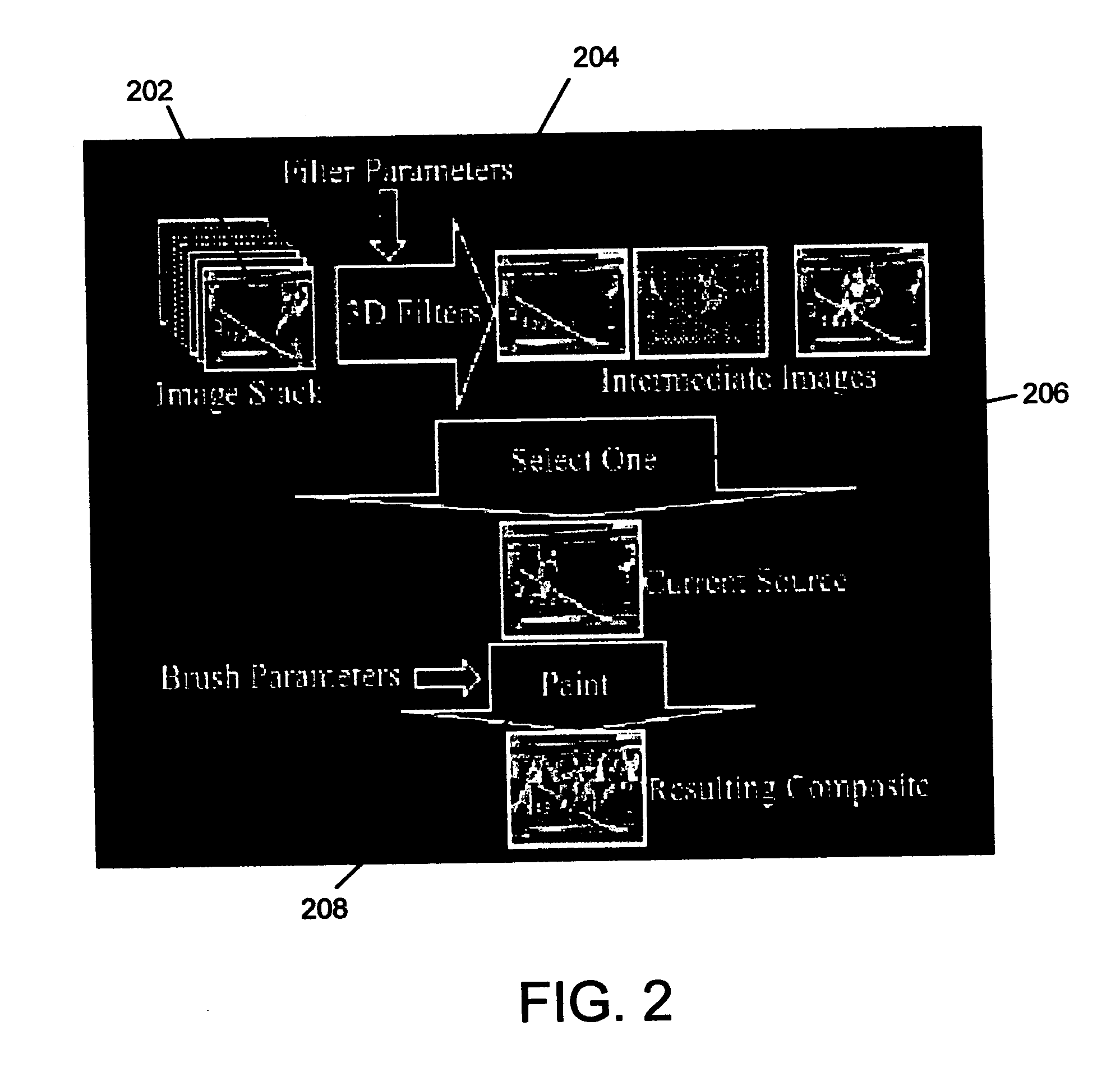
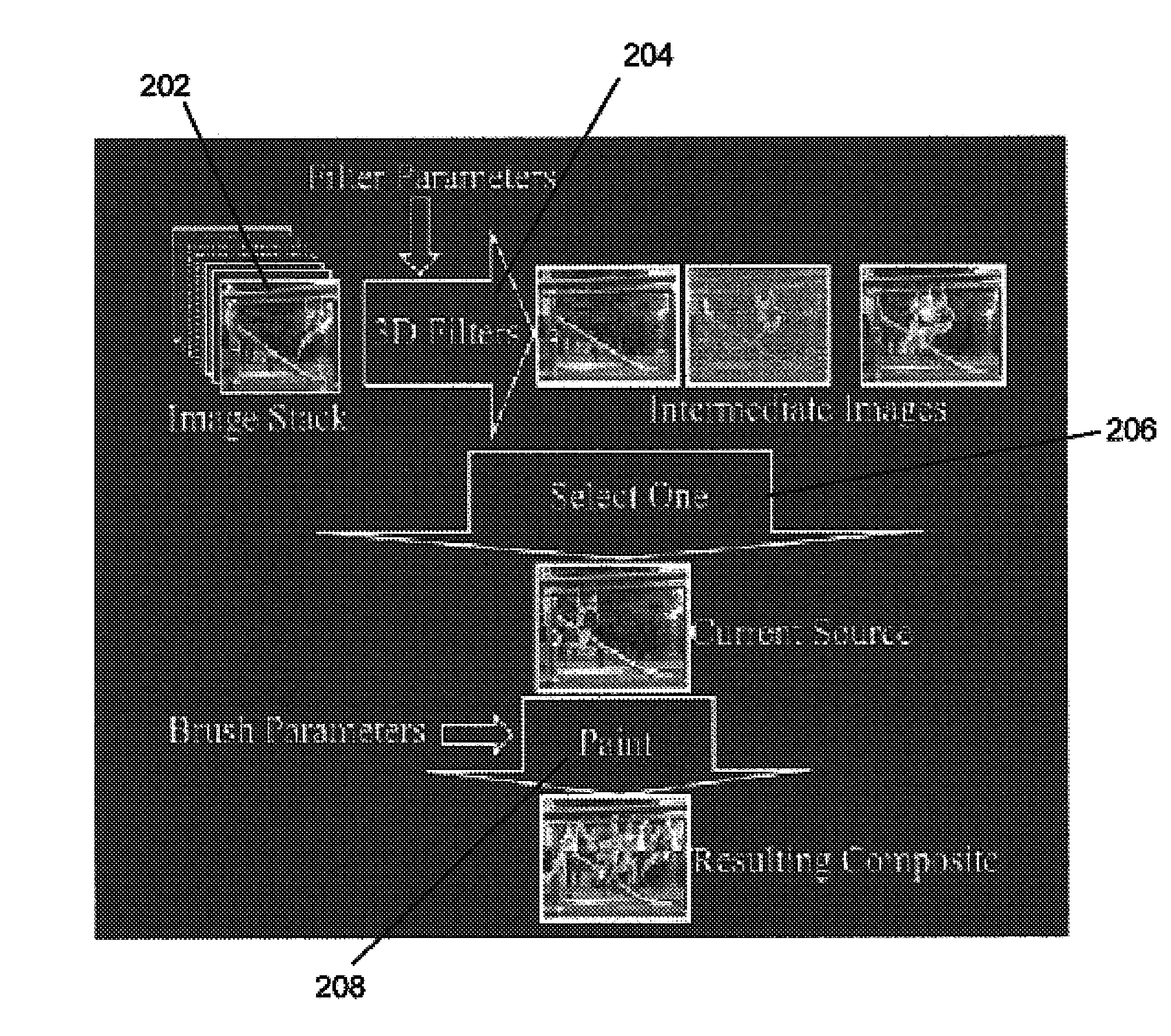
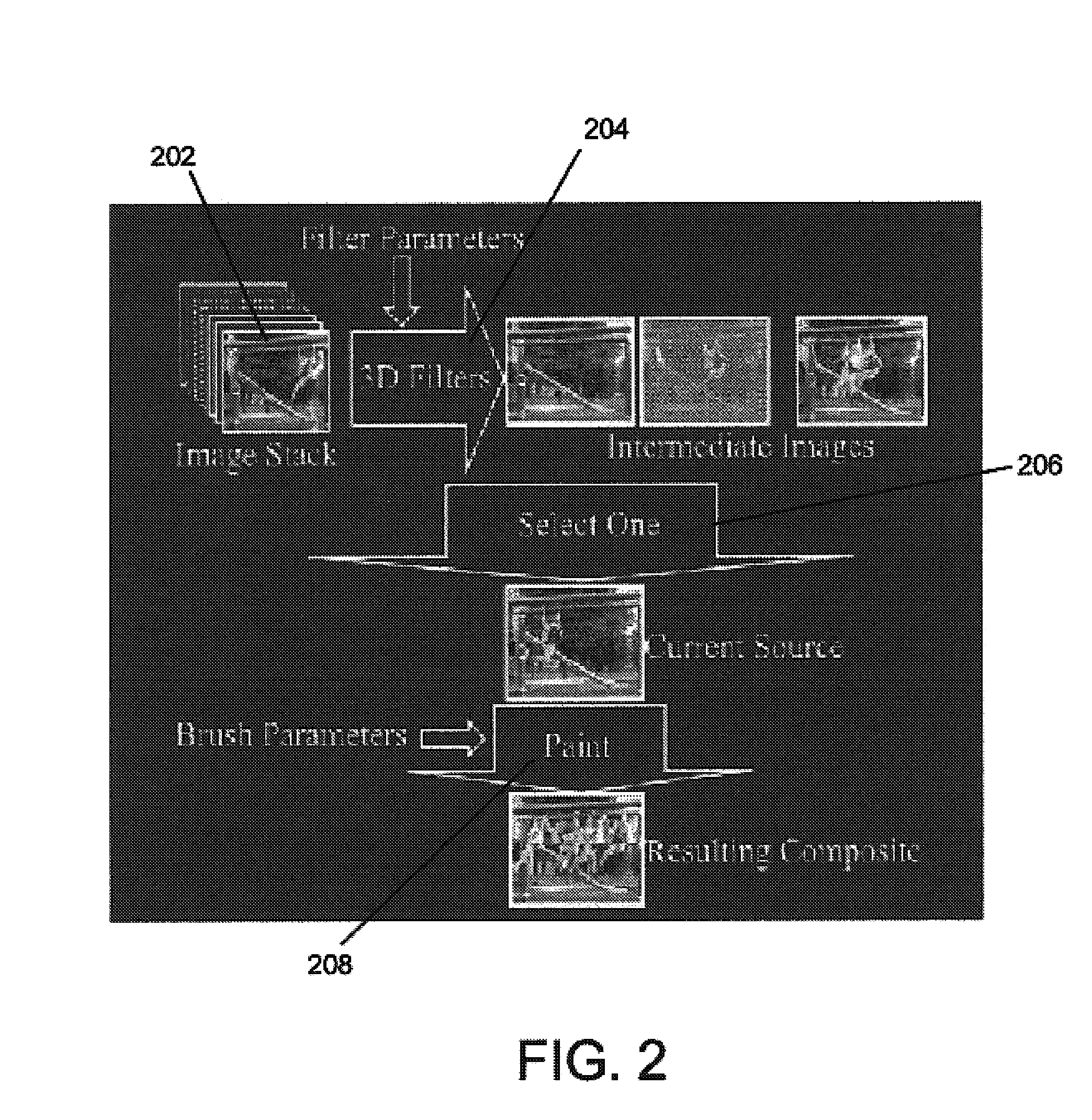
System and method for image editing using an image stack
InactiveUS20050030315A1Easy to combineEnhance the imageImage codingSound input/outputMulti-imageImage capture
A system and method for editing images. A simple but powerful image stack is employed in creating an enhanced image from a stack of registered images. This paradigm combines pixels using multi-image operations on the image stack. Image Stacks can help create group photographs, create high dynamic range images, combine images captured under different lighting conditions, remove unwanted objects from images, and combine images captured at different times and with different focal lengths.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
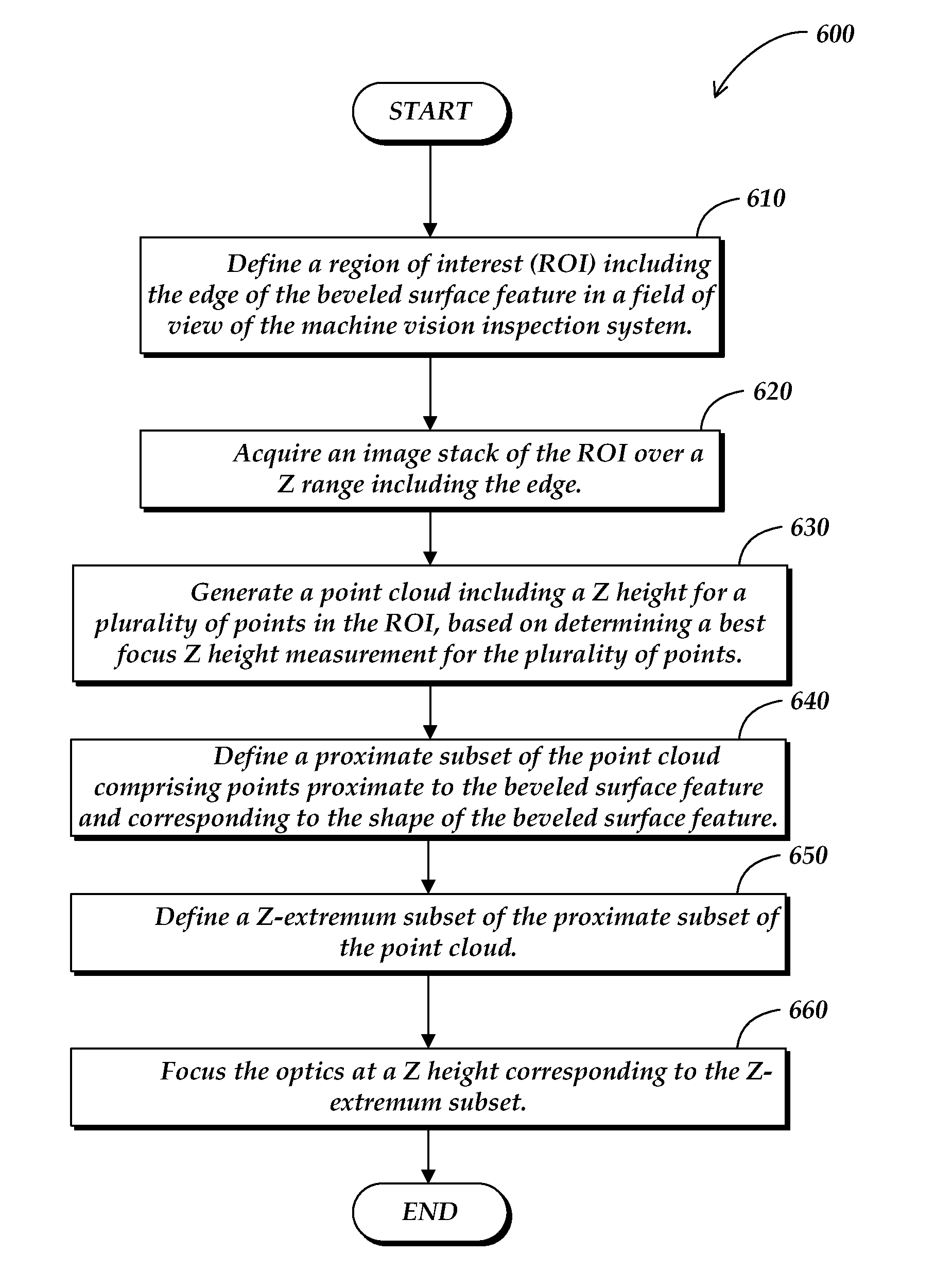
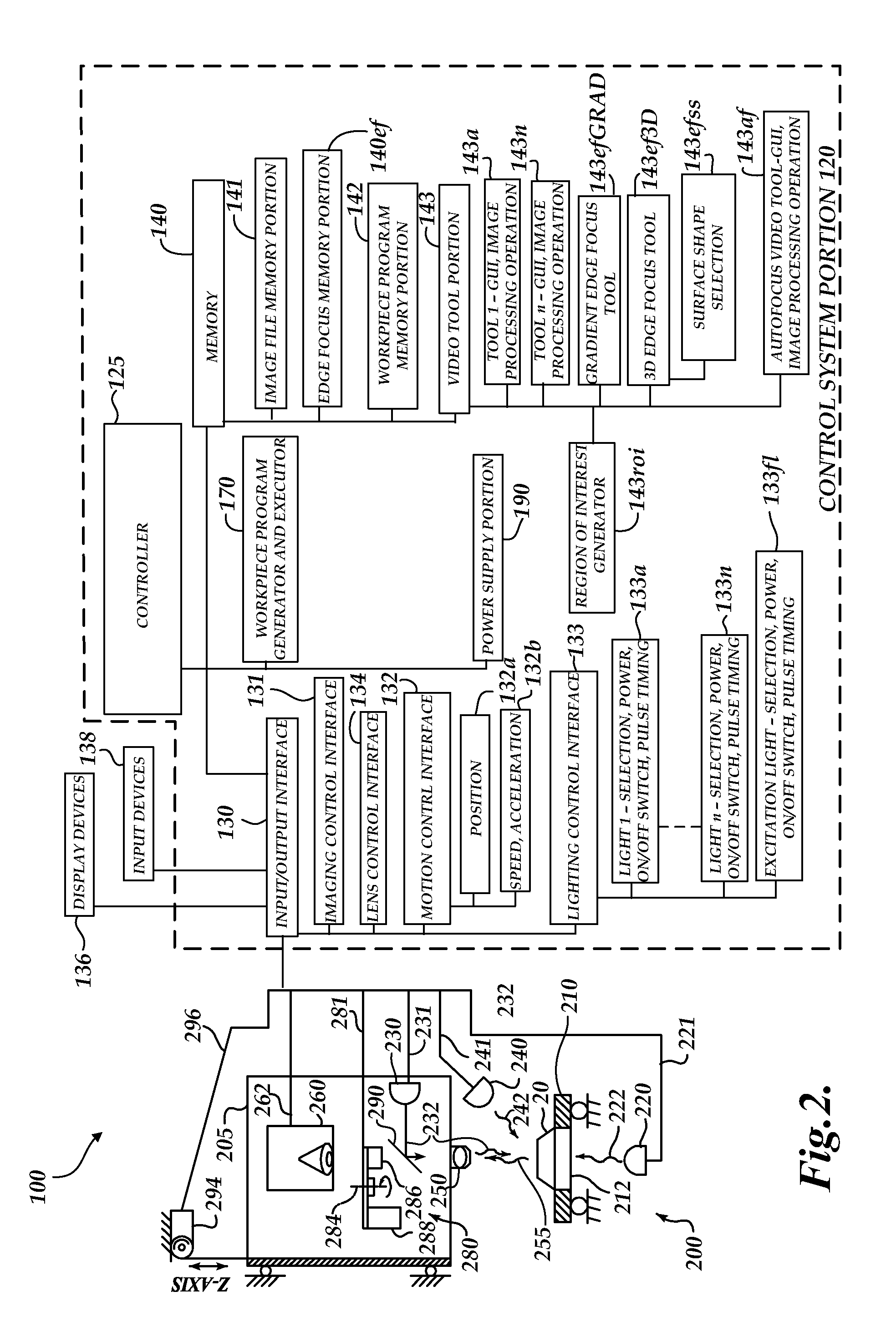
Enhanced edge focus tool
InactiveUS20130162806A1Well formedCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPoint cloudMachine vision
A method for operating an edge focus tool to focus the optics of a machine vision inspection system proximate to an edge adjacent to a beveled surface feature is provided. The method comprises defining a region of interest (ROI) including the edge in a field of view of the machine vision inspection system; acquiring an image stack of the ROI over a Z range including the edge; generating a point cloud including a Z height for a plurality of points in the ROI, based on determining a best focus Z height measurement for the plurality of points; defining a proximate subset of the point cloud comprising points proximate to the beveled surface feature and corresponding to the shape of the beveled surface feature; defining a Z-extremum subset of the proximate subset of the point cloud; and focusing the optics at a Z height corresponding to the Z-extremum subset.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
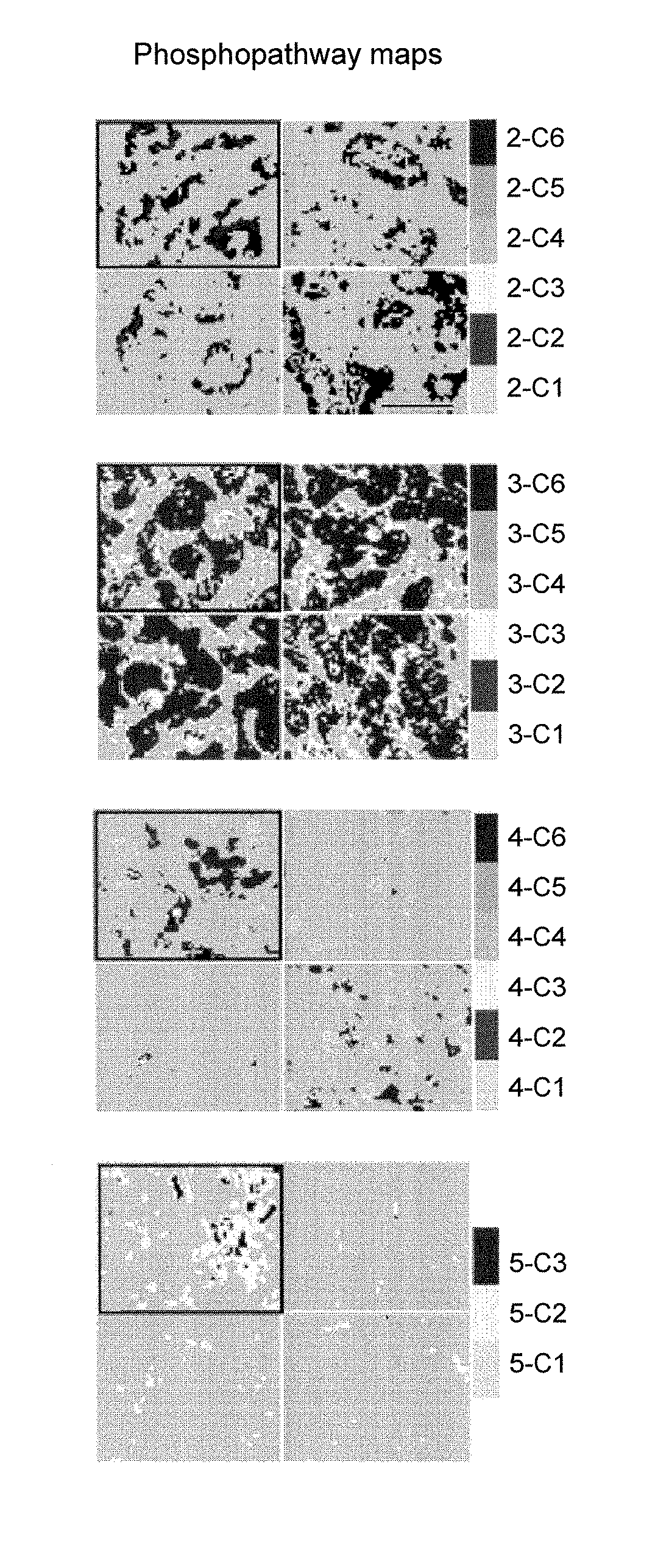
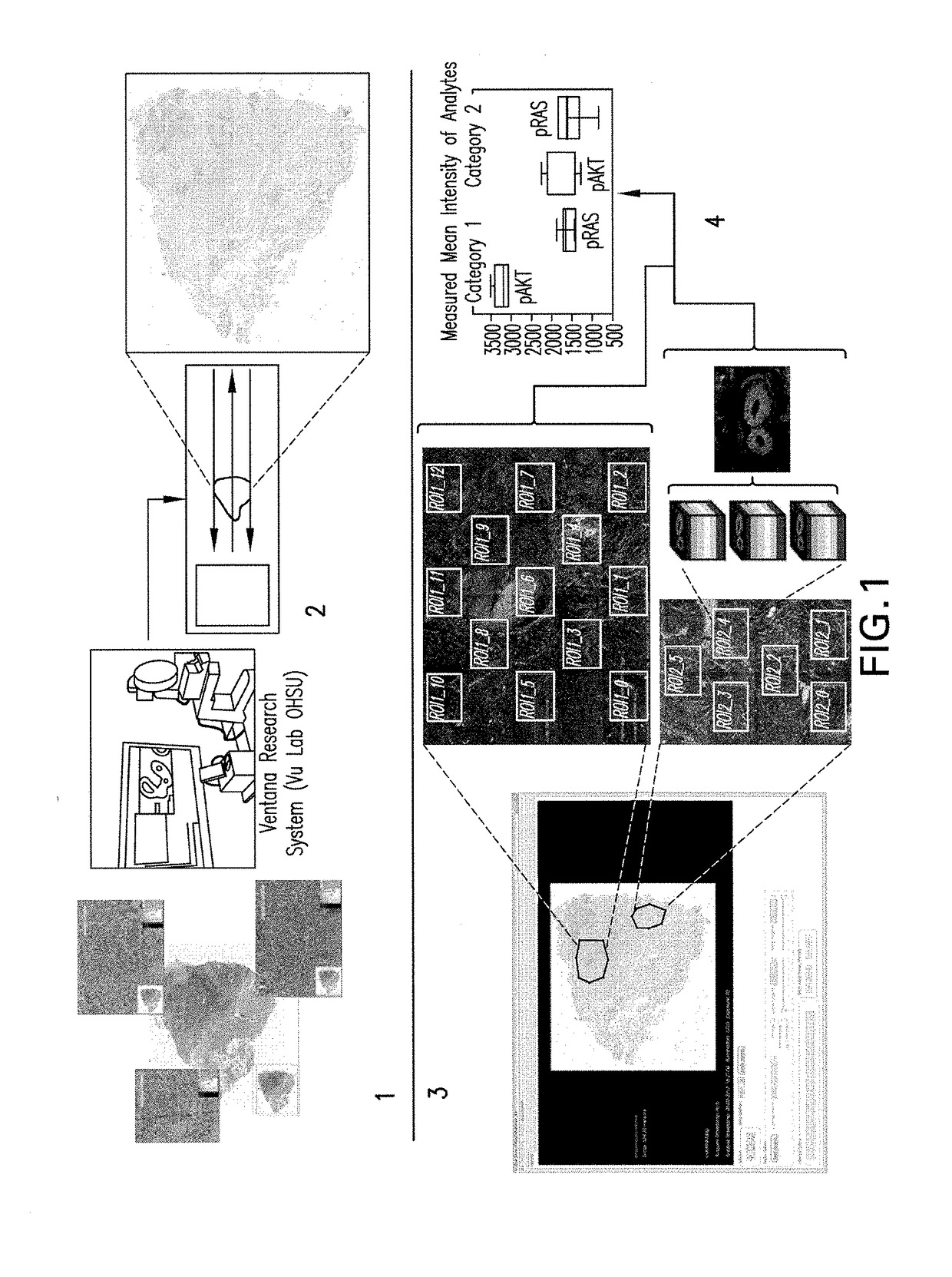
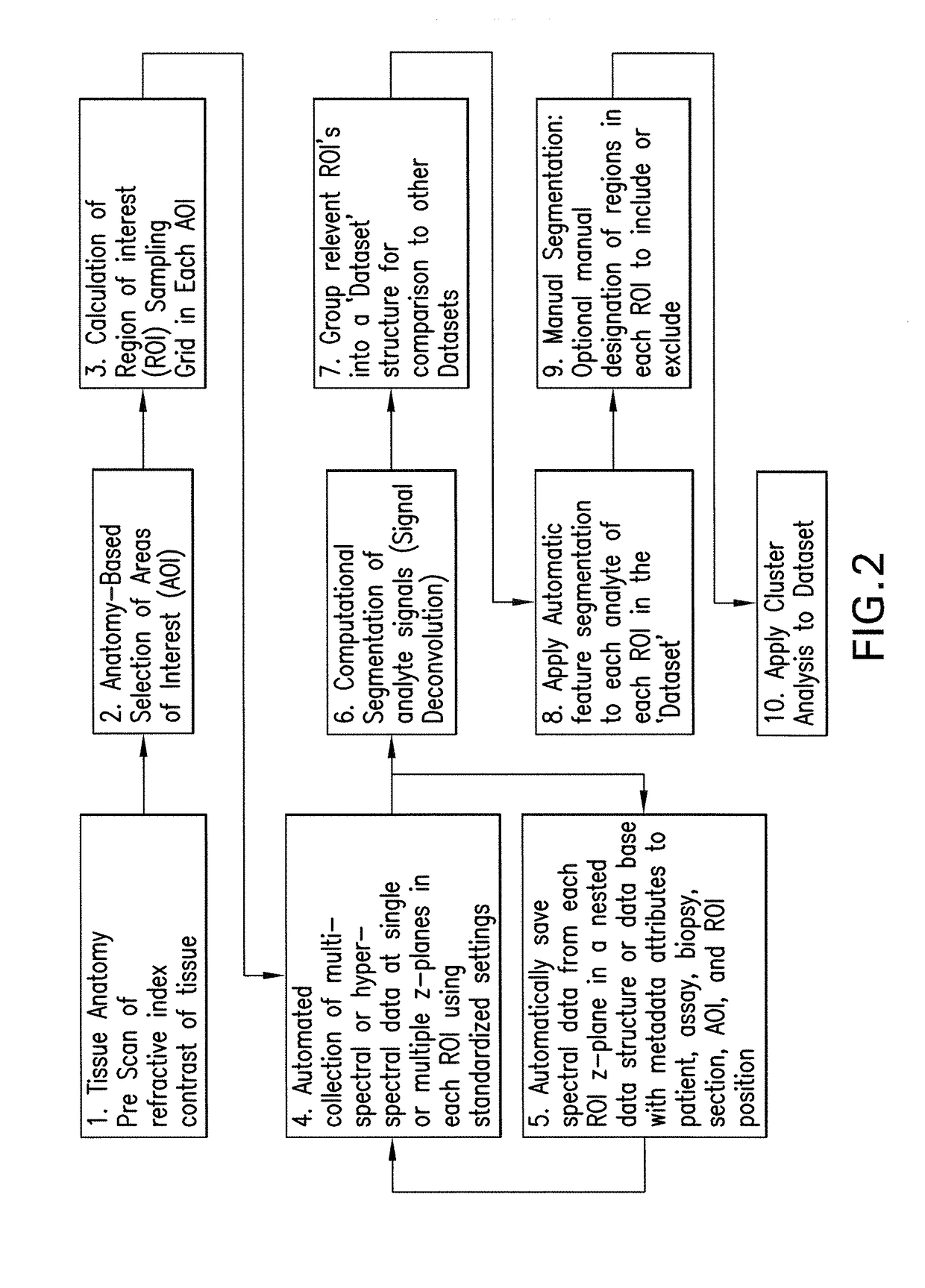
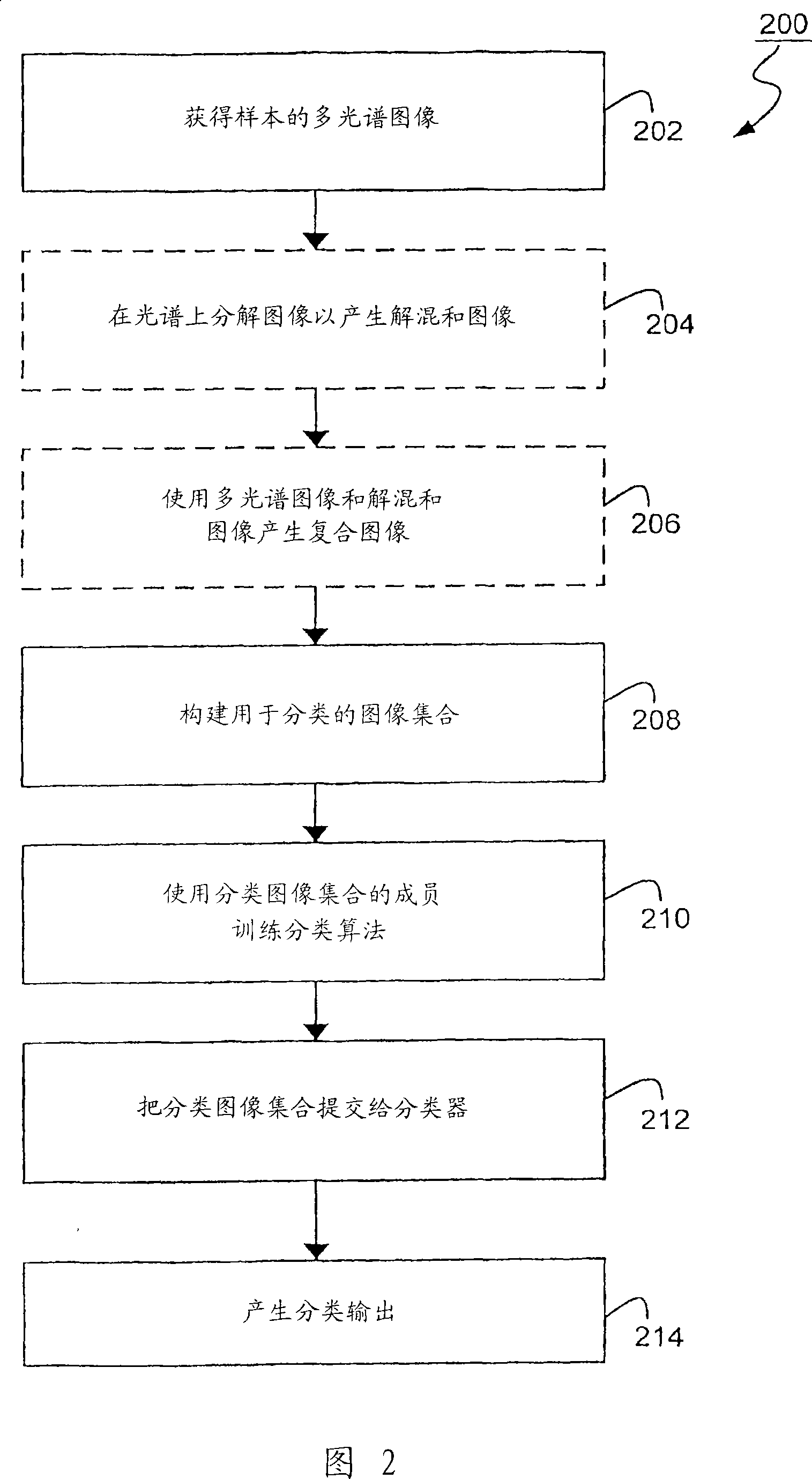
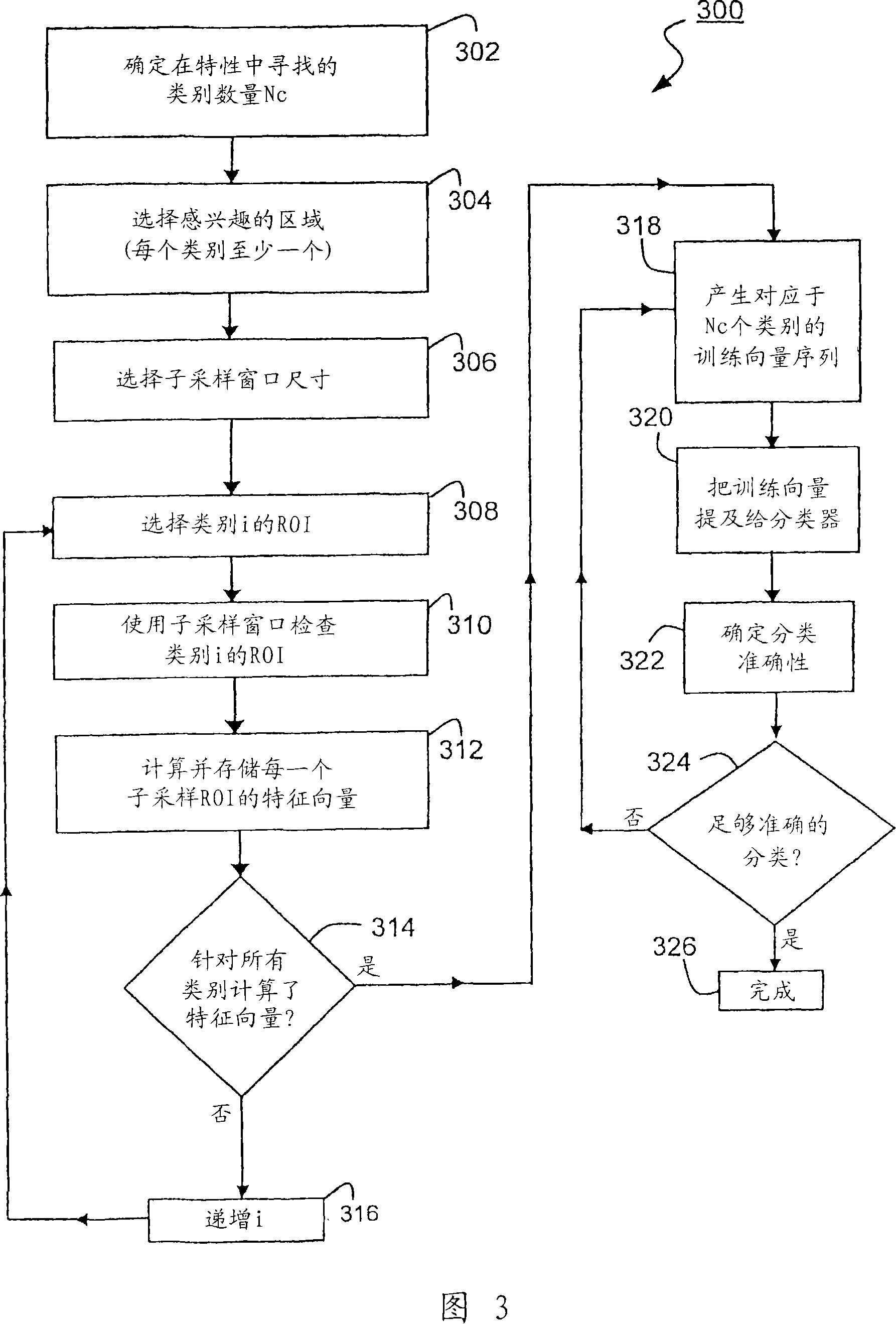
Methods, Systems, and Apparatuses for Quantitative Analysis of Heterogeneous Biomarker Distribution
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for detecting and describing heterogeneity in a cell sample are disclosed herein. A plurality of fields of view (FOV) are generated for one or more areas of interest (AOI) within an image of the cell sample are generated. Hyperspectral or multispectral data from each FOV is organized into an image stack containing one or more z-layers, with each z-layer containing intensity data for a single marker at each pixel in the FOV. A cluster analysis is applied to the image stacks, wherein the clustering algorithm groups pixels having a similar ratio of detectable marker intensity across layers of the z-axis, thereby generating a plurality of clusters having similar expression patterns.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV OF PORTLAND OREGON +1
System and method for fast approximate focus
ActiveUS20100158343A1Improve throughputQuick focusTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionAutofocusThroughput
Fast approximate focus operations providing an approximately focused image that is sufficiently focused to support certain subsequent inspection operations. The operations are particularly advantageous when used to provide images for successive inspection operations that predominate when inspecting planar workpieces. Improved inspection throughput is provided because, in contrast to conventional autofocus operations, the fast approximate focus operations do not acquire an image stack during a run mode as a basis for determining a best focused image. Rather, during learn mode, a representative feature-specific focus curve and a focus threshold value are determined and used during run mode to provide an approximately focused image that reliably supports certain inspection operations. In one embodiment, an acceptable approximately focused inspection image is provided within a limit of two focus adjustment moves that provide two corresponding images. The adjustment moves are based on the representative feature-specific focus curve provided in learn mode.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
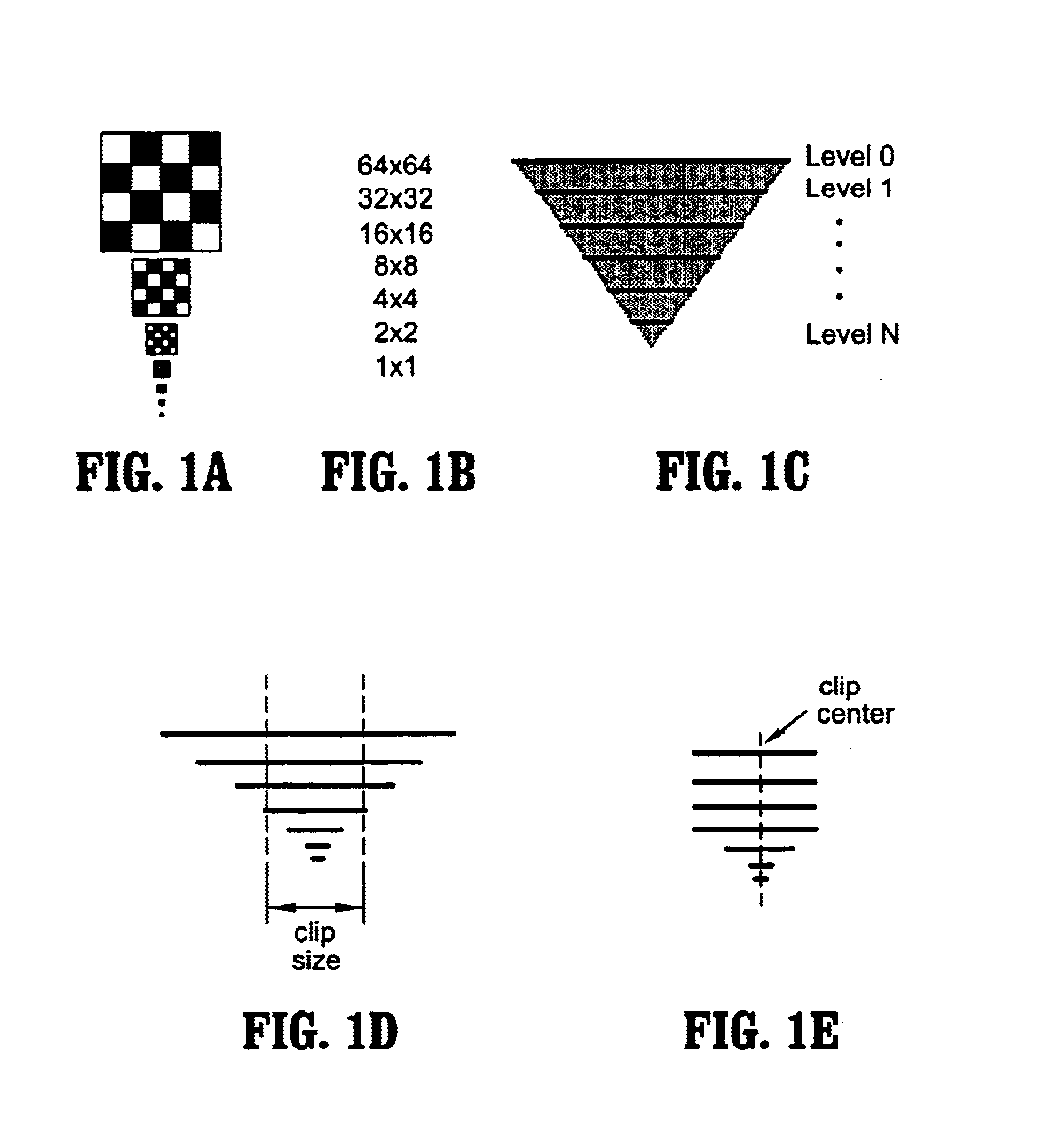
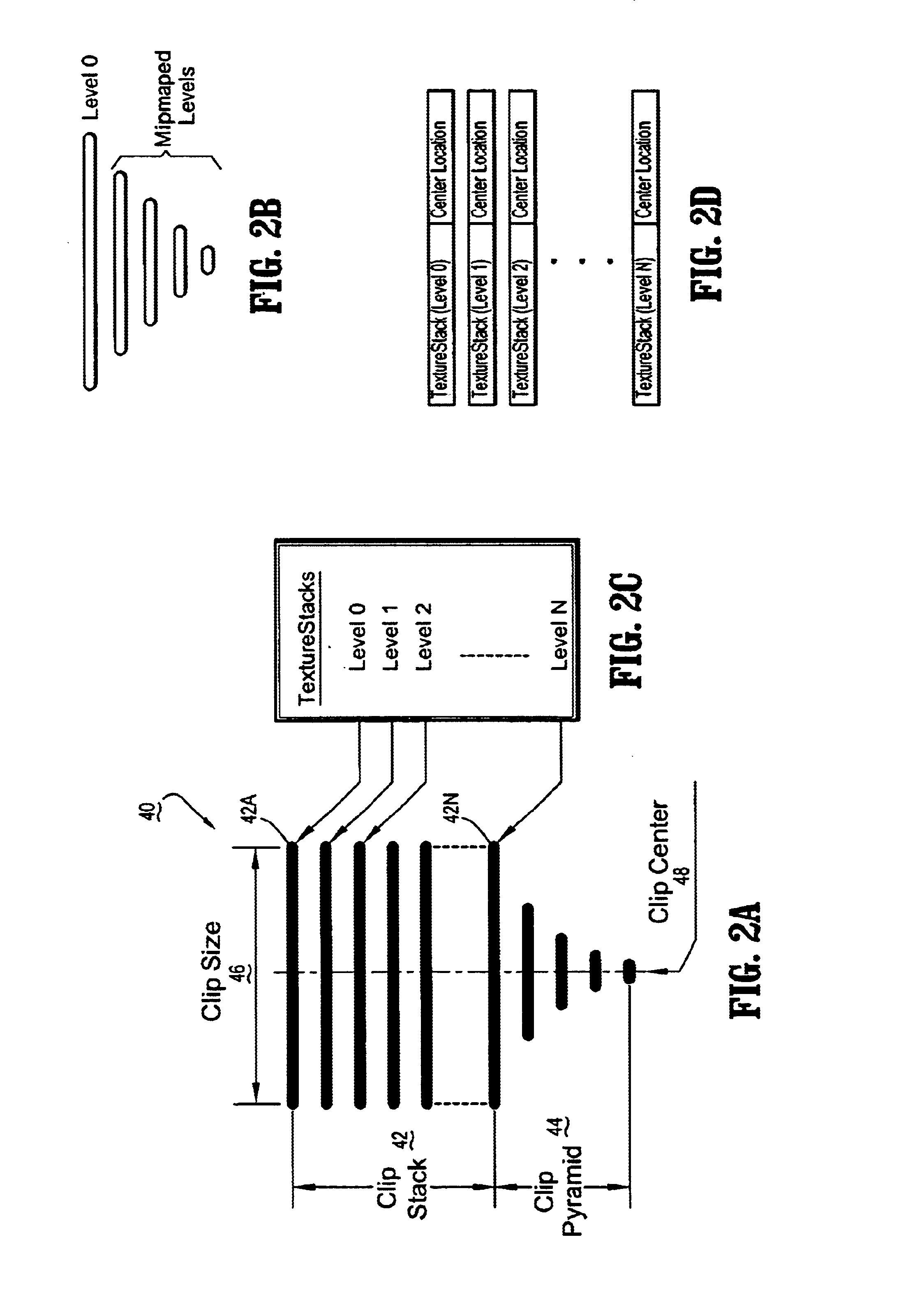
System and method for simulating clip texturing
Owner:COMP ASSOC THINK INC
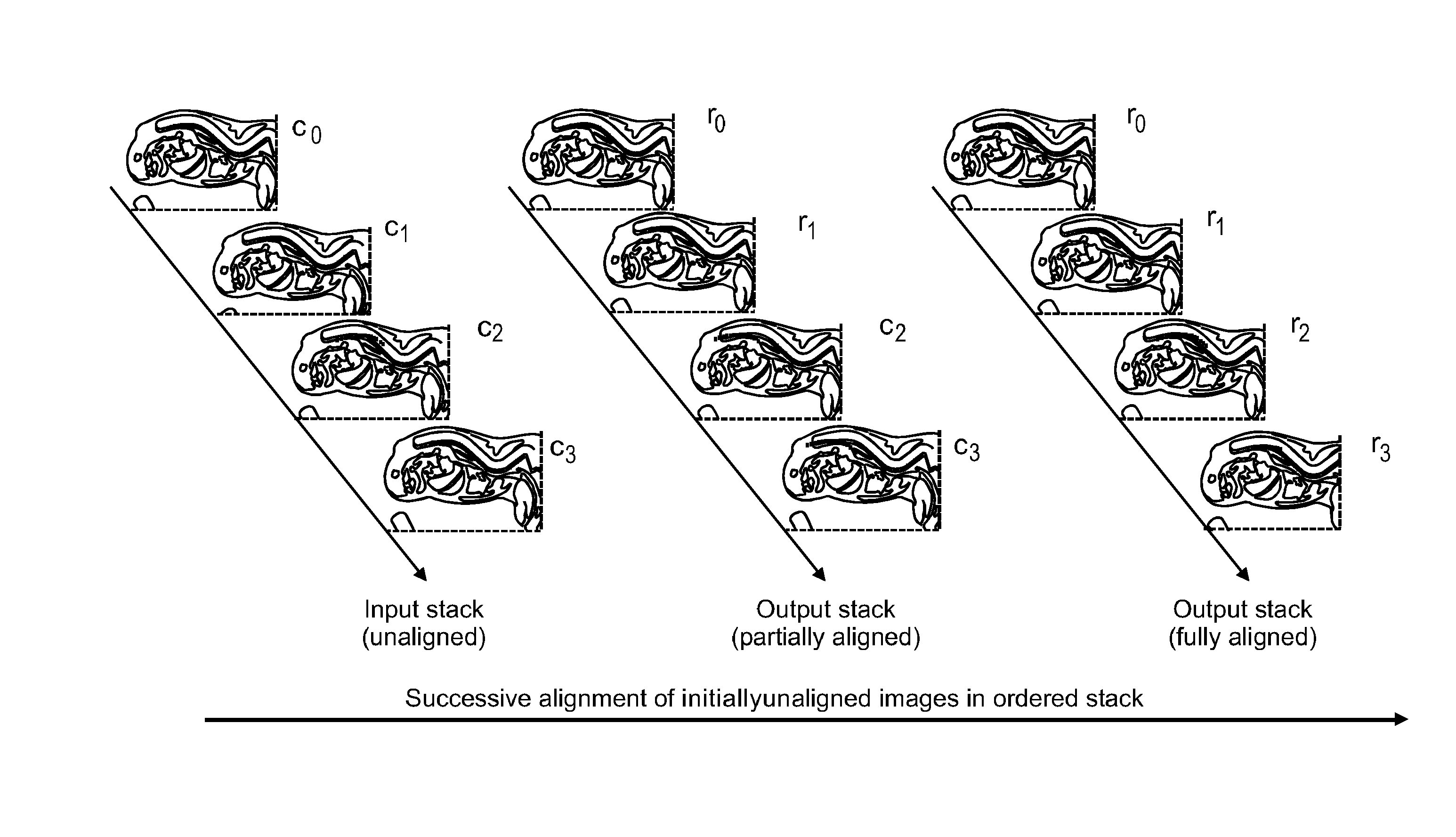
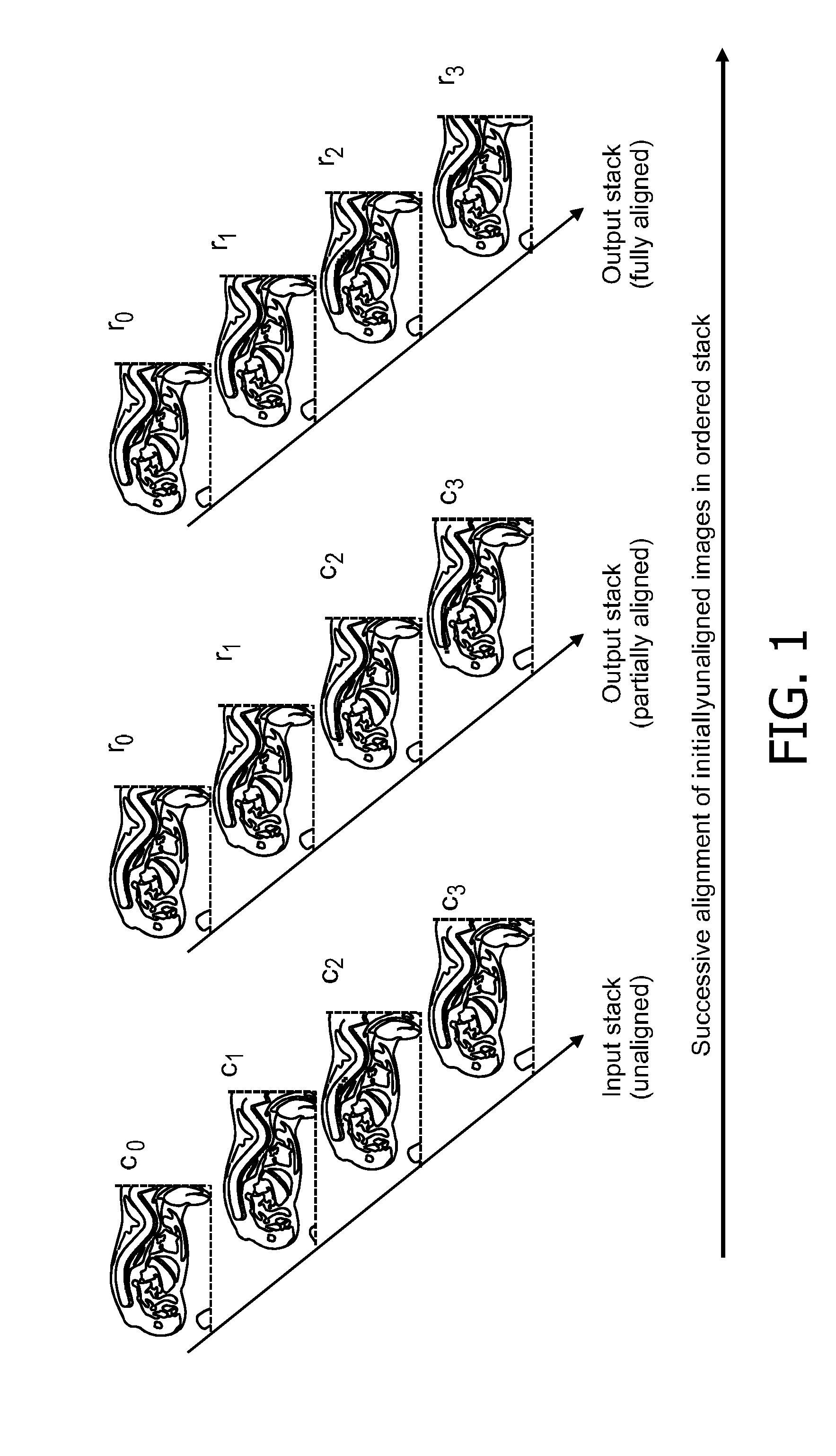
Alignment of an ordered stack of images from a specimen
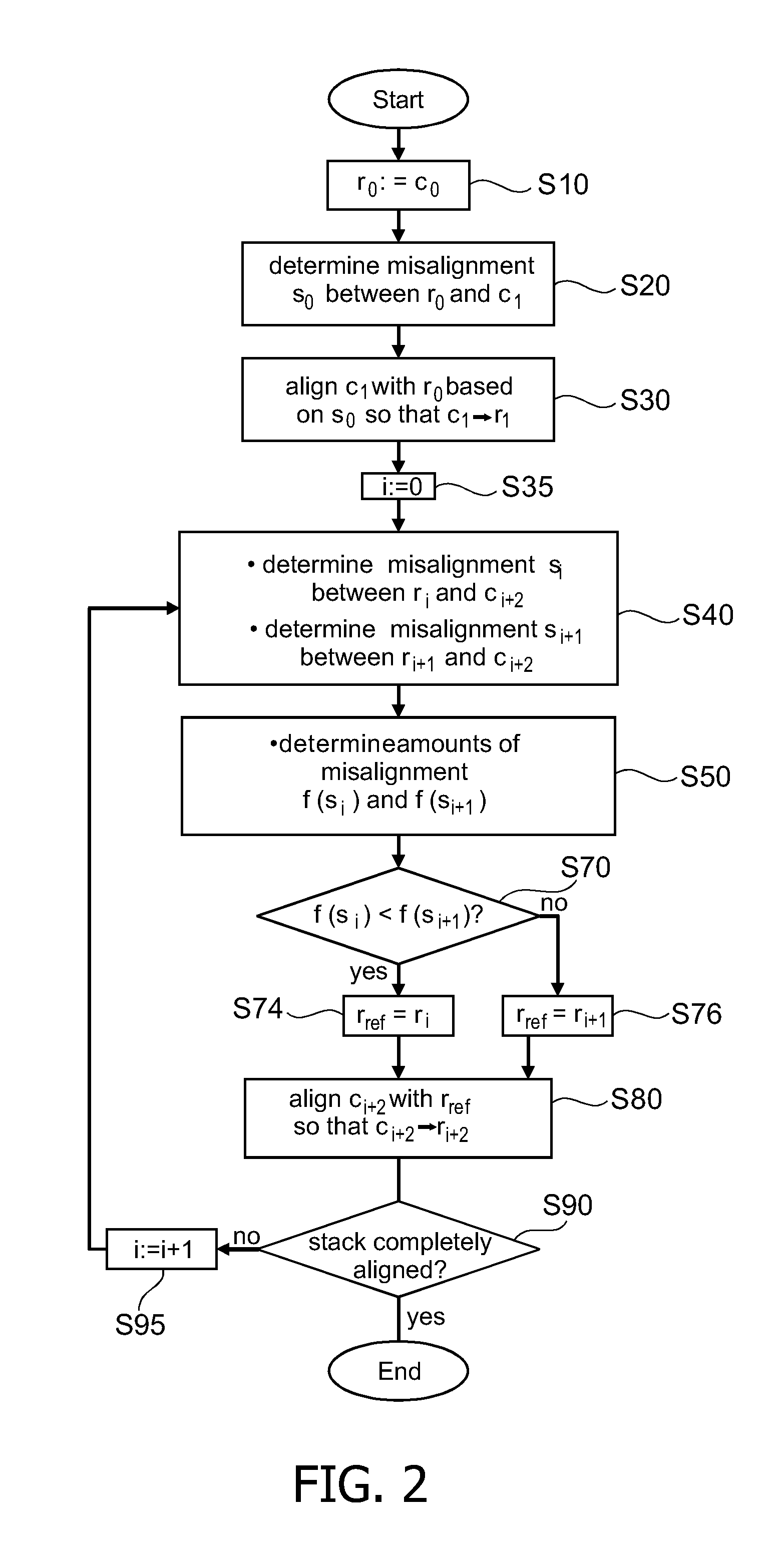
ActiveUS20120207367A1Lighten the computational burdenImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisPresent methodReference image
The present invention relates to the field of alignment of an ordered stack of images from a sliced specimen. According to the present method and apparatus, the ordered stack of images is aligned by successively determining, for at least two already aligned images of the ordered stack, the respective misalignments with an unaligned image which is to be aligned next, selecting from the at least two aligned images as a reference image that aligned image with which the unaligned image has the smallest amount of misalignment, and aligning the unaligned image with the selected reference image. This is intended to provide a robust and computationally cheap aligning method and apparatus.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Automated extended depth of field imaging apparatus and method
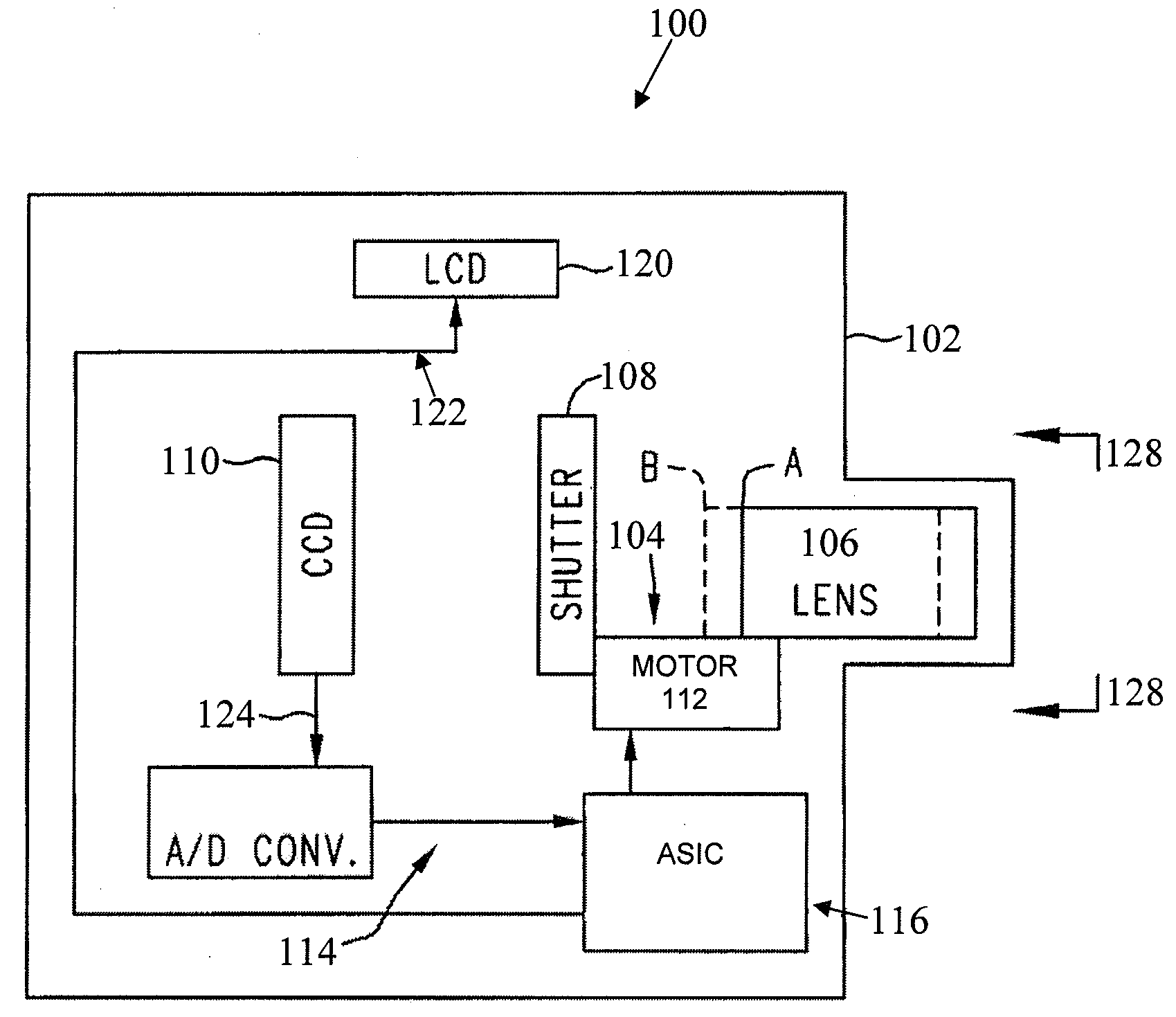
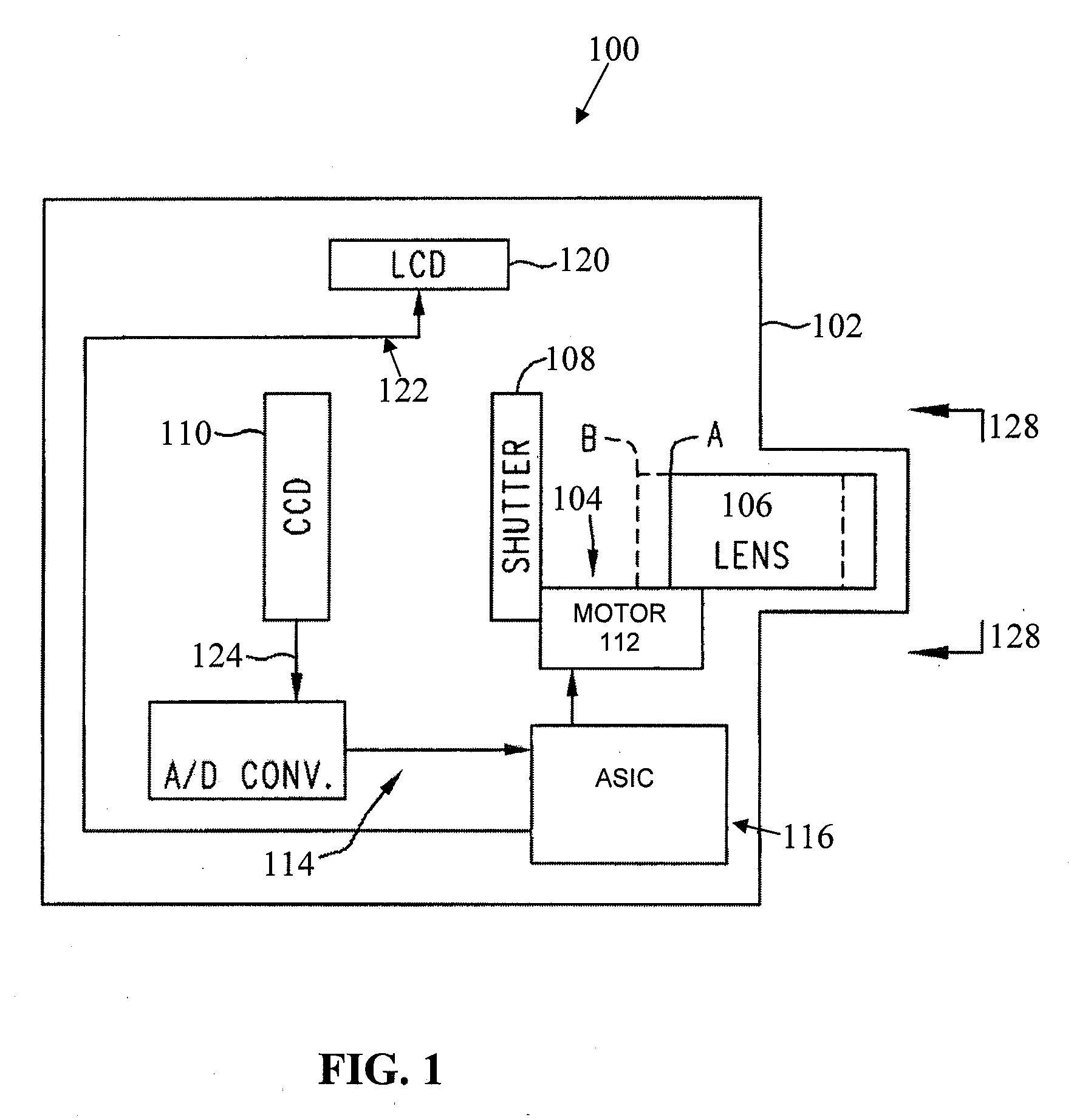
ActiveUS20090225199A1Automates and simplifies processEasy to produceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOn boardImage processing software
An imaging apparatus and method enables an automated extended depth of field capability that automates and simplifies the process of creating extended depth of field images. An embodiment automates the acquisition of an image “stack” or sequence and stores metadata at the time of image acquisition that facilitates production of a composite image having an extended depth of field from at least a portion of the images in the acquired sequence. An embodiment allows a user to specify, either at the time of image capture or at the time the composite image is created, a range of distances that the user wishes to have in focus within the composite image. An embodiment provides an on-board capability to produce a composite, extended depth of field image from the image stack. One embodiment allows the user to import the image stack into an image-processing software application that produces the composite image.
Owner:APPLIED MINDS
System and method for image editing using an image stack
InactiveUS7519907B2Easy to combineEnhance the imageImage codingSound input/outputMulti-imageImage capture
A system and method for editing images. A simple but powerful image stack is employed in creating an enhanced image from a stack of registered images. This paradigm combines pixels using multi-image operations on the image stack. Image Stacks can help create group photographs, create high dynamic range images, combine images captured under different lighting conditions, remove unwanted objects from images, and combine images captured at different times and with different focal lengths.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
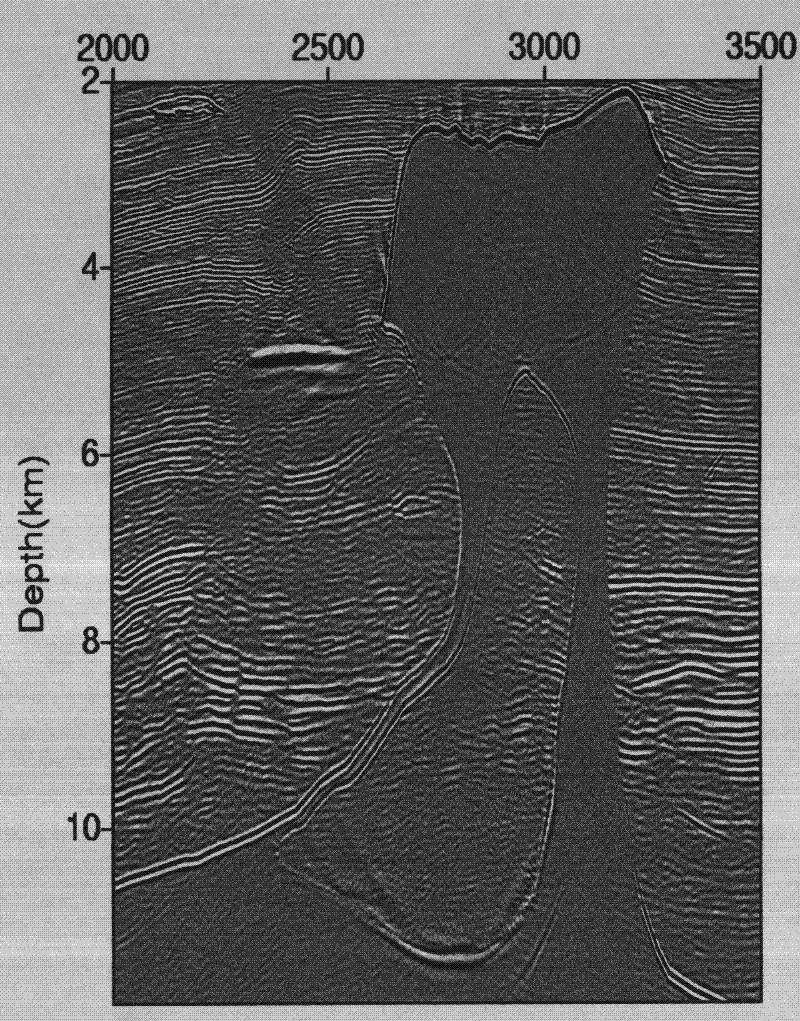
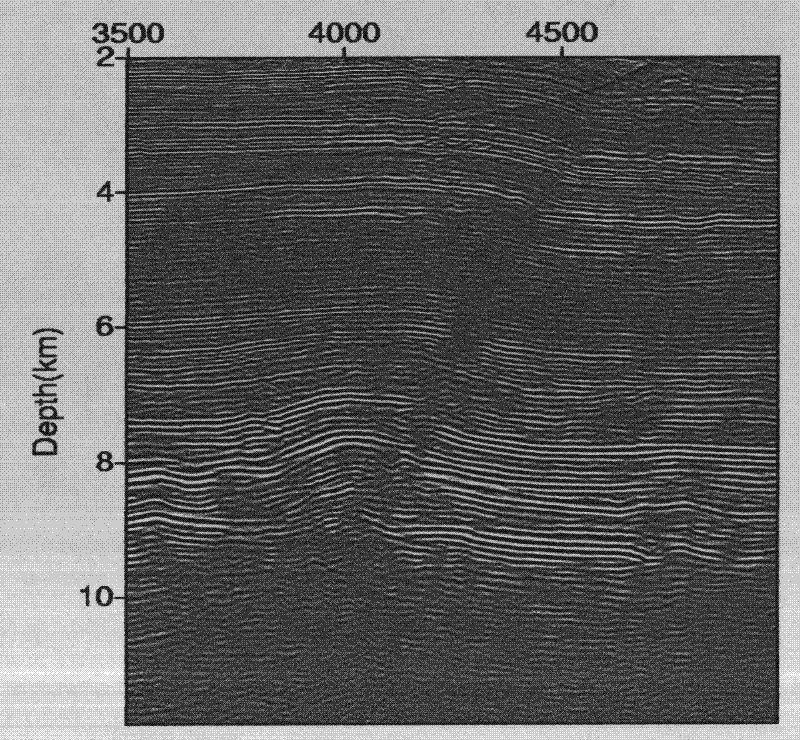
A Staggered Grid 3D Seismic Prestack Reverse Time Migration Imaging Method Based on Small GPU Storage
ActiveCN102269820ASuppress low frequency noiseDispersion suppressionSeismic signal processingWave equationReflected waves
A staggered grid 3D seismic prestack reverse time migration imaging method based on GPU small storage capacity is a very important technology for 3D prestack depth migration imaging of complex structures. The reverse time migration method based on the two-way wave equation has been realized, which can accurately image the rotary wave and the large-angle reflected wave, and at the same time solve the problem of the large amount of calculation of this method. Utilizing parallel computing technology based on GPU hardware, staggered grid difference format, checkpoint storage and other technologies, and relying on Laplace imaging conditions, the pre-stack reverse time migration imaging of 3D seismic data is realized, which greatly shortens the computing time. The efficiency has been increased hundreds of times, and the imaging accuracy has been significantly improved.
Owner:SINO GEOPHYSICAL CO LTD
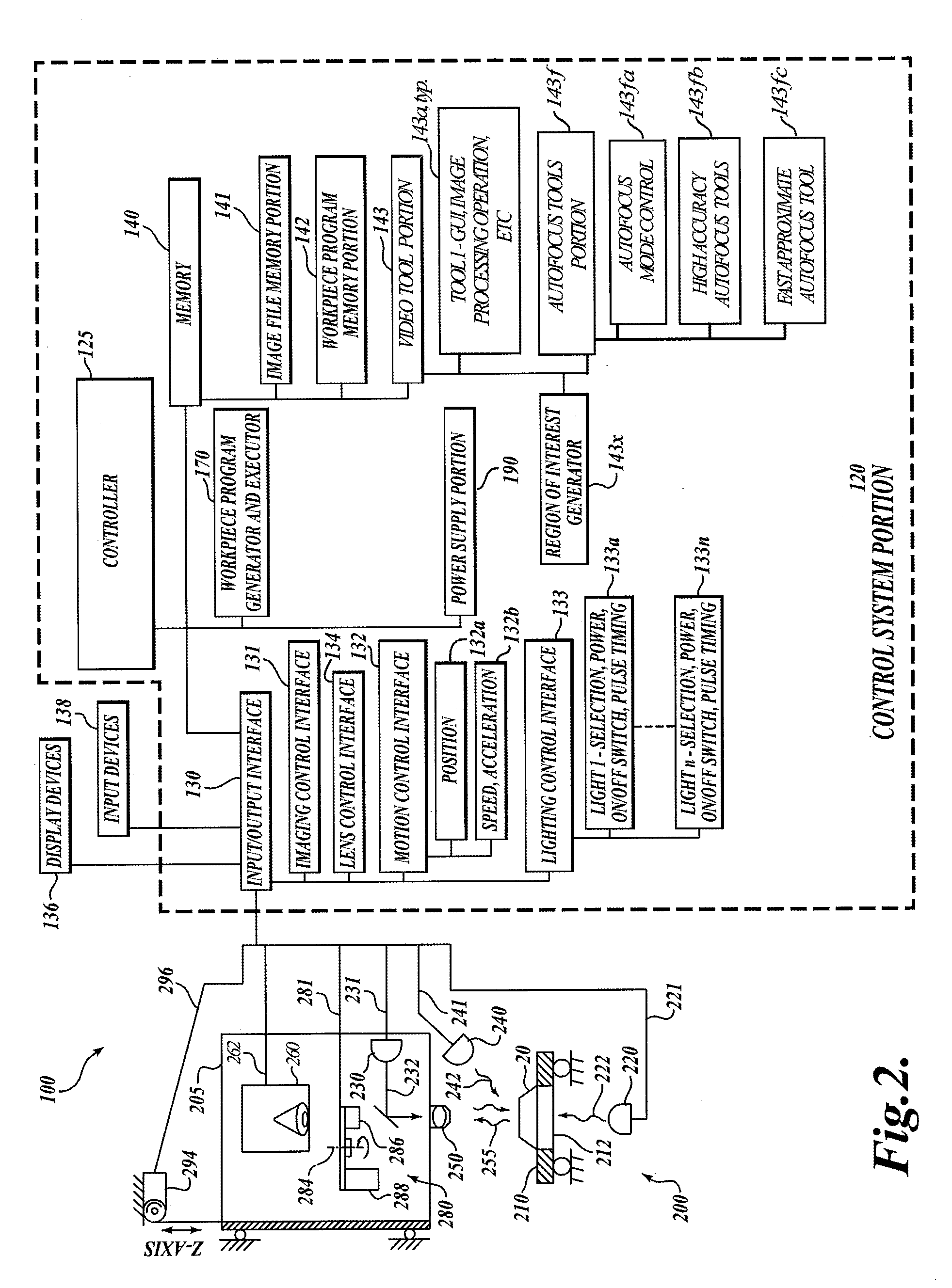
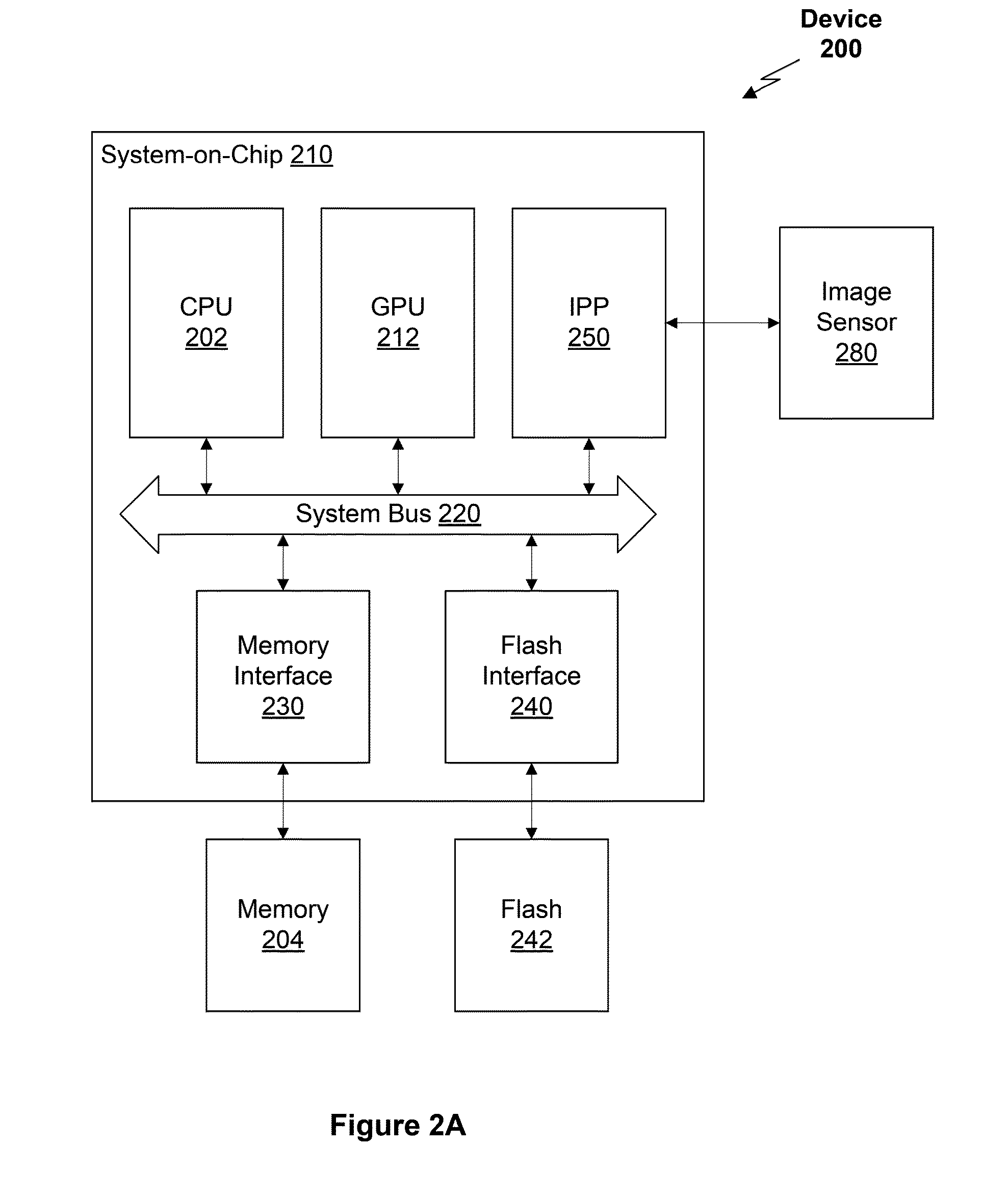
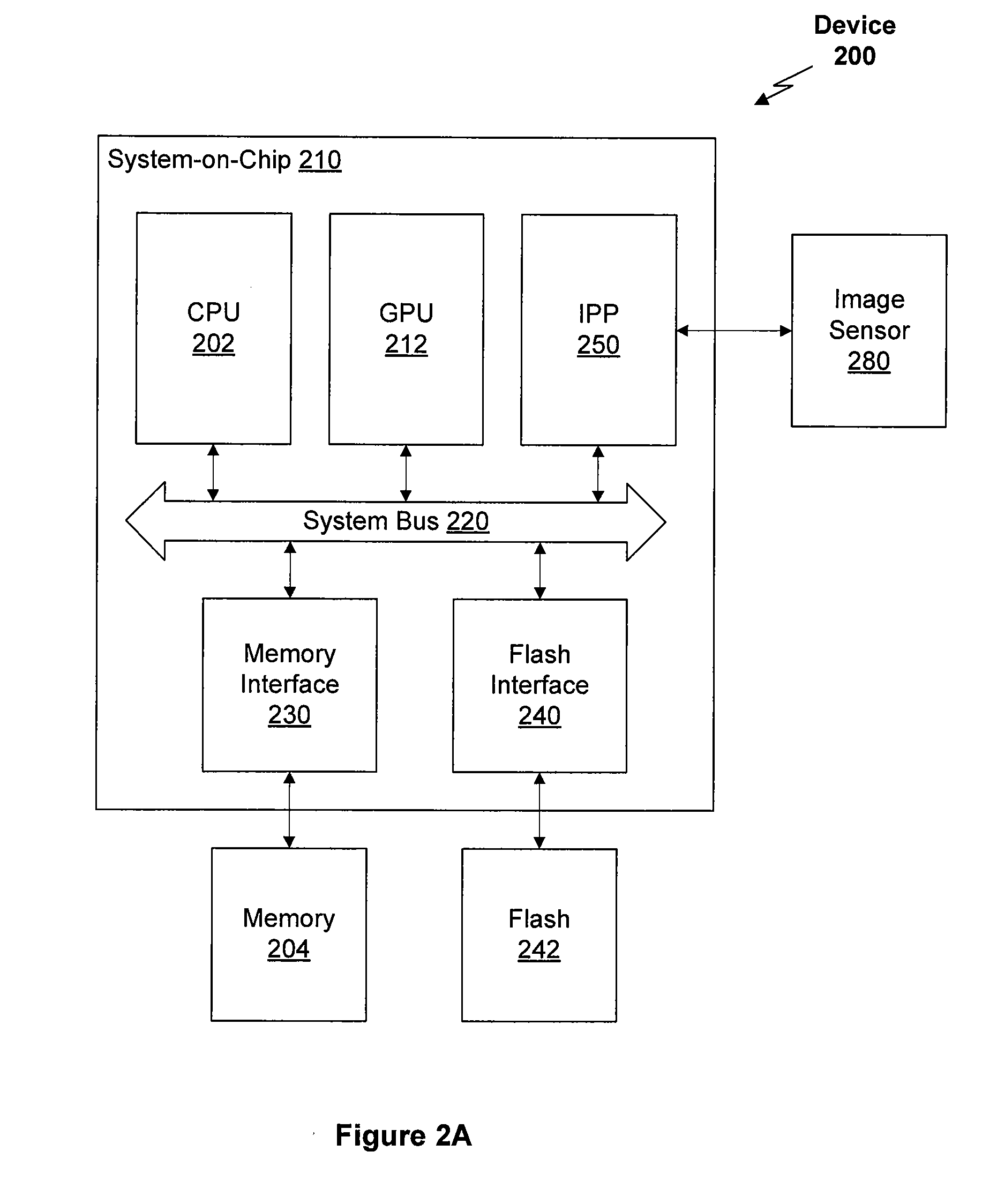
Optical aberration correction for machine vision inspection systems
ActiveUS20090088999A1Reduce memoryReduce storage requirementsCharacter and pattern recognitionUsing optical meansMachine visionAutofocus
A system and method for correcting surface height measurements for optical aberration is provided. Heights determined by an autofocus tool, which may depend on surface feature angles in a focus region of interest (ROI) and on the ROI location in the field of view, are corrected based on a novel error calibration. Error calibration data includes height corrections for different feature angles in images, and for multiple locations in a field of view. Height corrections are determined by weighting and combining the angle dependent error calibration data, e.g., based on a gradient (edge) angle distribution determined in the ROIs. When Z-heights are determined for multiple ROIs in a field of view, storage of image data from particular images of a global image stack may be efficiently controlled based on determining early in processing whether a particular image is a sufficiently focused “near-peak” focused image or not.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Image processing method and equipment
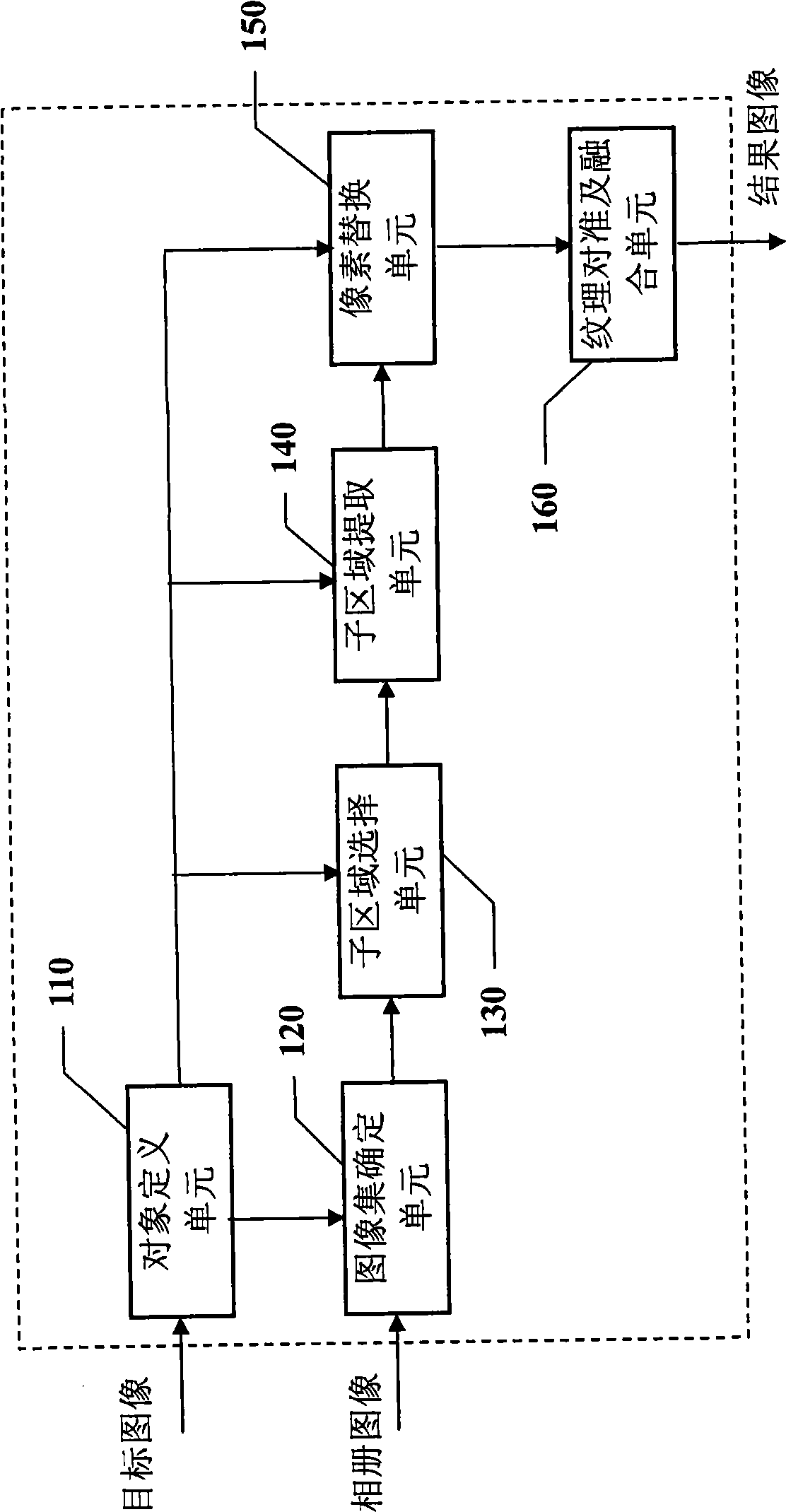
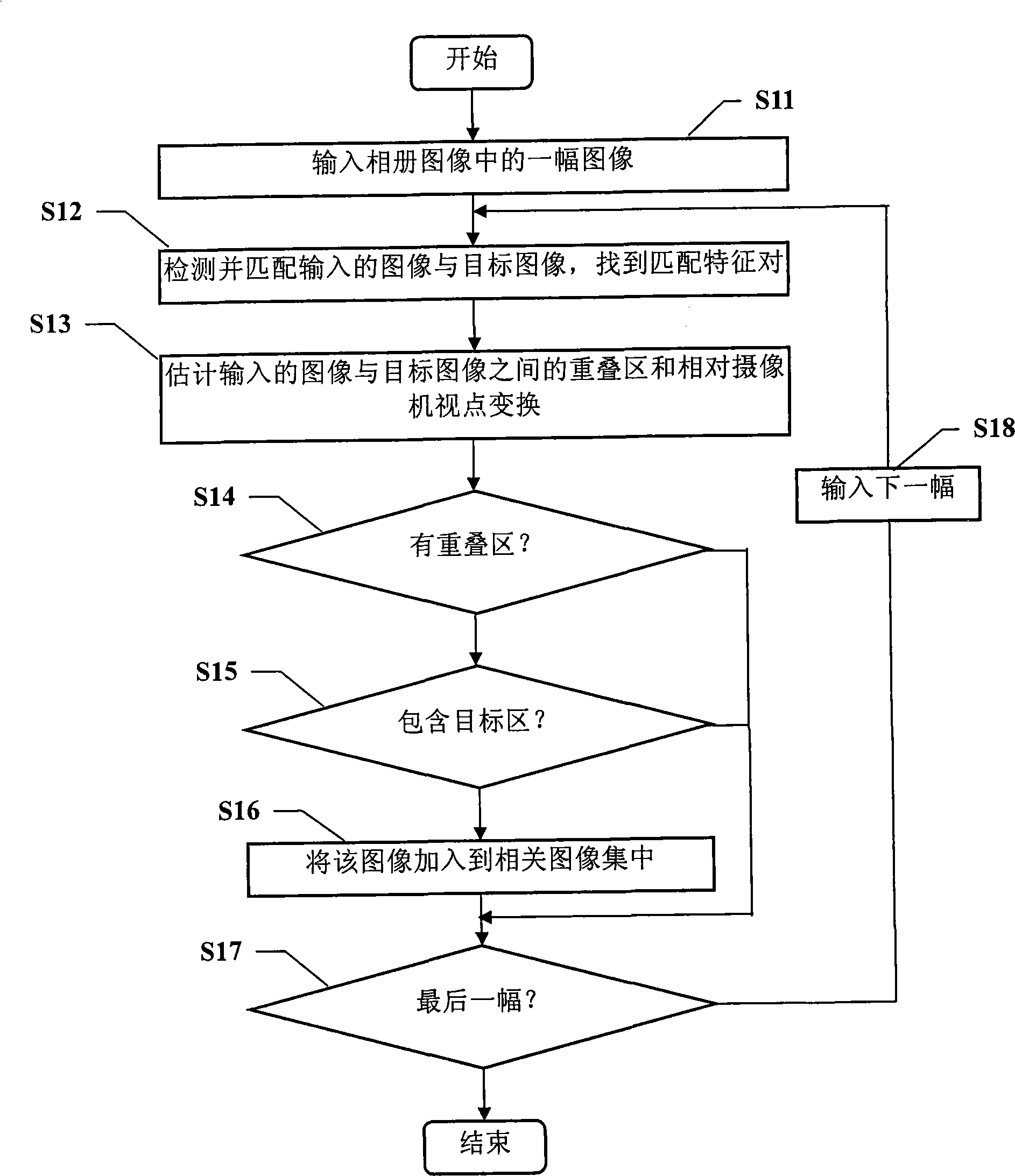
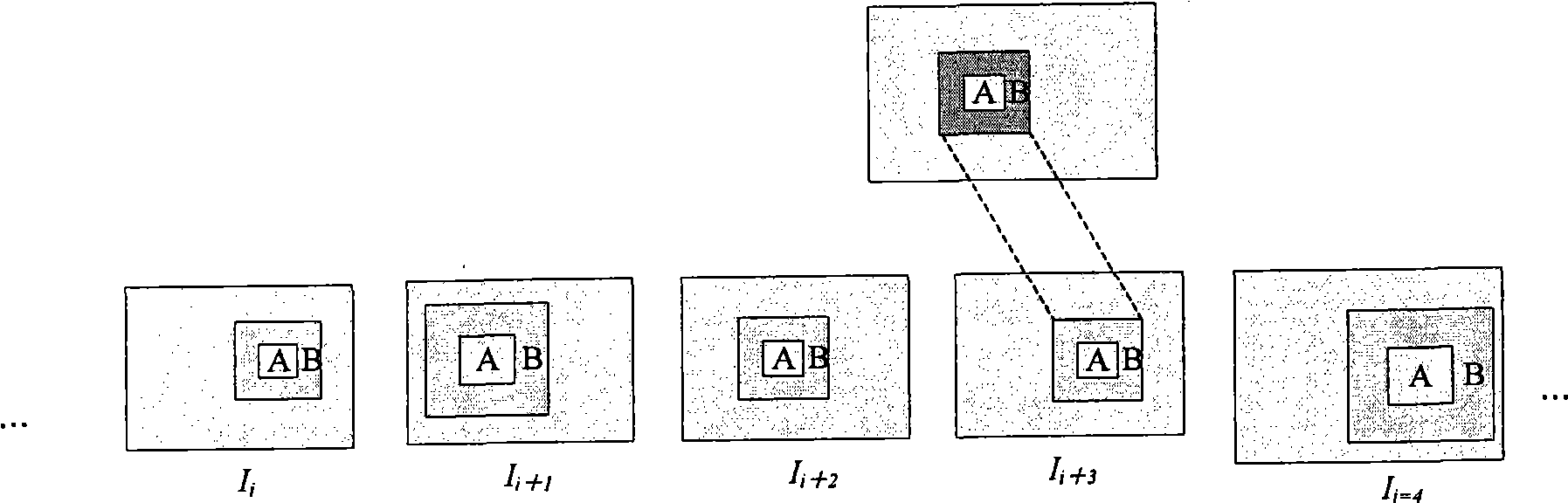
The invention discloses a method and a device for processing an image, used to remove a removed object in a target image and repair the target image. The method for processing the image comprises steps of defining a target area containing the removed object in the target image; extracting at least a sub area as an image from other images related with the target image stack, wherein all aforesaid other images a removed object different from a shooting view point of the target image; selecting pixels pf same position corresponding to the sub area from the image stack pixel by pixel based on theoptimization method to substitute pixels in the target area. Through the inventive method and device for processing images, a user can repair images so as to form ideal images while removing removed images from shot imaged to his delight.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
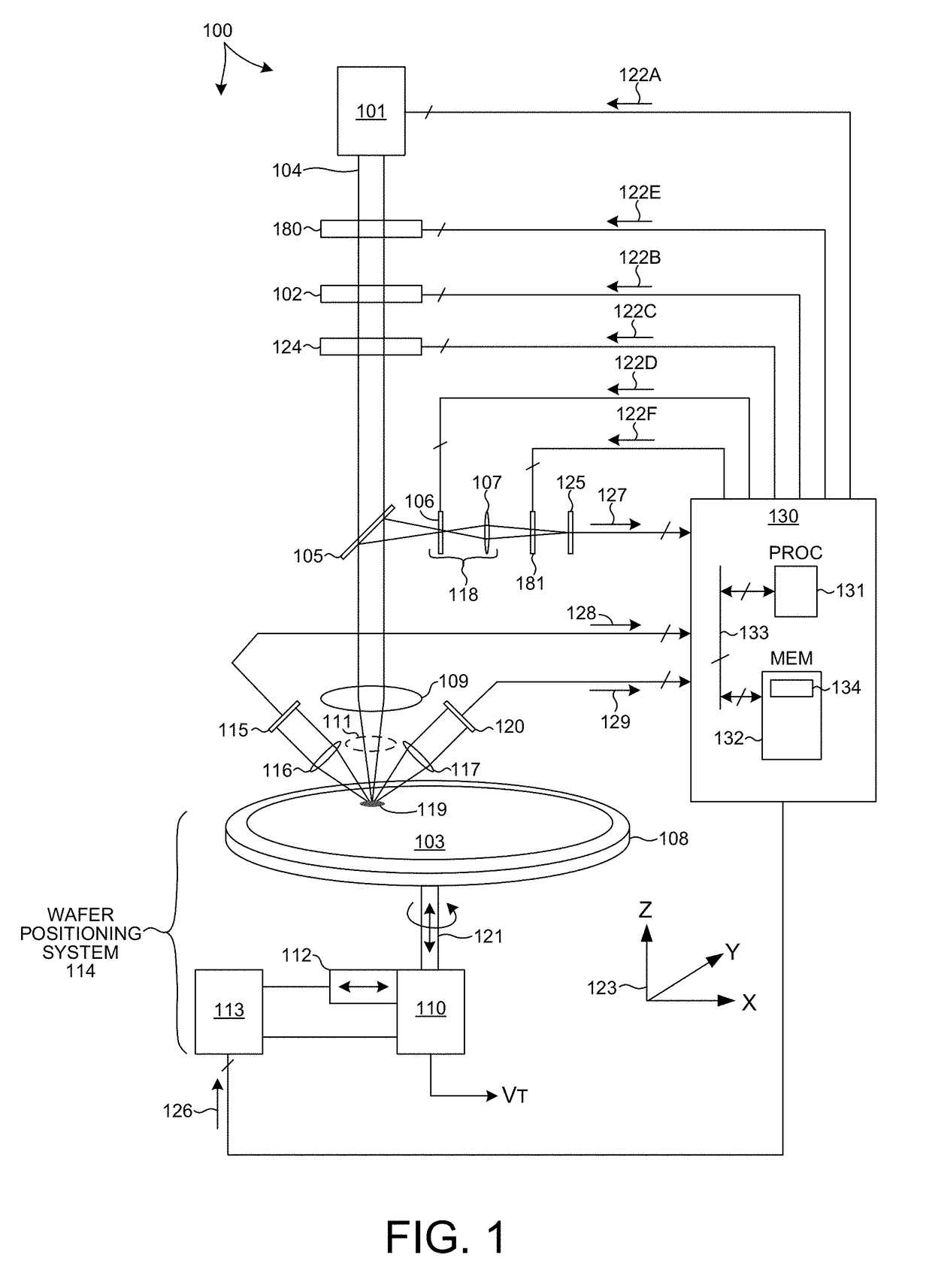
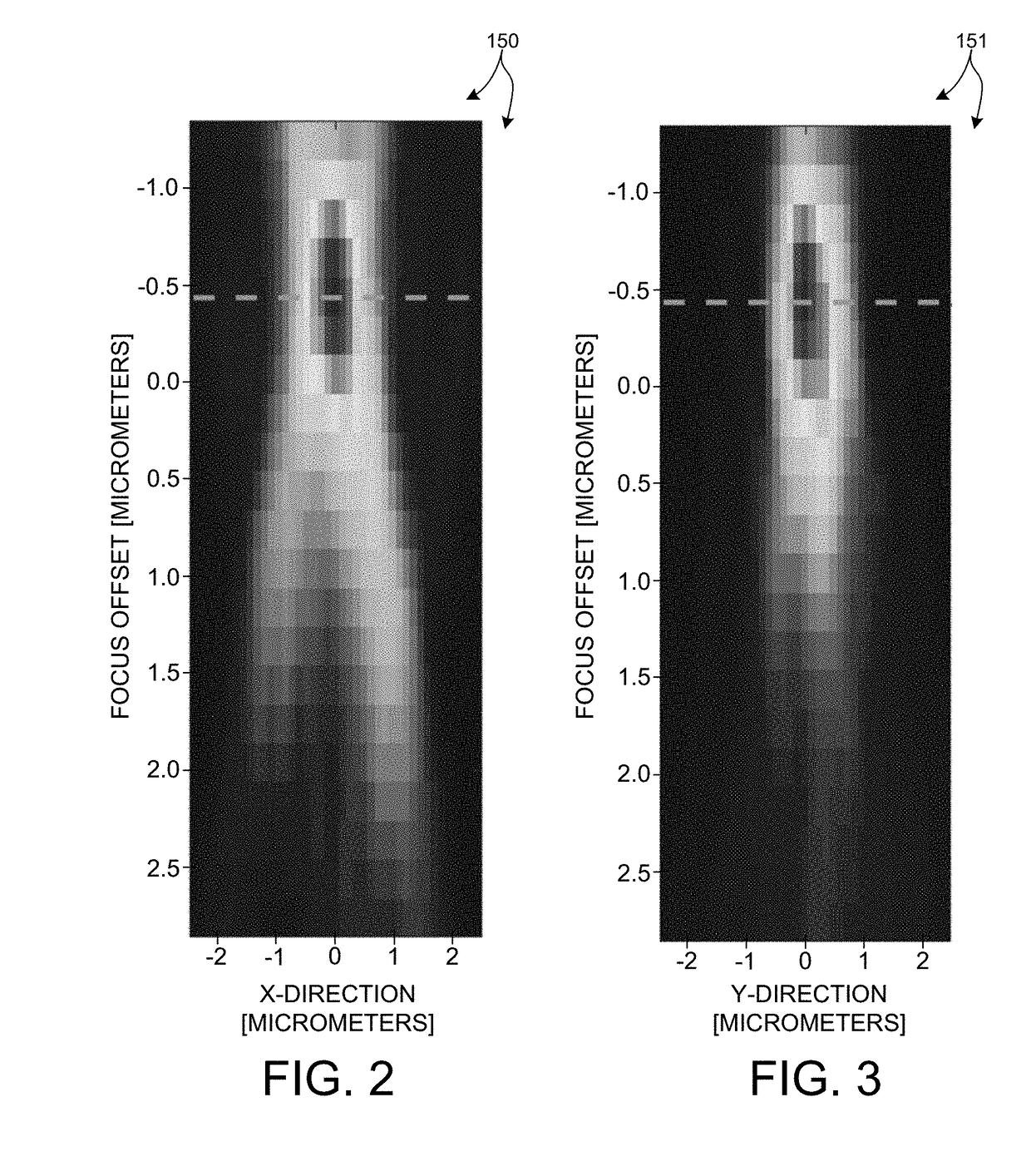
Three-Dimensional Imaging For Semiconductor Wafer Inspection
ActiveUS20180103247A1Easy to detectAccurate Defect DetectionImage enhancementImage analysisSemiconductor structureDimensional modeling
Methods and systems for improved detection and classification of defects of interest (DOI) on semiconductor wafers based on three-dimensional images are described herein. Three dimensional imaging of volumes of thick, layered structures enables accurate defect detection and estimation of defect location in three dimensions at high throughput. A series of images are acquired at a number of different wafer depths. A three dimensional image of a thick semiconductor structure is generated from the series of images. Defects are identified and classified based on an analysis of the three dimensional image of the thick semiconductor structure. In some examples, the three-dimensional image stack is visualized by contour plots or cross-sectional plots to identify a characteristic defect response. In some examples, the three-dimensional image is processed algorithmically to identify and classify defects. In another aspect, the location of a defect is estimated in three dimensions based on the three dimensional image.
Owner:KLA CORP
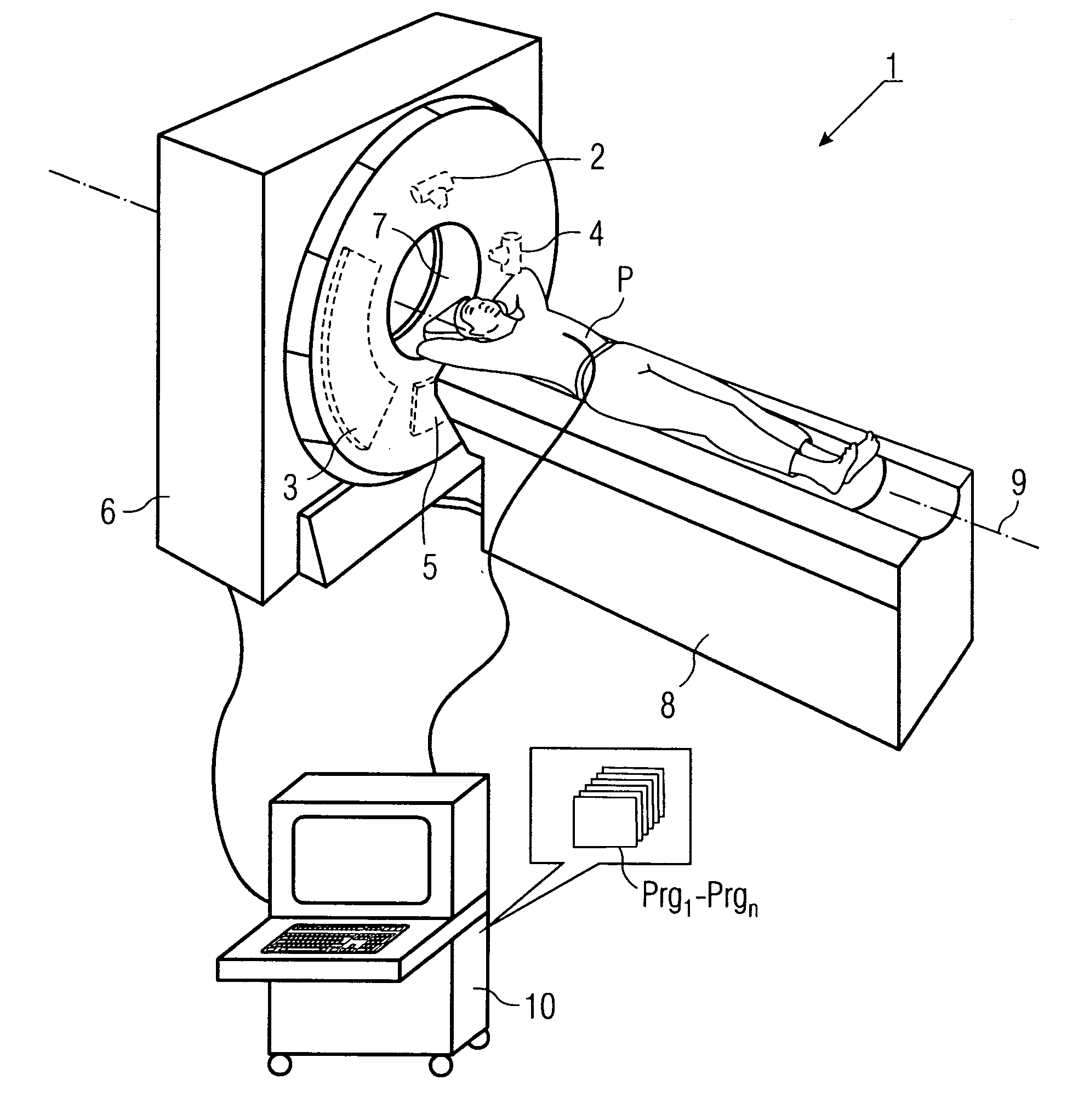
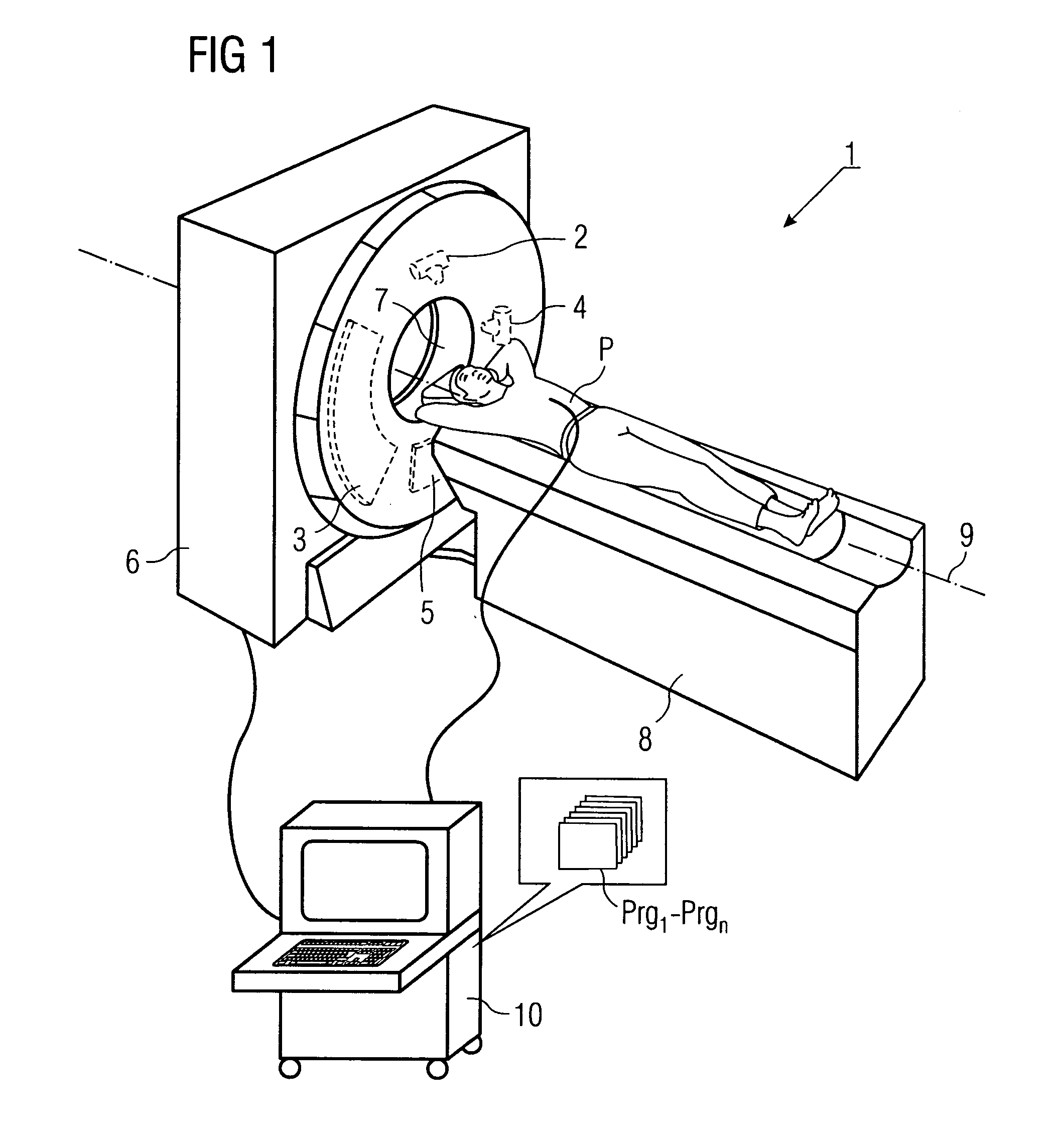
Method for production of tomographic section images of a periodically moving object with a number of focus detector combinations
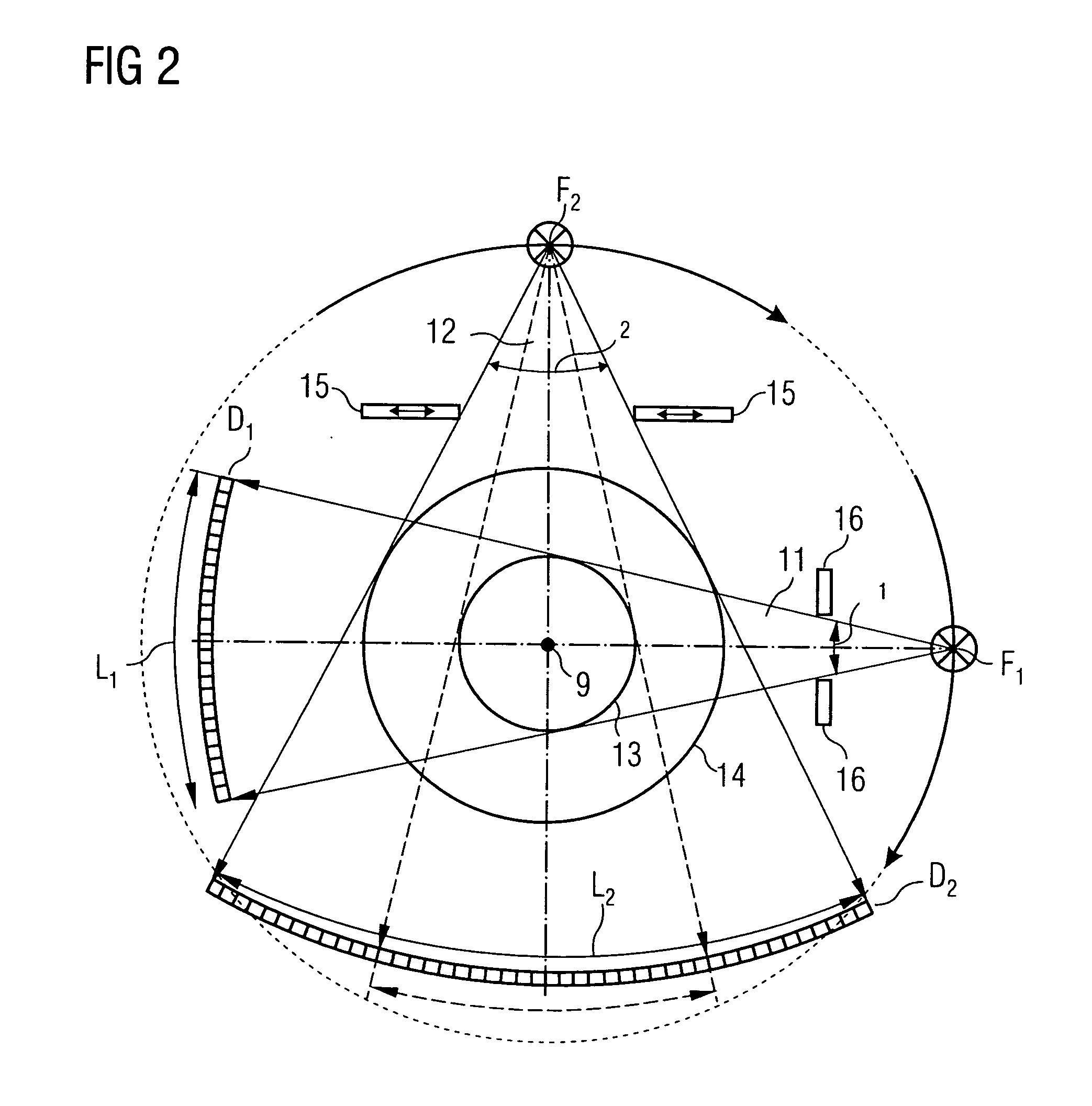
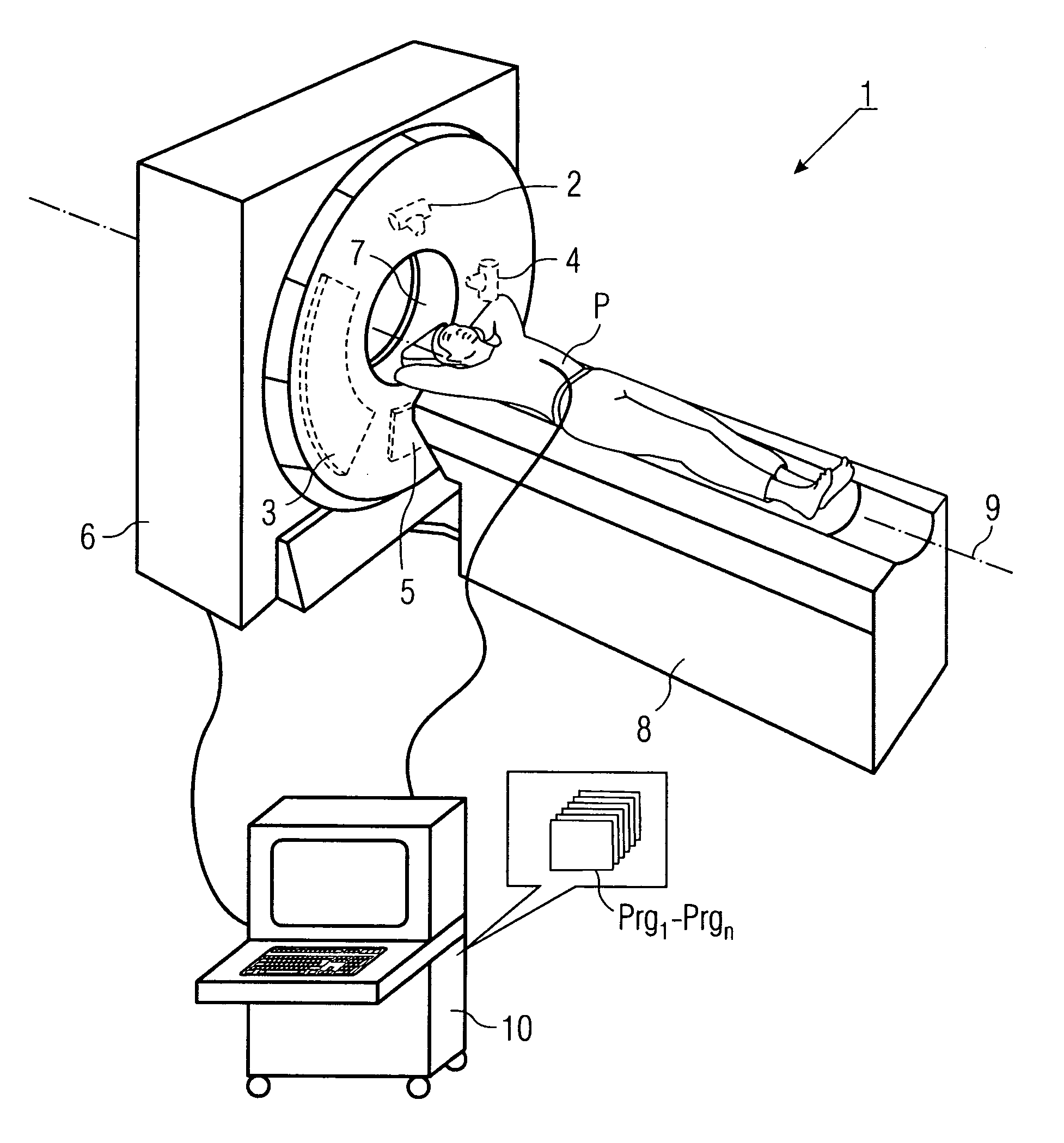
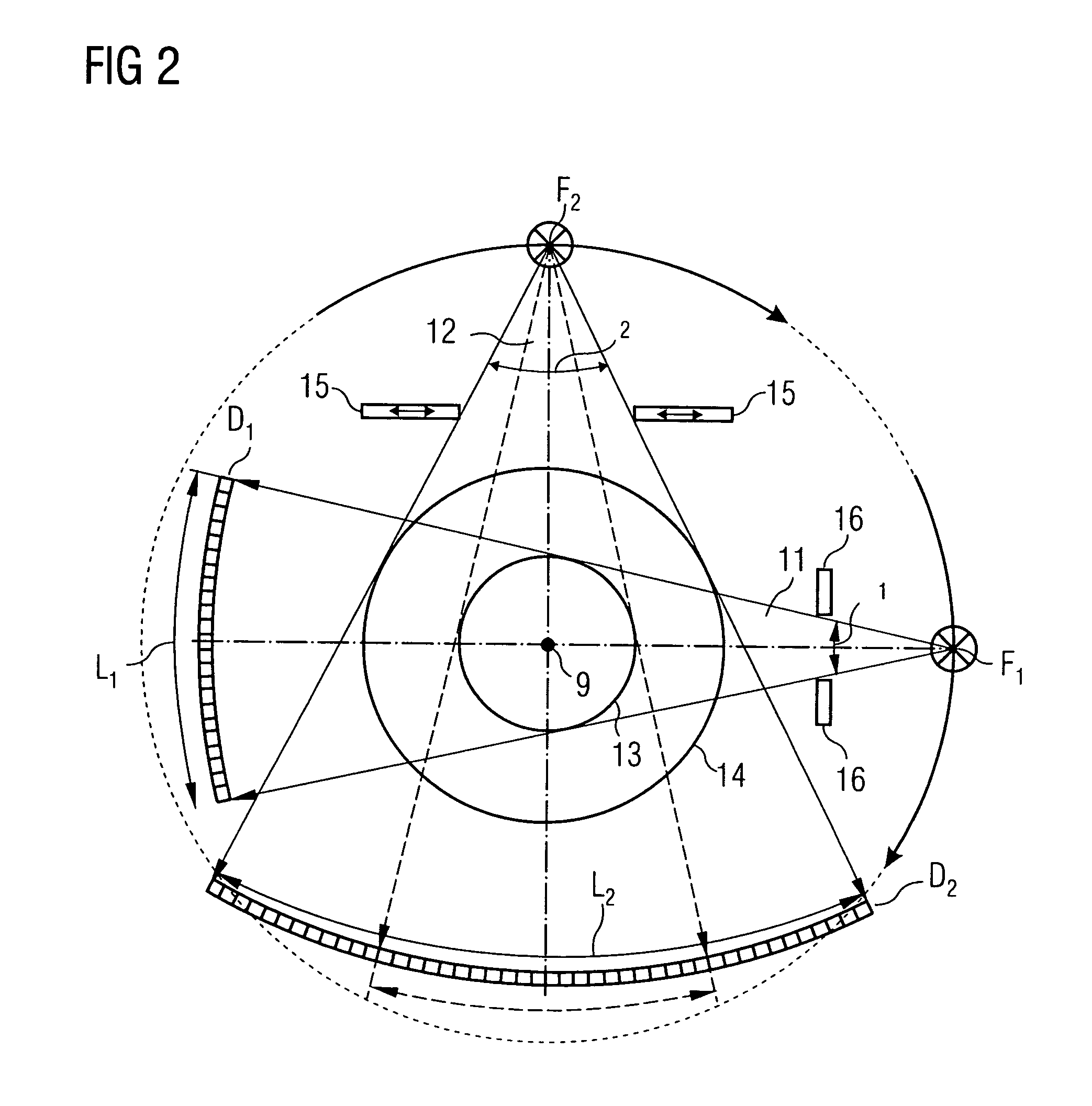
InactiveUS20050111622A1Reduce dose loadOptimize timingRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsTime correlationCt scanners
A method and CT scanner are proposed for the production of tomographic section images, in particular X-ray CT images, of a periodically moving object with periodically changing movement and rest phases. For scanning, a number of focus detector combinations with flat detectors are moved on coaxial spiral paths and movement signals from the moving object are measured at the same time in order to detect movement and rest phases. Further, the time correlation between the movement data and the detector output data stored and axial segment image stacks are then reconstructed independently of one another from sub-segments of the spiral paths using the detector output data from each detector which represent a rest phase of the moving object. Additionally, segment image stacks from the n spiral paths of the n focus detector combinations at the correct time are added up in a complementary angle form and in layers to form 180° tomography section images. The axial segment image stacks are reconstructed in a first step from double-inclined reconstruction planes. Further, in a second step, they are reformatted to produce axial segment image stacks, and detector data from a number of successive movement periods are used for this purpose.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for obtaining volume of interest of four-dimensional heart image
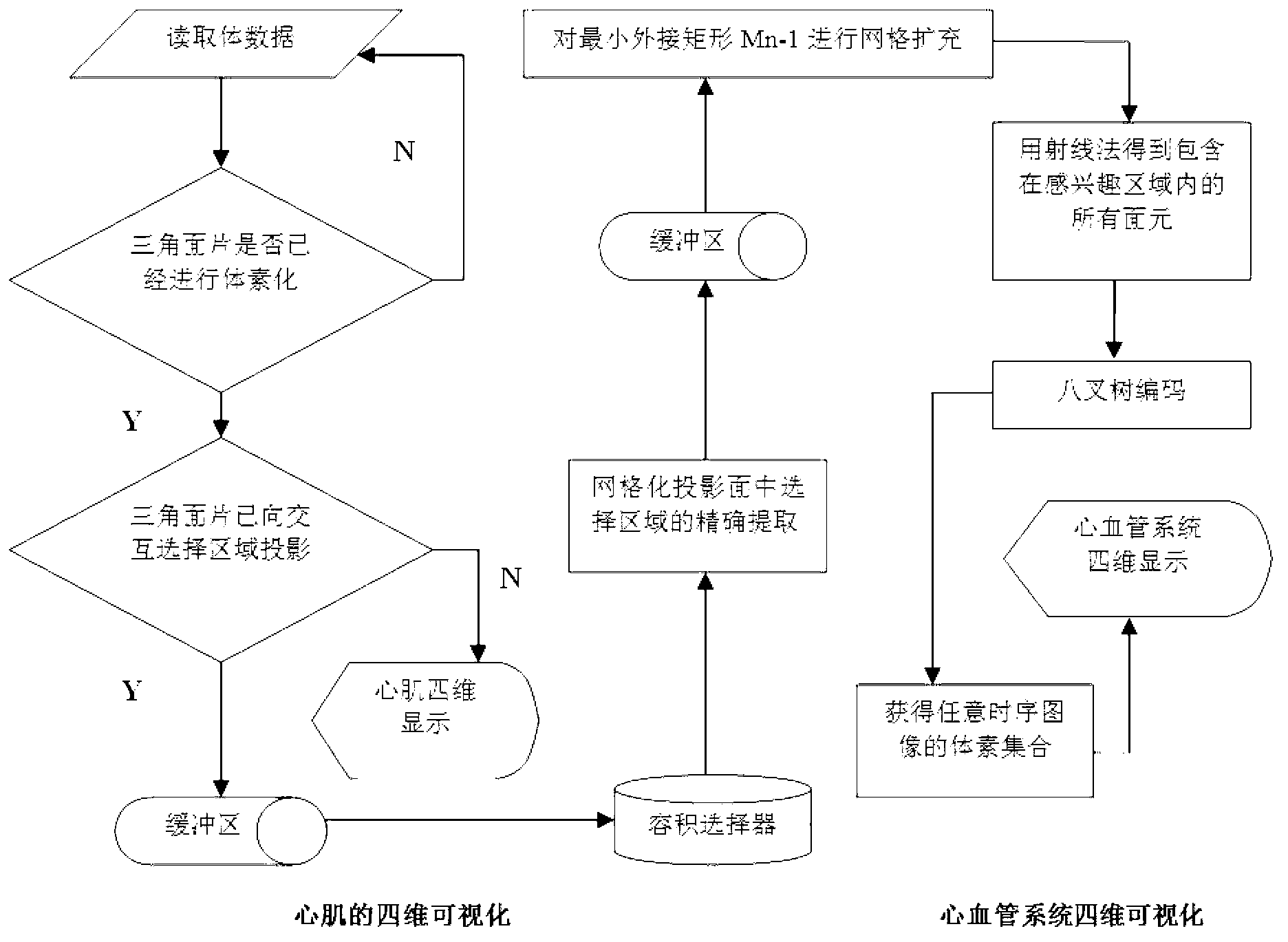
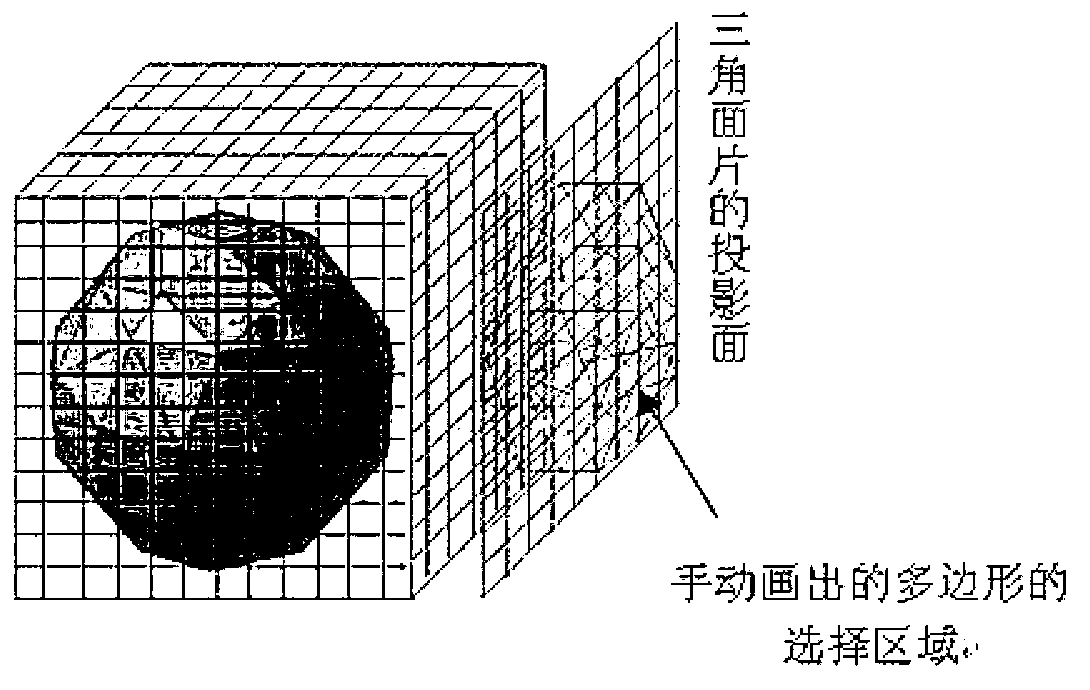
The invention relates to a method for obtaining the volume of interest of a four-dimensional heart image, which belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises the following steps that volume data of a tissue structure is read, voxelization treatment is performed, and regional projection is selected to an interactive polygon through a set of triangular patches, so as to obtain myocardial four-dimensional visualization data based on the volume data; then precise extraction and grid expansion are performed on a selected region in a gridding projection surface, so as to obtain all surface elements involved in a region of interest; and finally, octree encoding and consistency extraction are performed to obtain a voxel set of any sequential image, thereby realizing four-dimensional visualization data of a cardiovascular system on the basis of the volume data. By using the method, a local tissue volume data set corresponding to a contour of the extracted heart region of interest can be automatically obtained, and finally, local extraction and visualization of the four-dimensional heart image are realized. Because the space occupied by the extracted local volume data set is obviously less than the space occupied by the integral volume data set, compared with the space occupied by an image stack before extraction, the space occupied by the extracted image stack is greatly reduced, and therefore, the time consumed by four-dimensional visualization is greatly reduced.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
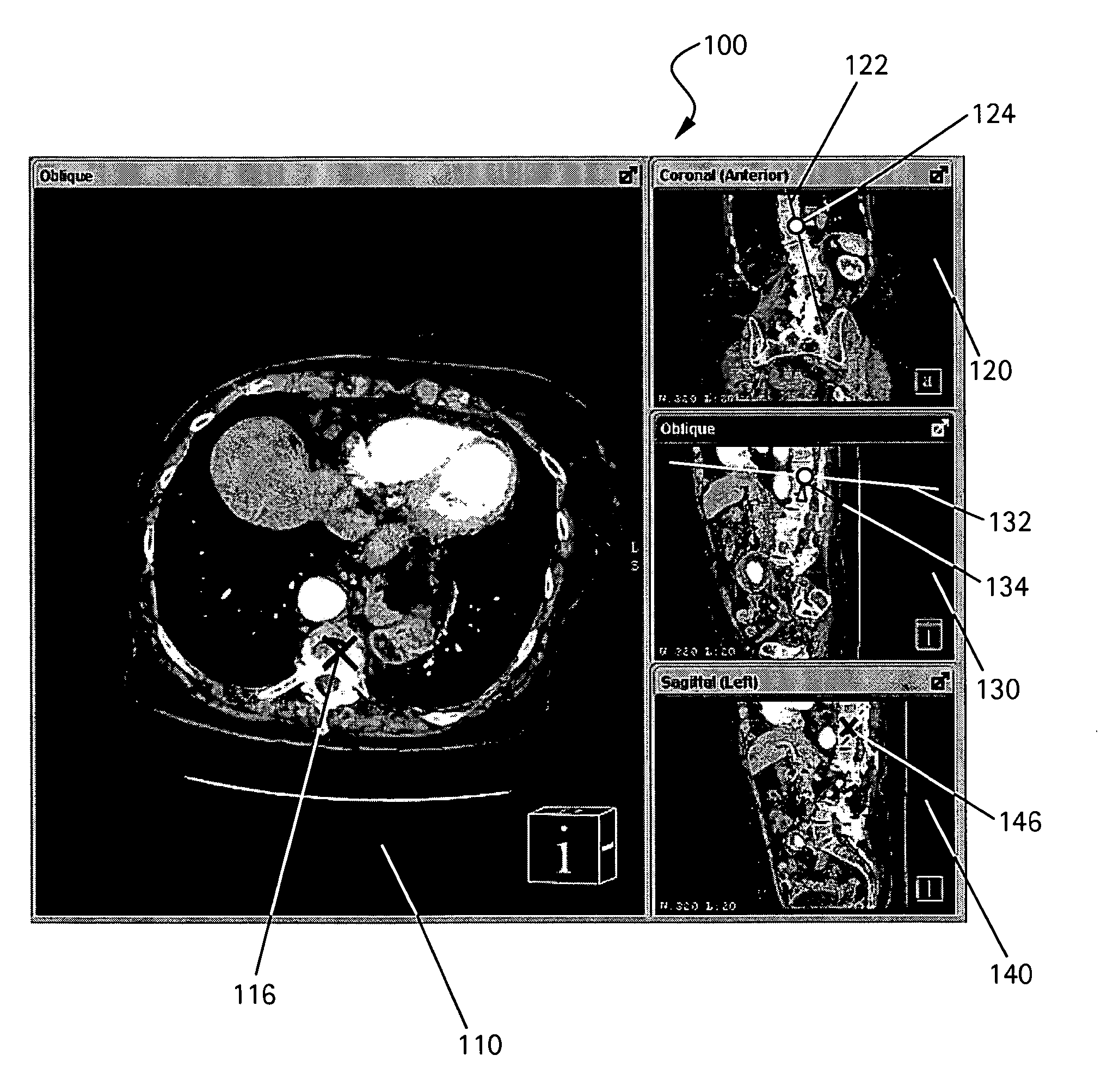
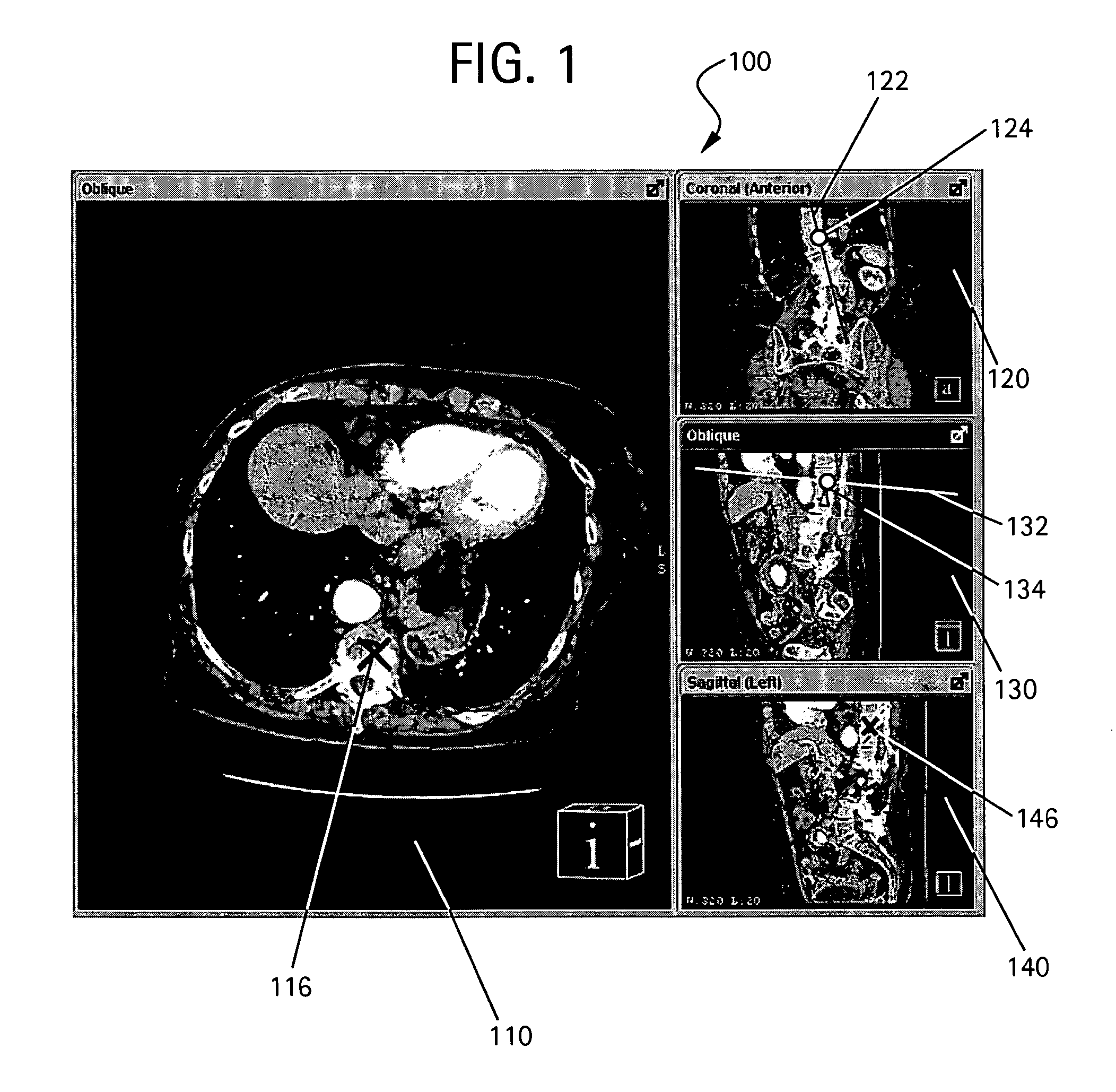
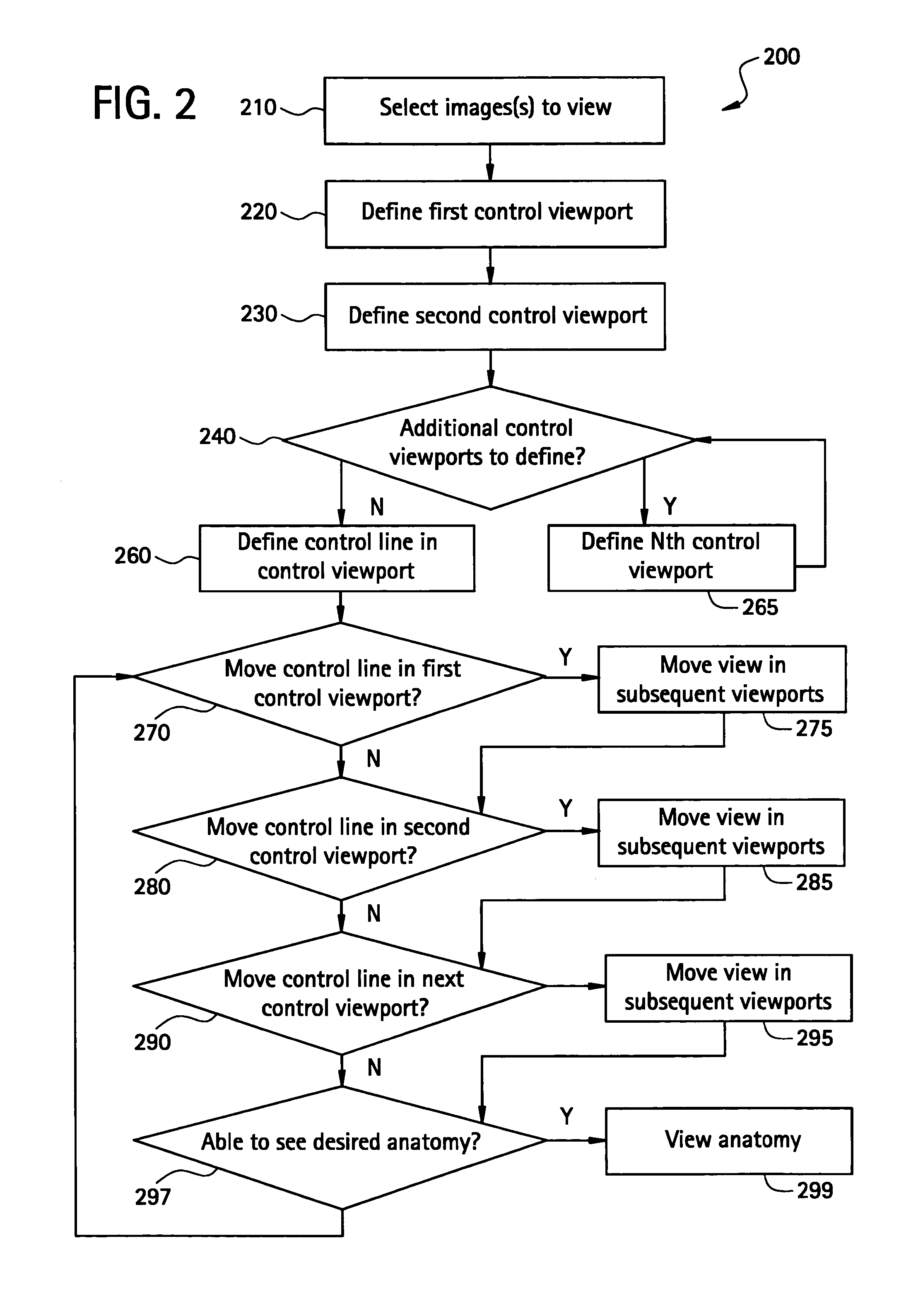
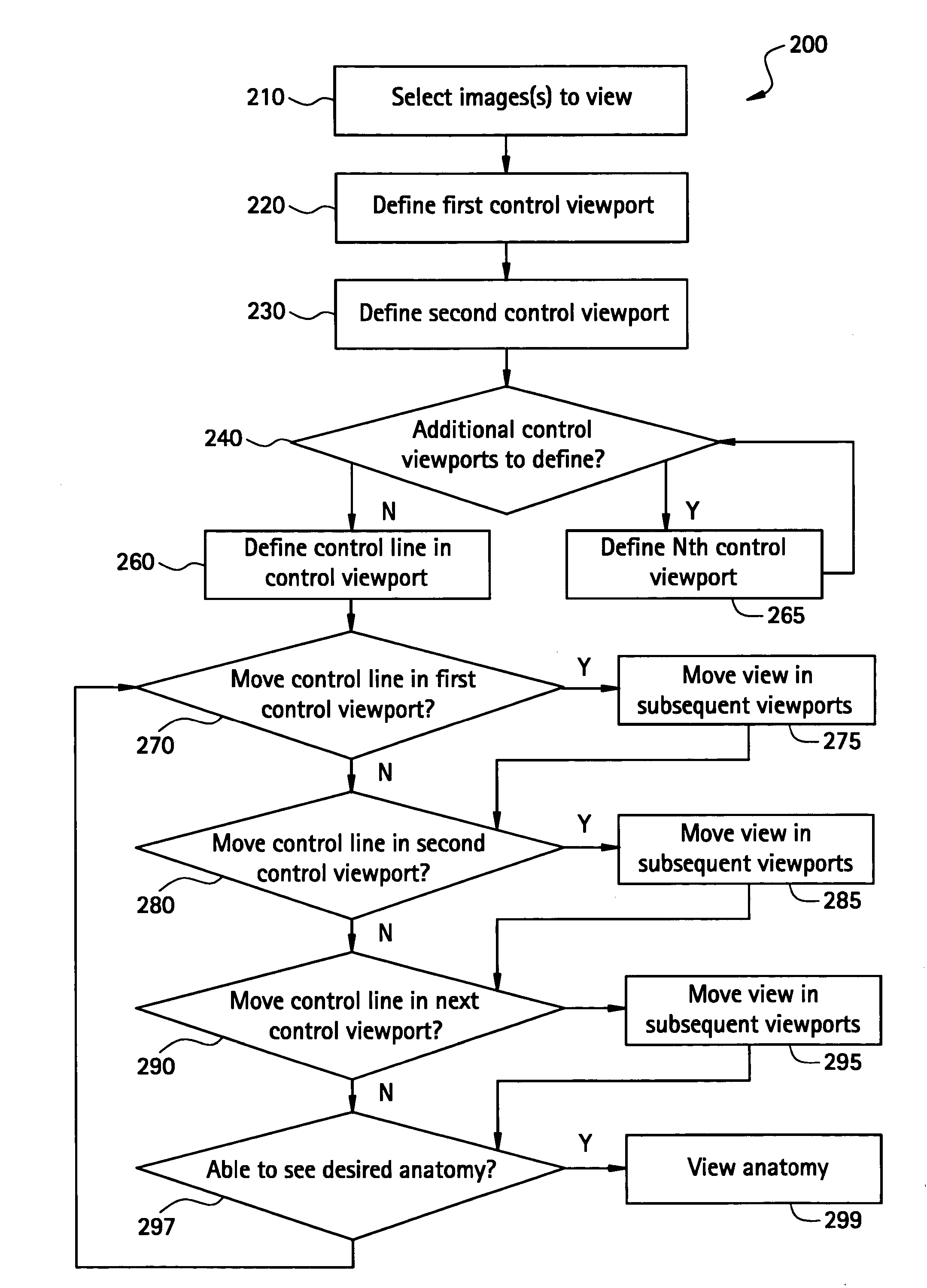
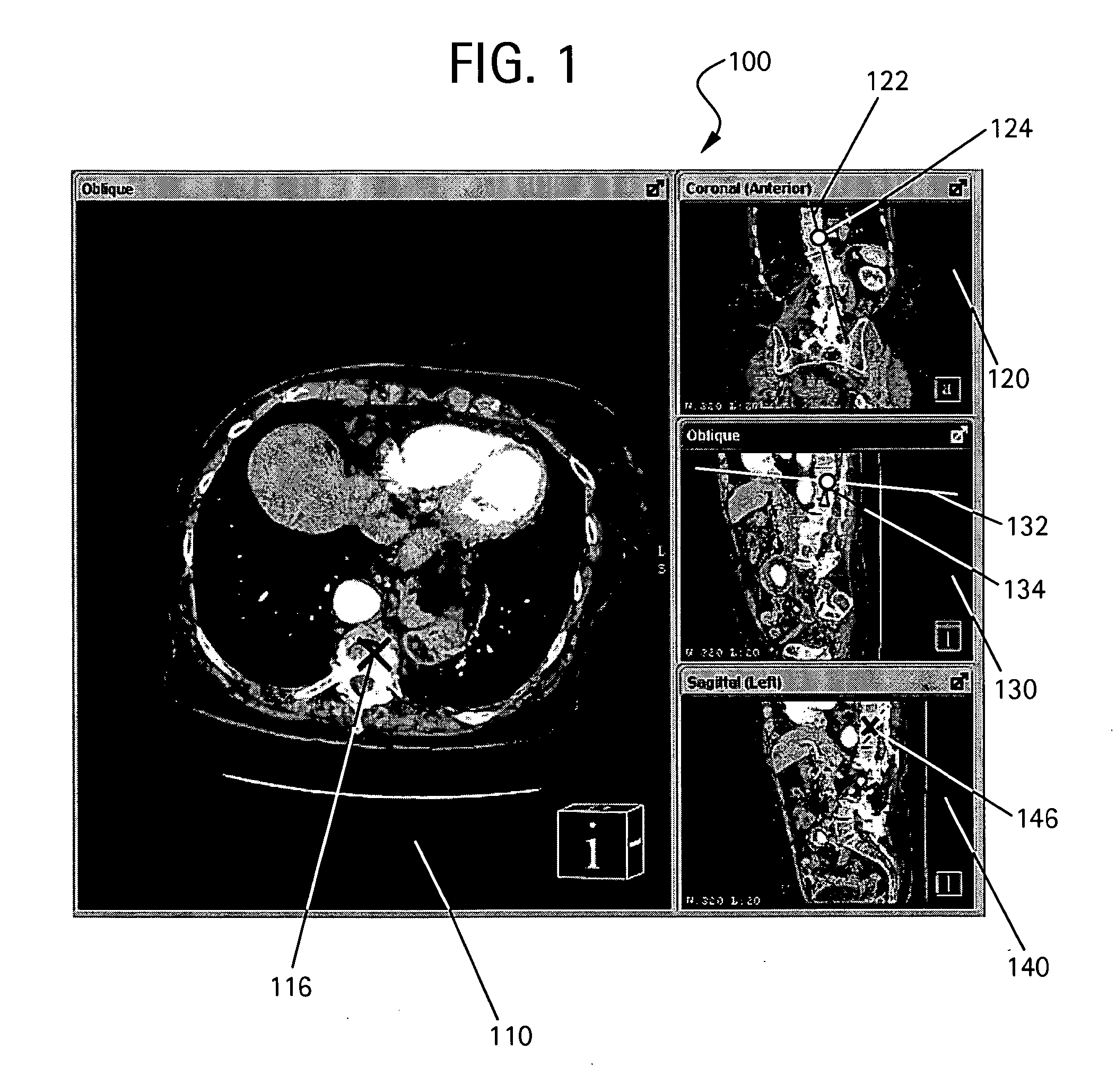
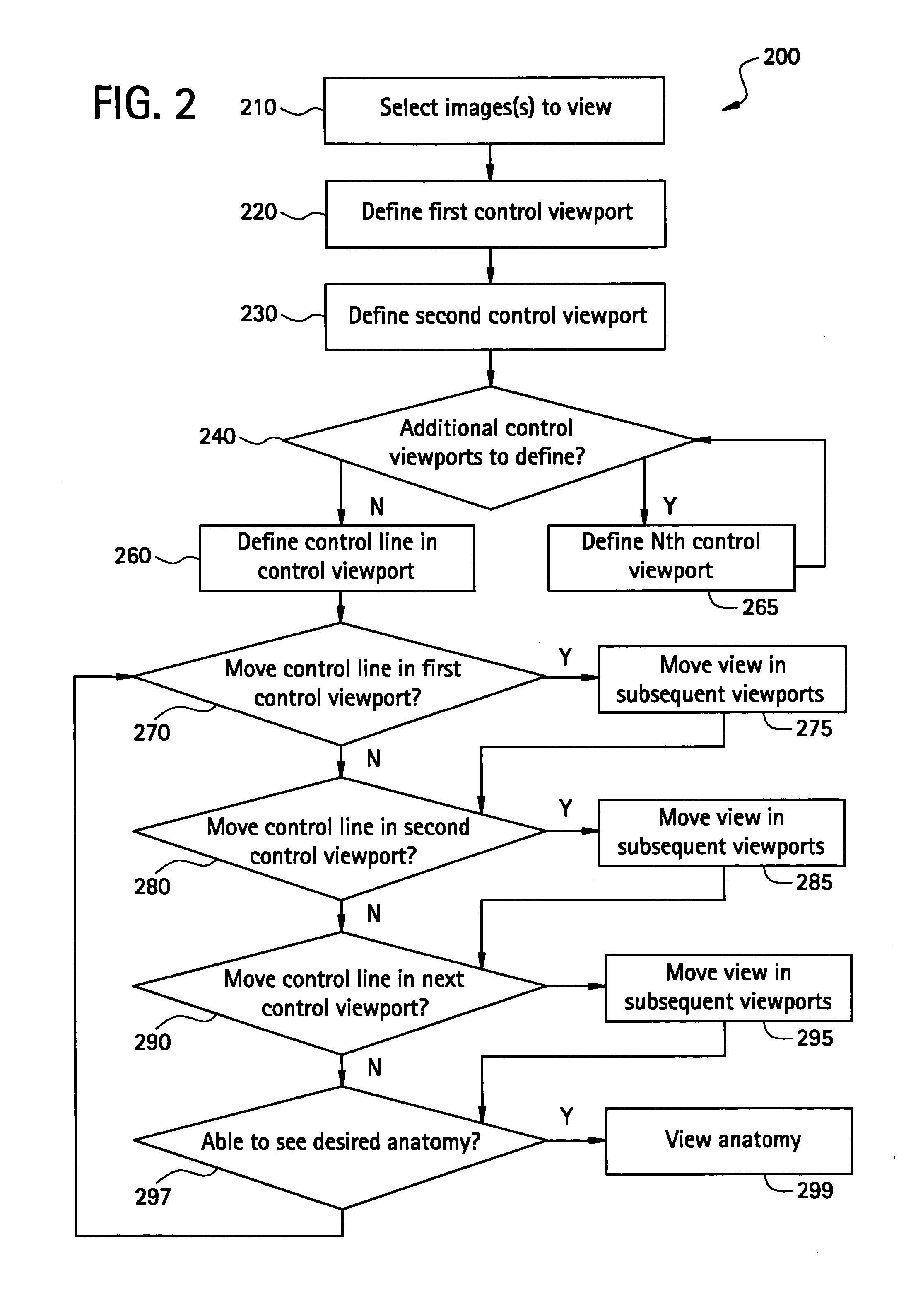
Method to define the 3D oblique cross-section of anatomy at a specific angle and be able to easily modify multiple angles of display simultaneously
The present invention provides a system and a method for simultaneously modifying one or more angles of cross-sections in one or more cross-sectional images or stacks of images of a 3D volume. A plurality of viewports is displayed to a user. Each viewport includes a 2D cross-sectional image or stack of images and all 2D images or stacks of images are displayed simultaneously. One or more viewports may also include a control line representative of an angle of cross-section or image plane of a 2D image or stack of images displayed in another viewport. If a control line is moved in a selected viewport, the angle of cross-section or image plane of a 2D image or stack of images in another viewport is accordingly altered simultaneous with such control line movement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
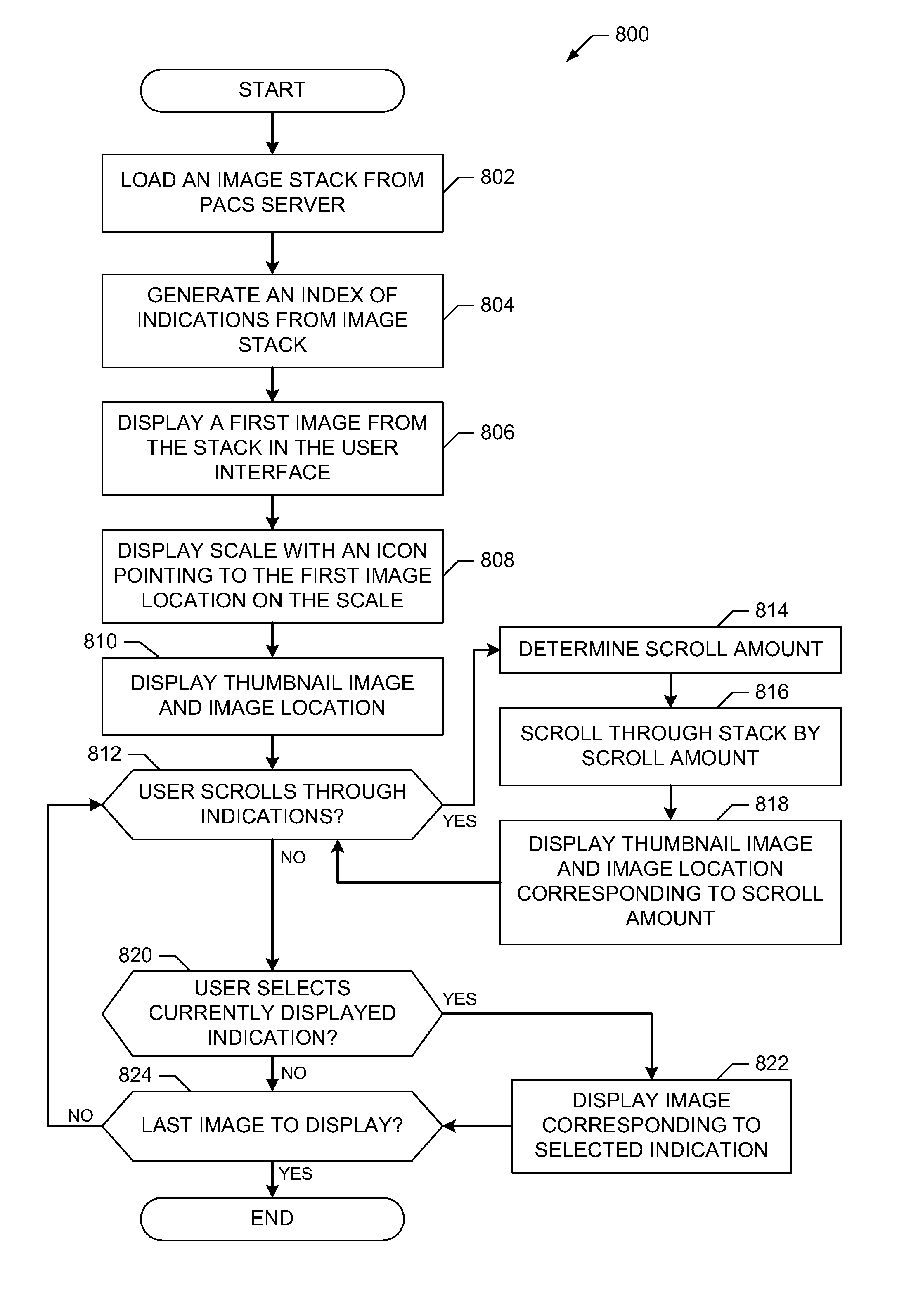
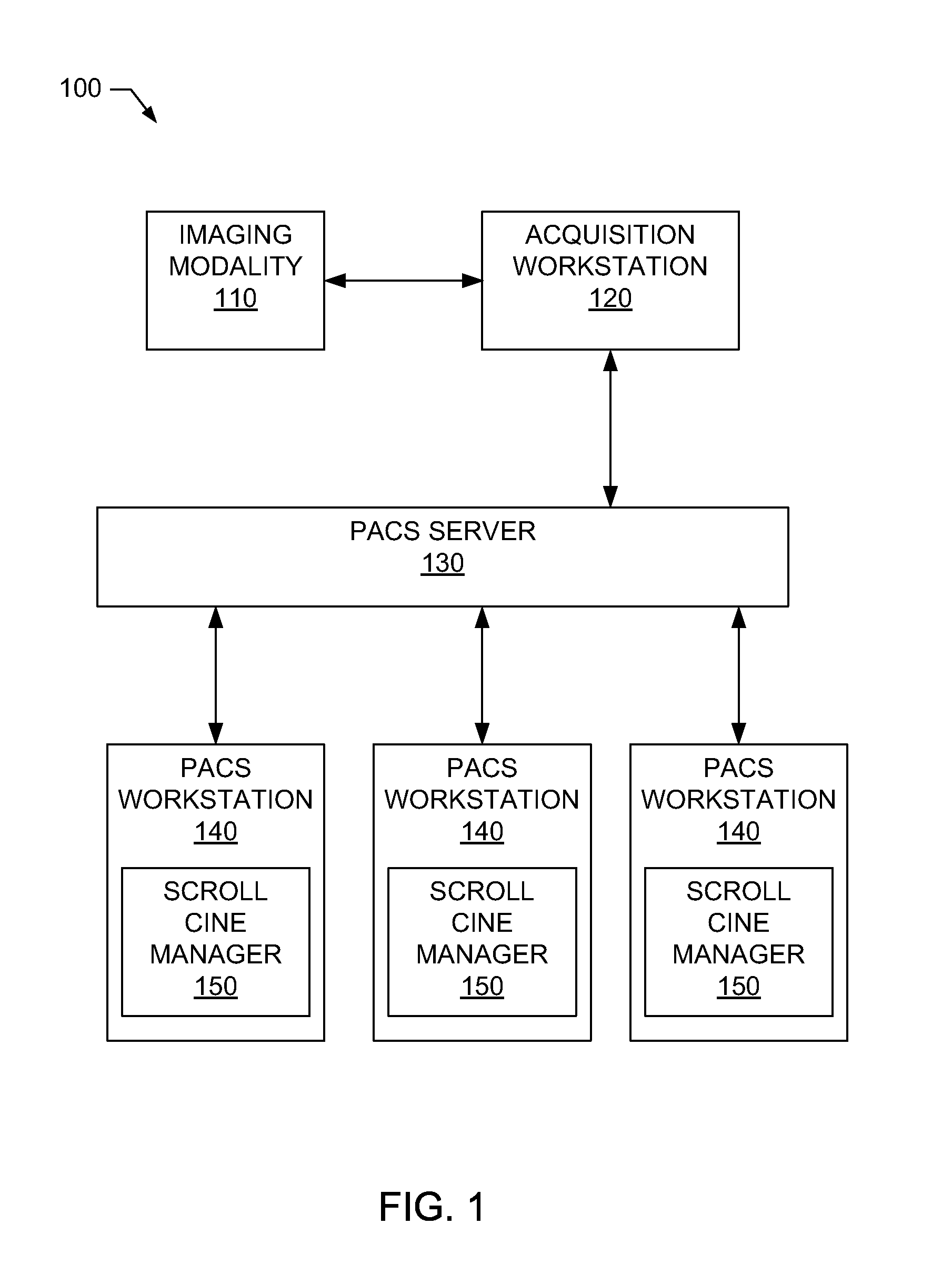
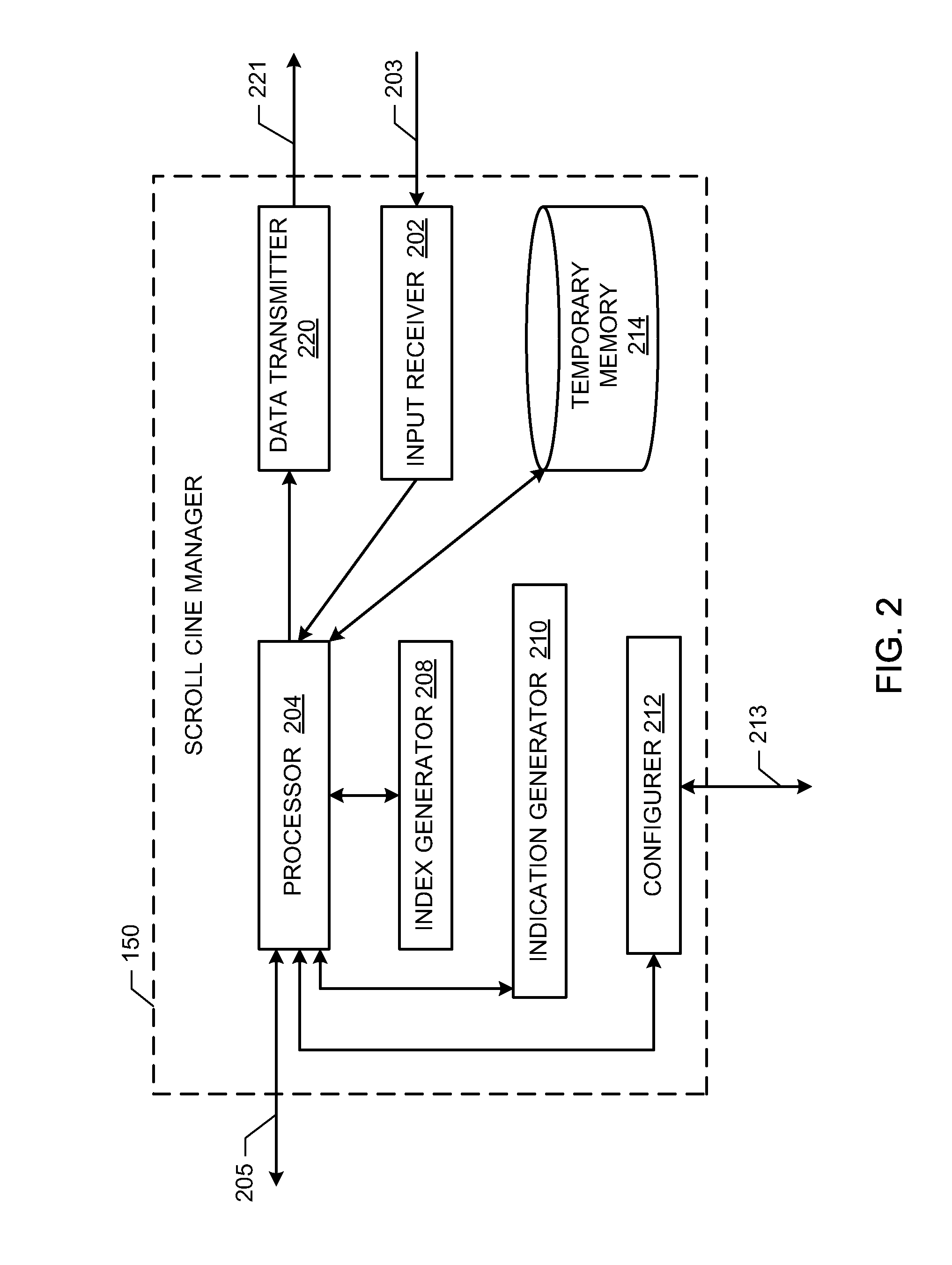
System and methods for indicating an image location in an image stack
InactiveUS20100063842A1Data processing applicationsDiagnostic recording/measuringUser interfaceImage stack
System and methods for indicating an image location in an image stack are disclosed. An example method includes generating an index of indications of medical image locations in a medical image stack including a first indication of a first medical image location in a medical image stack and a second indication of a second medical image location in the medical image stack, displaying in a user interface the first medical image and the first indication of the first medial image location within the medical image stack, receiving a scroll input and scroll through the index displaying indications of medical image locations in the image stack until the second indication of the second medical image is displayed, receiving a selection of the second indication of the second medical image, and displaying in the user interface the second medical image and the second indication of the second medical image location within the medical image stack.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
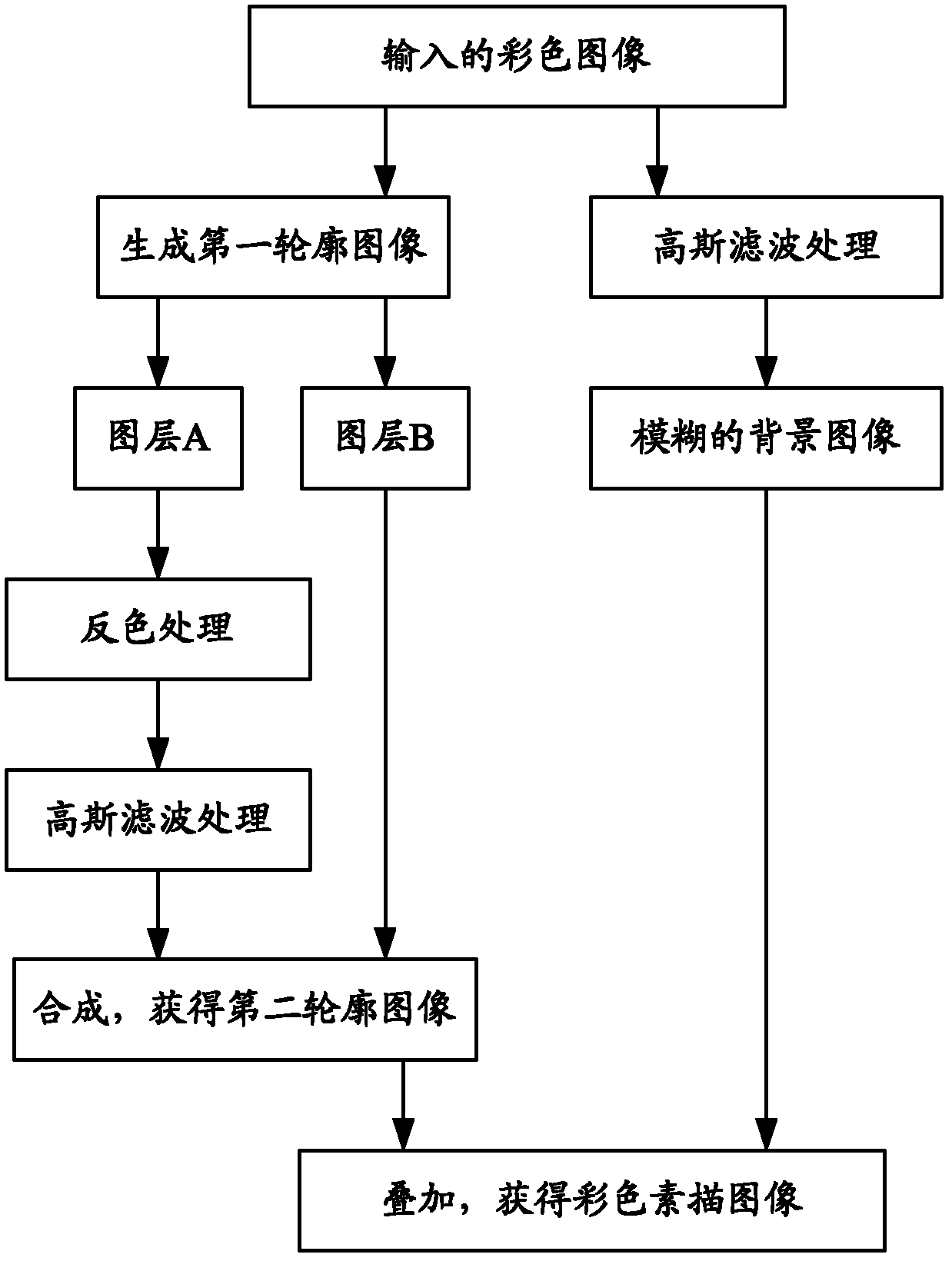
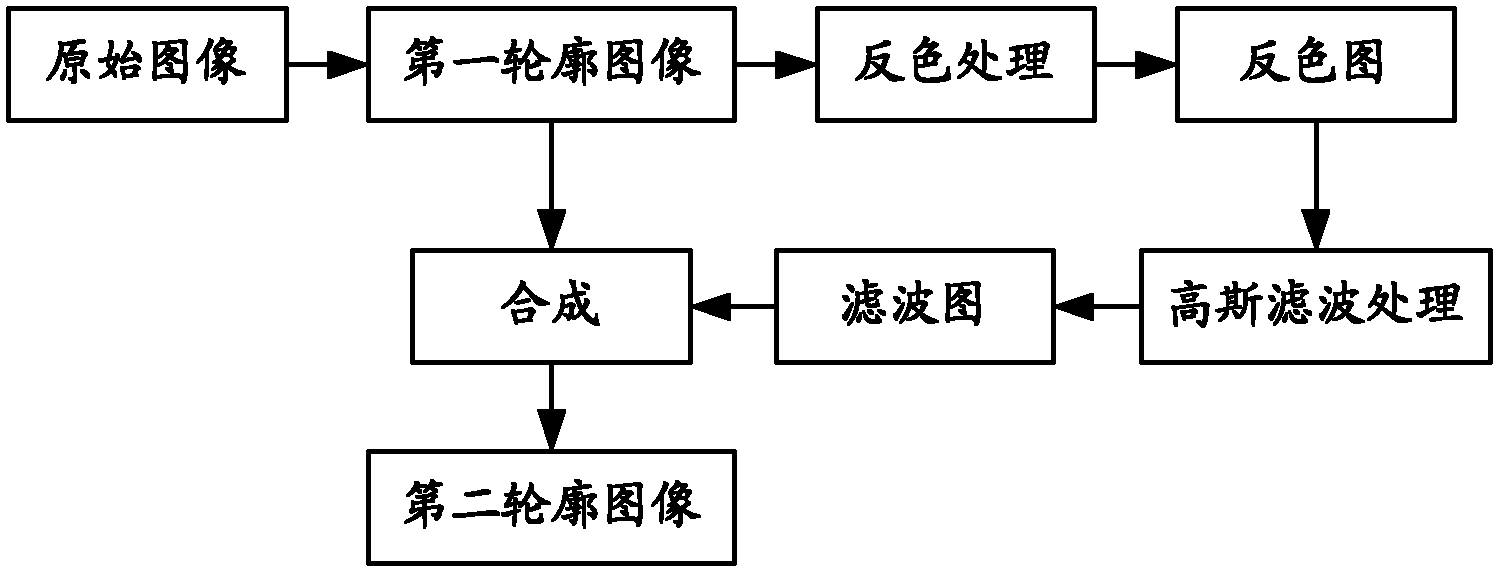
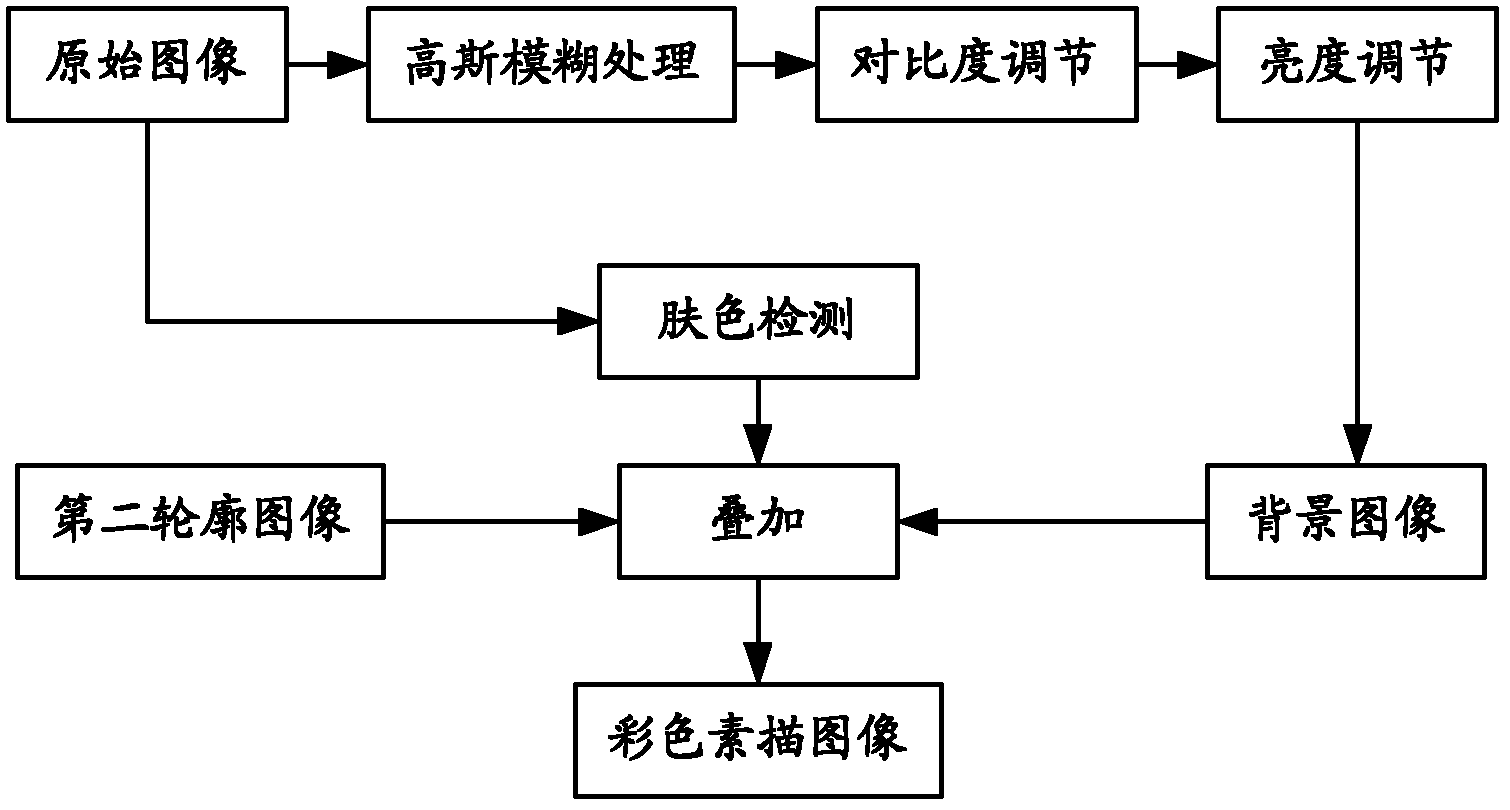
Colorful sketch image generating method
The invention provides a colorful sketch image generating method. The colorful sketch image generating method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: generating a first profile image by a grey synthetic method; copying the generated grey image as an image layer A and an image layer B; synthesizing the image layer A with the image layer B after carrying out color-inversing and Gaussian filter treatment on the image layer A in sequence to obtain a second profile image; carrying out Gaussian filter treatment on the input colorful image to obtain a blurred background image; and stacking the second profile image with the blurred background image to obtain the colorful sketch image. The colorful sketch image generating method provided by the invention can quickly generate colorful sketch images which are satisfying and of a hand-drawn style. Furthermore, an image stacking threshold value can be controlled by skin color detection, so that the skin color parts of the images are smooth; and the non-skin color parts of the images have clear profiles.
Owner:SHENZHEN KONKA TELECOMM TECH
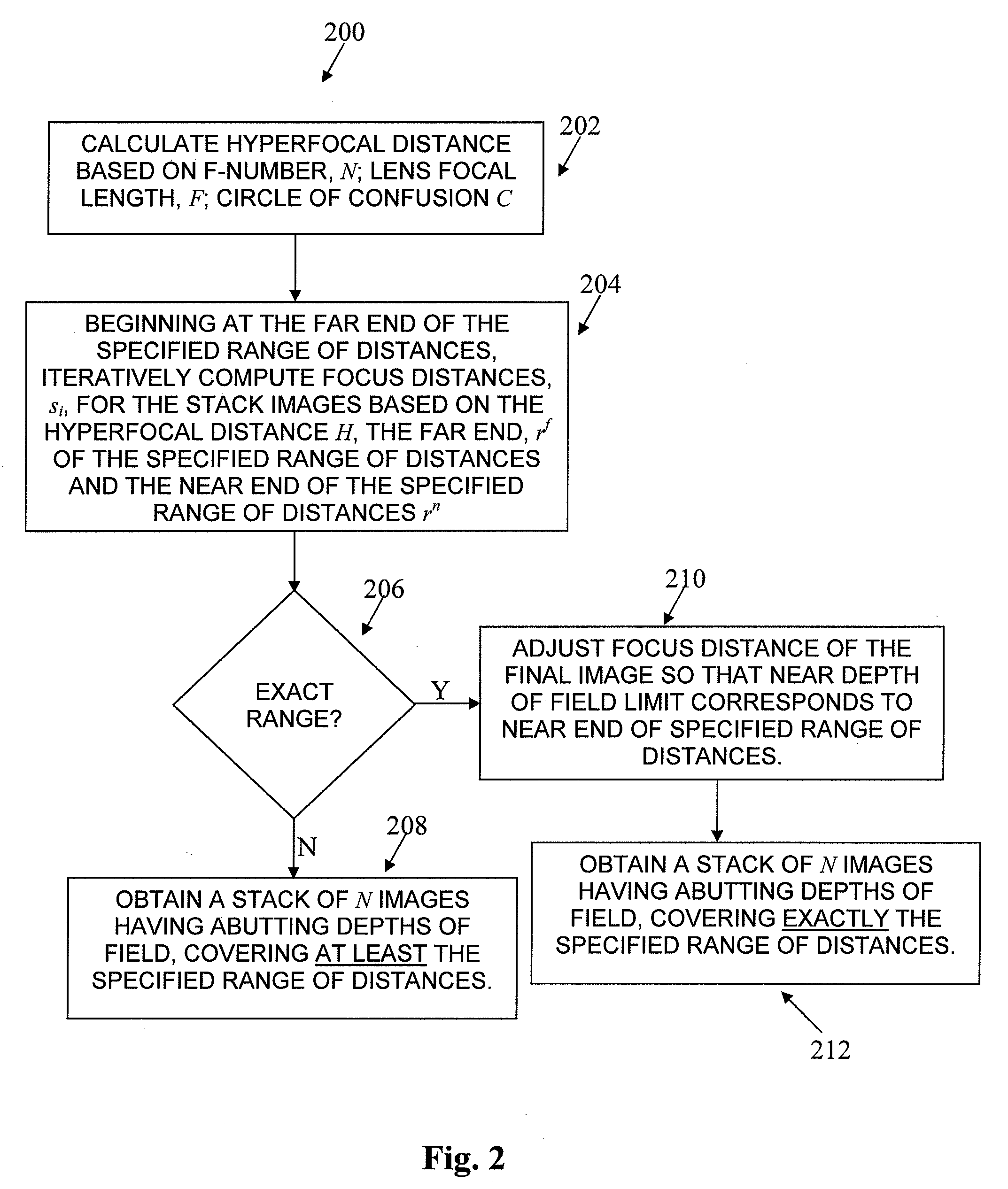
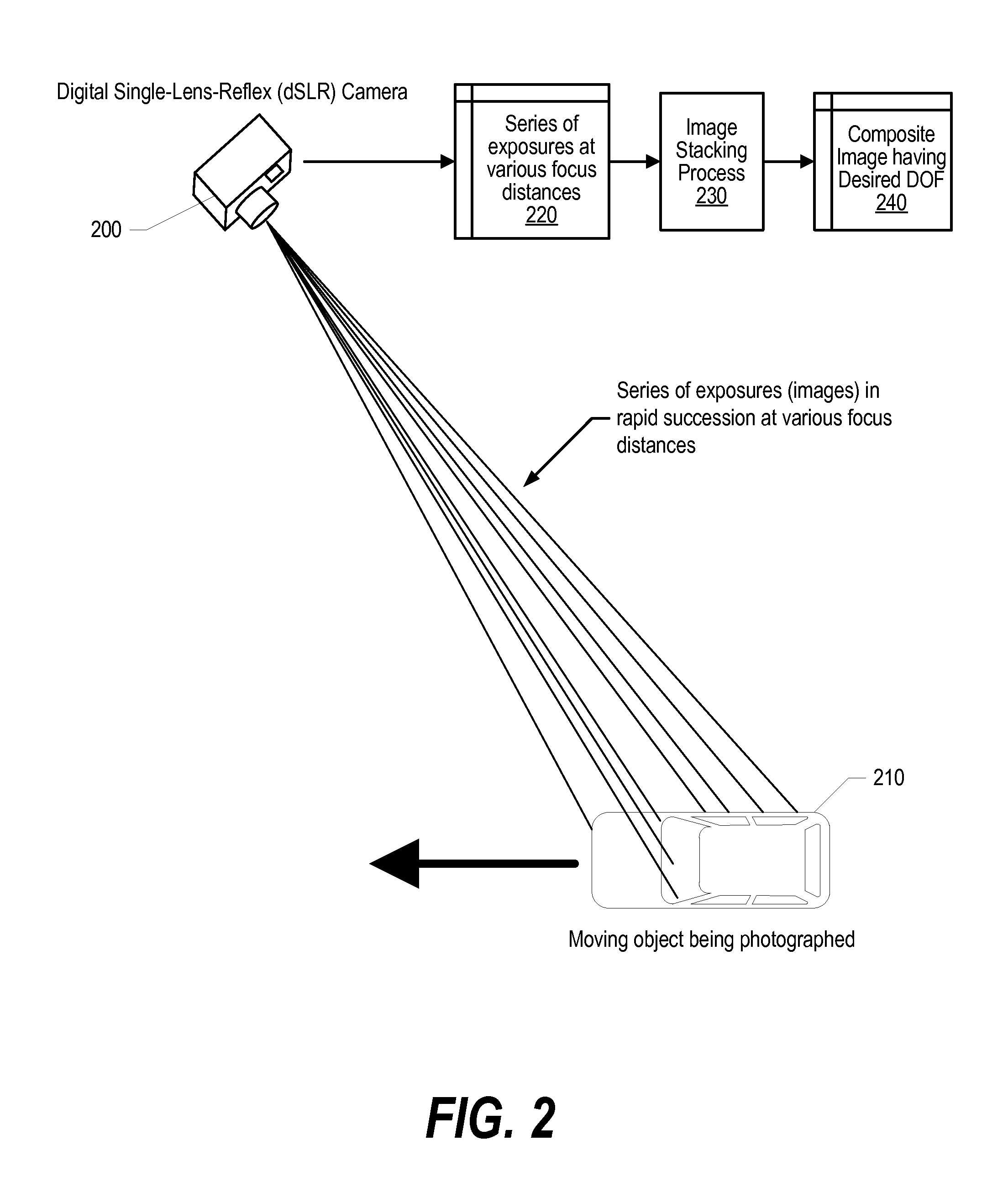
Depth of Focus in Digital Imaging Systems
InactiveUS20140002712A1Television system detailsColor television detailsDigital imagingDepth of field
An approach is provided to generate a composite image of a moving object by using image stacking on a set of captured digital images of the moving subject. A composition depth-of-field of the moving subject is identified. A digital camera with a focus distance setting and an auto-focus system is used to capture the set of digital images with each of the digital images are at a different focus distance within the composition depth-of focus. Each of the digital images is focused using the digital camera's auto-focus system. The captured digital images are stored in a memory and the composite image is generated from the stored images by using an image stacking process on the set of images.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for seeking discharge regions of power devices on ultraviolet images
ActiveCN101726693AEasy to identifySmall discharge areaImage enhancementTesting dielectric strengthElectricityUltraviolet
The invention discloses a method for seeking discharge regions of power devices on ultraviolet images, which comprises the following steps: firstly collecting the ultraviolet images, carrying out pretreatment on the ultraviolet images, further detecting corona regions on the ultraviolet images by treating visible light images stacked together on the collected ultraviolet images, initially detecting the discharge regions, and then removing the interferences of a plurality of backgrounds according to the features of the corona regions for each ultraviolet image; determining whether the devices in the region discharge or not by using a plurality of frames of images for tracking; and the method can simultaneously track a plurality of discharge regions on each image. The method can carry out analysis and diagnosis on the collected images in a real-time on-line manner under the airborne real-time detection requirement in a helicopter patrol inspection system, and determine whether a power transmission line has defects or not; furthermore, the method is characterized by improving the efficiency of line inspection and improving the accuracy of defect diagnosis.
Owner:STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD SHAOXING POWER SUPPLY CO +1
Methods and apparatus for registering and warping image stacks
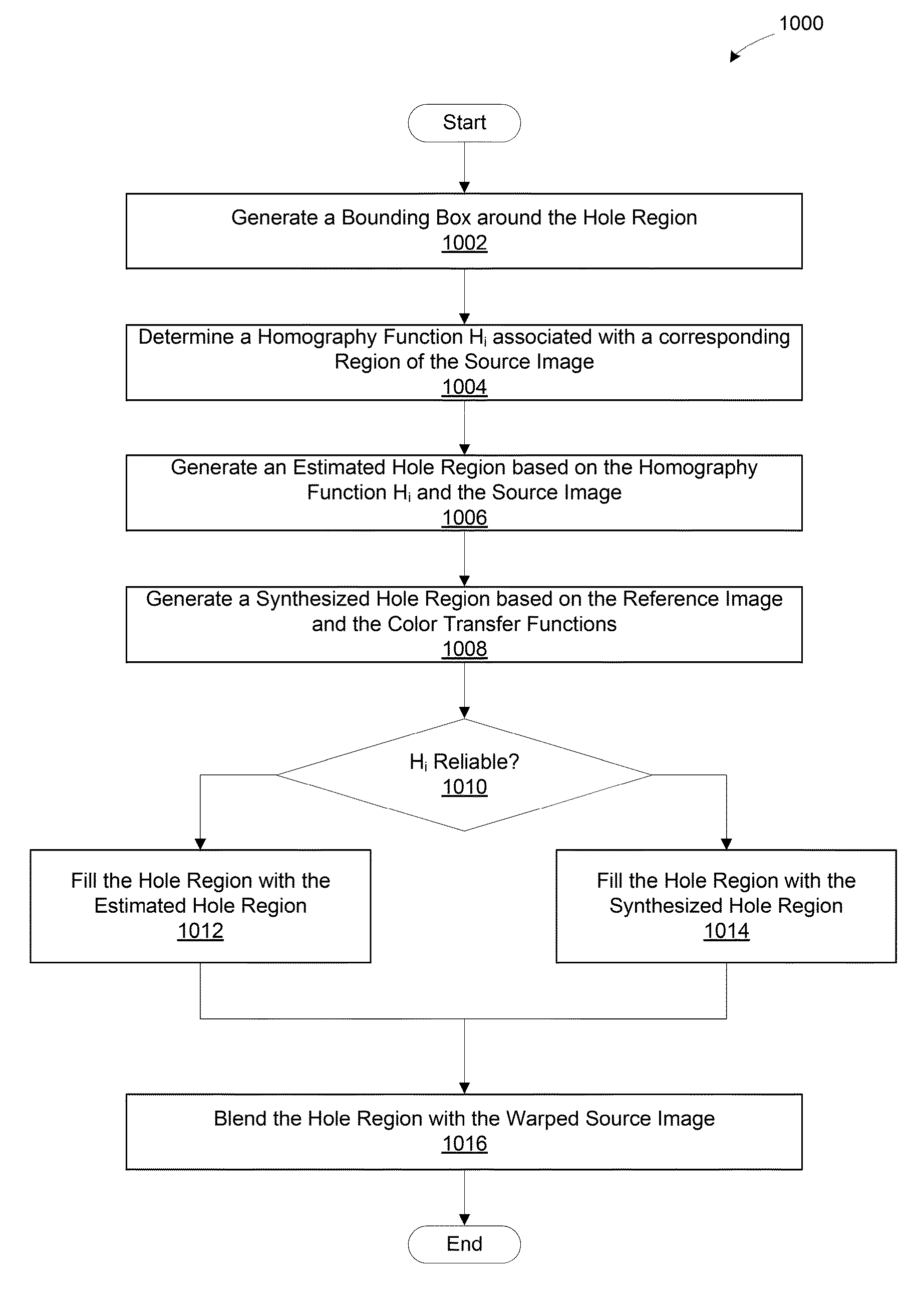
ActiveUS20140119595A1Promote resultsGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionReference imageSource image
A set of images is processed to modify and register the images to a reference image in preparation for blending the images to create a high-dynamic range image. To modify and register a source image to a reference image, a processing unit generates a correspondence map for the source image based on a non-rigid dense correspondence algorithm, generates a warped source image based on the correspondence map, estimates one or more color transfer functions for the source image, and fills the holes in the warped source image. The holes in the warped source image are filled based on either a rigid transformation of a corresponding region of the source image or a transformation of the reference image based on the color transfer functions.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Techniques for registering and warping image stacks
ActiveUS20140118402A1Less computational effortRobust resultImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageRigid transformation
A set of images is processed to modify and register the images to a reference image in preparation for blending the images to create a high-dynamic range image. To modify and register a source image to a reference image, a processing unit generates correspondence information for the source image based on a global correspondence algorithm, generates a warped source image based on the correspondence information, estimates one or more color transfer functions for the source image, and fills the holes in the warped source image. The holes in the warped source image are filled based on either a rigid transformation of a corresponding region of the source image or a transformation of the reference image based on the color transfer functions.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Image feature extraction method and saliency prediction method using the same
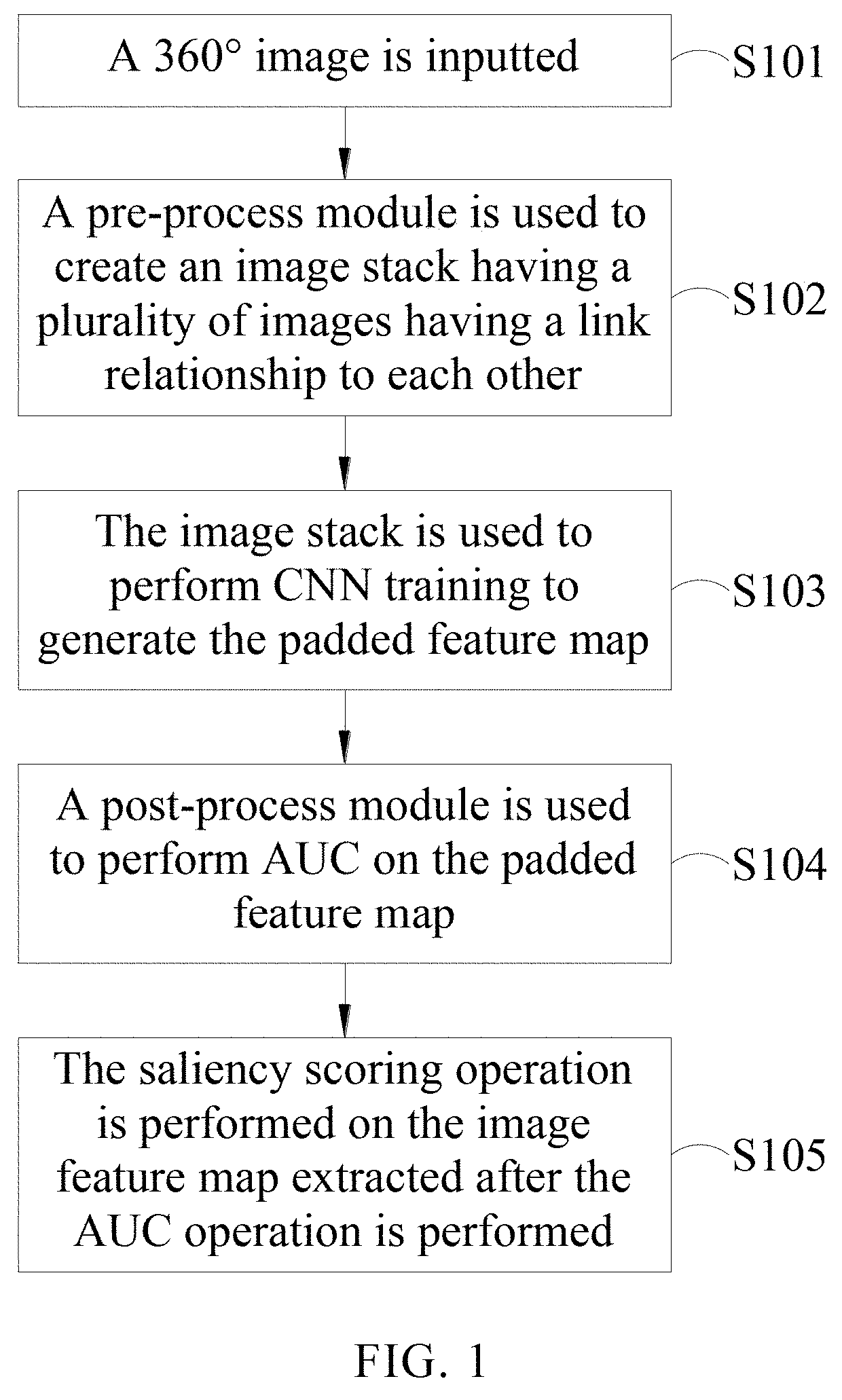
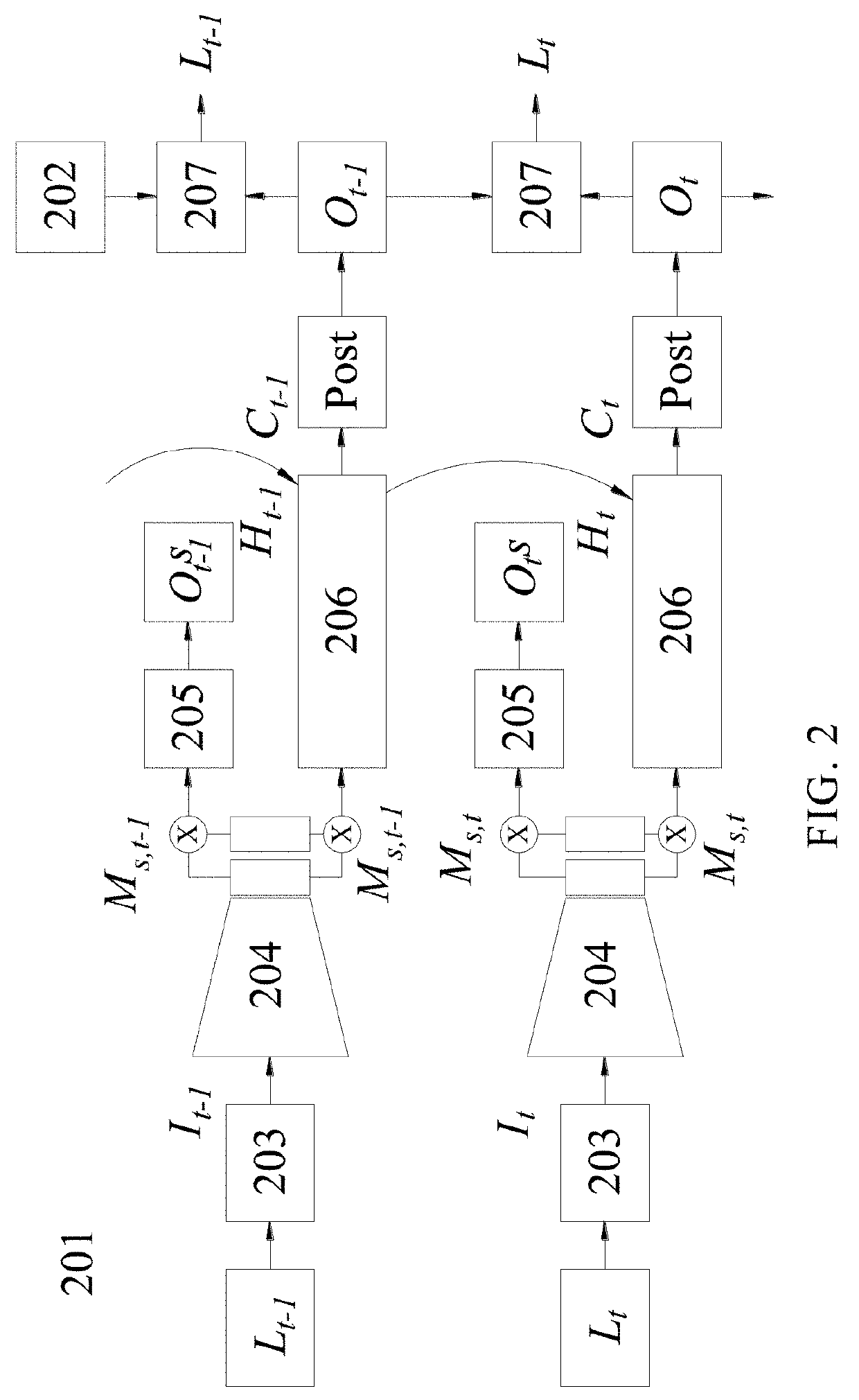
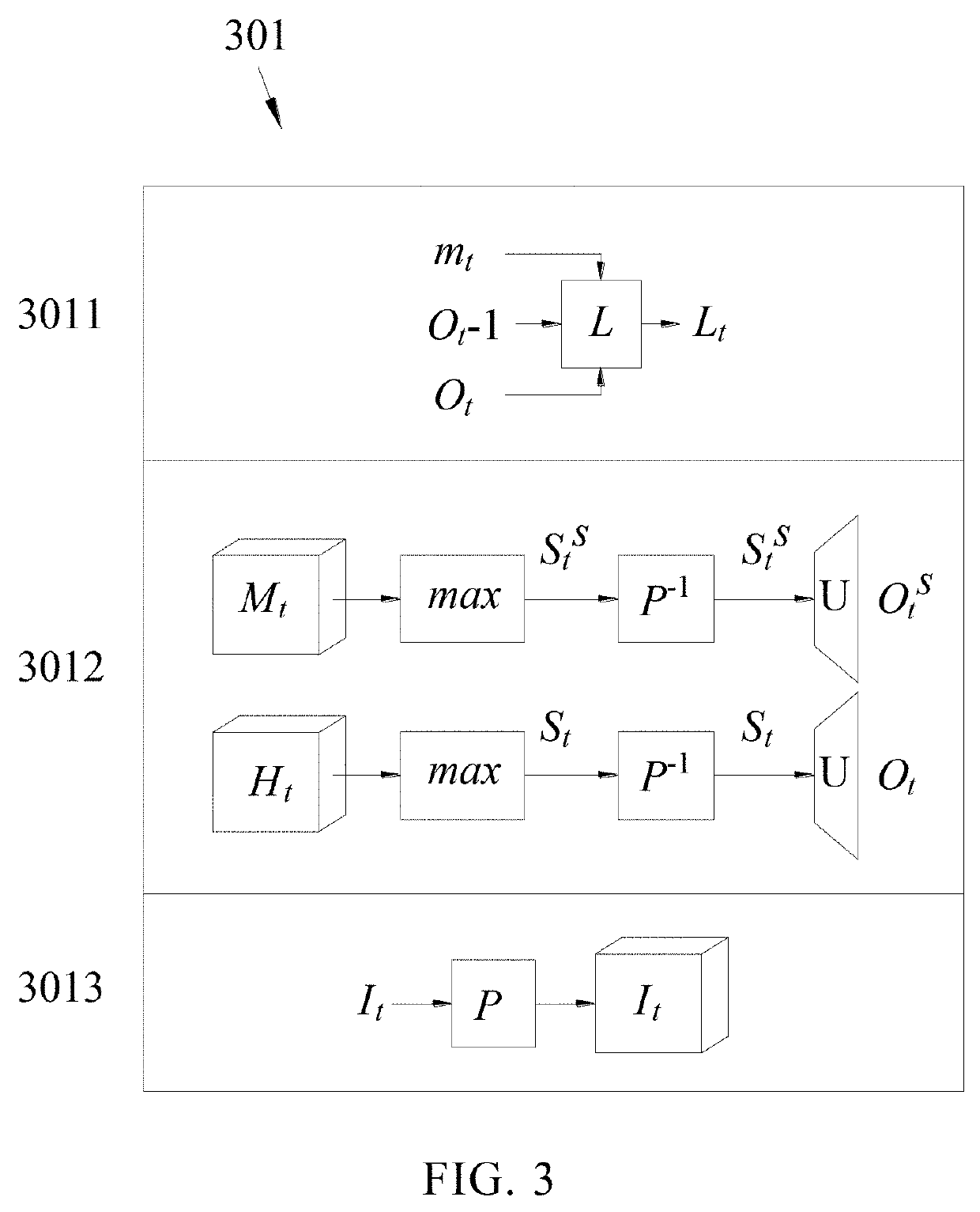
InactiveUS20190355126A1Reduce distortion problemsImprove image feature map extraction qualityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionImaging Feature
An image feature extraction method for a 360° image includes the following steps: projecting the 360° image onto a cube model to generate an image stack including a plurality of images having a link relationship; using the image stack as an input of a neural network, wherein when operation layers of the neural network performs padding operation on one of the plurality of images, the link relationship between the plurality of adjacent images is used such that the padded portion at the image boundary is filled with the data of neighboring images in order to retain the characteristics of the boundary portion of the image; and by the arithmetic operation of the neural network of such layers with the padded feature map, an image feature map is generated.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Classifying image features
Methods are disclosed for classifying different parts of a sample into respective classes based on an image stack that includes one or more images.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
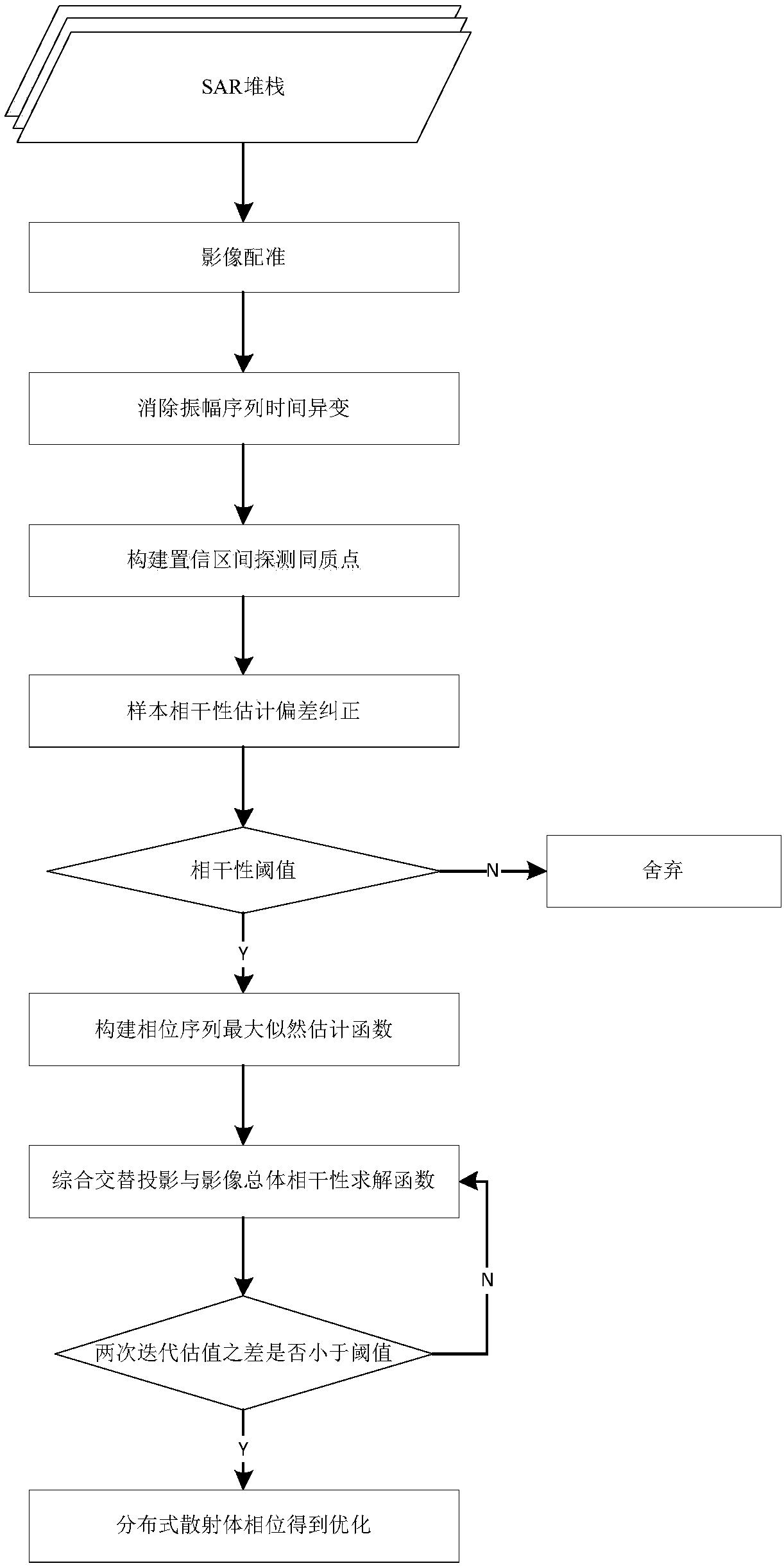
InSAR distributed scatterer phase optimization method
ActiveCN108051810AHigh precisionImprove computing efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmConfidence interval
The invention belongs to the technical field of interferometry synthetic aperture radar data processing, and discloses an InSAR (Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar) distributed scatterer phase optimization method. The InSAR distributed scatterer phase optimization method includes the steps: acquiring SAR image stacks of the same region, selecting the main image, and successively registering the residual images to the main image geometrical space; detecting the amplitude sequence time variation values of the pixels in the image, and rejecting the amplitude sequence time variation values; constructing a confidence interval, determining whether the amplitude sequence mean value of each pixel in a fixed window taking the pixel as the center in the image falls into the confidence interval,and if so, determining that the point is the statistical homologous points SHPs of the central pixel; calculating the value of assessment of the sample coherent coefficient of the pixel, and performing deviation correction; according to the threshold, identifying the distributed scatterers in the image; constructing the maximum likelihood estimation function of the distributed scatterer phase sequence; and solving the maximum likelihood estimation function to obtain the optimal solution and complete phase optimization. Compared with the prior art, the InSAR distributed scatterer phase optimization method has the advantages of high accuracy, wide application range, and high operation efficiency.
Owner:南京市测绘勘察研究院股份有限公司
Method to define the 3D oblique cross-section of anatomy at a specific angle and be able to easily modify multiple angles of display simultaneously
InactiveUS20060291717A1Easy to modifyCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyControl lineImage plane
The present invention provides a system and a method for simultaneously modifying one or more angles of cross-sections in one or more cross-sectional images or stacks of images of a 3D volume. A plurality of viewports is displayed to a user. Each viewport includes a 2D cross-sectional image or stack of images and all 2D images or stacks of images are displayed simultaneously. One or more viewports may also include a control line representative of an angle of cross-section or image plane of a 2D image or stack of images displayed in another viewport. If a control line is moved in a selected viewport, the angle of cross-section or image plane of a 2D image or stack of images in another viewport is accordingly altered simultaneous with such control line movement.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for production of tomographic section images of a periodically moving object with a number of focus detector combinations
InactiveUS7039152B2Optimize timingNone is suitable for purposeRadiation/particle handlingComputerised tomographsTime correlationCt scanners
A method and CT scanner are proposed for the production of tomographic section images, in particular X-ray CT images, of a periodically moving object with periodically changing movement and rest phases. For scanning, a number of focus detector combinations with flat detectors are moved on coaxial spiral paths and movement signals from the moving object are measured at the same time in order to detect movement and rest phases. Further, the time correlation between the movement data and the detector output data stored and axial segment image stacks are then reconstructed independently of one another from sub-segments of the spiral paths using the detector output data from each detector which represent a rest phase of the moving object. Additionally, segment image stacks from the n spiral paths of the n focus detector combinations at the correct time are added up in a complementary angle form and in layers to form 180° tomography section images. The axial segment image stacks are reconstructed in a first step from double-inclined reconstruction planes. Further, in a second step, they are reformatted to produce axial segment image stacks, and detector data from a number of successive movement periods are used for this purpose.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
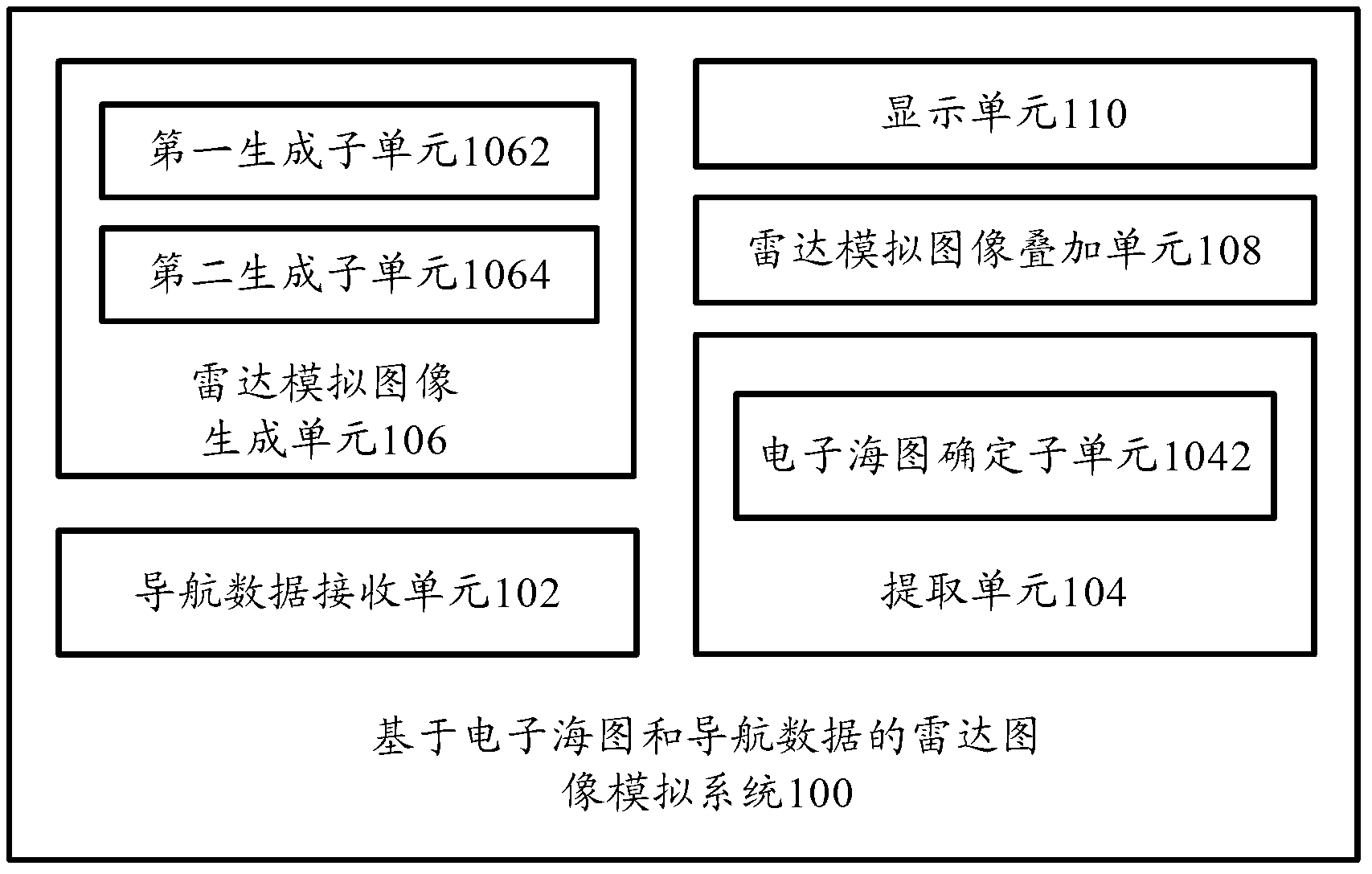
Radar image simulation system and method based on electronic chart and navigation data
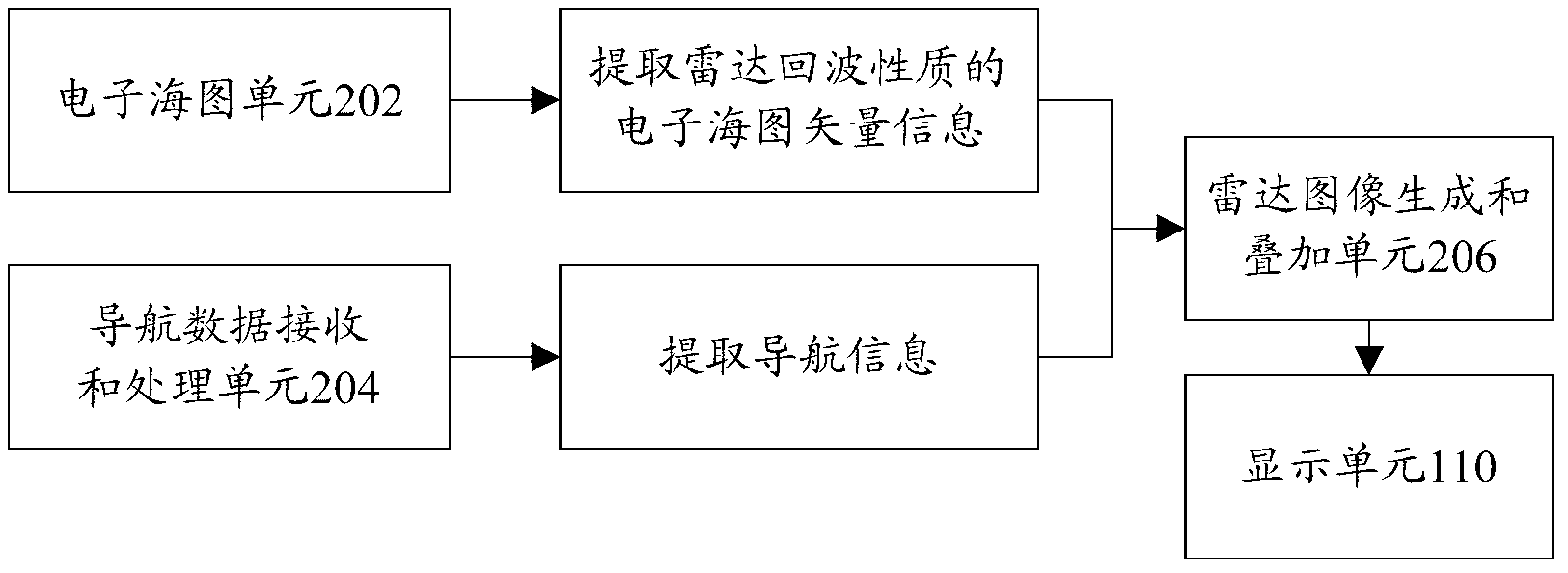
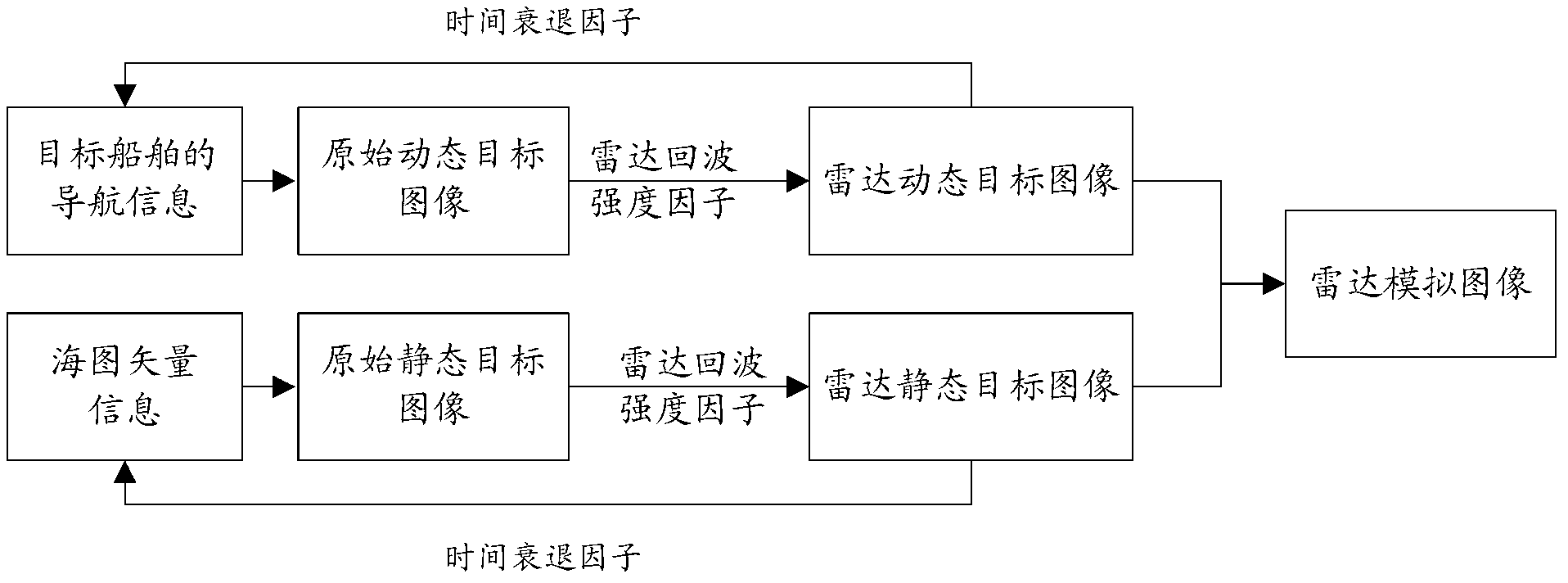
ActiveCN103175525AReduce display effectReduce dead addresses and other phenomenaNavigation instrumentsReal time navigationRadar
The invention provides a radar image simulation system and method based on an electronic chart and navigation data. The radar image simulation system comprises a navigation data receiving unit for receiving and processing real-time navigation data of a ship, an extracting unit for extracting electronic chart vector information from the electronic chart in a corresponding range according to the real-time navigation data, a radar analog image generating unit for generating radar analog images according to the electronic chart vector information and the real-time navigation data, a radar analog image stacking unit for stacking the radar analog images on the electronic chart in the corresponding range, and a display unit for displaying the stacked electronic chart. According to the invention, the radar images of the real-time dynamic ship are stacked, no radar data needs to be acquired, and the radar images can be generated without a complex coordinate transformation algorithm, so that the product cost is reduced while the offset of the stack of the radar images of the electronic chart and the storage space of a computer are reduced.
Owner:无锡挪瑞科技股份有限公司
Fluorescent microscopic image rebuilding method and system based on space variation point spread function
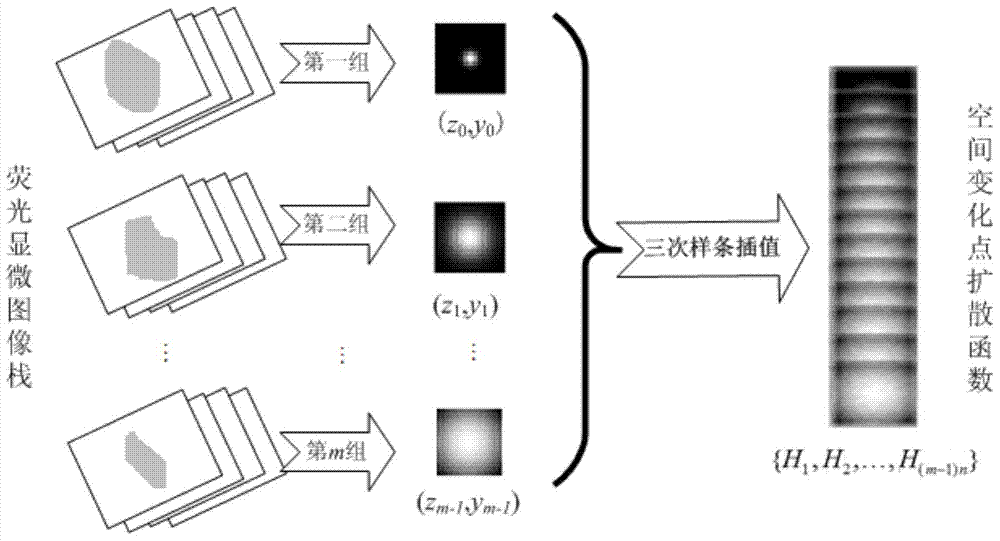
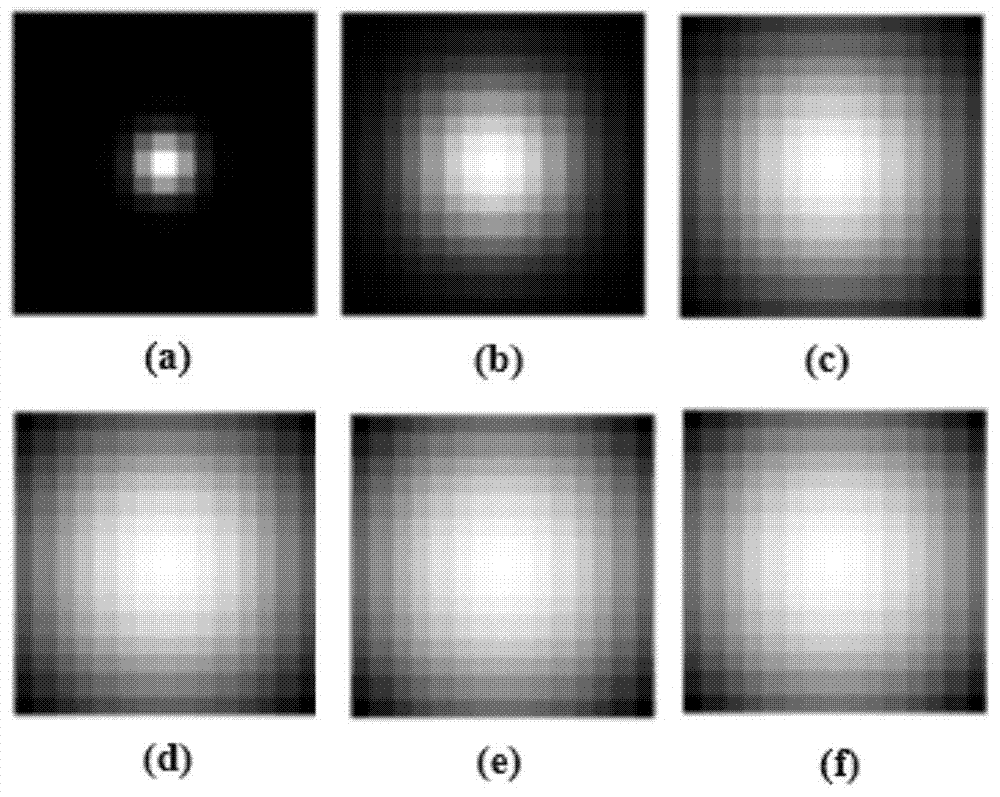
InactiveCN104751425ASmooth transitionOvercome local shortcomingsImage enhancementMicroscopic imagePoint spread
The invention provides a fluorescent microscopic image rebuilding method based on a space variation point spread function. The method comprises the following steps: S1, inputting a fluorescent microscopic image sequence, and dividing the fluorescent microscopic image into a plurality of groups of image stacks according to a preset condition; S2, obtaining a pot spread functions of images in the central positions of each group of image stacks, and taking the point spread functions as the point spread functions of the image stacks; S3, forming a point spread function sequence by the point spread functions of each group of image stacks, and processing the point spread function sequence to obtain an interpolation function of a preset spatial depth; S4, obtaining the spatial point spread functions of each group of image stacks according to the interpolation function; S5, carrying three-dimensional rebuilding of the fluorescent microscopic image according to the spatial point spread functions. The method provided by the invention is good in integrity and high in interpolation function. The invention further provides a fluorescent microscopic image rebuilding system based on the space variation point spread function.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
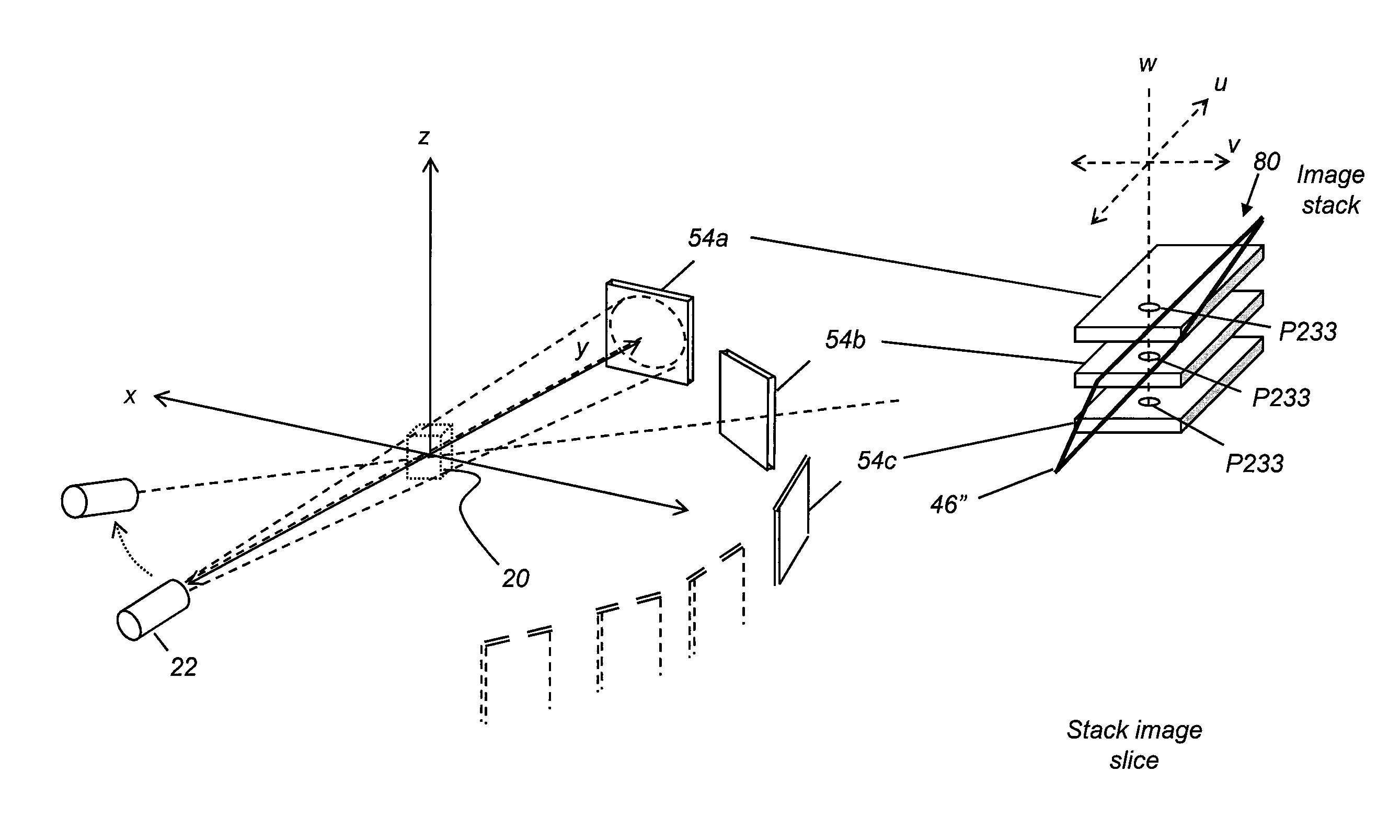
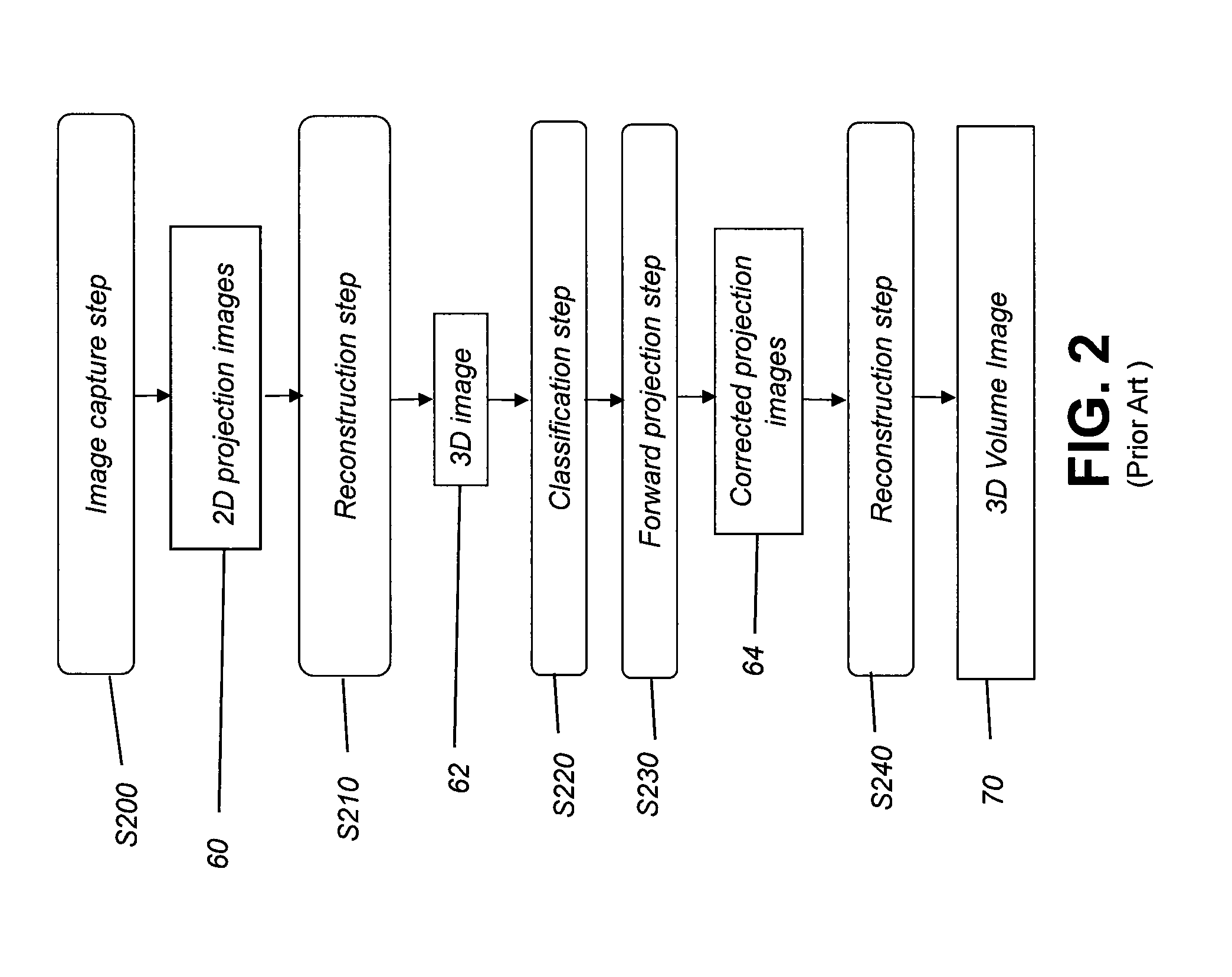
Metal artifacts reduction for cone beam ct using image stacking
InactiveUS20150178917A1Improve efficiencyReduce computing needsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactLight beam
Method and / or apparatus embodiments can process volume image data of a subject. An exemplary method includes obtaining a first group of two-dimensional radiographic images of the subject, wherein each of the images is obtained with a detector and a radiation source at a different scan angle. The method arranges image data from the first group of images in an image stack so that corresponding pixel data from the detector is in register for each of the images in the image stack. Pixels that represent metal objects are segmented from the image stack and data replaced for at least some of the segmented pixels to generate a second group of modified two-dimensional radiographic images. The second group of images is combined with the first group to generate a three-dimensional volume image according to the combined images and an image slice from the three-dimensional volume image is displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com