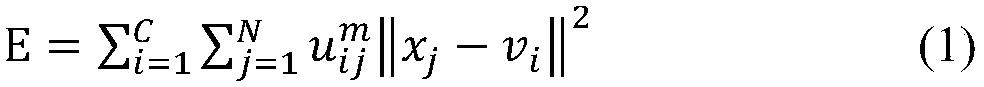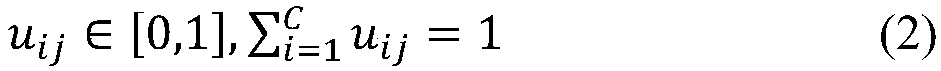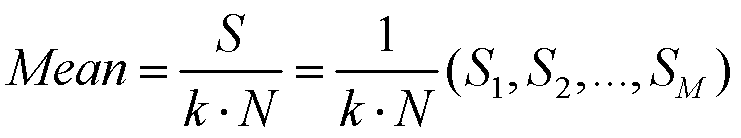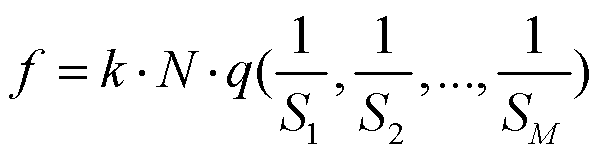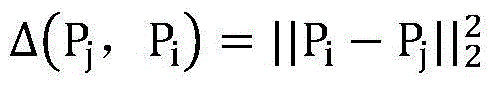Patents
Literature
234 results about "Ideal image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Steel rail surface defect image adaptive segmentation method
InactiveCN106251361AQuick extractionEfficient extractionImage enhancementImage analysisIdeal imageNon local
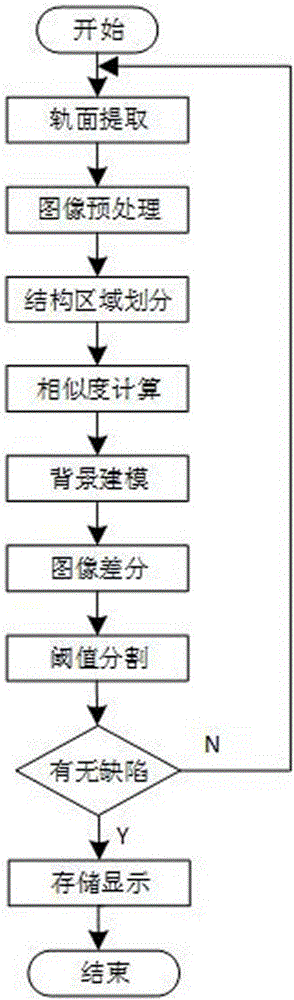
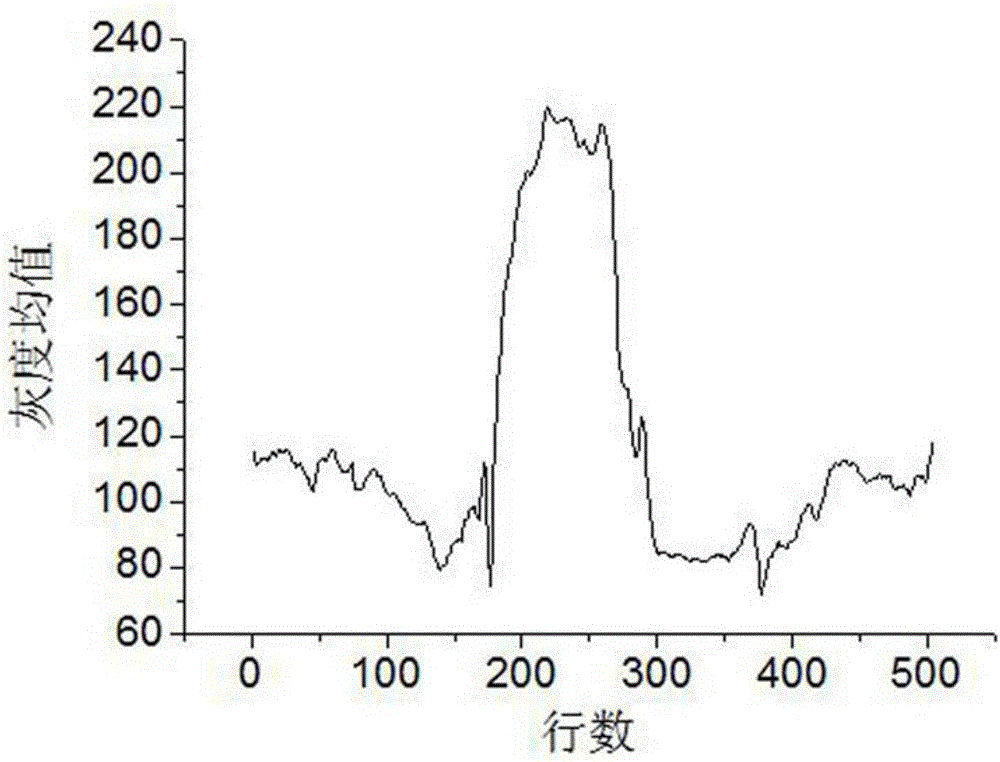
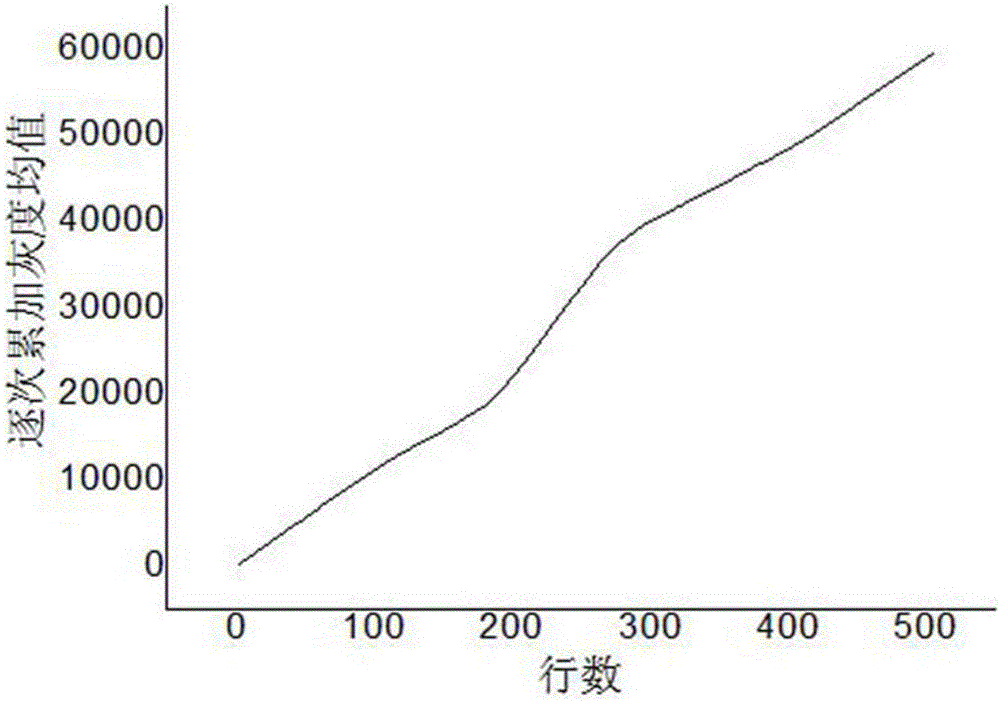
The invention discloses a steel rail surface defect image adaptive segmentation method. The method comprises the following steps of S1, extracting a steel rail region by adopting a row grayscale mean successive summation method; S2, preprocessing a steel rail region image; S3, performing structure region and non-structure region division on the steel rail region image; S4, further distinguishing a defective region and a shadow region by utilizing a non-local feature of the image in the structure region; S5, adaptively building a background image model according to different features in the image; S6, performing image difference; and S7, performing dynamic threshold segmentation. The image is divided into the structure region and the non-structure region by utilizing image local information, the size of a pixel neighborhood window is adaptively adjusted by utilizing non-local information to calculate a mean, the accurate background image model is built, and the image difference and the dynamic threshold setting are performed, so that while a defective part of the image is highlighted, the influence of uneven illumination and steel rail surface reflection property on steel rail surface defect detection is effectively reduced, an ideal image segmentation effect is achieved, and the rail surface detection precision is ensured.
Owner:LANZHOU JIAOTONG UNIV
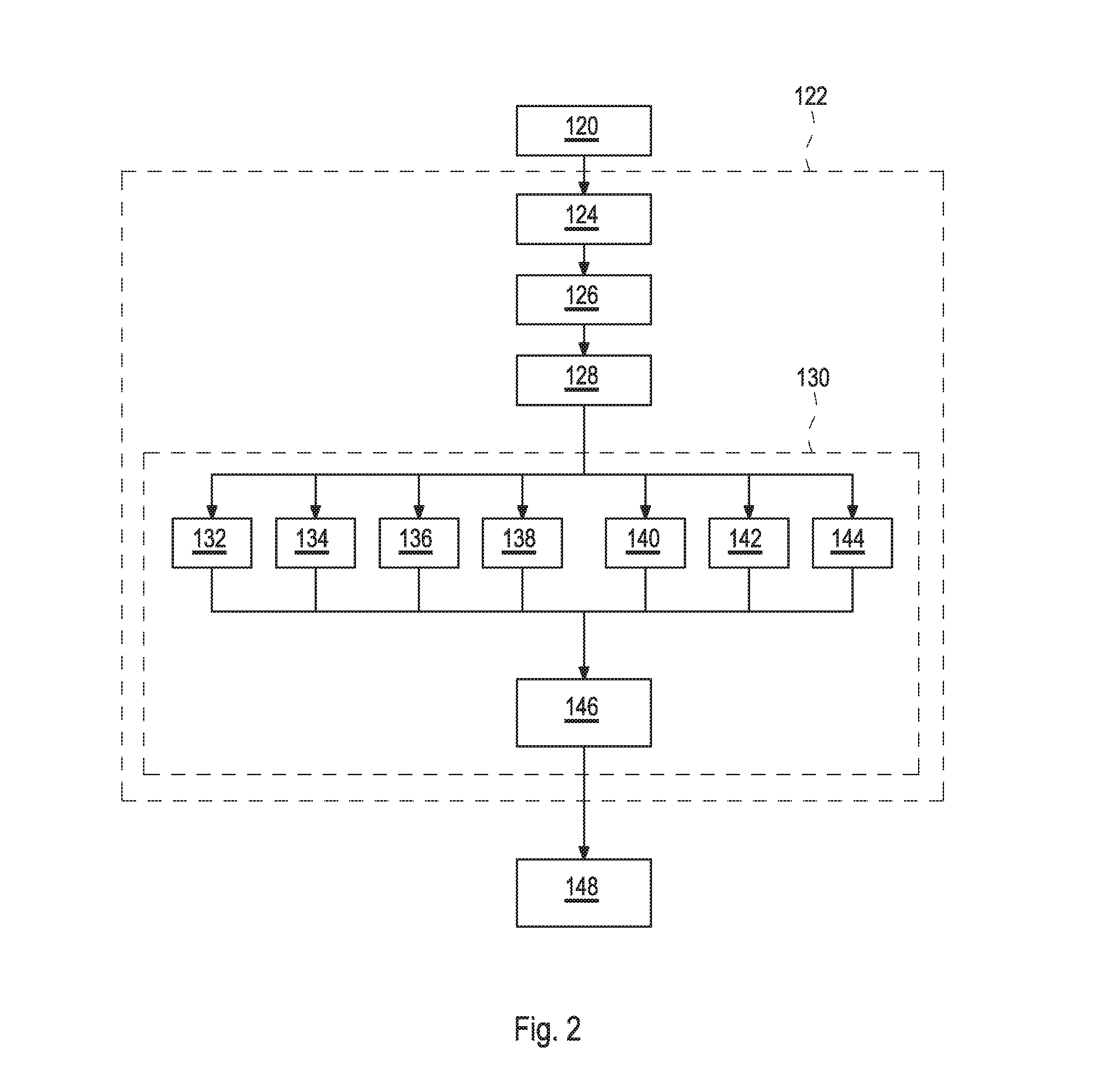
Modification of an image of a pattern during an imaging process
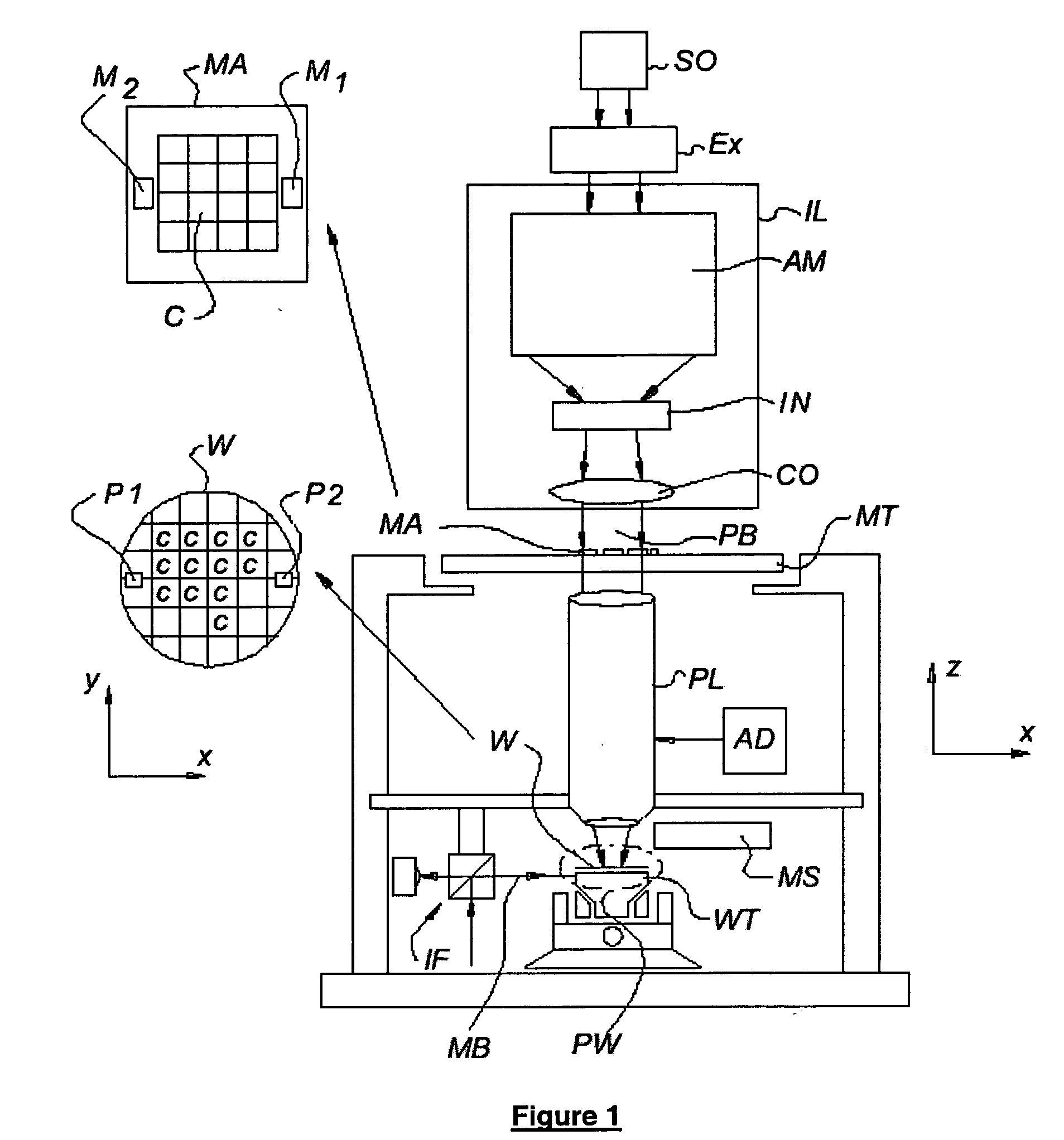
InactiveUS20050210438A1Correction errorMinimize biasSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIdeal imageImaging quality
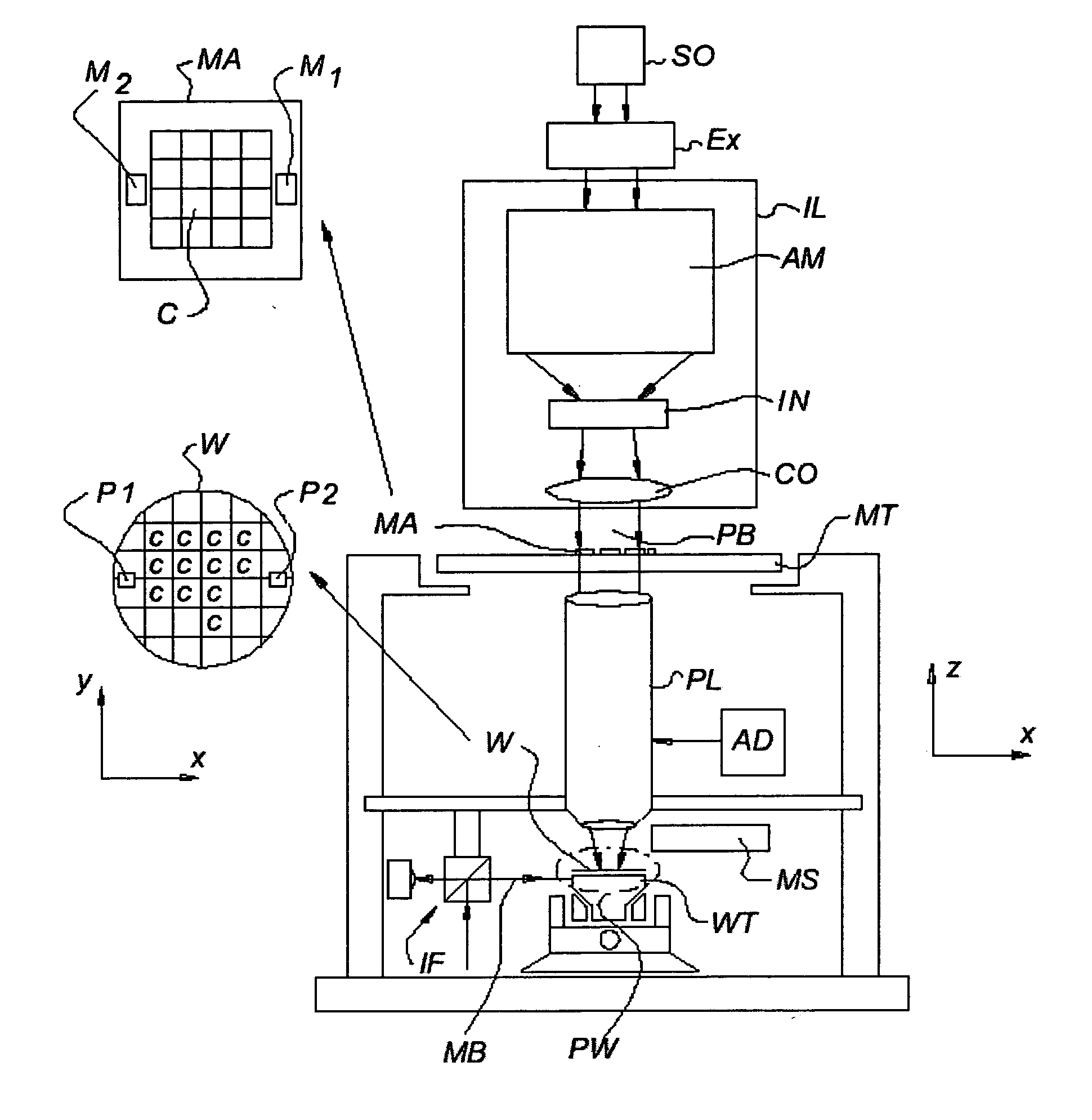
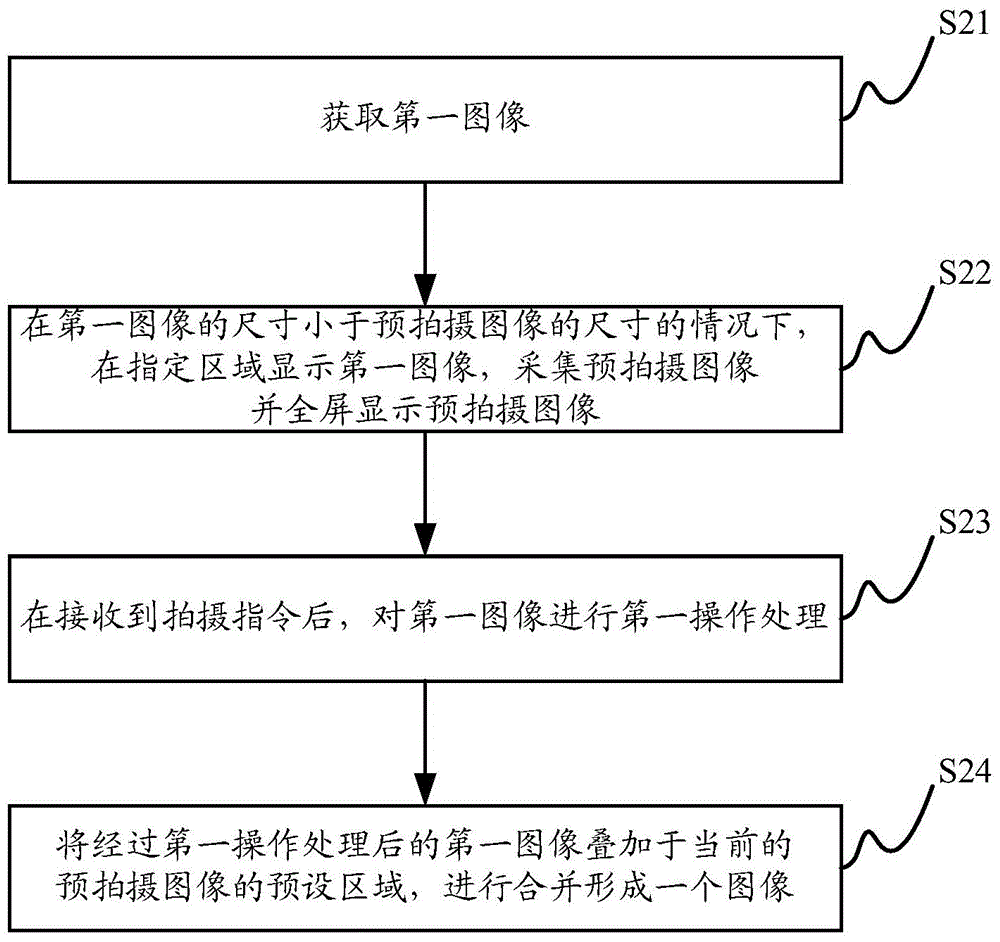
A method is provided for modifying an image of a pattern during a lithographic imaging process, where the pattern is arranged on a mask for imaging by a projection system on a surface, and the image is an image formed from the pattern by the projection system. In this method the imaging quality of the projection system is described by selected imaging quality parameters, and the image is adjustable by image adjustment parameters of the projection system. The method comprises the steps of determining an ideal image of the pattern, determining a simulated distorted image of the pattern based on the selected imaging quality parameters; determining a deviation between the simulated distorted image and the ideal image, and adapting the image adjustment parameters during the imaging process to minimize the deviation between the simulated distorted image and the ideal image on the basis of the selected imaging quality parameters.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
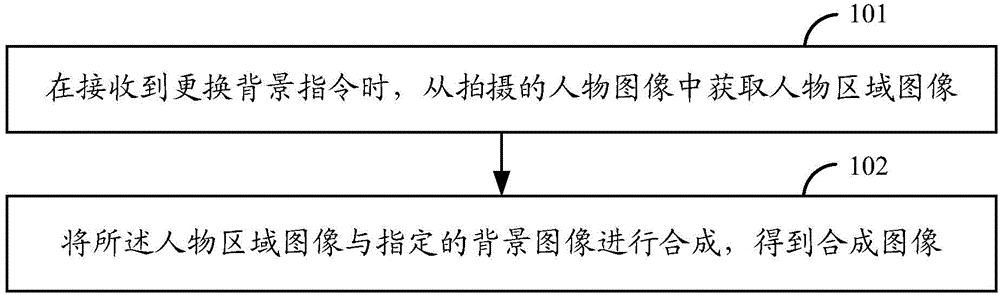
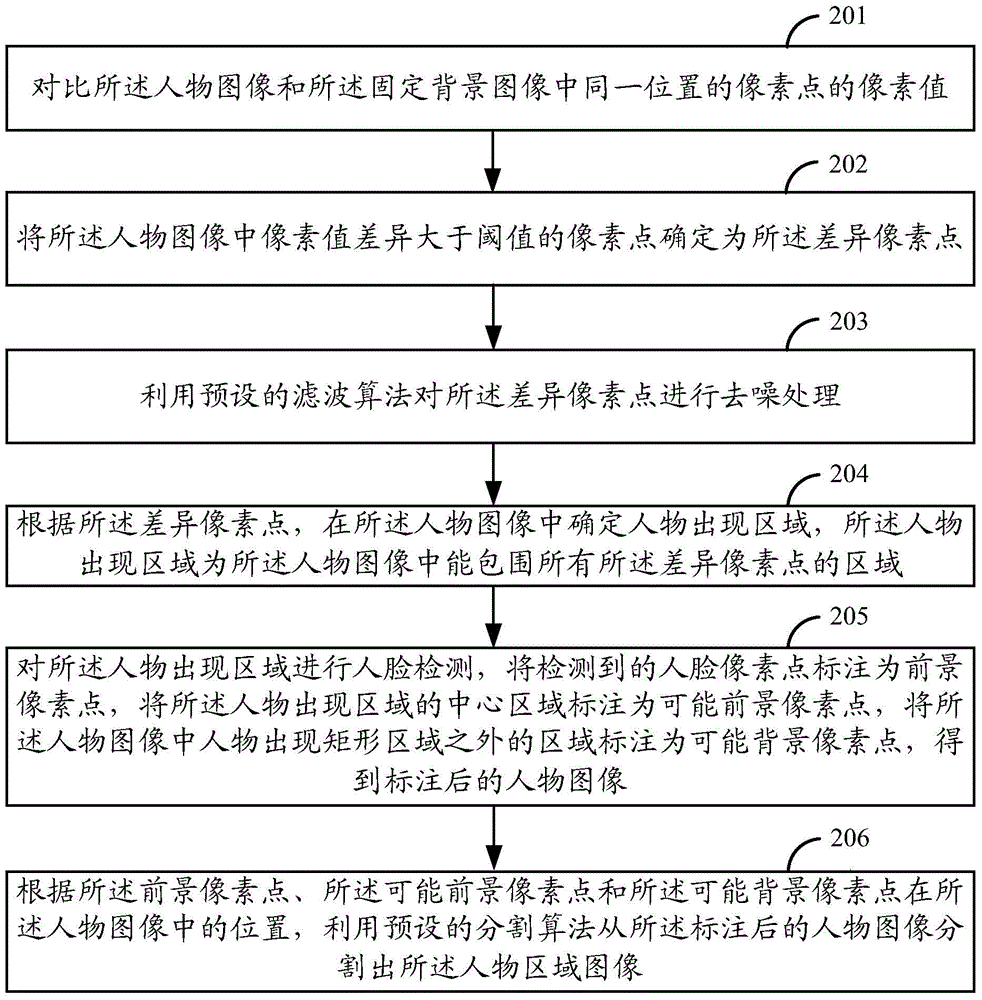
Picture processing method and picture processing device
InactiveCN104902189AImprove experienceAdjust the imaging effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsIdeal imageUser input
The present invention relates to a picture processing method and a picture processing device. The method comprises acquiring a figure region image from a photographed figure image when receiving a background replacing command; and compositing the figure region image and an appointed background image, to obtain a composite image. According to the method, when a user inputs the background replacing command, the figure region image can be acquired from the figure image of the user and then can be composited with the background image appointed by the user. Therefore, the user can replace the background of an image at will to his / her preference and can flexibly adjust the imaging effect of the composite image by replacing different background images so as to ultimately acquire an ideal image, and the user experience is excellent.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
Automated display quality measurement device
InactiveUS20090262341A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionIdeal imageQuality assurance
A method and apparatus for automating a quality assurance test conducted on display devices used for diagnostic imaging. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes an automated mechanical system for scanning a light meter over a test pattern displayed on a display device. In another embodiment, the method comprises an automated method of comparing the measured data from the light meter with an ideal image. In another embodiment, the method comprises obtaining a digital image of the test pattern displayed on the display device, and the digital image is compared with an ideal image.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
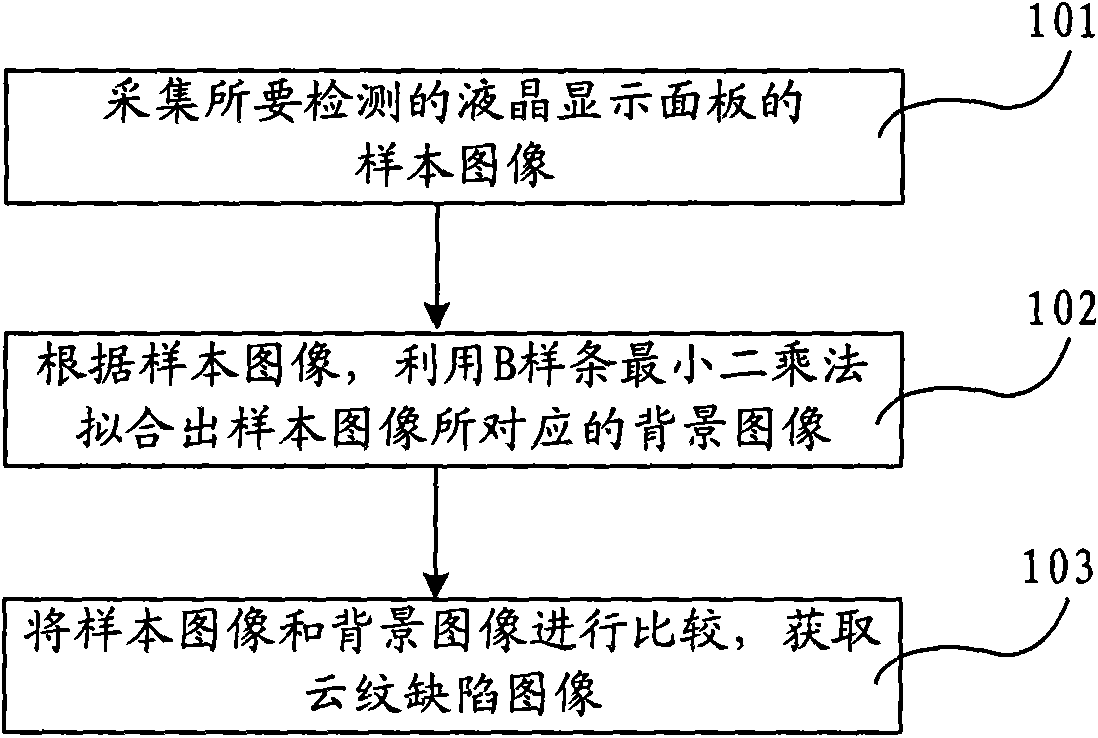
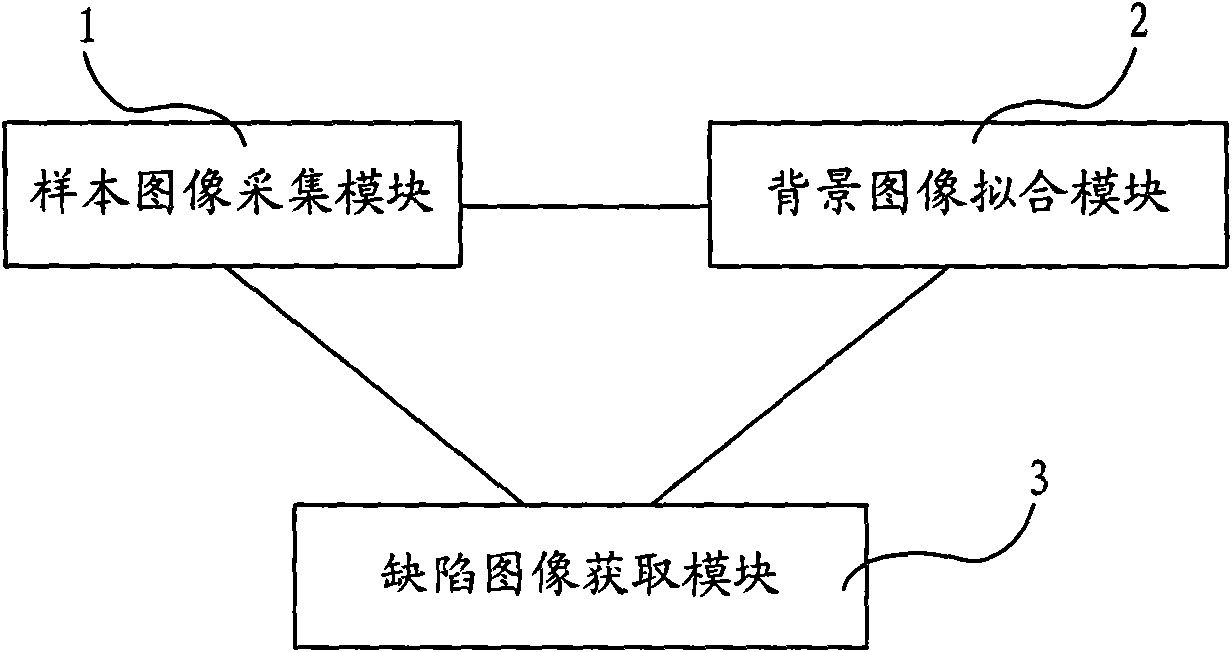
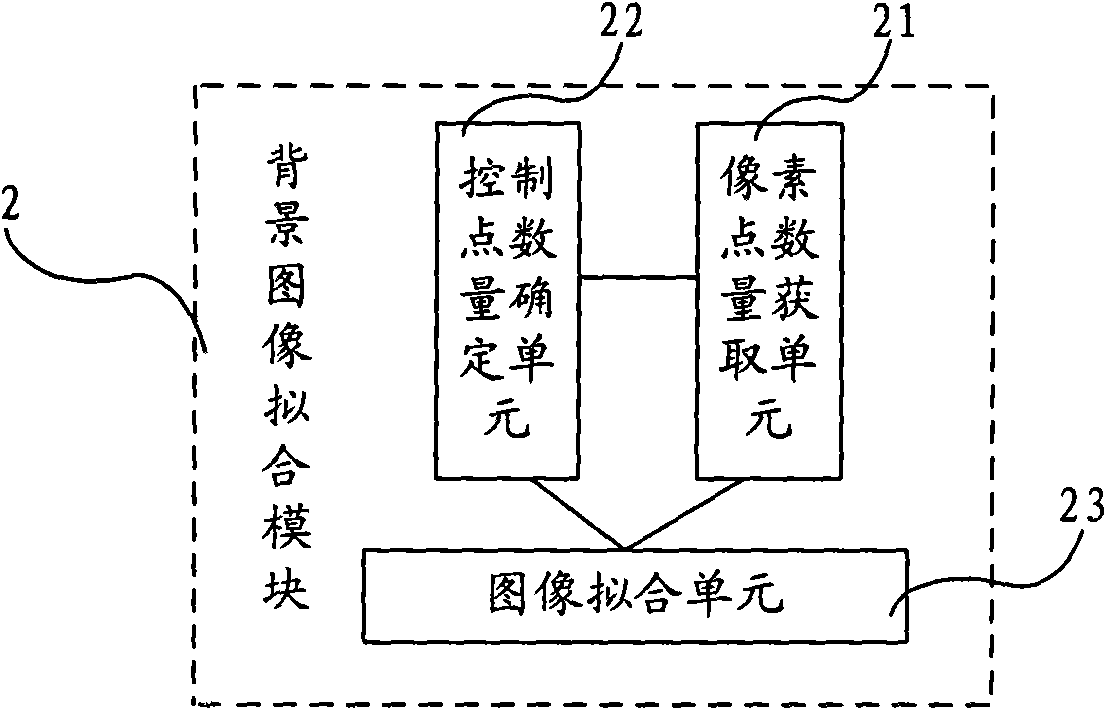
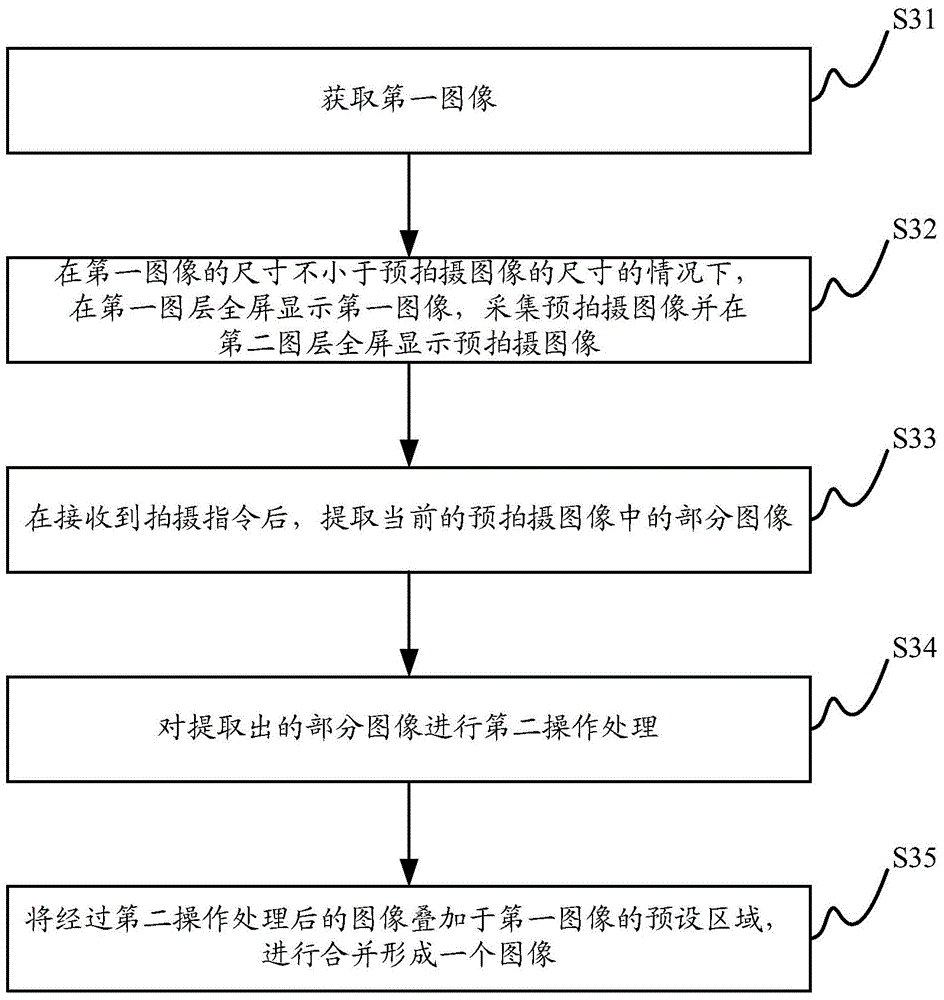
Method and device for detecting cloud pattern defects of liquid crystal display panel
InactiveCN101655614AImprove detection efficiencyImprove detection accuracyImage analysisNon-linear opticsIdeal imageSample image
The invention provides a method and a device for detecting cloud pattern defects of a liquid crystal display panel, wherein the method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring sample images of theliquid crystal display panel to be detected; 2, according to the sample images, fitting out background images corresponding to the sample images by using a B spline least square method; and 3, comparing the sample images with the background images so as to obtain images of the cloud pattern defects. The device for detecting the cloud pattern defects of the liquid crystal display panel comprises asample image acquisition module, a background image fitting module and a defect image acquisition module. The method and the device for detecting the cloud pattern defects of the liquid crystal display panel can improve the efficiency and the accuracy of detecting the cloud pattern defects of the liquid crystal display panel, and can acquire ideal images of the cloud pattern defects.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
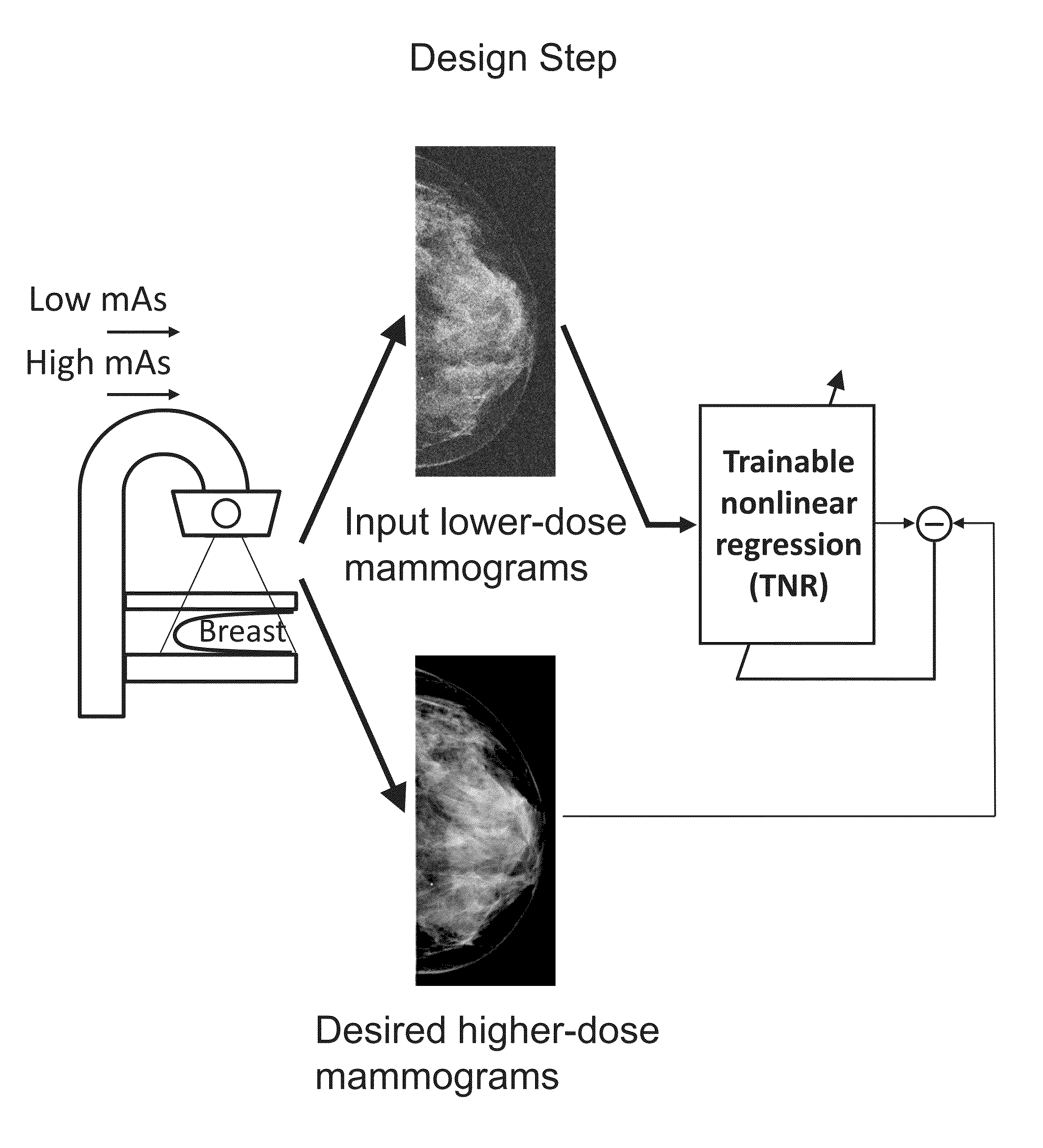
Converting low-dose to higher dose mammographic images through machine-learning processes
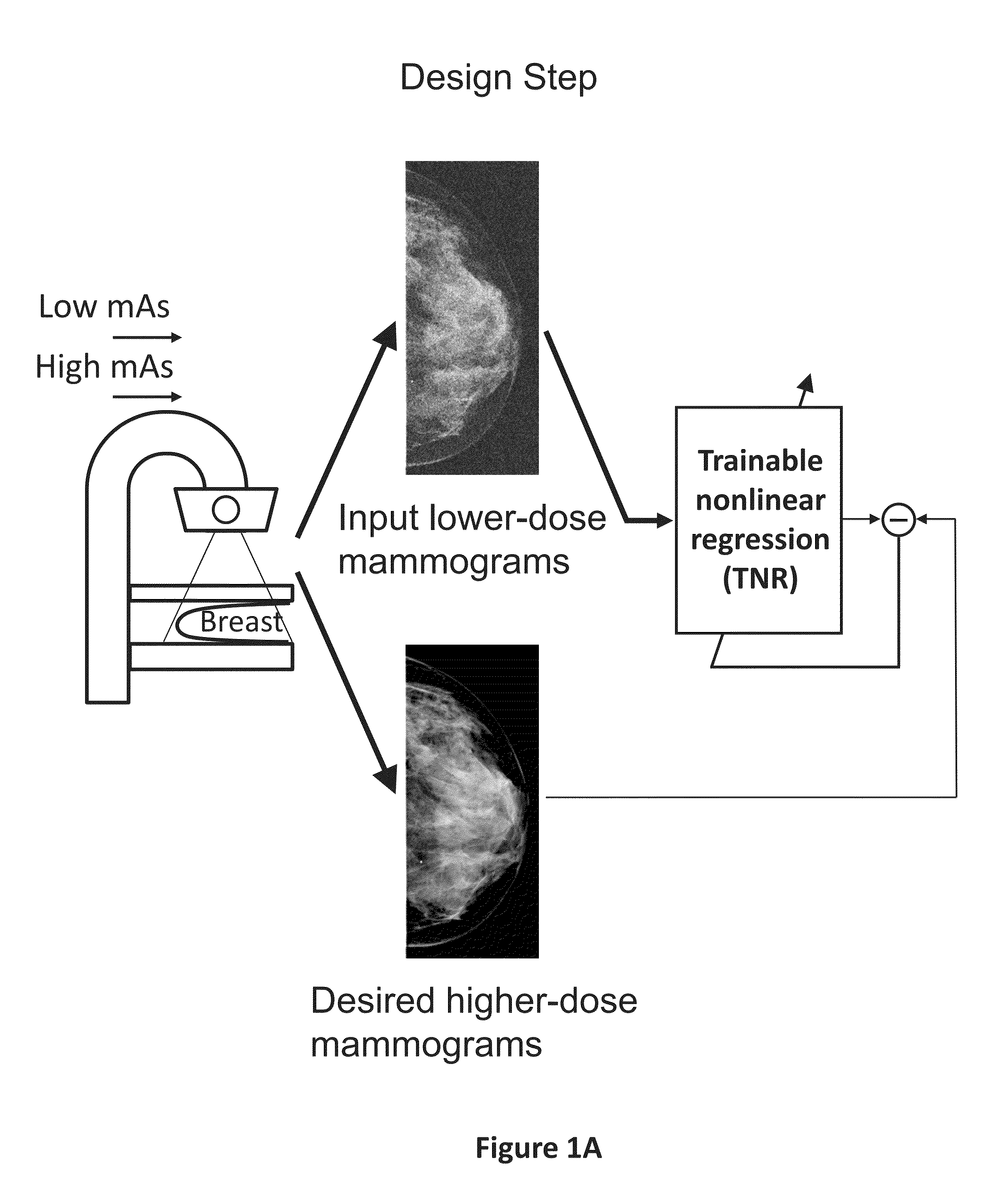
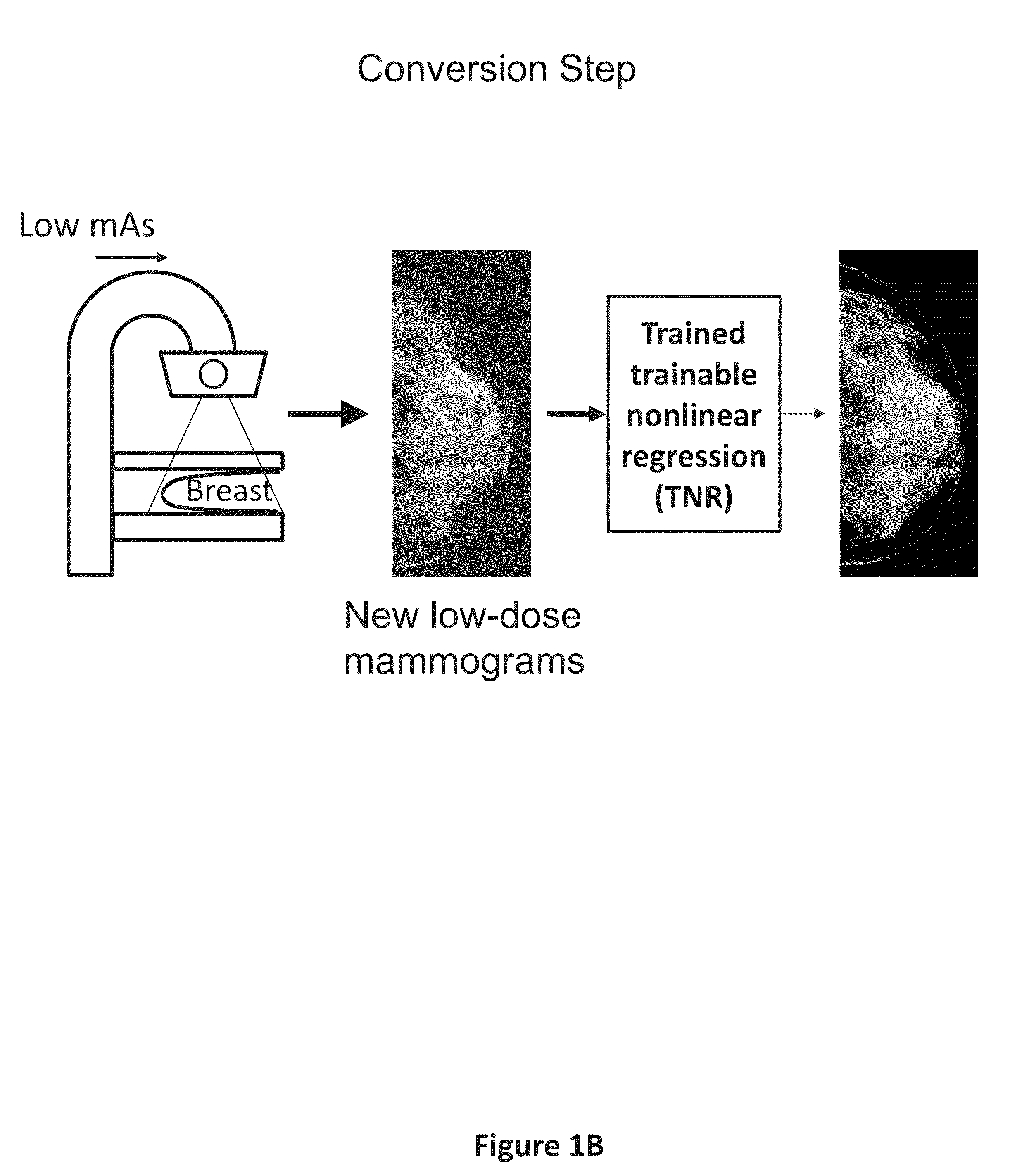
ActiveUS20150196265A1Improve image qualityEasy to detectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging qualityX-ray
A method and system for converting low-dose mammographic images with much noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like mammographic images, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme, which can be called a call pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input mammogram acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of mammograms, inputting low-dose mammograms together with corresponding desired standard x-ray radiation dose mammograms (higher-dose), which are ideal images for the output images. Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose mammograms to high-dose-like mammograms. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose mammograms anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) mammogram is entered, the trained PTNR would output a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it would output high-dose-like mammograms or “virtual high-dose” mammograms where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. With the “virtual high-dose” mammograms, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
Image processing method and equipment
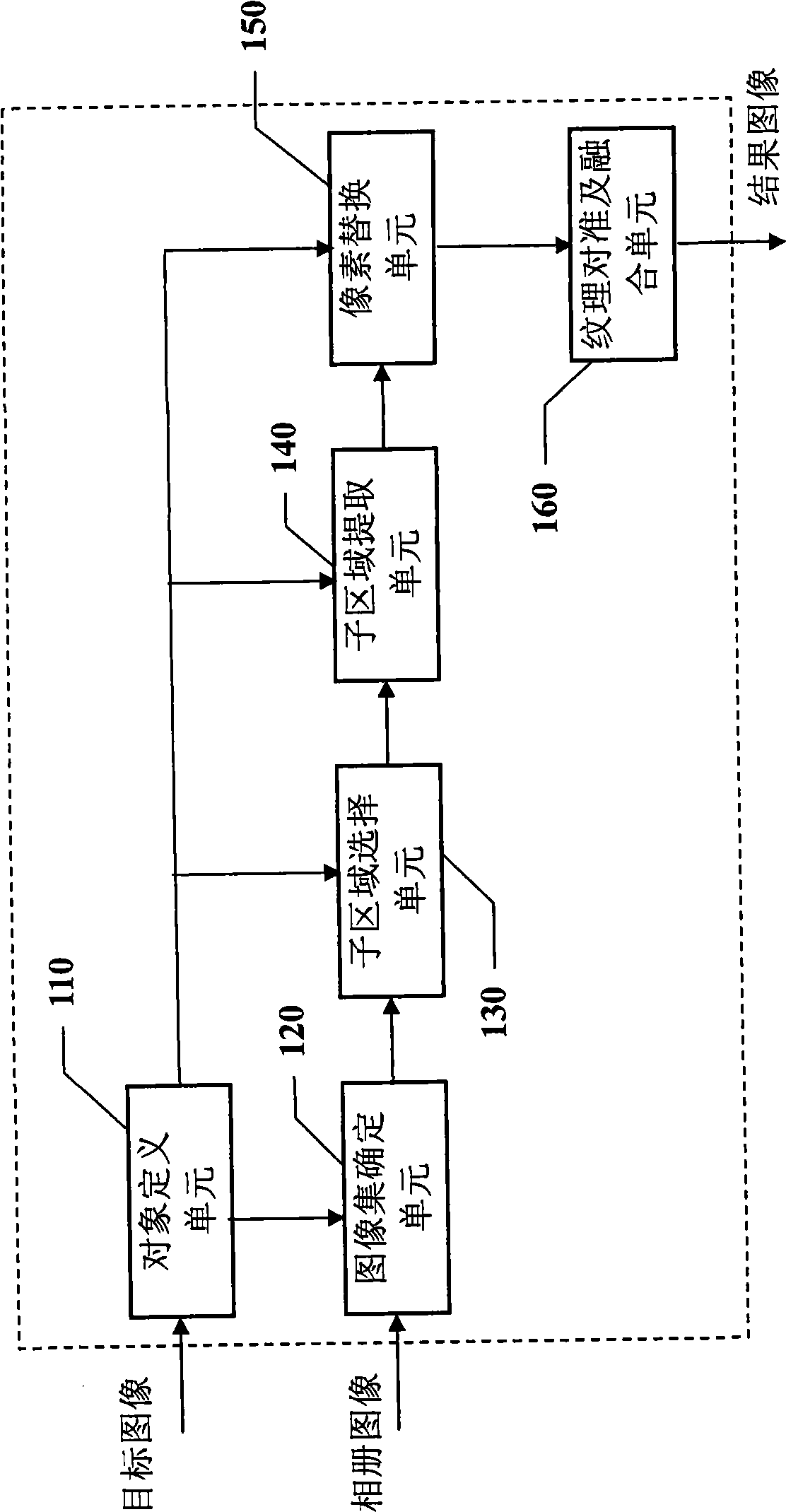
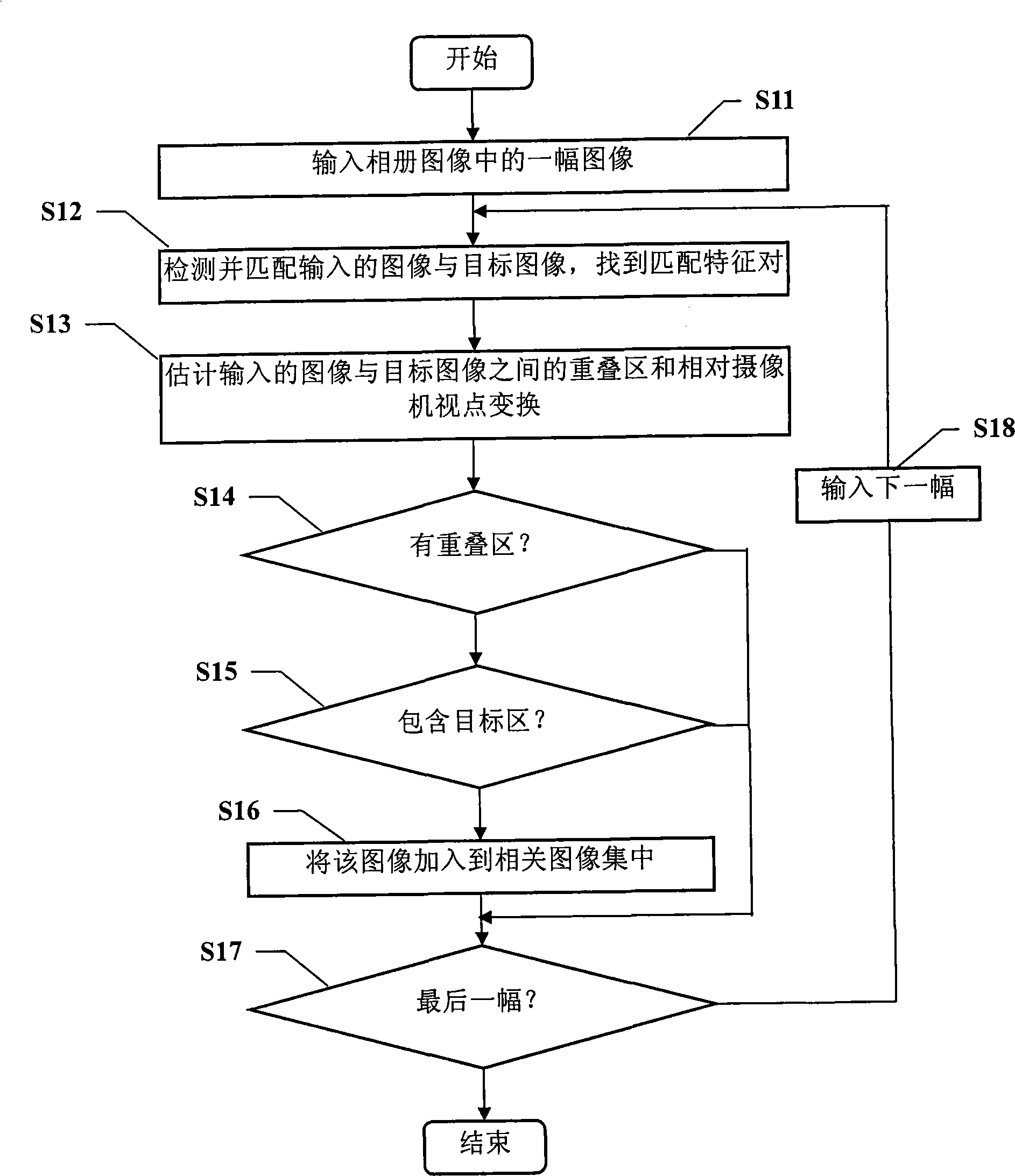
The invention discloses a method and a device for processing an image, used to remove a removed object in a target image and repair the target image. The method for processing the image comprises steps of defining a target area containing the removed object in the target image; extracting at least a sub area as an image from other images related with the target image stack, wherein all aforesaid other images a removed object different from a shooting view point of the target image; selecting pixels pf same position corresponding to the sub area from the image stack pixel by pixel based on theoptimization method to substitute pixels in the target area. Through the inventive method and device for processing images, a user can repair images so as to form ideal images while removing removed images from shot imaged to his delight.
Owner:NEC (CHINA) CO LTD
Method for quickly correcting distortion of camera based on collinear feature point
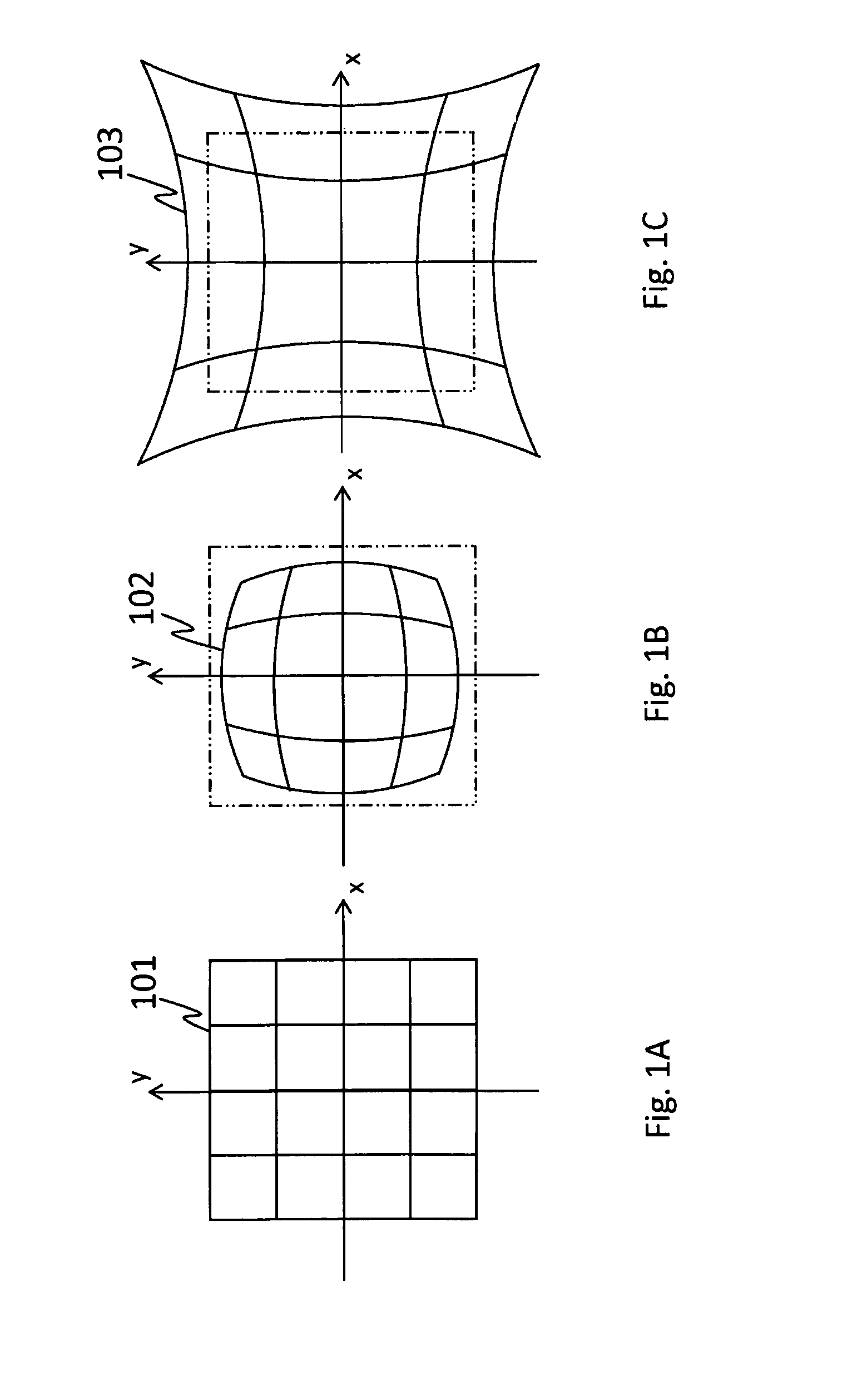
InactiveCN1996389ALow costImprove real-time performanceImage analysisTesting optical propertiesIdeal imageComputer graphics (images)
The invention relates to a camera deformation calibration method and quick calibration method based on predicted template. Based on the unchanged linear perspective projection to calculate the ideal image coordinate to the analog linear distance and the minimum target, predicting the lens deformation coefficient through nonlinear optimization function. Based on camera deformation coefficient, it predict the deformation coordinate of the ideal image coordinate and stores it into the template matrix, directly searching the template reading ideal image corresponding deforming coordinate, completing the quick calibration of deformed image through linear insert value to get the gray value of the ideal image pixel. The put forward deformation coefficient calibration method is low in cost, simple in algorithm, and easy realization.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Large visual field camera nonlinear distortion correction device and method
InactiveCN104034514AHigh precisionRealize Distortion CorrectionTesting optical propertiesNeural learning methodsNonlinear distortionCorrection algorithm
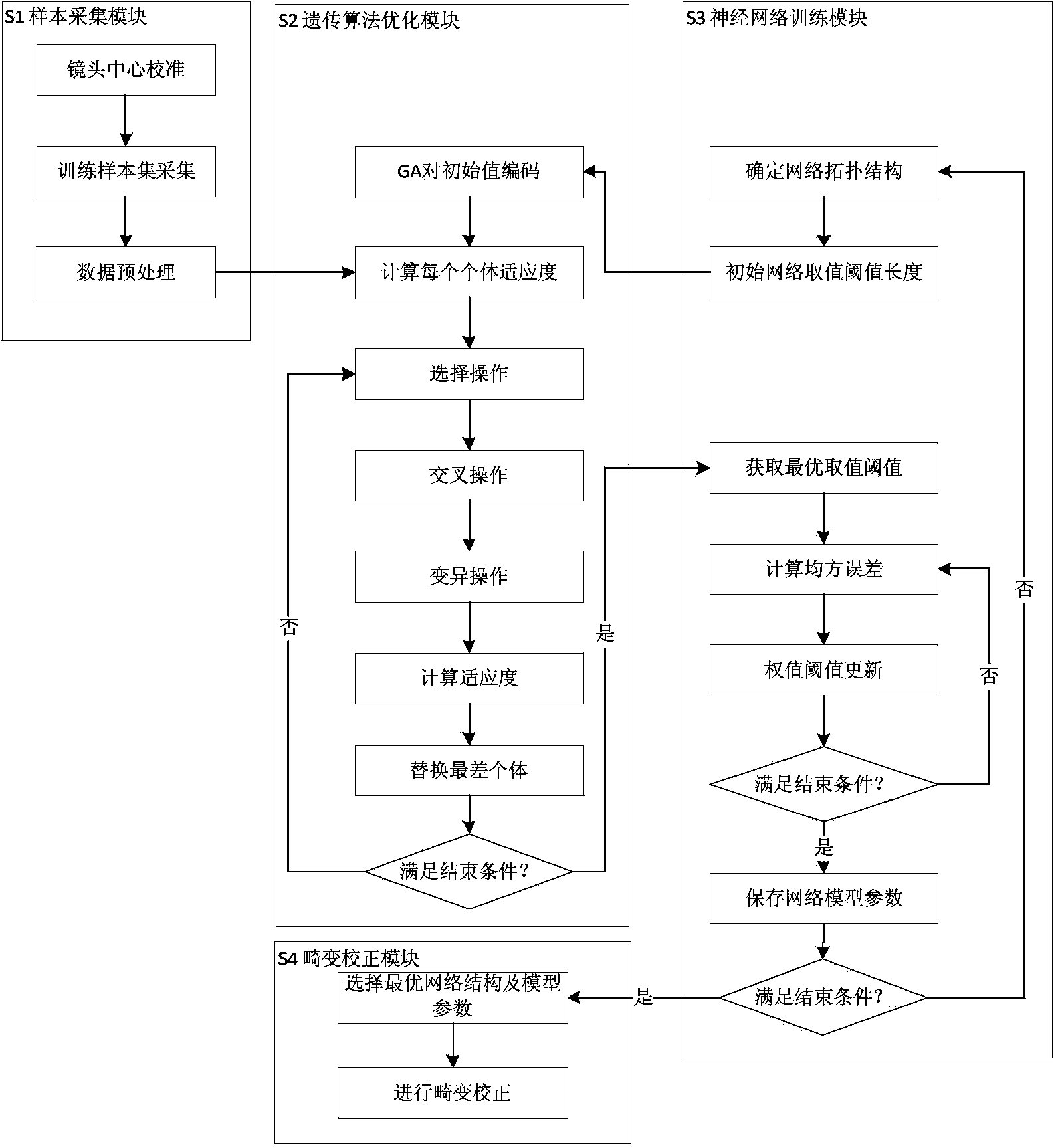
The invention discloses a large visual field camera nonlinear distortion correction device and method. The device comprises a single-star starlight simulator, a two-dimensional turntable, a two-dimensional turntable control system, an optical table and a computer. The method comprises the steps of utilizing a mass center positioning algorithm to confirm mass center position coordinates of star point images at different positions in a camera visual field range, establishing a projection imaging model to calculate ideal imaging position coordinates corresponding to the star point images, fitting a nonlinear distortion model through a BP neural network optimized by a genetic algorithm and achieving distortion correction of a camera to be detected. The large visual field camera nonlinear distortion correction device has the advantages of having simple structure, automatic operation, convenient measurement and high correction algorithm accuracy and easily achieves large visual field camera nonlinear distortion correction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-viewing-angle image distortion correction and processing method
The invention discloses a large-viewing-angle image distortion correction and processing method. The large-viewing-angle image distortion correction and processing method comprises the steps of S1, calculating a distance between any point in a corrected image and the center of the image, namely ideal image height; S2 adopting an improved distortion rate formula to calculate the distortion rate D corresponding to the point; S3, calculating distortion point coordinates according to the distortion rate D; S4 adopting a bilinear interpolation method and ideal coordinates corresponding to the obtained distortion point coordinates to perform interpolation so as to obtain a corrected image. A distortion correction approximation model of the method can conveniently obtain the distortion rate of each point, accordingly the corresponding distortion point coordinates can be calculated according to the coordinates of ideal points, and a 'void' phenomenon produced on the corrected image is avoided. The large-viewing-angle image distortion correction and processing method does not need a specially manufactured template to calibrate lens distortion parameters, accordingly a large number of iterative operation during parameter calculation is omitted, and the method is simple and easily achieved in hardware. In addition, when the image size is large, the calculation time can be effectively shortened, and the universality is good.
Owner:玉振明 +3
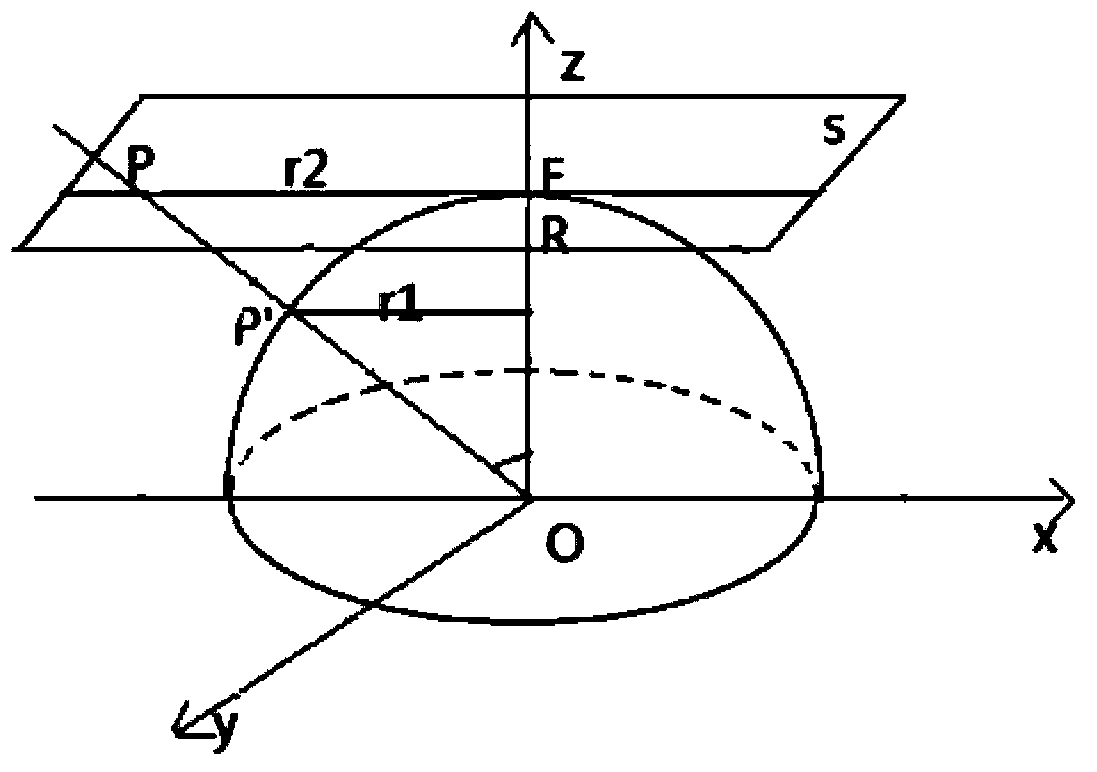
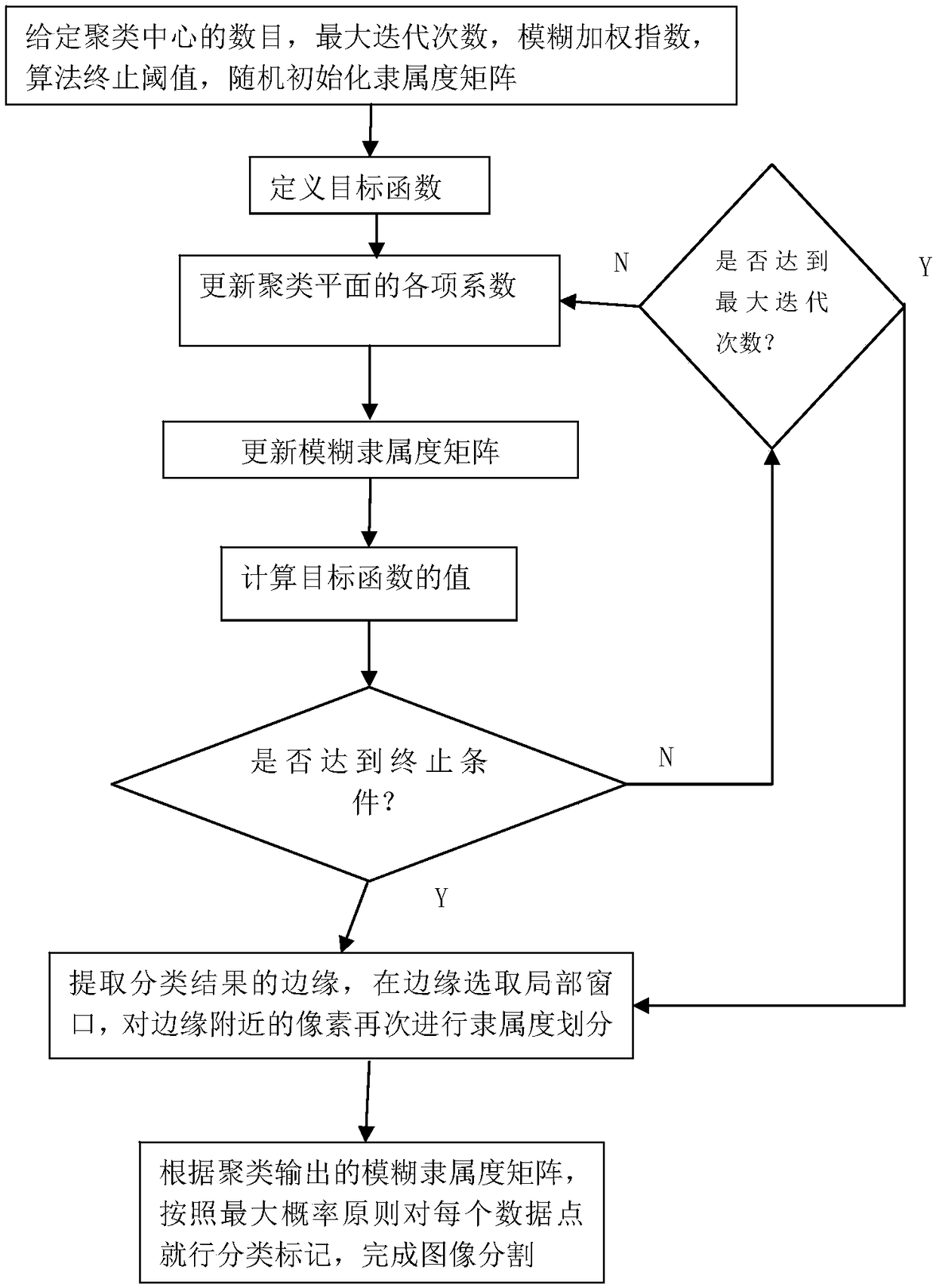
Fuzzy clustering image segmentation method with plane as clustering center and anti-noise ability
ActiveCN109389608AEfficient use ofBalance weight relationshipImage enhancementImage analysisIdeal imageImage segmentation
The invention discloses a fuzzy clustering image segmentation method with plane as clustering center and anti-noise ability. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, defining an objective function, initializing various coefficients and thresholds in the objective function, and randomly initializing a membership matrix; minimizing the objective function to calculate and update the coefficients and fuzzy membership matrices of the clustering plane. calculating the value of the objective function based on the updated fuzzy membership matrix, when the absolute value of the difference between the objective function values of the two successive iterations is less than the termination condition or the method exceeds the maximum iteration number limit, the iteration ends, otherwise, theiteration continues to perform the updating, and each pixel point is classified and marked according to the criterion of the maximum membership, so as to complete the initial classification; The edgeof the image is extracted from the classification result, and the local window is selected to divide the membership degree again with the edge point as the center pixel. According to the fuzzy membership matrix of clustering output, the membership degree of data points belonging to a certain class is obtained, and each data point is classified and marked according to the maximum probability principle, and the image segmentation is completed. The method of the invention uses a clustering plane instead of a clustering center for image segmentation, can simultaneously consider the gray value information and the position information of pixels, obtains an ideal image segmentation effect, eliminates the influence of noise well, and improves the quality of image segmentation and the stability ofthe segmentation effect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Distortion measurement and correction method for CCD shooting system and comprehensive test target
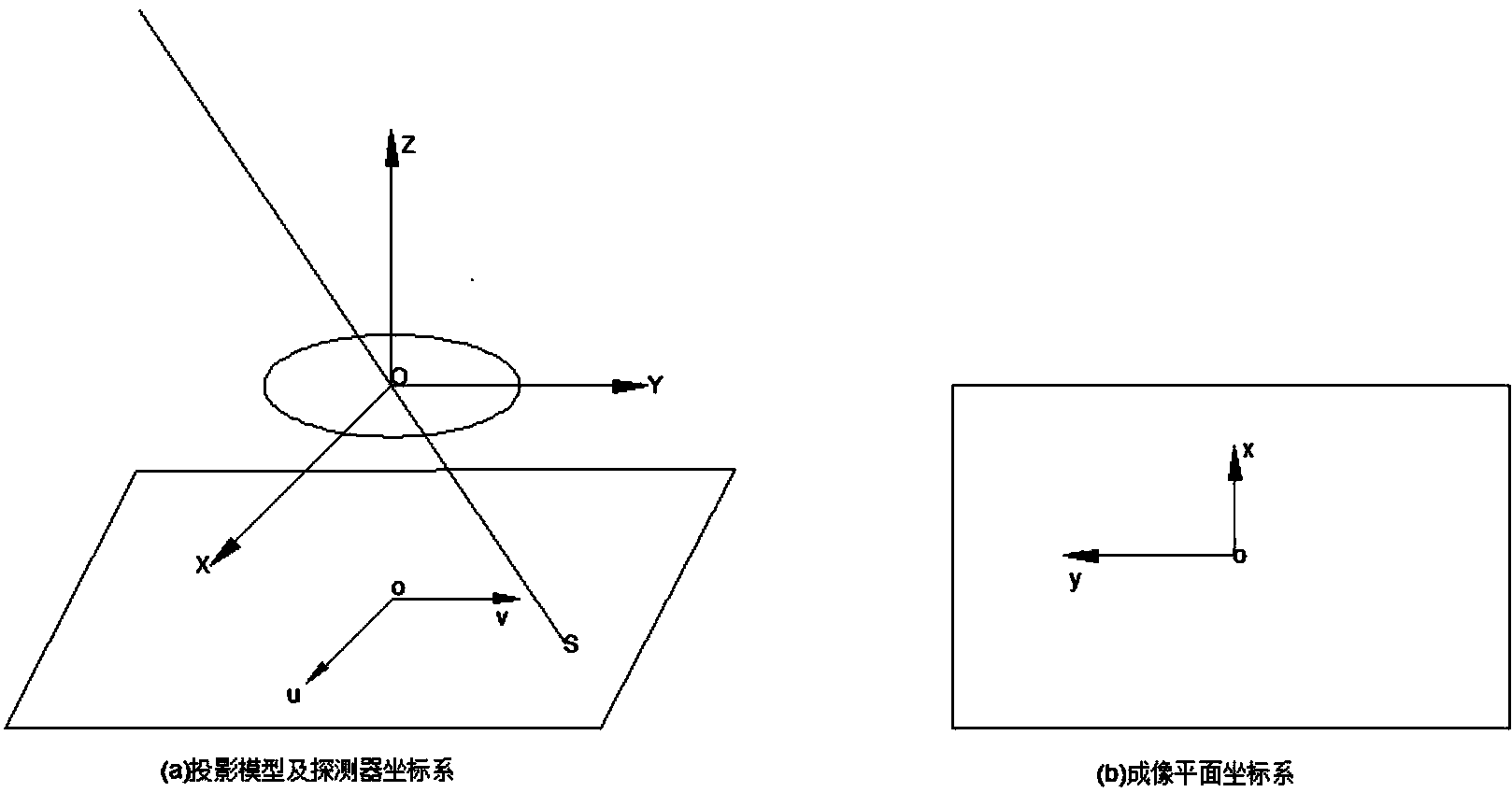
InactiveCN101026778AAchieve precisionAchieve calibrationImage analysisTelevision systemsCombined testIdeal image
The integrated testing target is composed of black / white interband and gray object points on the black / white interband. The method includes steps: establishing transformation relations between world coordinate system (CS) and camera CS, between pixel CS and image CS, between camera CS and image CS in sequence; collecting imaging polar coordinates (PC) of distortion image; plotting ideal imaging PC without distortion; determining coincidence relation between coordinate points (CP) of ideal image and CP of distortion image, and building polynomial model; based on polynomial coefficient to measure and correct distortion. The invention considers combined information of point target and row target for the integrated testing target. Using the integrated testing target replaces traditional three discrete target boards so as to solve issues of low position precision of target sample points, and difficult to make corresponding positions between target sampling points and image points.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Camera calibration board, calibration data acquisition method, distortion correction method and device
ActiveCN110458898ARealize CalibrationImplement sortingImage enhancementImage analysisMachine visionIdeal image
The invention relates to a camera calibration board, a calibration data acquisition method and a distortion correction method and device, and relates to the technical field of machine vision, and themethod comprises the steps: collecting a checkerboard image through employing the camera calibration data acquisition method, and obtaining the serial numbers of all image corners in the checkerboardimage and the corresponding three-dimensional coordinates; selecting a plurality of angular points in the center of the checkerboard image, and determining the three-dimensional coordinates corresponding to the plurality of angular points; and optimizing the initial distortion parameter to obtain an optimized distortion parameter, and performing distortion correction according to the calculated optimized distortion parameter. Only one checkerboard image needs to be collected, and one-to-one correspondence of collected image corners and three-dimensional coordinates is completed through specialfixed corners. An ideal image corner is obtained to calculate an initial distortion parameter of the camera, and an accurate distortion parameter is obtained for correction after optimization. The accuracy of distortion correction is improved, the operation process is simplified, and the method is suitable for rapid production.
Owner:MEGVII BEIJINGTECH CO LTD
Color image super-pixel segmentation method based on similarity between pixels
ActiveCN109389601AImprove regularityReduce computing timeImage enhancementImage analysisColor imagePattern recognition
The invention discloses a color image superpixel segmentation method based on similarity between pixels. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, an image to be segmented is initially clustered; then, a seed point is determined based on the initial clustering; whether a seed point needs to be added is judged; if so, the seed point is added; if so, the seed point is added; an initial superpixel is generated according to the initial clustering and the marker of the seed point; For unmarked pixel points, the defined energy function is used to calculate the energy of the seed point andthe pixels in its searching range, The superpixel marker of the seed point with the least energy is selected as the superpixel marker of the unmarked pixel. Finally, the isolated pixel satisfying thethreshold condition and the isolated very small superpixel are merged into the neighboring superpixels which are most similar to the superpixel marker until the number of the current superpixels reaches the desired number, so as to realize the superpixel segmentation of the image. The method of the invention can obtain the ideal image segmentation effect, and provides higher regularity in the image flat area, thereby improving the quality and the segmentation effect of the image segmentation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
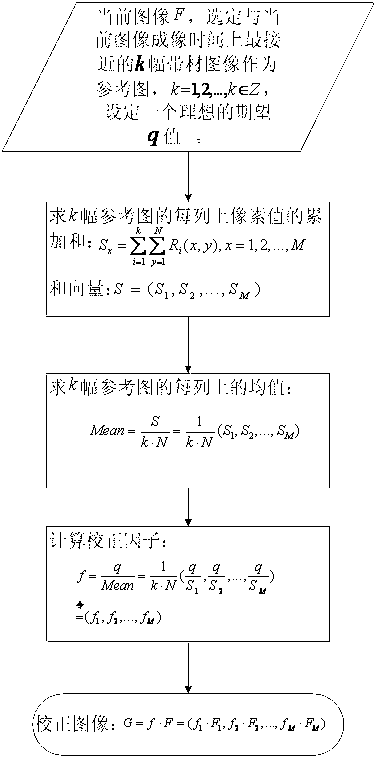
Dynamic non-uniformity correction method for linear scanned image based on image sequence analysis
InactiveCN102938137AEliminate the effects ofUniform gray distributionImage enhancementUltrasound attenuationIlluminance
The invention provides a dynamic non-uniformity correction method for a linear scanned image based on image sequence analysis. The dynamic non-uniformity correction method comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting k (k is equal to 1, 2,..., and belongs to Z) images for the existing image to be corrected, and setting an ideal desired value q; then, calculating the average value of pixel values on each row of the k images to acquire a mean vector; and finally, using a ratio of the mean vector to the set ideal desired value as a correction coefficient to correct the images, so that a novel image which is uniform in background, clear in defect contour and convenient to position a subsequent defect target is acquired. The method can effectively overcome influences of changes of such factors as parameters including material specification, thickness and the like of the detected object, detection angle, plate type consistency and light source illumination attenuation, so as to dynamically acquire in real time an ideal image which is uniform in grey distribution, high in definition and remarkably enhanced in the detected object, thus greatly simplifying subsequent image processing difficulty and effectively improving the real-time performance of the integral system.
Owner:苏州有色金属研究院有限公司
Super-smooth surface defect detection system and distortion correction method thereof
ActiveCN102661956AReduce the impact of shape changesOptically investigating flaws/contaminationIdeal imageWide field
The invention provides a super-smooth surface defect detection system and a distortion correction method thereof. The invention aims to solve the problem that defects are fractured when subimages are spliced due to the fact that optical distortion exists in the super-smooth surface defect detection system. The invention is technically characterized in that the super-smooth surface defect detection system, a distortion correction on-gauge plate and a clamping device for the on-gauge plate are designed. The on-gauge plate is collected to obtain a distortion image of a dark field by utilizing the detection system; a distortion degradation model is established through the distortion image and a computer by matching with an ideal image of the on-gauge plate reconstructed according to the relation between the dimension of an object plane and the pixel of an image plane, and the distortion correction method based on secondary polar coordinate positive and negative transformation and secondary gray level linear interpolation is provided. The method can be used for correcting the distortion in the super-smooth surface defect detection system to avoid splicing dislocation of adjacent subimages, and meanwhile, is also suitable for correcting the distortion existing in other wide-field optical systems based on image splicing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-precision joining method of uneven surface object picture
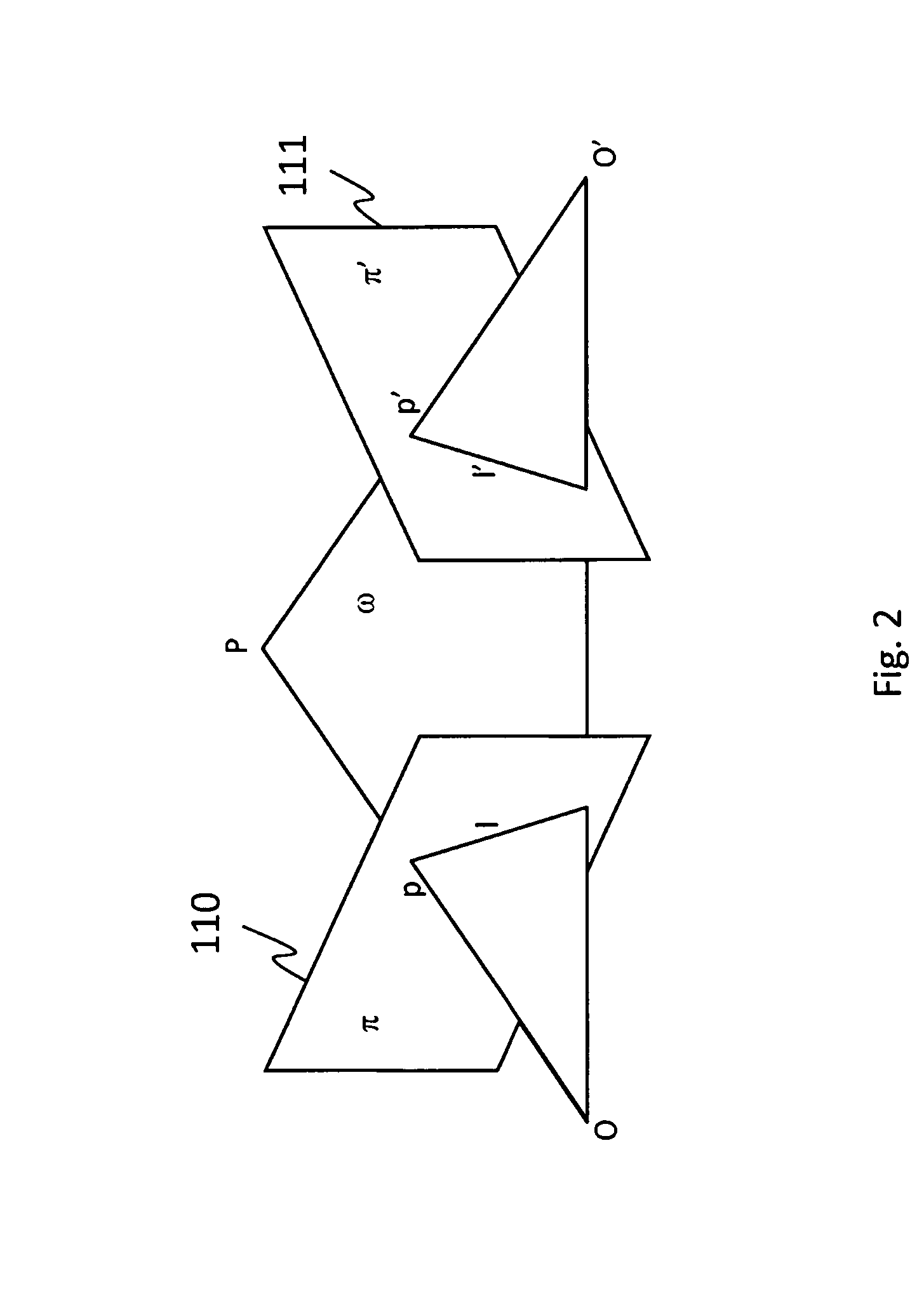
The invention discloses a high-precision joining method of an uneven surface object picture. A coordinate in a world coordinate system of a plurality of sampling points on an uneven surface object is obtained by utilizing three-dimensional scanning according to an overlapped area of a first image and a second image to be joined, the coordinate is fitted in a least square method to obtain a best re-projection plane, and a best re-projection coordinate system is established; the coordinate of each sampling point in the world coordinate system is converted to a coordinate in the best re-projection coordinate system, and an error between an ideal image coordinate and a real image coordinate of the sampling point is calculated according to the internal and the external parameters of a camera; the error between the ideal image coordinate and the real image coordinate of all pixels in the overlapped area is obtained through interpolation; the first and the second images are corrected so as to obtain and to join the first image and the second image with no error. Pin-hole model simulates imaging of infinite focal-length lens, which is followed by the imaging of the camera, so the generated picture eliminates the joining error caused by the uneven surface perspective projection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Real-time blind image restoration method
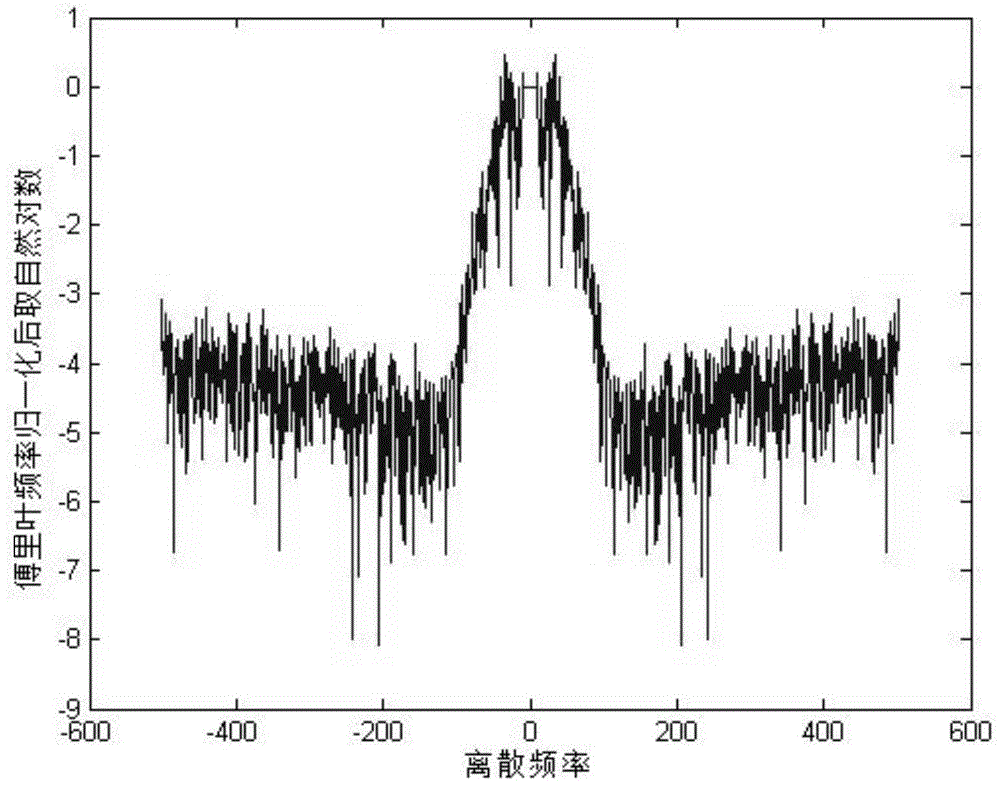
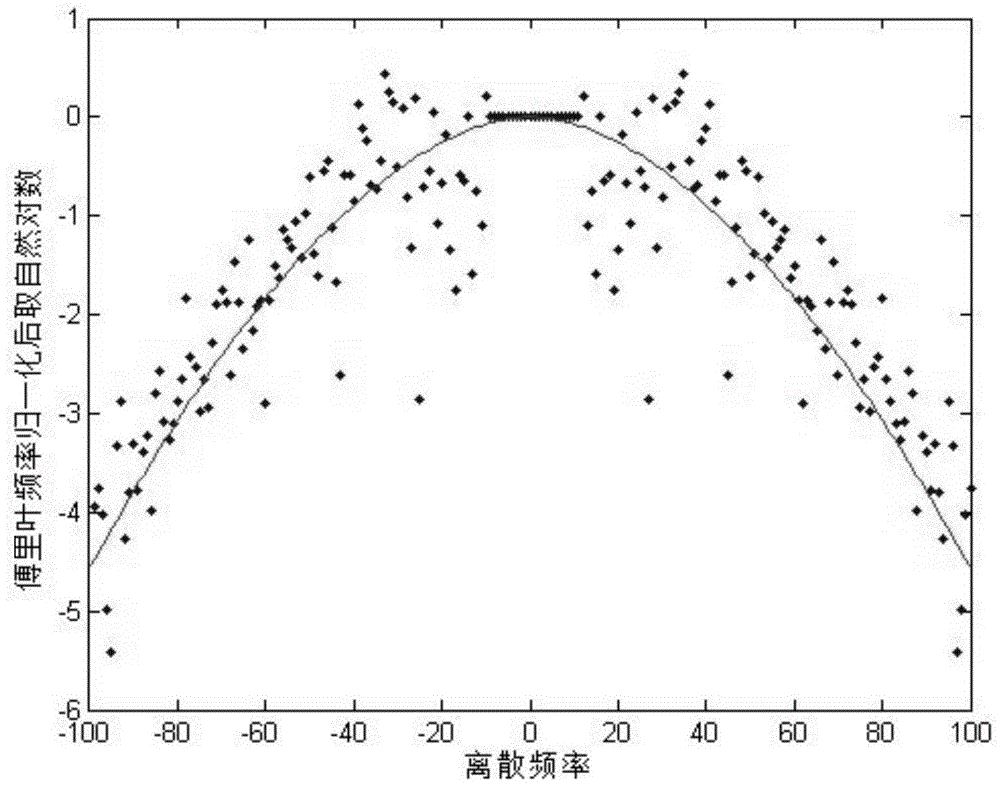
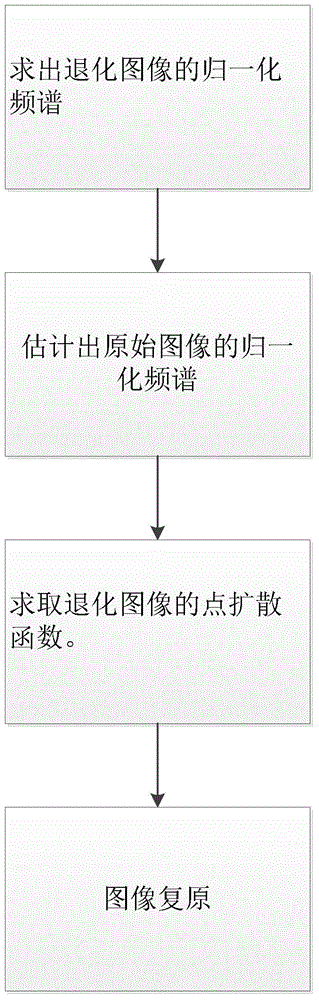
InactiveCN104820969AEnhance resilienceEnhanced inhibitory effectImage enhancementFrequency spectrumTime-Consuming
The invention provides a real-time blind image restoration method, which comprises the following steps of carrying out Fourier transformation on a degraded image, and then obtaining a normalized spatial spectrum of the degraded image; reconstructing a frequency spectrum of an original image of the degraded image according to a spectral distribution rule of a natural image and estimating a normalized spatial spectrum of the original image; comparing the normalized spatial spectrum of the degraded image and a reconstructed frequency spectrum, and obtaining an optical transfer function of a system so as to obtain a point spread function of the degraded image; and carrying out Wiener filtering restoration on the degraded image according to the obtained point spread function so as to obtain an ideal image. The real-time blind image restoration method does not contain time-consuming iteration, and is simple and easy to implement, so that algorithm complexity is reduced, meanwhile, accurate estimation of the point spread function is obtained, and a good image restoration effect is realized.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
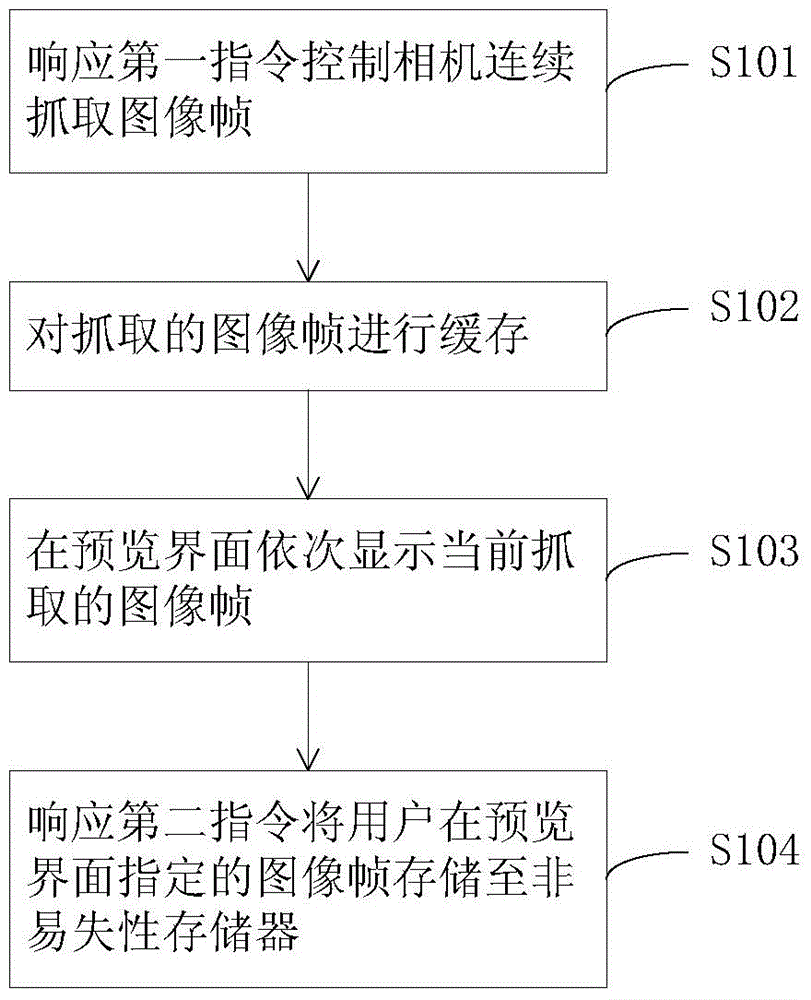
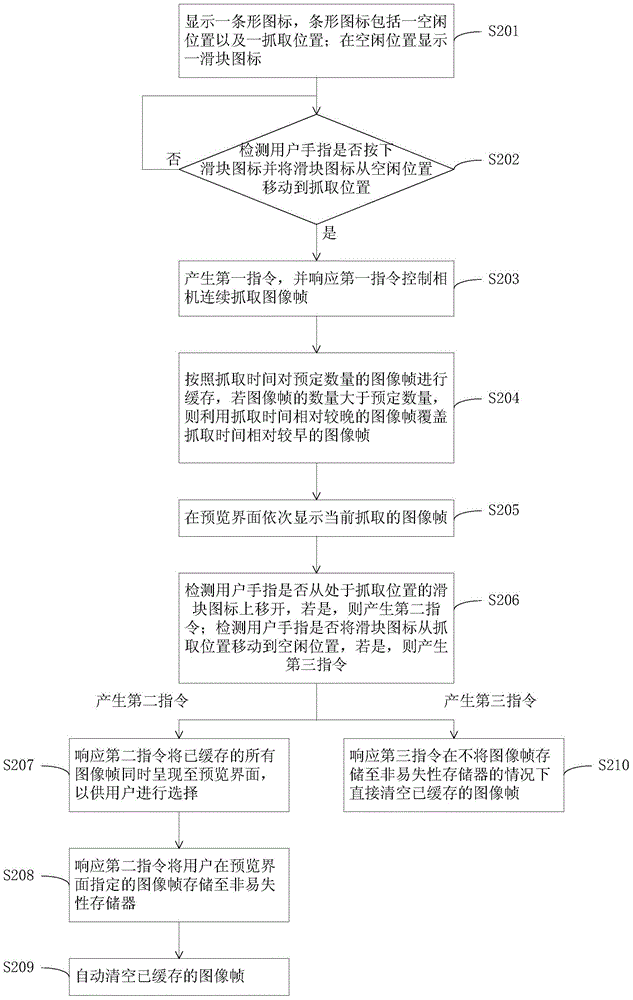
Snapshot method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN104580908ATelevision system detailsColor television detailsIdeal imageComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a snapshot method and a mobile terminal. The snapshot method comprises the steps that by responding to a first instruction, a camera is controlled to continuously snapshot image frames; the snapshot image frames are cached; the image frames which are snapshot currently are displayed on a preview interface; the image frame specified by a user on the preview interface is stored in a nonvolatile memory by responding to a second instruction. By the adoption of the snapshot method and the mobile terminal, ideal images can be snapshot.
Owner:HUIZHOU TCL MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Method and apparatus for proving an authentication of an original item and method and apparatus for determining an authentication status of a suspect item
ActiveUS20160342885A1Clearly markedLess effortDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionIdeal imageImage resolution
An apparatus and method for authenticating an item wherein a code is assigned to the item and includes a plurality of modules arranged in an ideal image. A barcode is encoded within the modules and a picture of the code is printed onto the item. A picture of the printed code is recorded with a low resolution camera at high speed during the production process from which the barcode content is decoded. Irregularities in the picture are analyzed and a numerical value describing an individual imperfection profile is calculated. The numerical value of the imperfection profile depends on at least one unique feature inherently related to the original printing device. The individual imperfection profile is printed onto the item and / or a database record is generated. To authenticate a suspect item, the imperfection profile of the suspect item is compared with the imperfection profile of the original item.
Owner:THYMARIS LTD
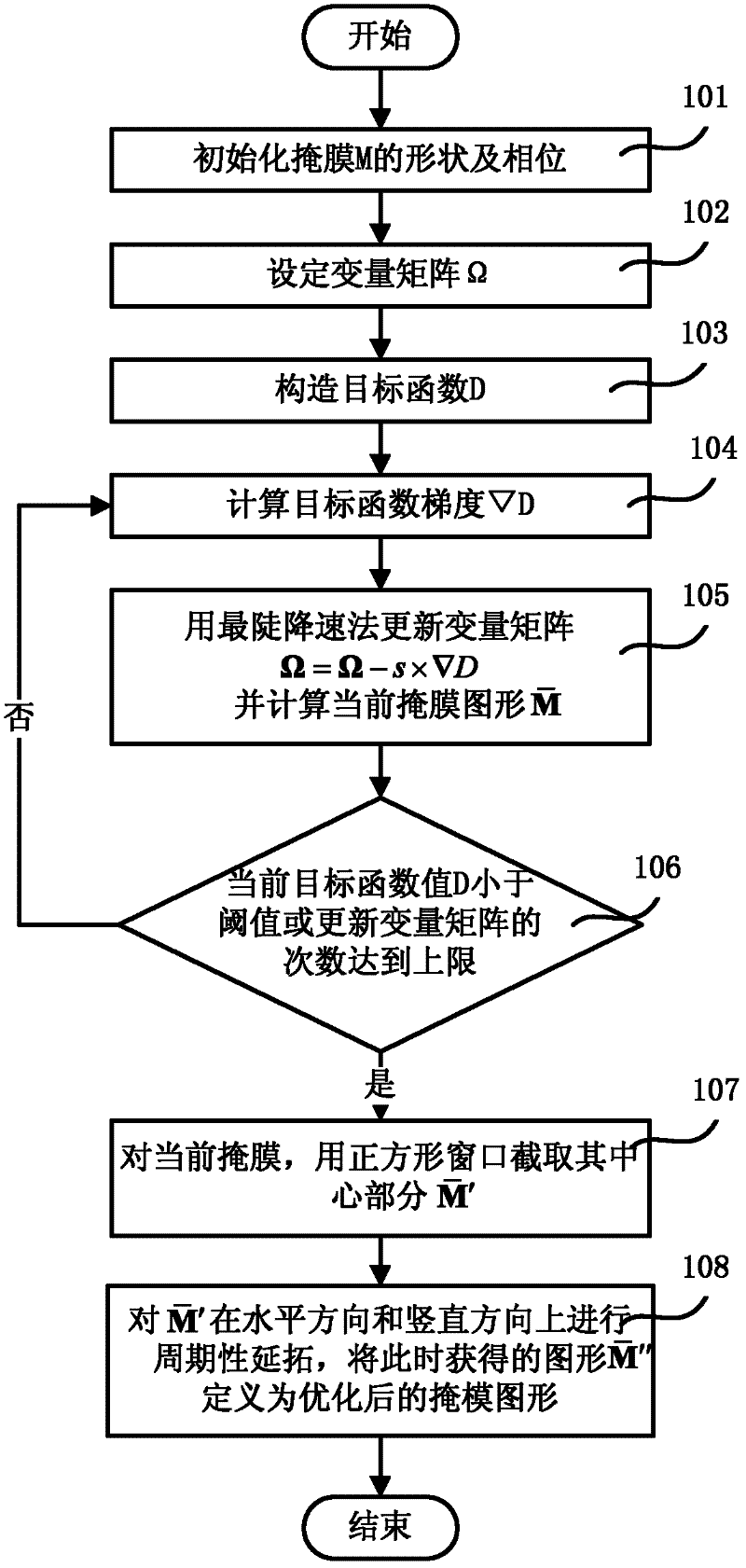
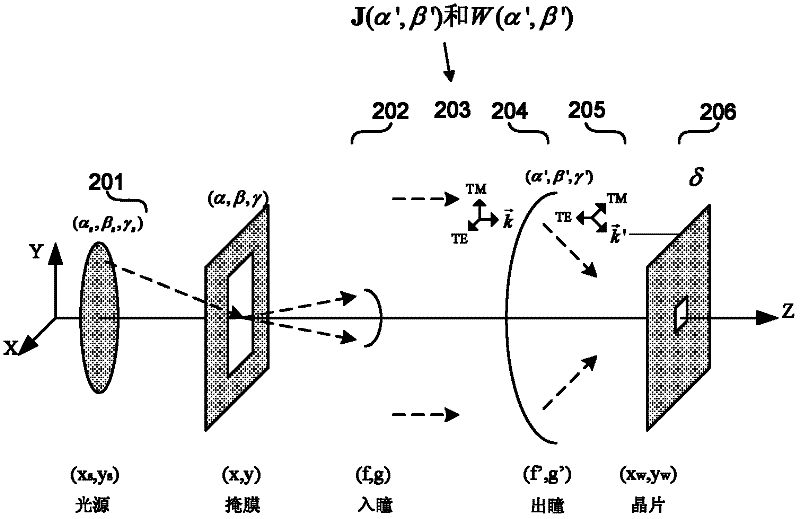
Optimization method of non-ideal lithography system opc based on abbe vector imaging model
The invention provides a method for optimizing optical proximity correction (OPC) of a nonideal photoetching system based on an Abbe vector imaging model. The method comprises the following steps of: setting transmittivity of an opening part and a light blocking part in a mask; setting a variable matrix Omega; setting a target function D as linear combination of an imaging evaluation function of an ideal image surface and an imaging evaluation function of an image surface of which the defocusing quantity is fnm; and guiding optimization on a mask pattern by using the variable matrix Omega andthe target function D. By using the vector imaging model and taking vector characteristic of an electromagnetic field into consideration during acquisition of a space image, the optimized mask is suitable for the photoetching system with small numerical aperture (NA) and also suitable for the photoetching system of which the NA is more than 0.6. By the method, the gradient information of optimizing the target function is utilized and a steepest descent method is combined to optimize the pattern and the phase of an attenuated phase-shifting mask, so the optimization efficiency is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method and system for alignment of a pattern on a spatial coded slide image
A method for preparing a spatial coded slide image in which a pattern of the spatial coded slide image is aligned along epipolar lines at an output of a projector in a system for 3D measurement, comprising: obtaining distortion vectors for projector coordinates, each vector representing a distortion from predicted coordinates caused by the projector; retrieving an ideal pattern image which is an ideal image of the spatial coded pattern aligned on ideal epipolar lines; creating a real slide image by, for each real pixel coordinates of the real slide image, retrieving a current distortion vector; removing distortion from the real pixel coordinates using the current distortion vector to obtain ideal pixel coordinates in the ideal pattern image; extracting a pixel value at the ideal pixel coordinates in the ideal pattern image; copying the pixel value at the real pixel coordinates in the real slide image.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
Design method of free-form surface imaging system
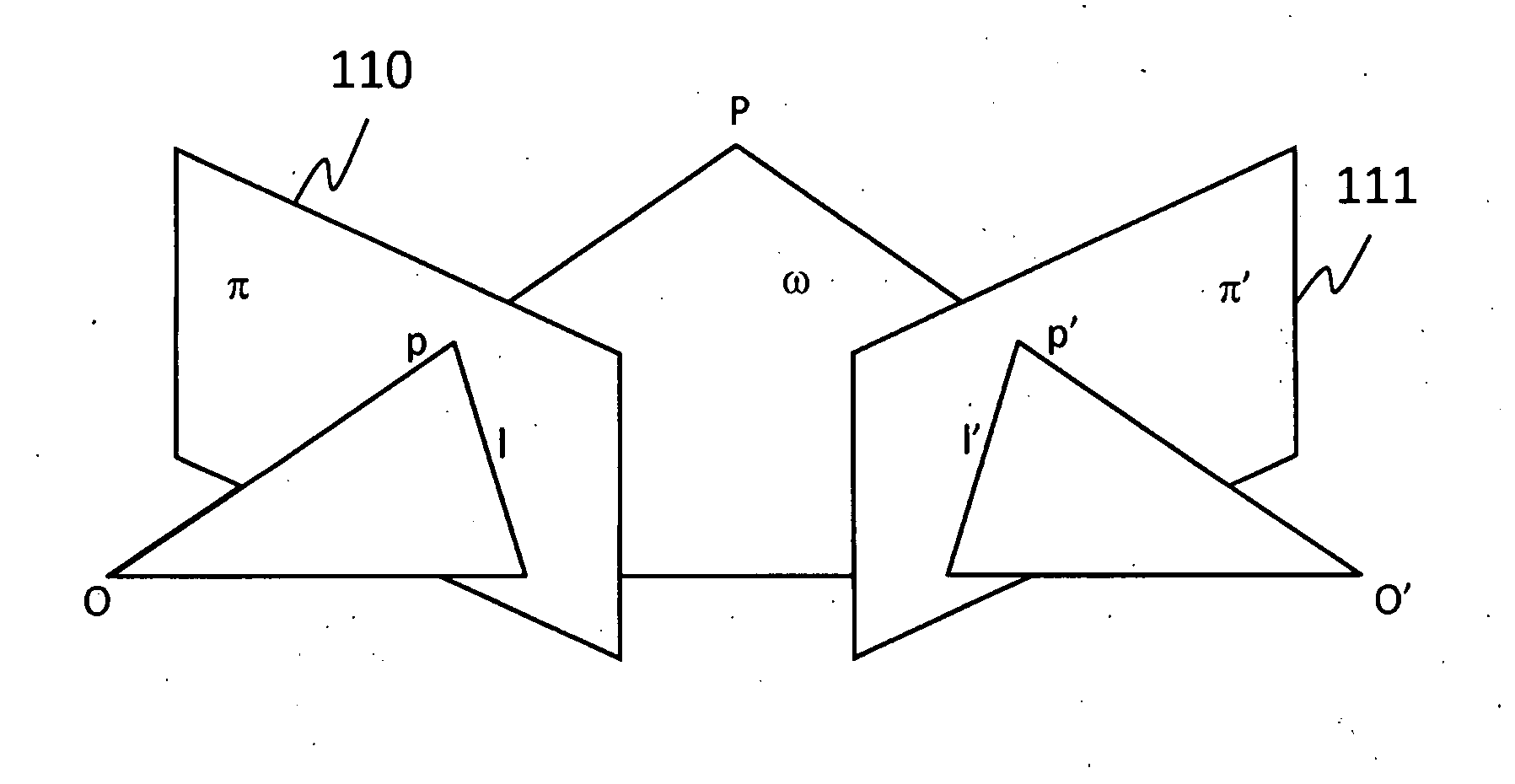
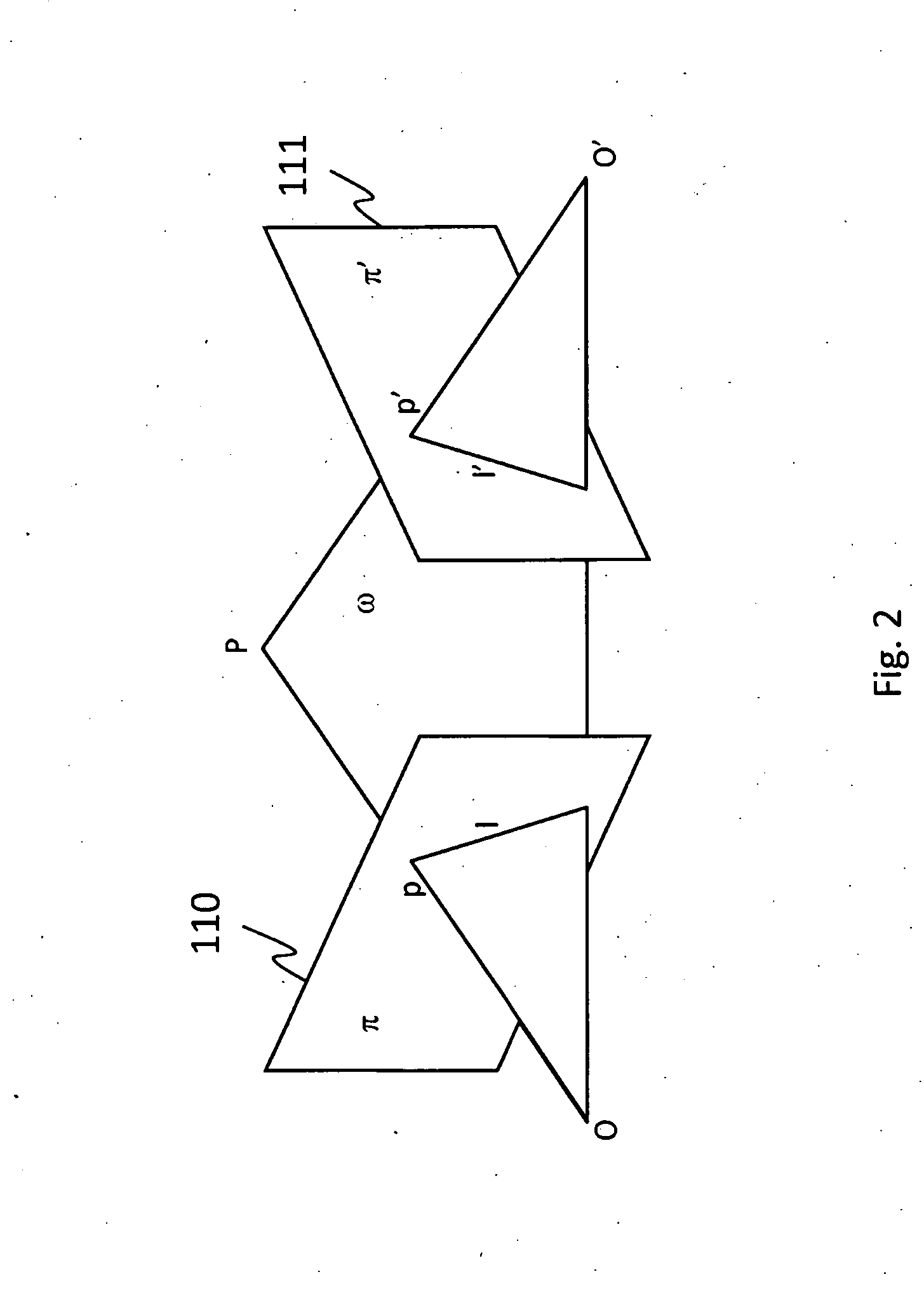
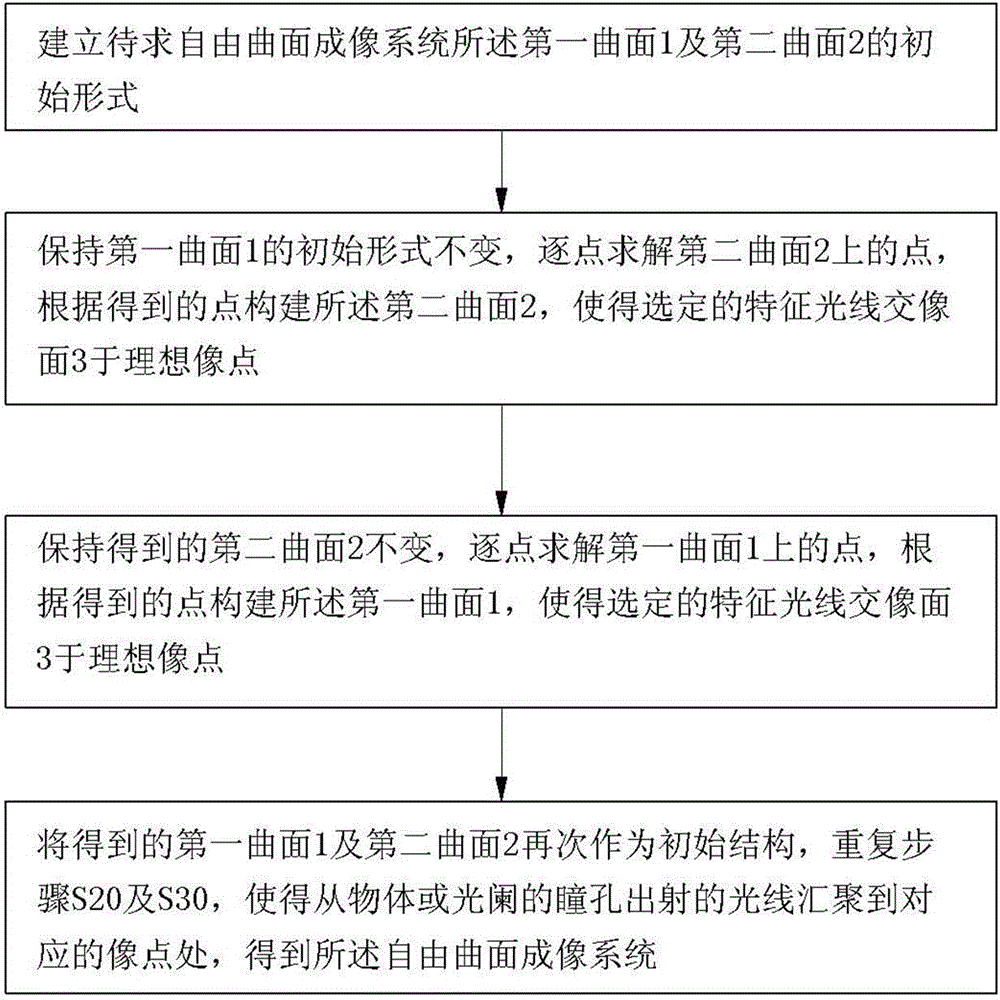
ActiveCN104570340ASimple methodUnlimited number of fields of viewOptical elementsIdeal imageFree form
A design method of freeform imaging system is provided. An initial freeform imaging system is provided, the initial freeform image system comprising a first initial surface and a second initial surface spaced from each other. A second surface is constructed by calculating a plurality of second data points of the second surface through a plurality of feature rays based on the given object-image relationship. A first surface is constructed by calculating a plurality of first data points of the first surface based on the given object-image relationship and Fermat's principle, wherein the second surface is fixed. The first surface and the second surface substitute for the first initial surface and second initial surface respectively, and repeating steps list above, wherein the plurality of feature rays are intersecting the image plane at the plurality of ideal image points.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
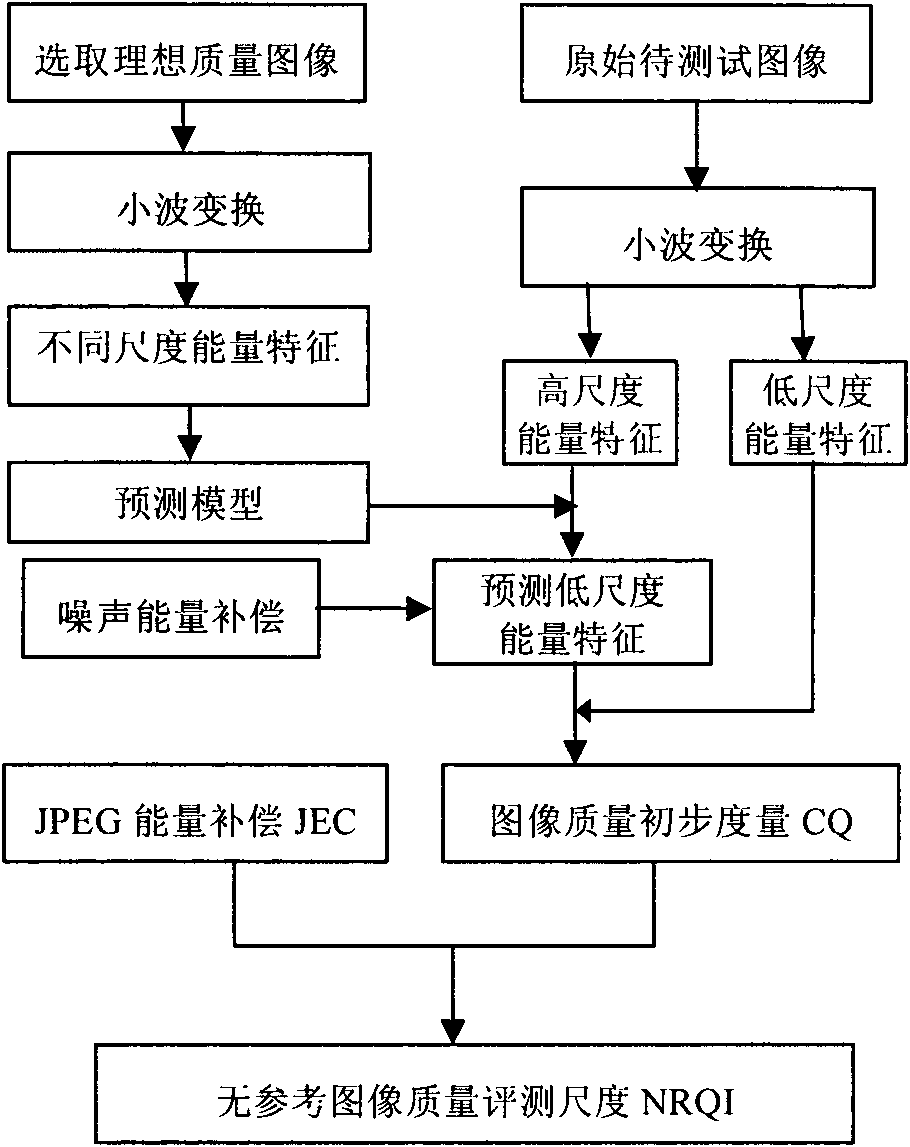
Non-reference image quality evaluation method based on wavelet-transformation multi-resolution prediction
The invention discloses a non-reference image quality evaluation method based on wavelet-transformation multi-resolution prediction. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting an ideal image and calculating average energy of each scale and each direction after the wavelet transformation; (2) using an approximate linear relation between scale energy characteristics to establish a prediction model; (3) according to the prediction model, using high-scale sub-band average energy of a distorted image to predict low-scale sub-band average energy of an ideal image; (4) properly adjusting the predicted average energy of the serious distortion image; (5) compensating the energy of the noise distortion image; (6) compensating the energy of the JPEG distortion type image; (7) combining a human visual system characteristic to construct a non-reference image quality evaluation scale. According to the invention, subjectively scored training is not needed. The method is highly consistent with the subjective evaluation. The method is suitable for a plurality of distortion types and can be used to detect effectiveness of an image video processing method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Image previewing and processing method
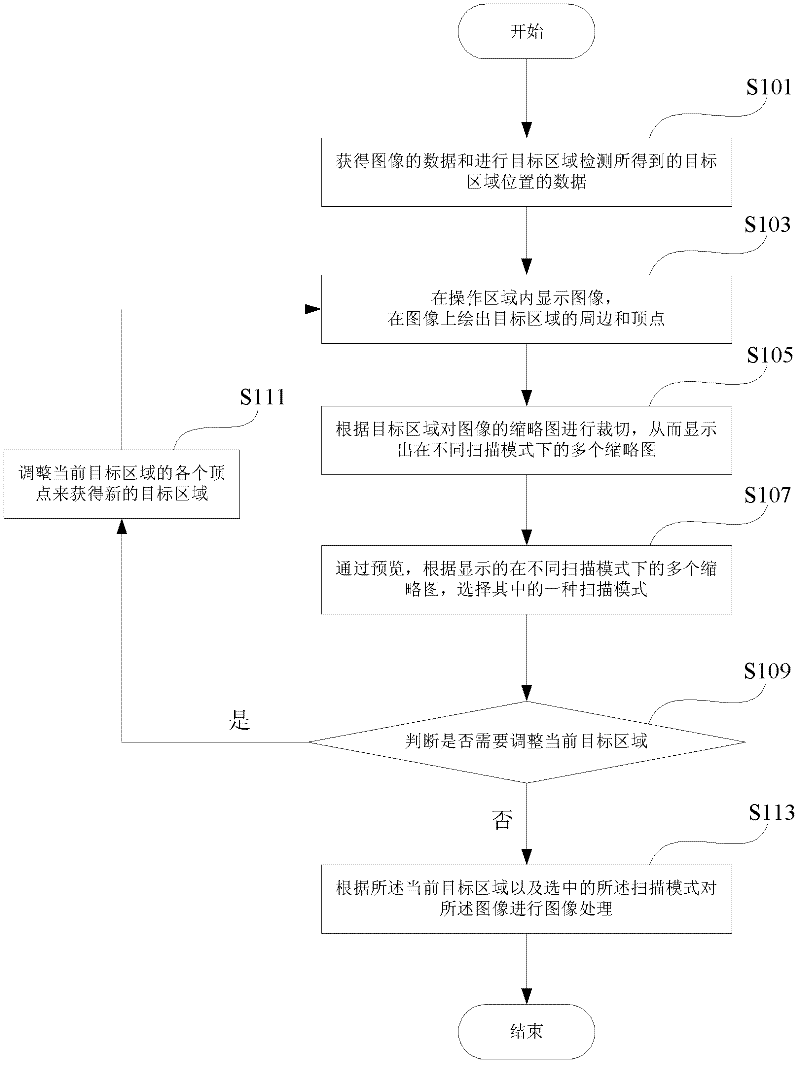
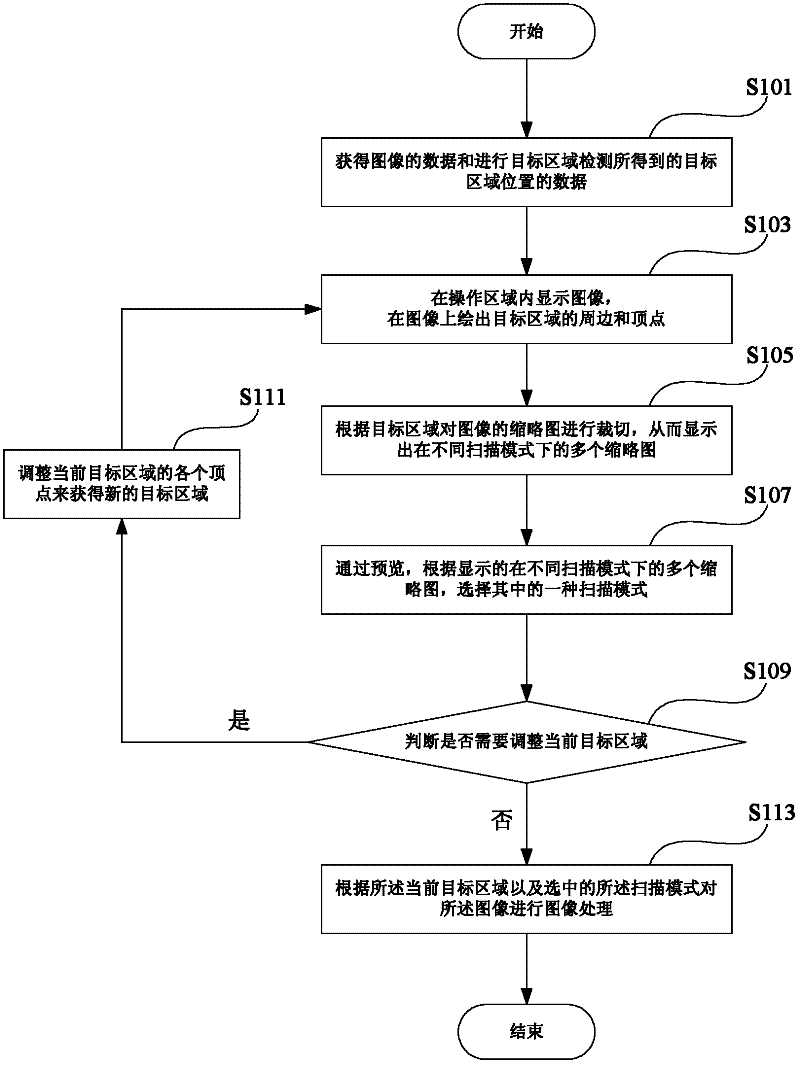
InactiveCN102436342AImage enhancementInput/output processes for data processingIdeal imageLive preview
The invention provides an image previewing and processing method, which comprises the following steps: acquiring data of an image and position data of a target area, obtained by carrying out detection on the target area; displaying the image in an operating area, and drawing the periphery and vertex of the target area on the image; cutting a thumbnail of the image according to the target area, thereby displaying a plurality of thumbnails in different scanning modes; through previewing, and according to the plurality of displayed thumbnails in different scanning modes, selecting one of the scanning mode; and preprocessing the image according to the current target area and the selected scanning mode. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention mainly has a characteristic that: after carrying out self-defined cutting on the obtained image in the target area, a plurality of thumbnails corresponding to the image in different scanning modes are displayed and previewed by users in real time so as to help the users to rapidly select the most ideal image processing scheme to finally obtain an image required by the users; therefore, the method is convenient and fast, and has a good user interaction experience.
Owner:SHANGHAI HEHE INFORMATION TECH DEV
Method and system for alignment of a pattern on a spatial coded slide image
A method for preparing a spatial coded slide image in which a pattern of the spatial coded slide image is aligned along epipolar lines at an output of a projector in a system for 3D measurement, comprising: obtaining distortion vectors for projector coordinates, each vector representing a distortion from predicted coordinates caused by the projector; retrieving an ideal pattern image which is an ideal image of the spatial coded pattern aligned on ideal epipolar lines; creating a real slide image by, for each real pixel coordinates of the real slide image, retrieving a current distortion vector; removing distortion from the real pixel coordinates using the current distortion vector to obtain ideal pixel coordinates in the ideal pattern image; extracting a pixel value at the ideal pixel coordinates in the ideal pattern image; copying the pixel value at the real pixel coordinates in the real slide image.
Owner:CREAFORM INC
Complementary blurred image acquisition system and blurred image recovery method using complementary blurred image acquisition system
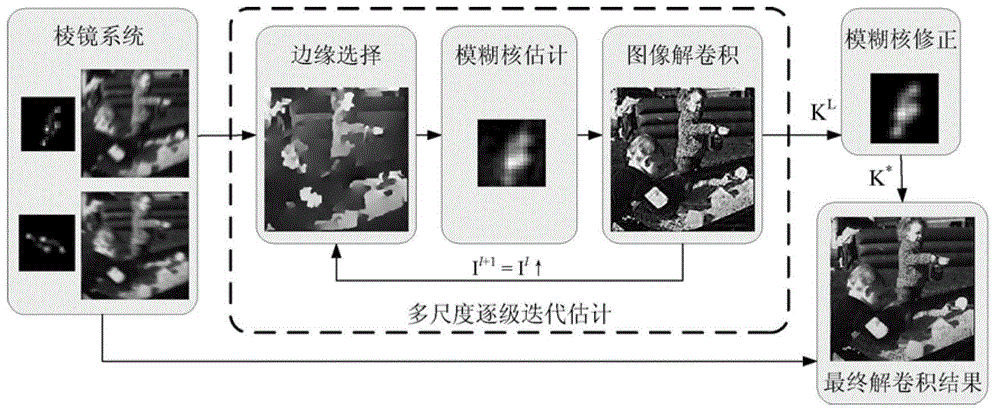
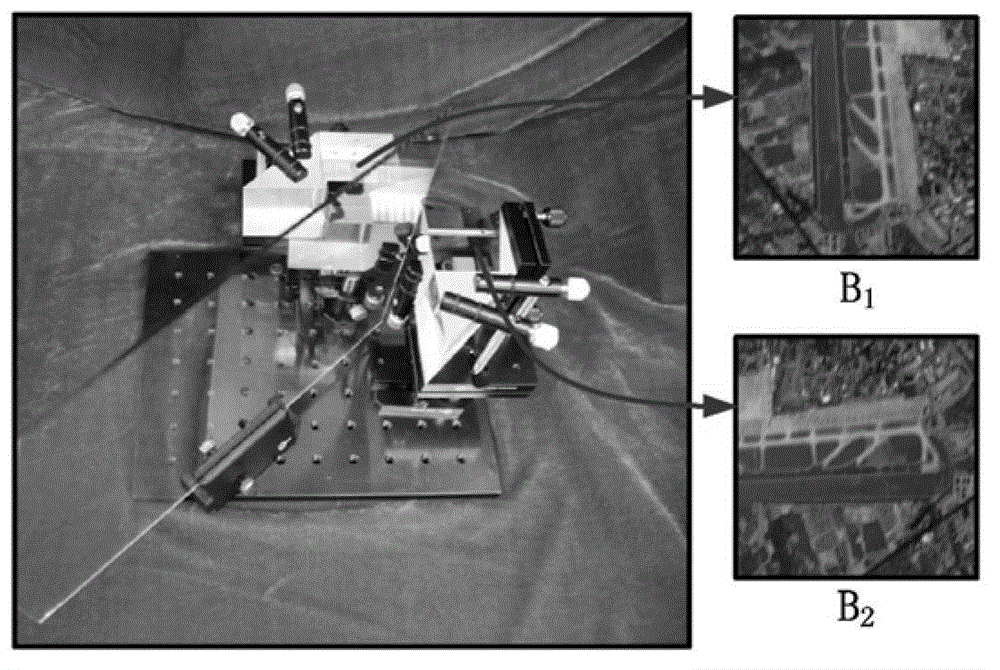
ActiveCN102867289AStrong real-timeReduce complexityImage enhancementMountingsIdeal imageRestoration method
The invention provides a complementary blurred image acquisition system and a blurred image recovery method using the complementary blurred image acquisition system. The system comprises a spectroscope, a first prism combination and a second prism combination. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing the complementary blurred image acquisition system; acquiring two degraded images of the same scene under the influence of motion blur; obtaining an initial blur core and the estimation of a clear image by taking the relationship between two blur cores as a constraint; thinning the blur cores; and performing deconvolution on the image by the finally obtained blur cores to obtain an ideal image deblurring result. According to the complementary blurred image acquisition system, the images of the two groups of prisms are arranged side by side, and images of a 90-degree rotation relationship can be shot by a camera. The motion blurred image recovery method is simple, effective, and high in robustness and real-time performance; and on the premise of low complexity, the recovery effect of the motion blurred image can be improved remarkably.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Iterative noise reduction method based on image low-rank performance
InactiveCN105761223AHigh PSNRHigh PSNR valueImage enhancementImage analysisIdeal imageImaging processing
The invention provides an iterative noise reduction method based on image low-rank performance. The method concretely relates to the field of image processing and computer vision. In the image representation, Y refers to an image having noise, X refers to an ideal image, N refers to Gaussian white noise of which the standard deviation is tau, and the image is described as Y=X+N and denoising means to reduce the value of N. In order to better utilize the image low-rank performance to perform denoising, firstly an observation image is divided into multiple small blocks which are identical in size. As for any image block P, image blocks similar to the image block P are searched according to a certain similarity criterion. The similar image blocks are vectorized so that a similar block matrix P is formed, based on which the P is estimated by utilizing the low-rank performance of the similar block matrix and the theory of minimum variance estimation so that the objective of suppressing image block noise can be achieved. Finally the denoised image is obtained through reconstruction of the image block estimation value. As for the problem of a small amount of residual noise, the denoised image is processed by adopting a synthetic iterative method.
Owner:SICHUAN YONGLIAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
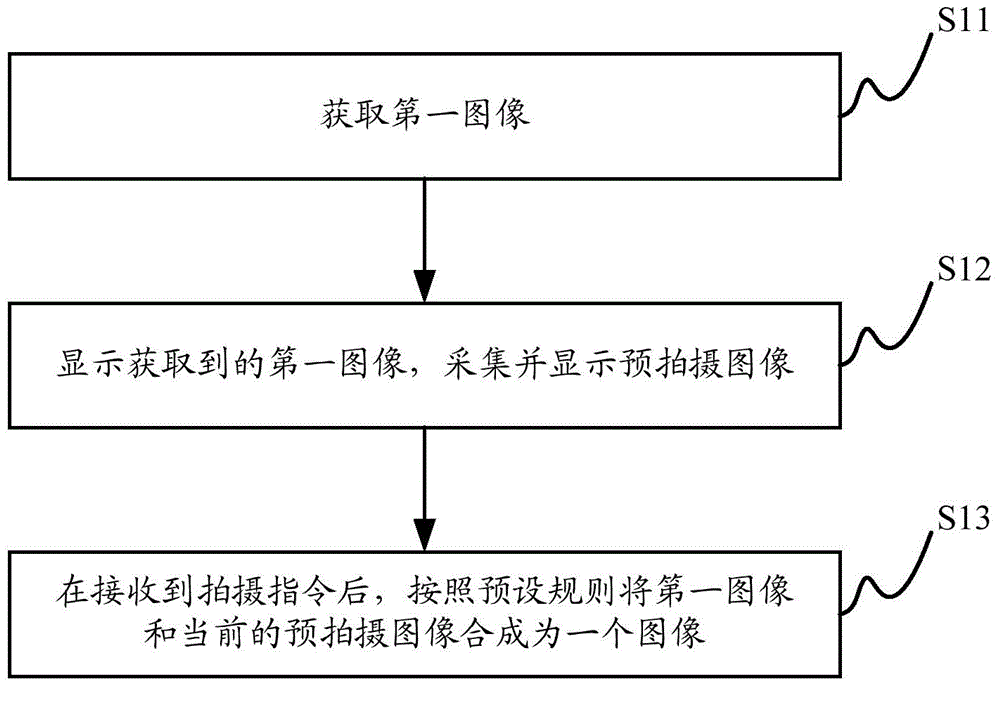
Image processing method and device and electronic device
ActiveCN104580918AImprove experienceFlexible adjustmentTelevision system detailsColor television detailsIdeal imageImaging processing
The invention discloses an image processing method which is applicable to an electronic device. The method includes: acquiring a first image; displaying the first image and acquiring and displaying a pre-photographed image; after receiving photographing instructions, synthesizing the first image and the current pre-photographed image into one image according to preset rules. Based on the image processing method, a user can see effect of the current pre-photographed image and the other image after synthesis, the synthesized image can be acquired after the user inputs the photographing instructions, and photographing objects can be flexibly adjusted by the user according to the current synthesized effect during photographing so as to have ideal images photographed, and user experience is improved. The invention further discloses a corresponding image processing device and the electronic device provided with the image processing device.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Tracking method and device based on electronic holder
InactiveCN107315992AMeet needsImprove experienceCharacter and pattern recognitionRegion selectionIdeal image
The invention discloses a tracking method and device based on an electronic holder. The method comprises steps of determining the original coordinate information of a region selection frame in the current display image, predicting a target region where a tracking target in the next frame of to-be-displayed image according to the original coordinate information and the pre-moving direction, and moving the target selection frame to the target region; and receiving the to-be-displayed image grabbed by an image senor of the electronic holder, and finally outputting the target region. According to the invention, it can be achieved that when a user is using a small portable shooting device to carry out shooting, a certain target with the quite quick moving frequency in the frame can be precisely tracked and shot, so the video with the ideal image quality can be shot; user demands can be met; and user experience is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN AEE AVIATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com