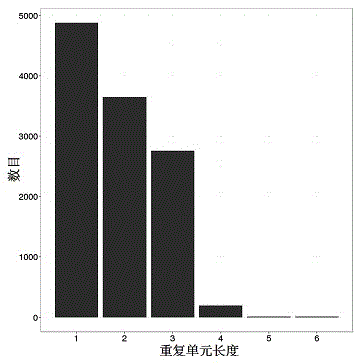
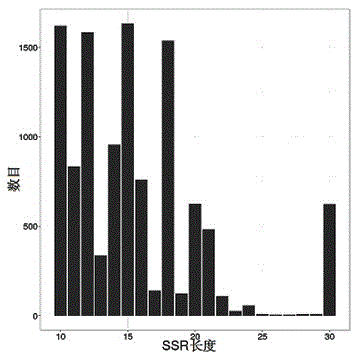
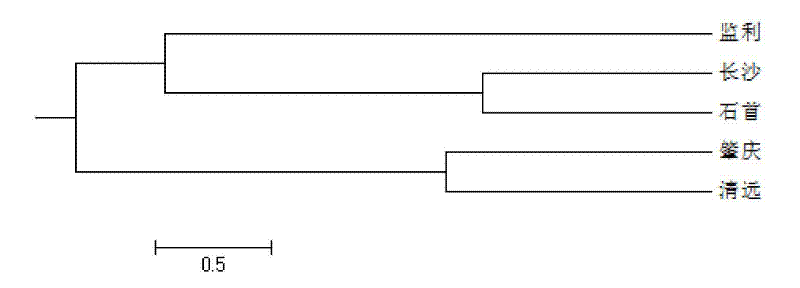
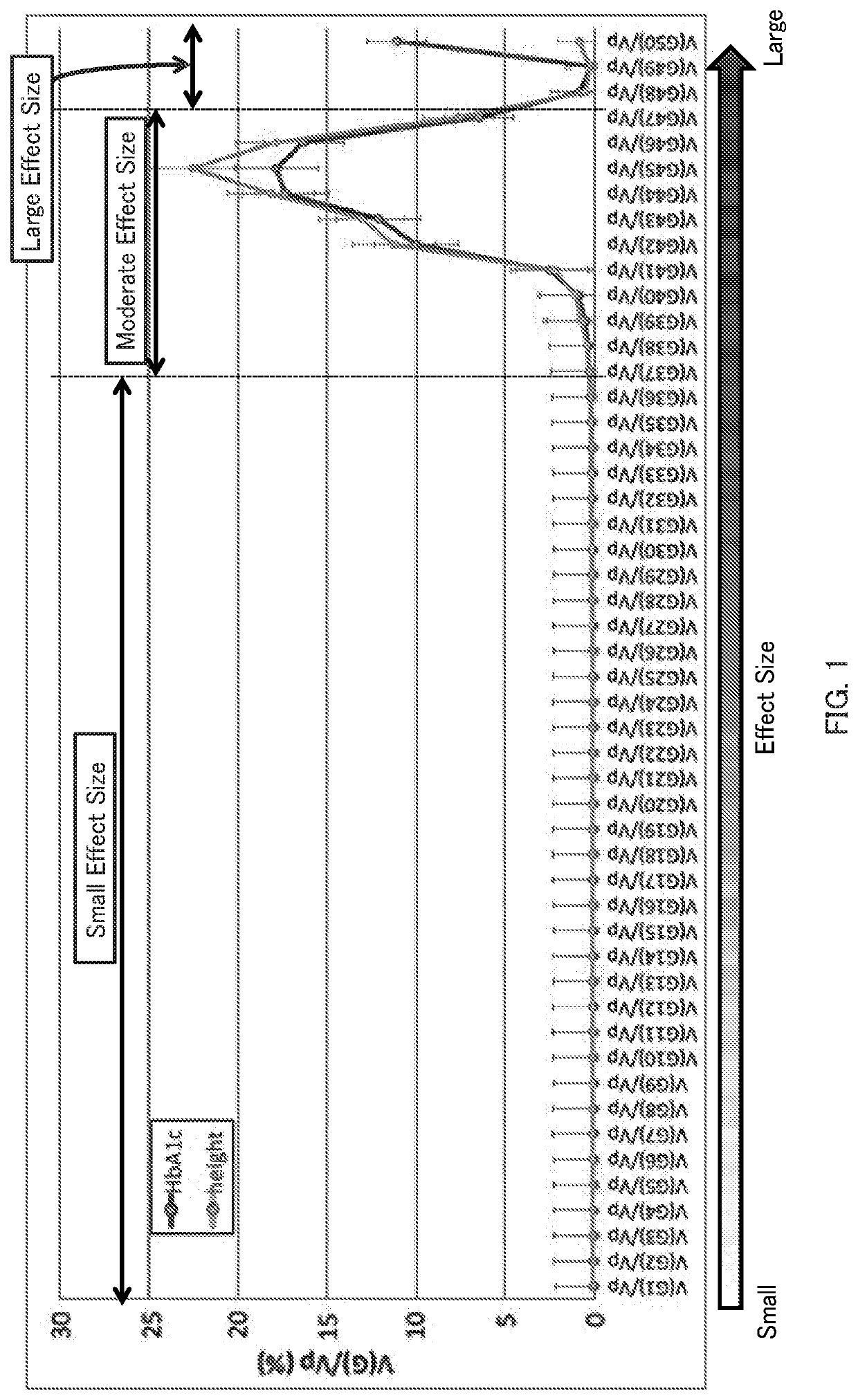
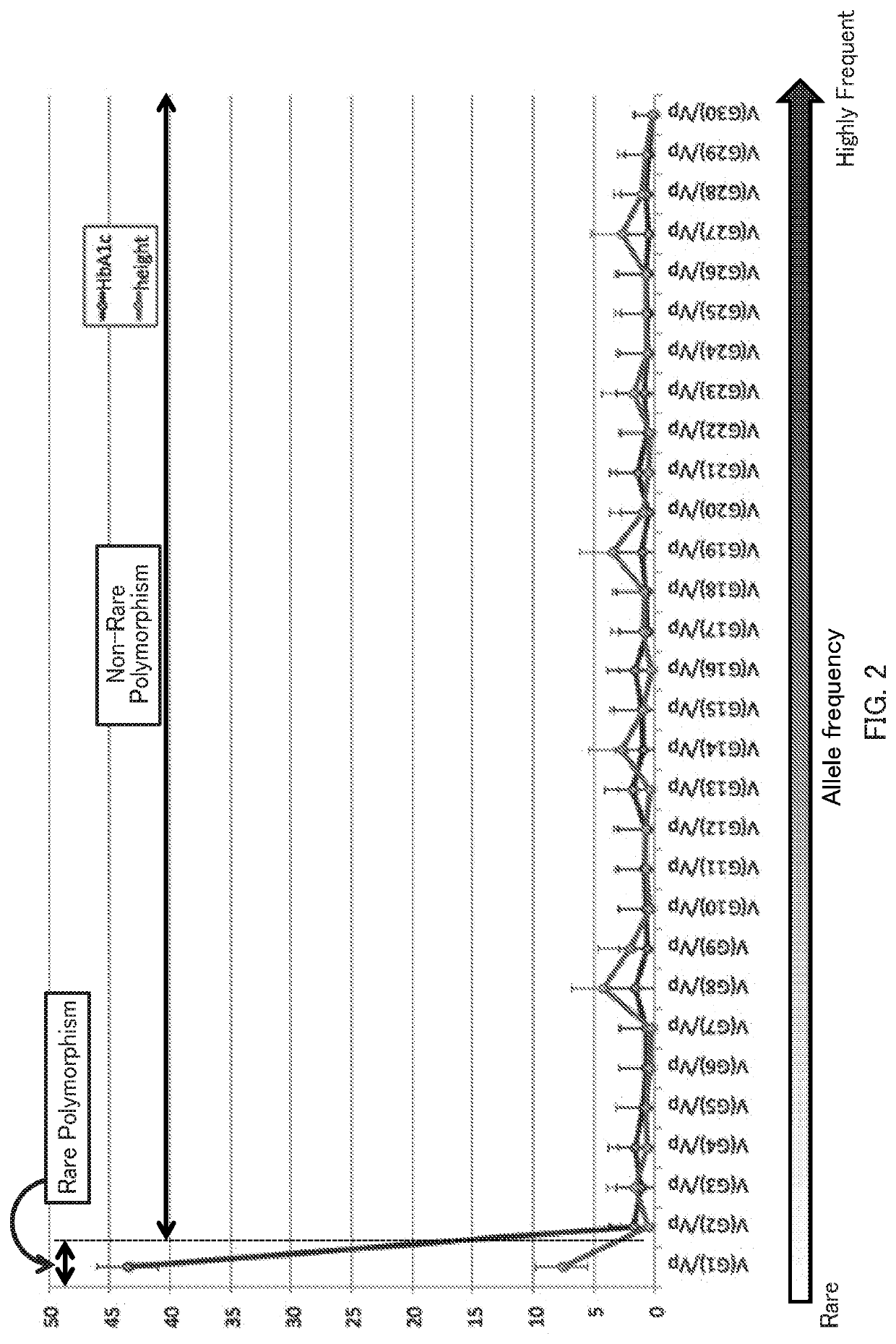
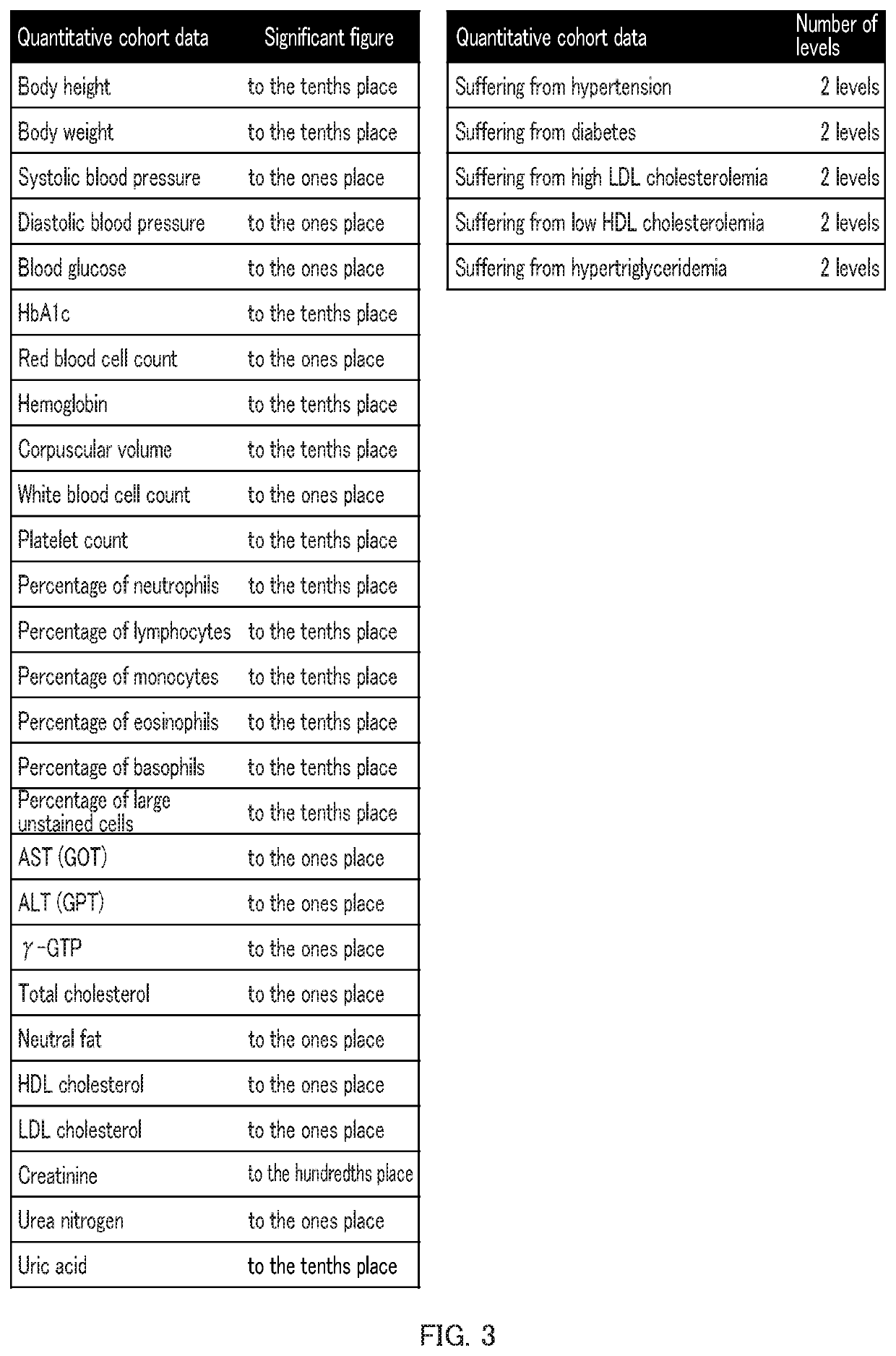
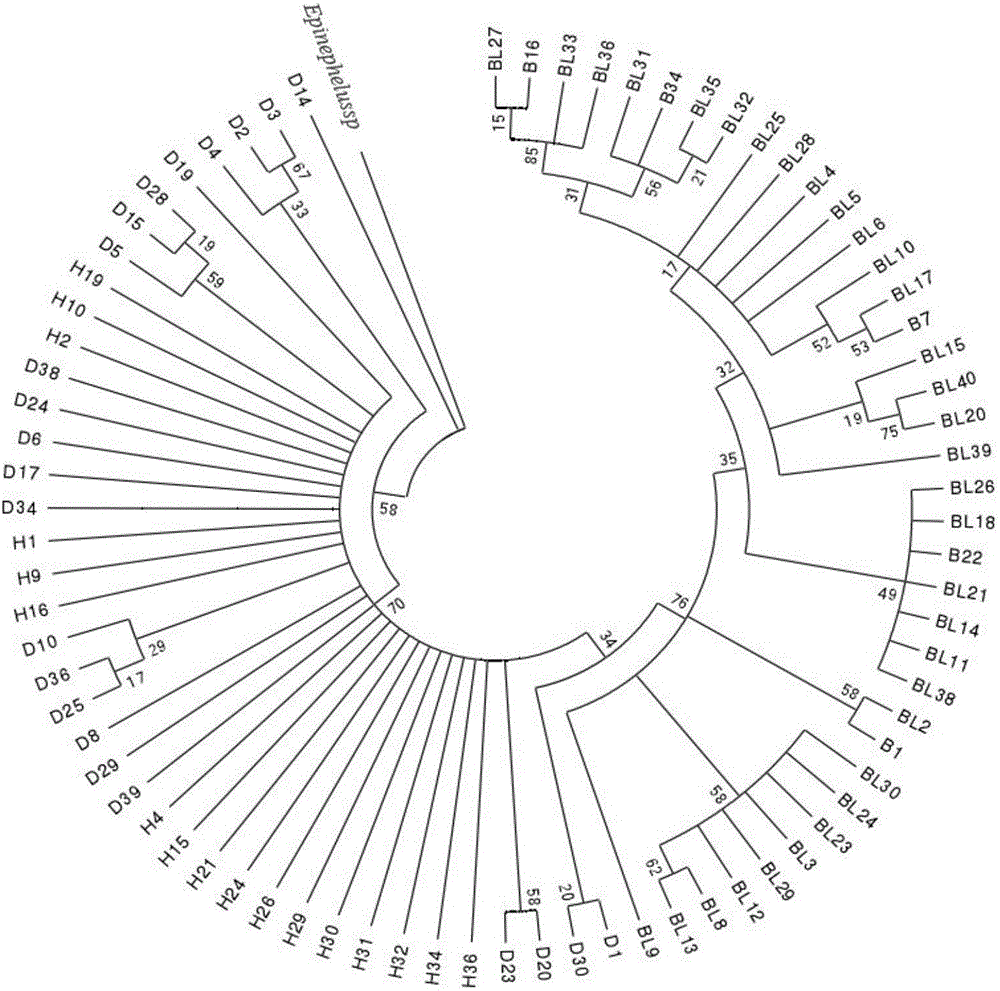
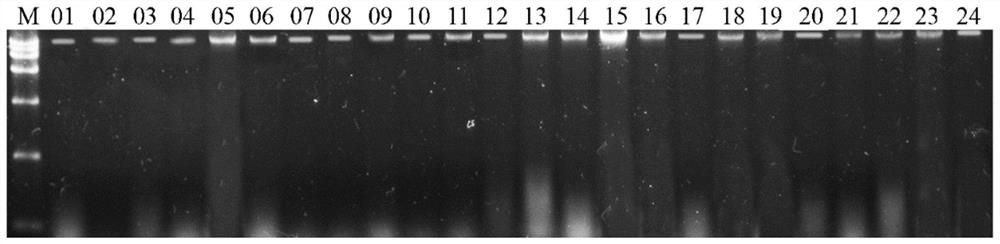
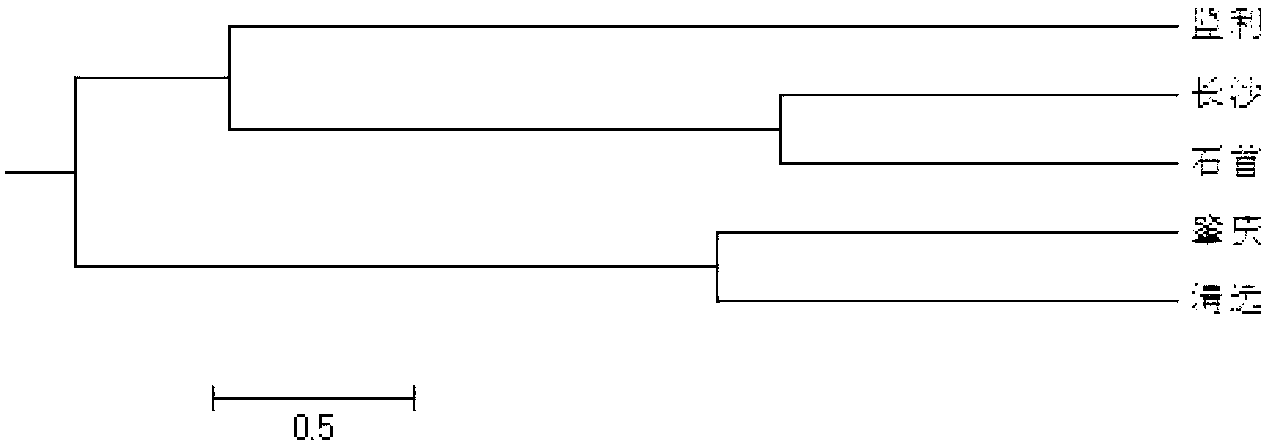
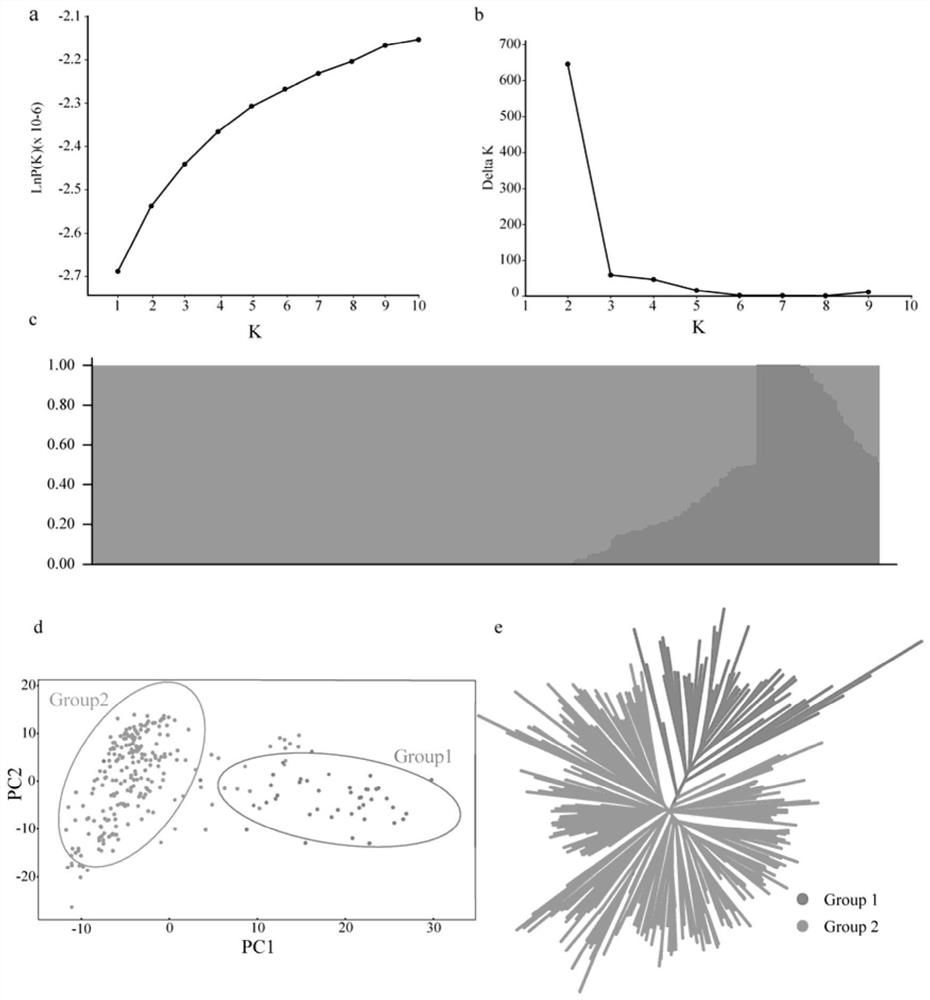
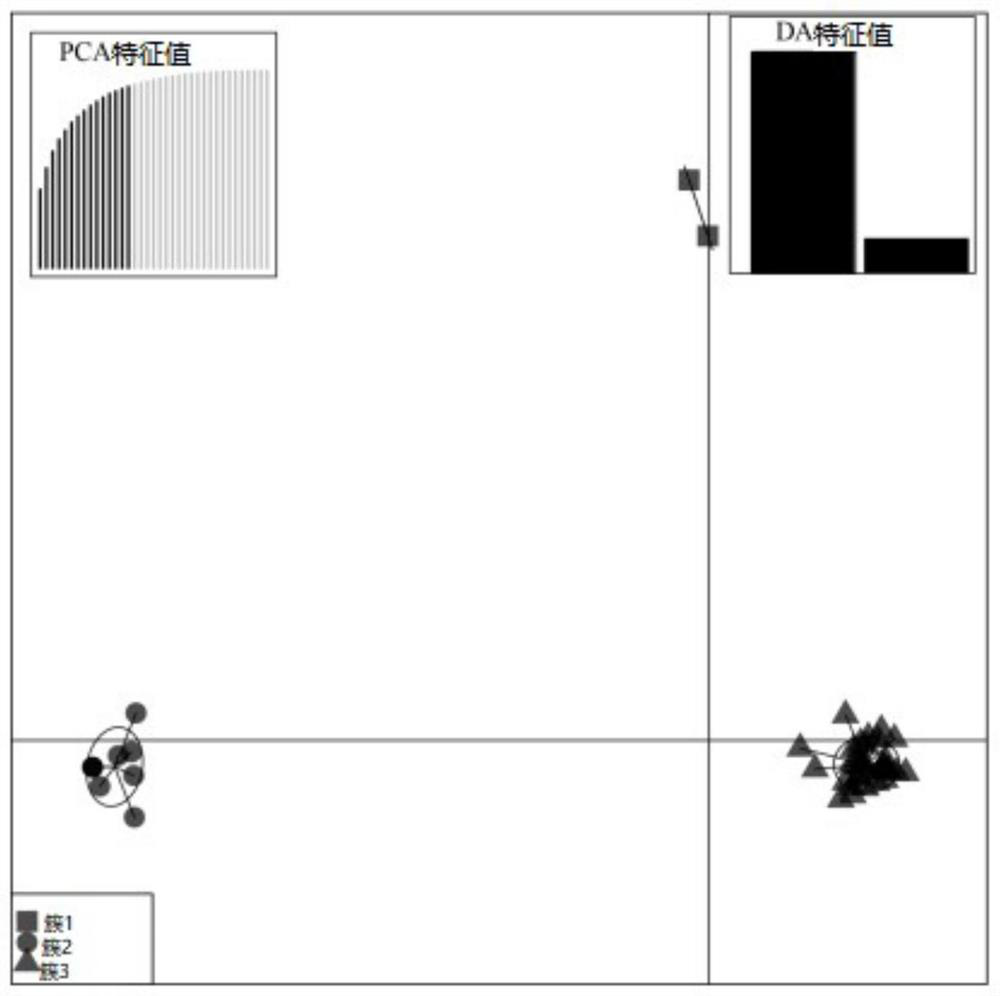
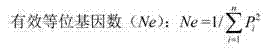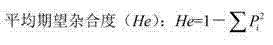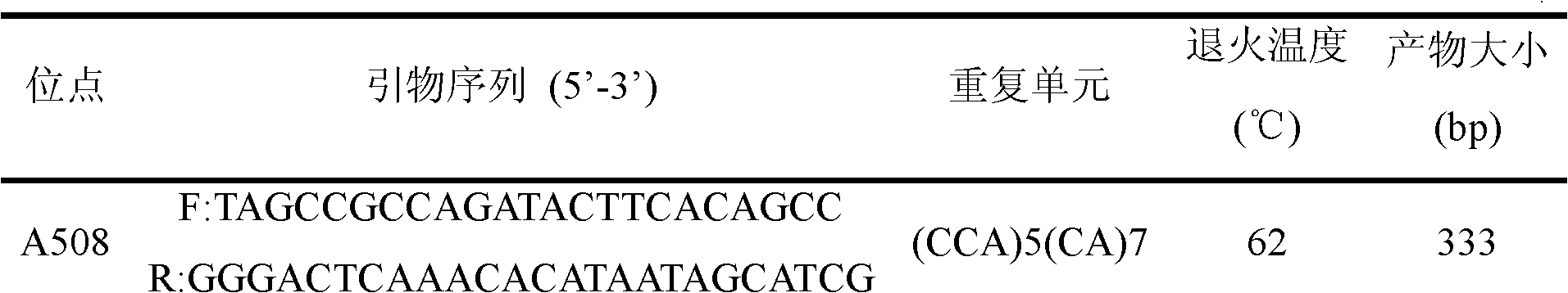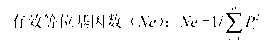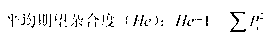Patents
Literature
58 results about "Genetic architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
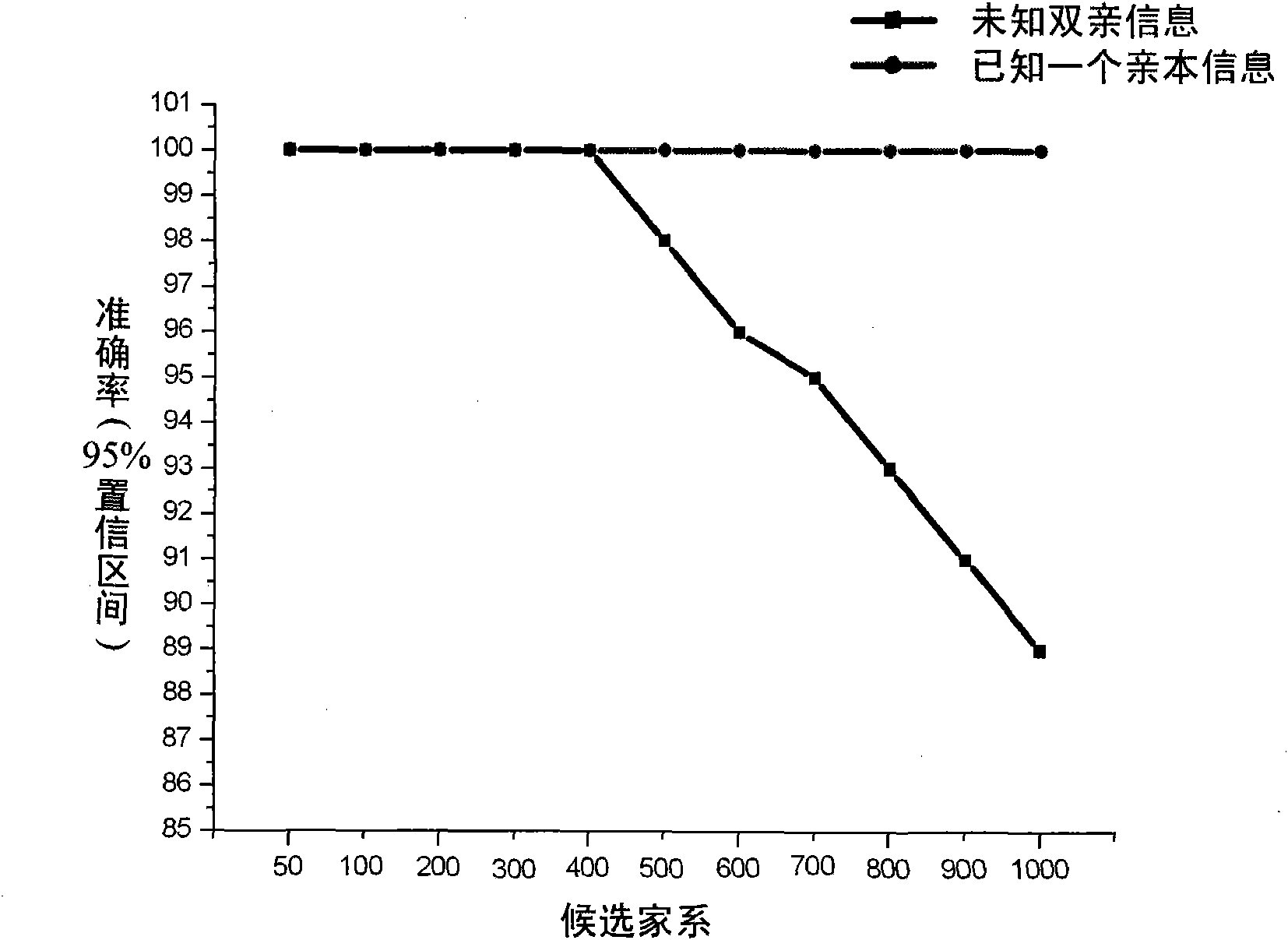
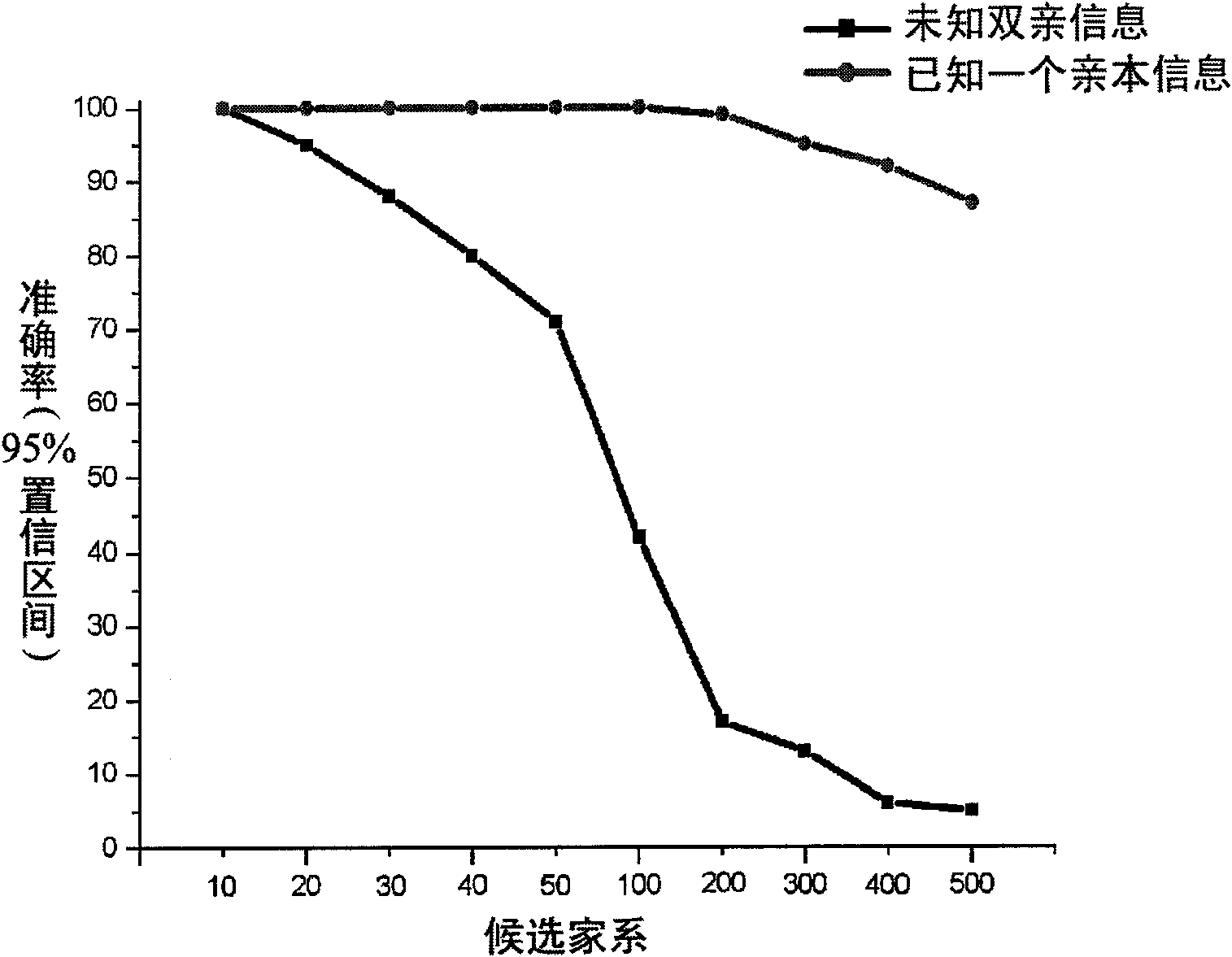
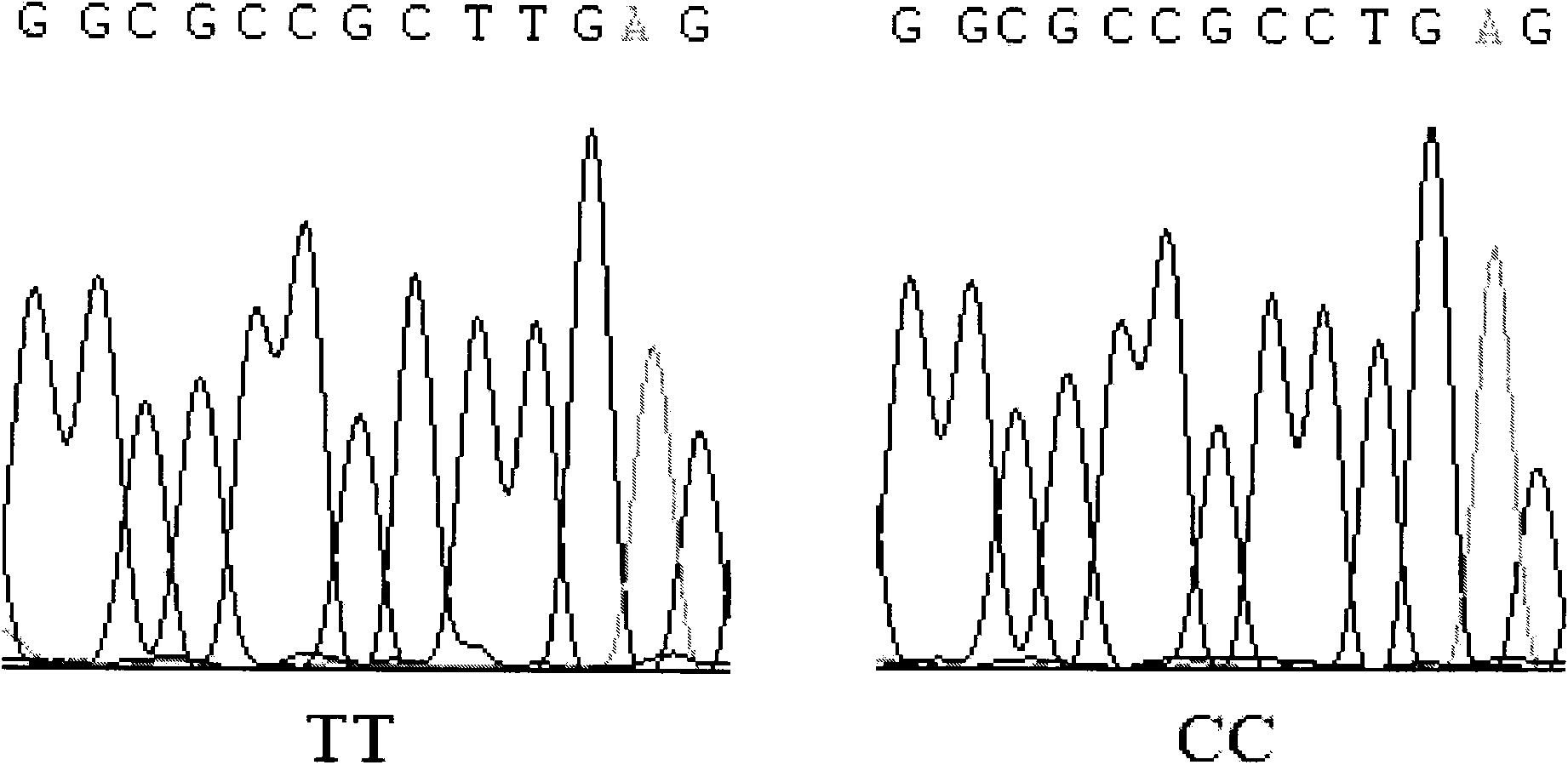
Genetic architecture is the underlying genetic basis of a phenotypic trait and its variational properties. Phenotypic variation for quantitative traits is, at the most basic level, the result of the segregation of alleles at quantitative trait loci (QTL). Environmental factors and other external influences can also play a role in phenotypic variation. Genetic architecture is a broad term that can be described for any given individual based on information regarding gene and allele number, the distribution of allelic and mutational effects, and patterns of pleiotropy, dominance, and epistasis.
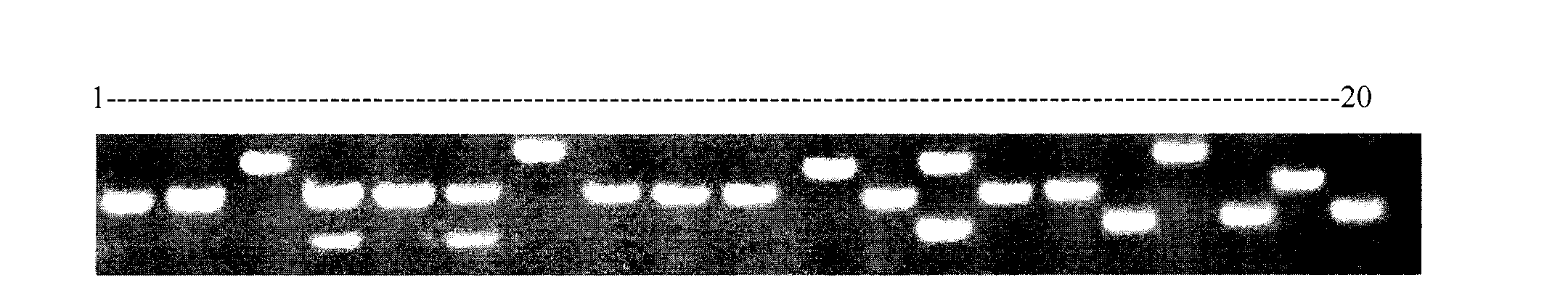
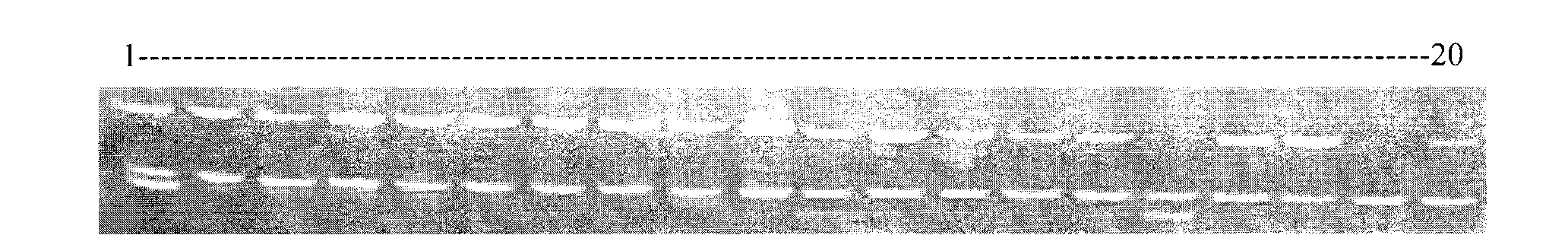
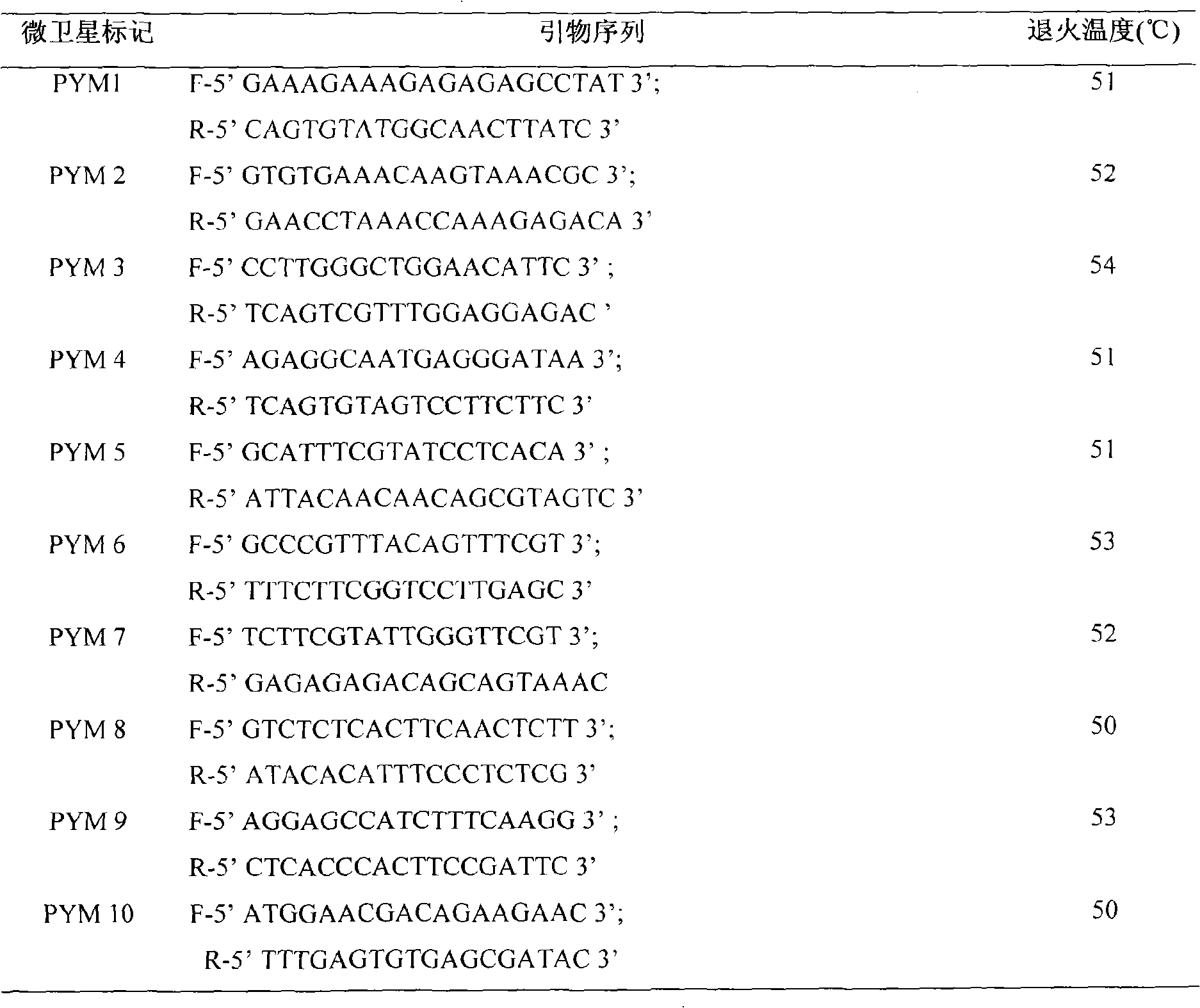
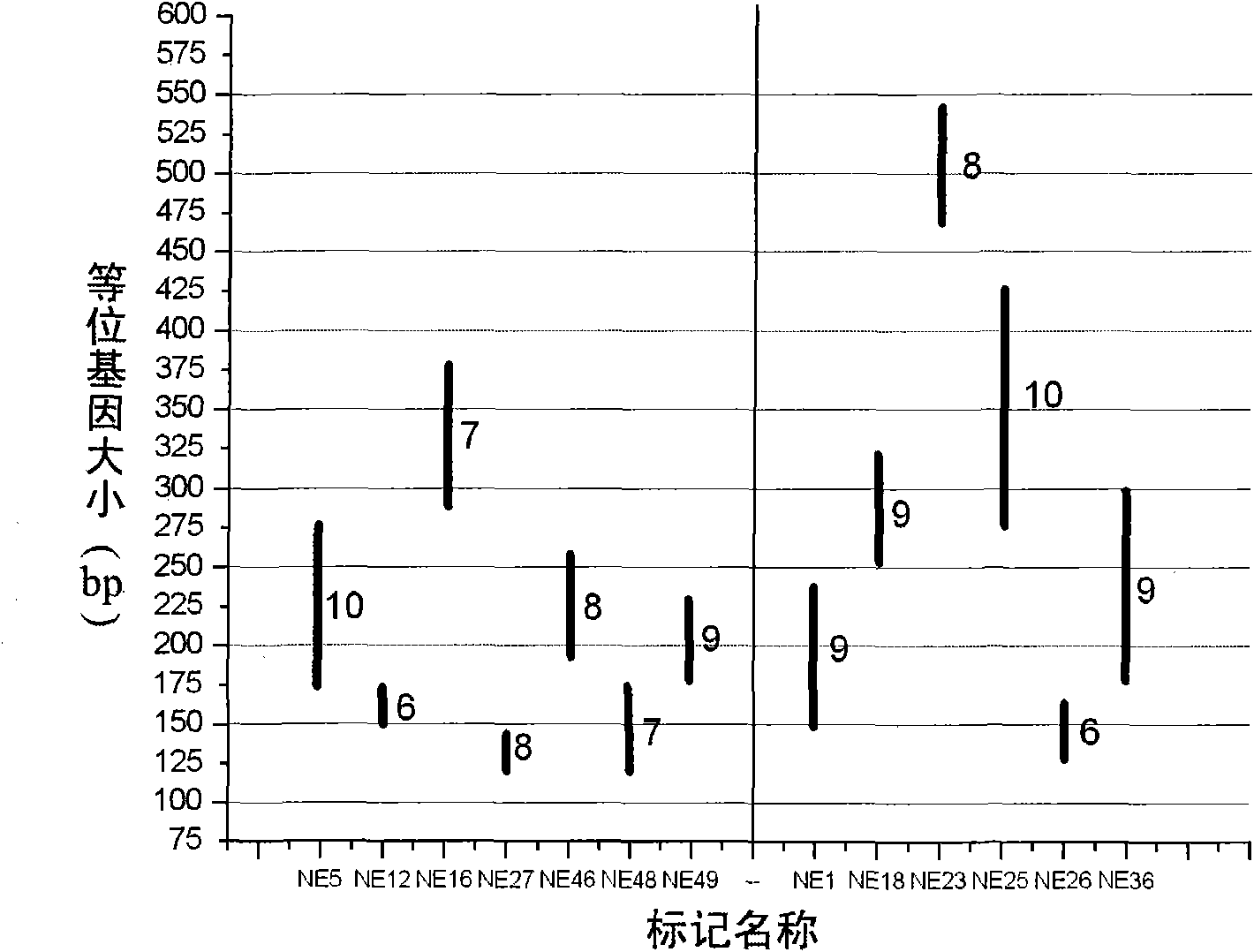
Porphyra yezoensis microsatellite marker screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN101550434AImprove reliabilityHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationResource protectionGermplasm
The invention belongs to molecular biology DNA labeling technique and application field, concretely relates to a porphyra yezoensis microsatellite marker screening method, and a method for analyzing germplasm genetic diversity by the makers, thereby lay foundations for genetic structure analysis of porphyra yezoensis, germplasm resource protection and molecular marker auxiliary breeding.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Multielement high flux genetic marking system and genetic analyzing method of Chinese mitten crabs
ActiveCN101613742AAvoid blindnessParsing Genetic DiversityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPolycultureMicrosatellite
The invention relates to the field of genetic thremmatology of aquatic products, in particular to a multielement high flux genetic marking system and a genetic analyzing method of Chinese mitten crabs. The genetic marking system is a mitochondria sequence information system and a microsatellite molecule marking system, wherein the microsatellite molecule marking system comprises 7 EST-SSR systems marked 1and 6 EST-SSR marked systems 2. The method comprises the following steps: later generations produced by the same parent and different parents in a polyculture family are separated according to hereditary constitution and genetic diversity through information of sequences of three pairs of primer amplifications COI, Cytb and CR of mitochondria, and male parent discrimination is performed on later generations of the discriminated parents according to genetic distance and genetic diversity through the EST-SSR microsatellite molecule marking system, thereby completing the genealogy authentication during the genetic breeding of the Chinese mitten crabs and determining the inbreeding coefficients. The invention discriminates the genetic relationship among filial generations by using the multielement high flux genetic marking system on the basis of effectively utilizing species genetic information, and effectively avoids the inbreeding recession.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular marker method for breeding meat performance of Aletail sheep and application thereof
ActiveCN103525920AImprove meat performanceIncrease economic incomeMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a molecular marker method for breeding meat performance of Altay sheep and application thereof. The molecular marker method comprises the following steps: using a MyoD1 (Myogenic Determination) gene as a candidate gene which influences meat yield of the Altay sheep; detecting a genetic structure of the MyoD1 gene in the Altay sheep variety by utilizing a PCR-SSCP (Polymerase Chain Reaction-Single-strand Conformation Polymorphism) technology; analyzing and judging a correlation between the genetic structure of the MyoD1 gene and the meat yield of the sheet; by a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sequence of the MyoD1 gene of the sheet, self-designing two pairs of specific primers; carrying out polymorphism detection on the MyoD1 gene of the Altay sheep in Sinkiang province by utilizing the PCR-SSCP technology; and carrying out correlation analysis with meat performance so as to find a molecular marker which is obviously related to the meat yield of the Altay sheep. The molecular marker method is used for improving meat performance of the Altay sheep to greatly improve the speed of improving and recovering excellent meat performance of the Altay sheep and has important significance and practical application value for improving economic income of farmers and herdsmen and quickening development of the mutton sheep industry in Sinkiang province.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method for developing SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) molecular mark of nibea albiflora for population identification
InactiveCN105624322AImprove work efficiencyReduce screening costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenomic DNAGrowing season
The invention discloses a method for developing an SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) molecular mark of nibea albiflora for population identification. The method comprises the following steps: extracting RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) by using a nibea albiflora mixed tissue of a plurality of nibea albiflora, performing RNA sequencing, performing splicing to obtain a nibea albiflora expression gene sequence, and obtaining a potential SSR mark with a bioinformatics method; designing primers by utilizing an SSR flanking sequence, extracting genomic DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) by using fins from a random sample, and screening the SSR primers; and performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on different nibea albiflora DNA templates by using each pair of the SSR primers, performing capillary electrophoresis detection on an amplification product by using a Qsep100 full-automatic nucleic acid analysis system, screening out primers with different amplification results, calculating allelic composition and allelic frequency by utilizing PopGene, and analyzing a nibea albiflora population relationship and a genetic structure. The SSR molecular mark method for identifying and verifying nibea albiflora groups, provided by the invention, is stable and reliable, is not influenced by ages, gender and growth seasons, and provides scientific bases for group analysis as well as species identification, breeding and evaluation of the nibea albiflora.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Method for classifying ctenopharyngodon idella based on expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeats (EST-SSR) marker
InactiveCN102242222AAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetic architecture
The invention discloses a method for classifying ctenopharyngodon idella based on an expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeats (EST-SSR) marker, which comprises the following steps of: extracting the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of the ctenopharyngodon idella, amplifying by using the EST-SSR marker, and analyzing the genetic structure of the ctenopharyngodon idella according to an amplification result. Compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantages of high purposiveness and direct action effect, and is easy to operate, high in detection speed, low in detection cost, and convenient to widely popularize and use.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Gene in significant correlation with characters of fiber yield, SNP marker and application of SNP marker
ActiveCN109628630AEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFiber
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology of characters of fiber yield, in particular to a gene in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield, a SNP marker and application of theSNP marker. The gene in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield is a Gh_D05G1124 gene and / or a Gh_D05G0313 gene. 276 upland cotton materials are taken as raw materials and planted in multiple environments, a CottonSNP63k gene chip is adopted for genetic typing, and 10660 high-quality SNPs are obtained and used for analyzing of the genetic structureand GWAS. According to the result, 23 SNPs in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield are discovered to correspond to 15 QTLs. In addition, through Qrt-PCR analyzing, the Gh_D05G1124 gene andthe Gh_D05G0313 gene are taken as candidate genes for adjusting the characters of the fiber yield, the SNP marker in significant correlation with the fiber yield is obtained, and theoretical support is provided for research and application of the characters of the fiber yield.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tilapia mossambica and microsatellite identification primer and method for genetic diversity of tilapia mossambica
PendingCN111286547AEasy to separateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyElectrophoreses
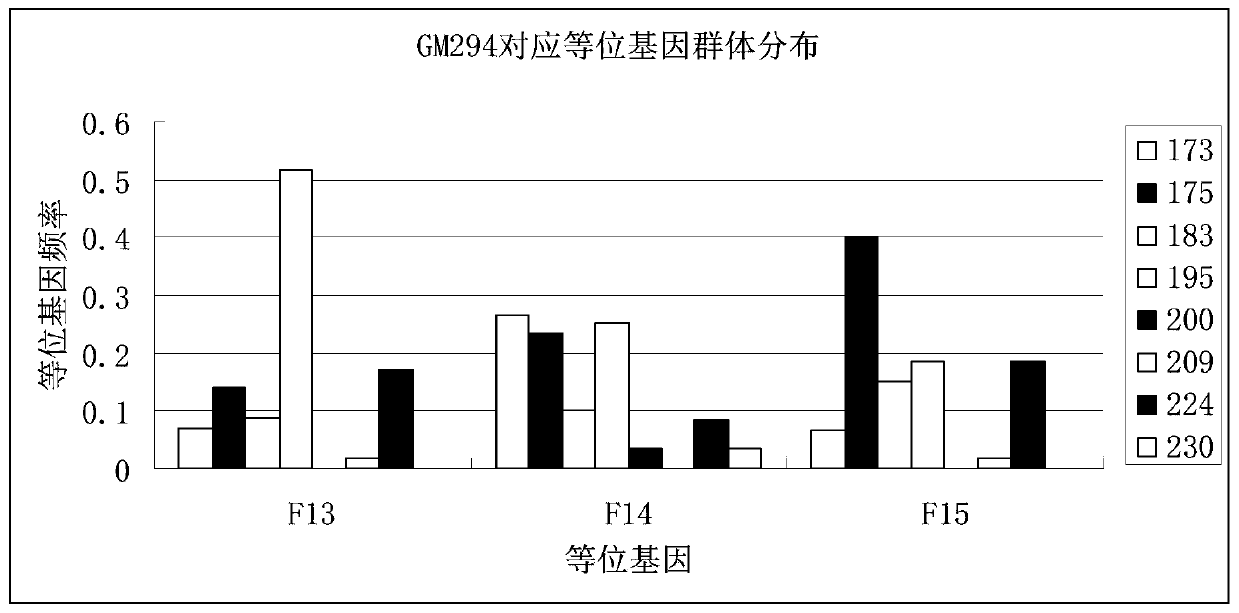
The invention provides a tilapia mossambica and a microsatellite identification primer and method for genetic diversity of the tilapia mossambica; the microsatellite identification primer and method are included, and the method comprises the following steps: material selection, genome DNA extraction, microsatellite primer screening, microsatellite primer PCR reaction, electrophoresis detection anddyeing, and data analysis. According to the method, a later generation (F13, F14 and F15) group for breeding the new GIFT tilapia is used as a research object; tracking and monitoring the genetic variation of the later generation population by using a microsatellite marker technology; on one hand, genetic diversity levels of different breeding generations are compared, and the influence of the breeding process on the genetic structure of the breeding population is analyzed; on the other hand, microsatellite identification markers capable of distinguishing different breeding generation populations are searched, and through comprehensive analysis of the two aspects, a scientific basis is provided for continuous breeding and breed conservation work of the later generation of new GIFT tilapiamossambica breeding.
Owner:茂名市伟业罗非鱼良种场 +1
Polymorphic primer of cinnamomum camphora nuclear genome SSR molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN110724760AReveal genetic diversityReveal structureMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a polymorphic primer of a cinnamomum camphora nuclear genome SSR molecular marker and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology. Thenucleotide sequence of the primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.14. The polymorphic primer is applied to the application of variety identification of cinnamomum camphora, and genetic structureand resource genetic diversity analysis of ancient cinnamomum camphora groups. A method includes the steps of genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and data analysis. 186 individuals of 18 ancient cinnamomum camphora groups are subjected to genetic structure and resource genetic diversity study; the possibly forming reasons are analyzed according to existinggenetic structure and resource genetic diversity patterns of the cinnamomum camphora; and theoretical basis is provided for the wild cinnamomum camphora resource protection and utilization. The repeatability of the SSR molecular marker is high, and the real level of the genetic diversity of the cinnamomum camphora can be comprehensively disclosed.
Owner:INST OF BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES JIANGXI ACAD OF SCI +1
Polymorphic primers of pheobe chekiangensis nuclear genome SSR molecular marker and application of polymorphic primers
ActiveCN113801959AHigh resolutionAccurate resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementInvasive species monitoringNucleotideGenetic architecture
The invention discloses polymorphic primers of a pheobe chekiangensis nuclear genome SSR molecular marker and an application of the polymorphic primers, and belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology. 15 pairs of polymorphic primers of the pheobe chekiangensis nuclear genome SSR molecular marker are developed through a PCR technology, a polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis technology and a capillary electrophoresis technology, and the nucleotide sequences of the primers are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.30. The polymorphic primers of the pheobe chekiangensis nuclear genome SSR molecular marker are good in specificity and high in polymorphism; and when the polymorphic primers are applied to analysis of the genetic structure and resource genetic diversity of the pheobe chekiangensis, the diversity and the genetic structure of the genetic level of the pheobe chekiangensis in China can be disclosed more comprehensively, and a foundation is laid for formulating a genetic protection strategy.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for constructing tobacco core germplasm based on genomics and application thereof
PendingCN112359102AGood repeatabilityEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenomics
The invention discloses a method for constructing tobacco core germplasm based on genomics and application of the method, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, genomics and germplasm resource science. The method comprises the steps: performing simplified genome sequencing on tobacco germplasm resource populations, adopting sequencing data quality control, SNP detection screeningand population stratification analysis, further dividing the whole germplasm resource large population into 200 subpopulations through IBS and K-means analysis, combining random selection in the subpopulations with background screening, and performing constructing to obtain the core germplasm capable of representing the whole tobacco germplasm resource large group. According to the method, the core germplasm construction efficiency can be improved, the genetic structure of an original population is well reserved, and the method has important significance in improving the germplasm resource utilization efficiency.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD +1
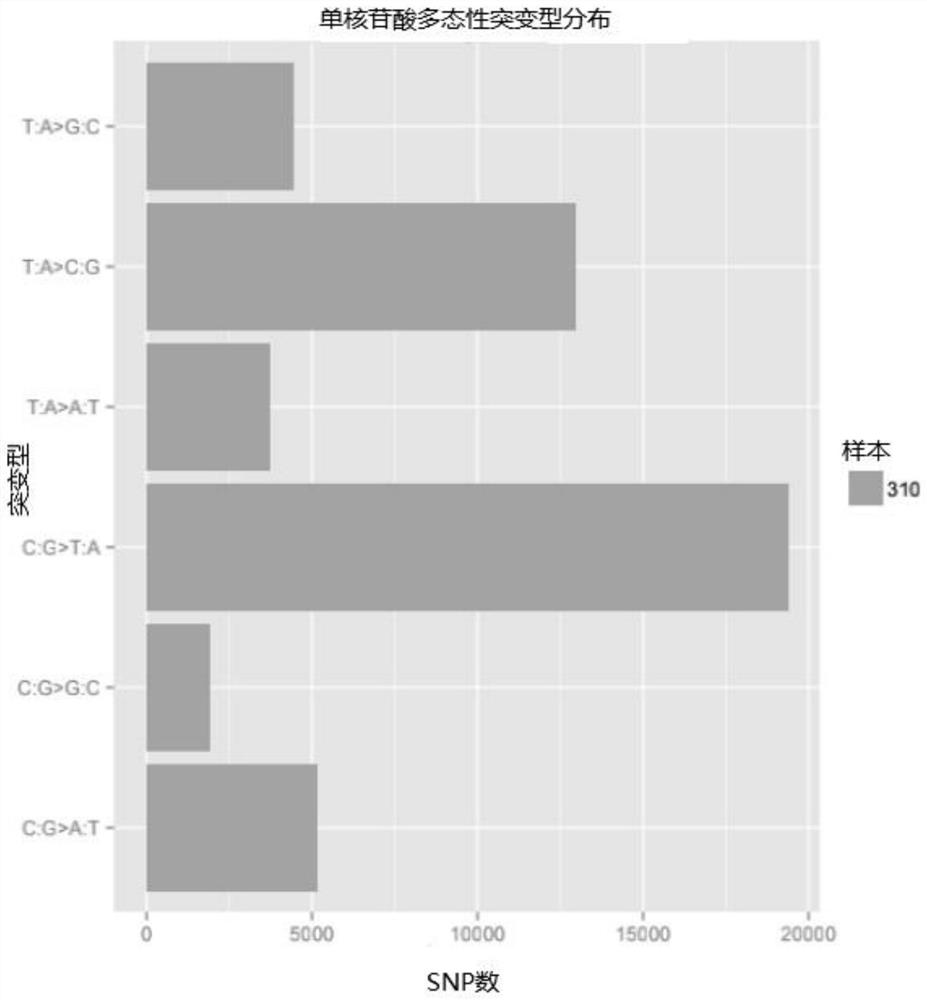
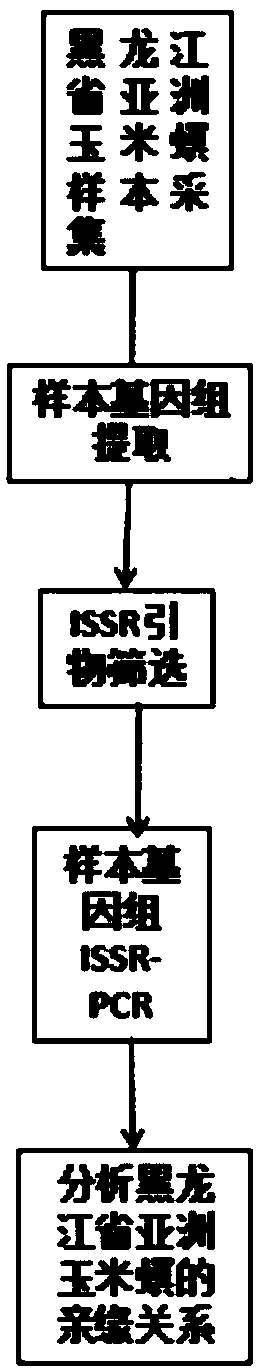
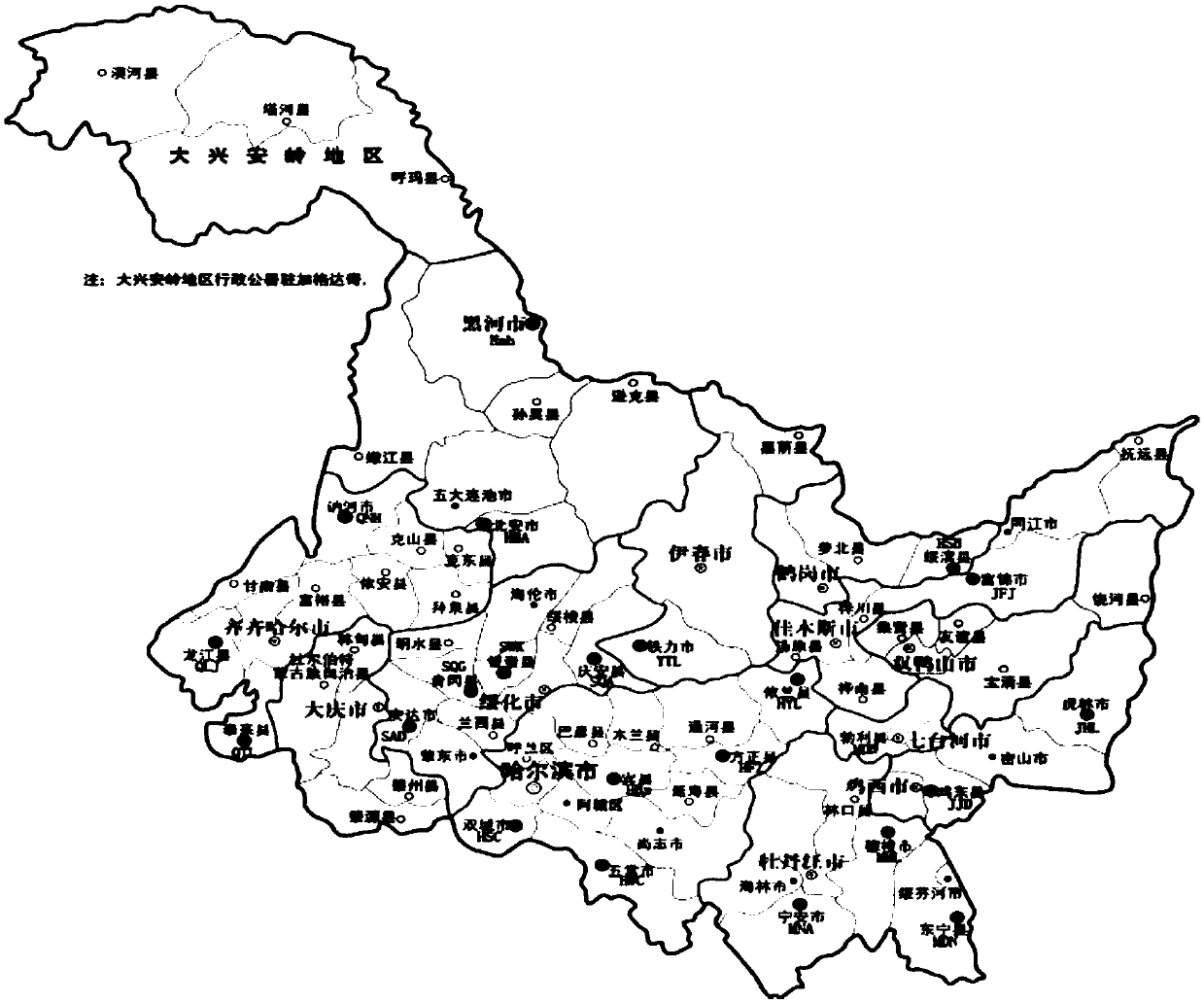
Method for analyzing corn borer population genetic diversity by ISSR system
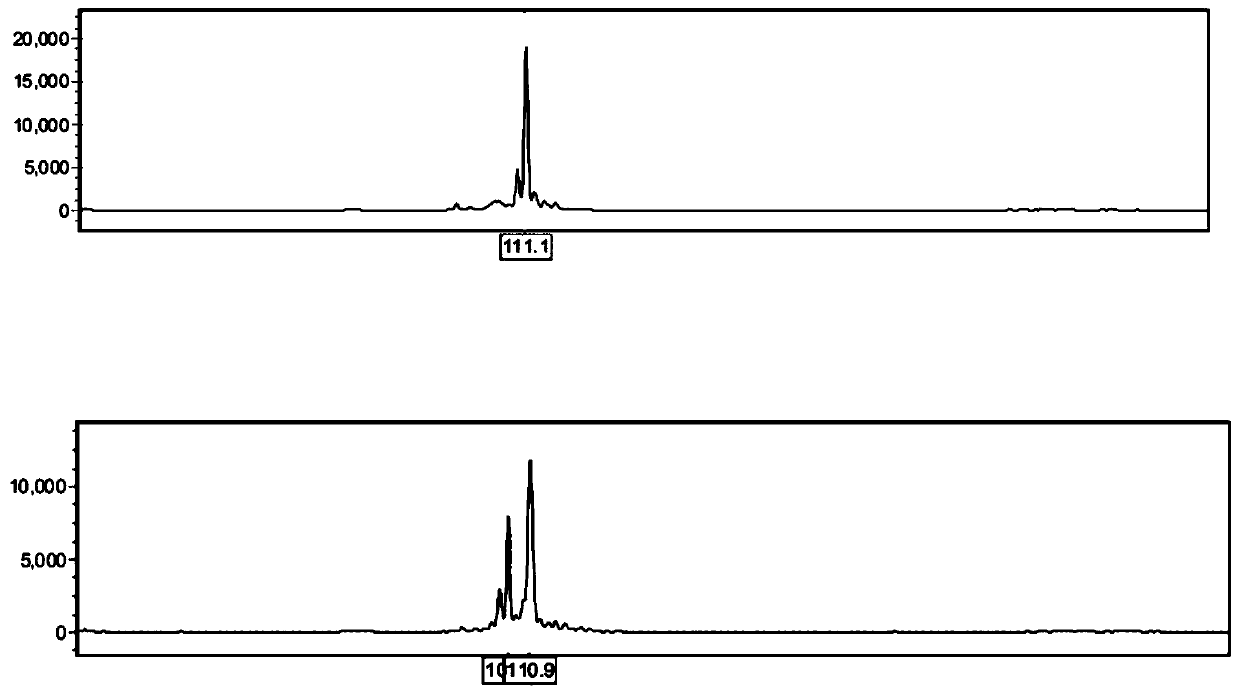
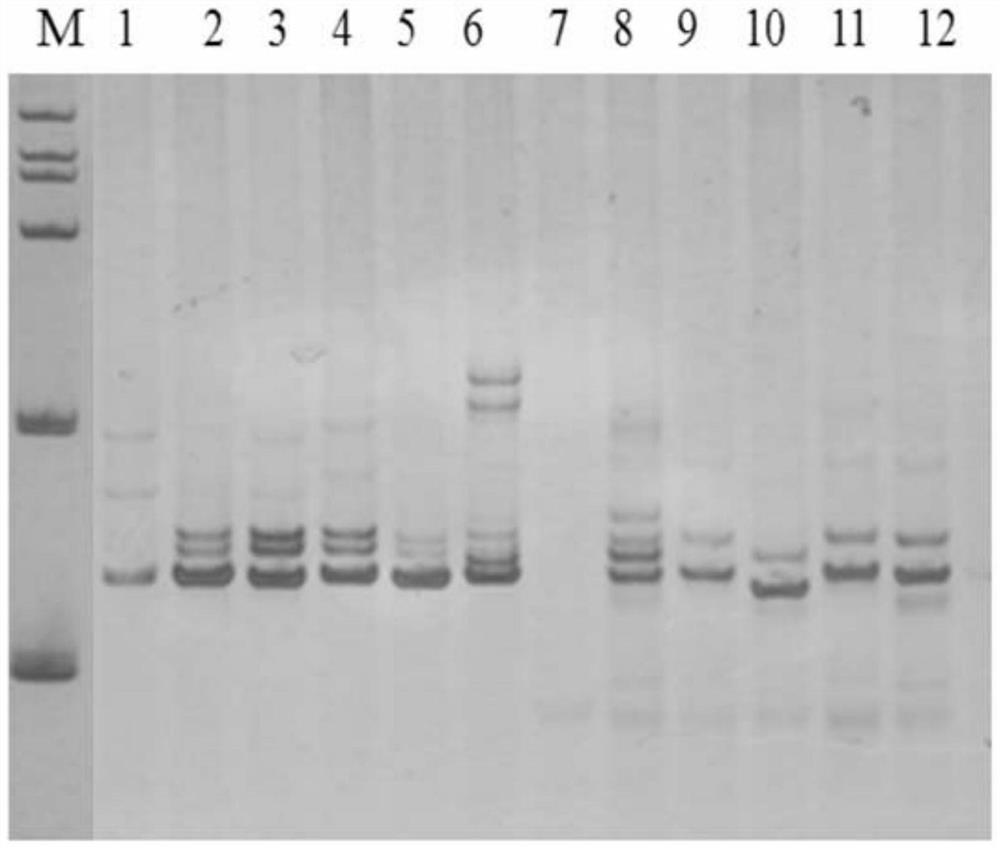
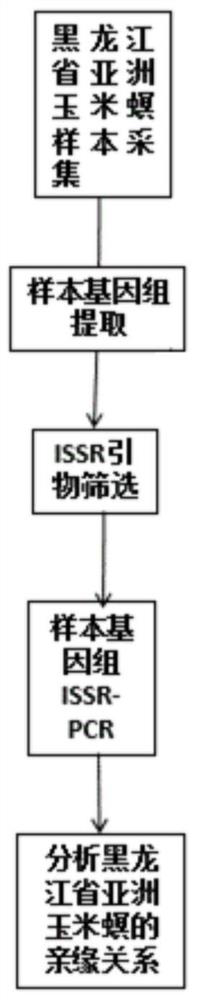
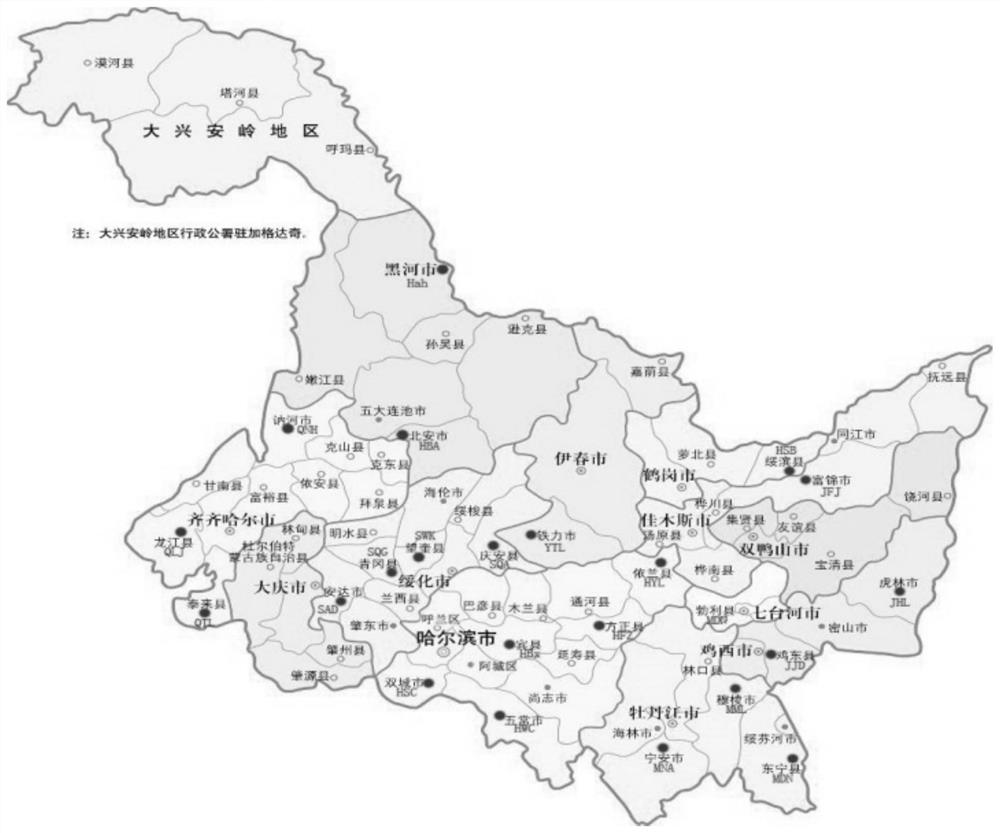
ActiveCN109576377AAmplification reaction is stableAmplified fragments are clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityGenetic architecture
The invention provides a method for analyzing the corn borer population genetic diversity by an ISSR system, and relates to a method for analyzing the corn borer population genetic diversity. The invention aims at solving the problems that in the prior art, no effective molecular marking method, particularly an ISSR molecular marking method is used for identifying the corn borer, particularly thegenetic structure and the affinity relationship of different geographical populations of asiatic corn borer, so that the migration change condition of the corn borer is specified. The invention provides the method for analyzing the corn borer population genetic diversity by the ISSR system. The method is a simple and easy-to-operate molecular marking technology; for 14 ISSR primer sequences selected by the method, the PCR amplification reaction in the corn borer is stable; the amplified fragments are clear; the polymorphism is high; the technical support is provided for scientific research such as corn borer resource identification and genetic diversity analysis. The method is applied to the field of the corn borer.
Owner:黑龙江省植检植保站
Methods of creating trait prediction models and methods of predicting traits
To provide methods of creating trait prediction models for predicting phenotypes of traits from single nucleotide polymorphism data and methods of predicting traits with which traits can be predicted with a high accuracy.This is a method of creating a trait prediction model for predicting a phenotype of a multifactorial trait using data of a plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms linked to a trait for each of a plurality of individuals of an organism: representing each of the plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms as a matrix; classifying the plurality of single nucleotide polymorphisms into a plurality of categories based on their genetic architectures; calculating, for each of the categories, a genomic similarity matrix using the represented matrix and the number of the single nucleotide polymorphisms belonging to the category; and applying the genomic similarity matrix and a parameter of the genetic architecture to a linear mixed model.
Owner:IWATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting genetic diversity and population genetic structure of wild Siniperca scherzeri
PendingCN105861683AObjectively and truly reflect the status of genetic diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementStructure analysisGenetic diversity
The invention provides a method for detecting the genetic diversity and population genetic structure of wild Siniperca scherzeri. The method includes the following steps that firstly, DNA of different populations of wild Siniperca scherzeri is extracted respectively; secondly, primary PCR amplification and secondary PCR amplification are carried out on DNA, obtained in the first step, of wild Siniperca scherzeri respectively, and first amplification products and second amplification products of DNA of wild Siniperca scherzeri are obtained; thirdly, bidirectional sequencing is carried out on the first amplification products and the second amplification products of DNA of wild Siniperca scherzeri respectively, Cyt b gene sequences of the first amplification products and D-loop gene sequences of the second amplification products are spliced and combined, and sequences of wild Siniperca scherzeri Perciformes are obtained; fourthly, genetic diversity and population genetic structure analysis is carried out on the sequences of different populations of wild Siniperca scherzeri Perciformes. According to the method, combinatory analysis with double gene sequence splicing is adopted, the defect of insufficient information amount in single gene sequences is overcome, and the condition of the genetic diversity of species is more objectively and truly reflected.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker and screening method thereof
InactiveCN102181535AGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementResource protectionGenetics
The invention relates to the technology of the DNA molecular marker and provides a Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker and a screening method thereof. The Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker can be numbered to be A508. The screening method comprises the following steps: constructing a Scylla paramamosain microsatellite enriched library, selecting monoclone for sequencing; using a microsatellite DNA locus searching software to obtain the positive clone containing the Scylla paramamosain microsatellite sequence, and determining the Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker. The microsatellite marker A508 can be used for the genetic structure analysis of Scylla paramamosain, idioplasm resource protection and molecular marker-assisted selection, have good repeatability and be a reliable and effective molecular marker. The obtained Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker lays the foundation for the genetic structure analysis of Scylla paramamosain, idioplasm resource protection, molecular marker-assisted selection and the like.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for researching corn southern rust group inheritance and transmission based on SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism)
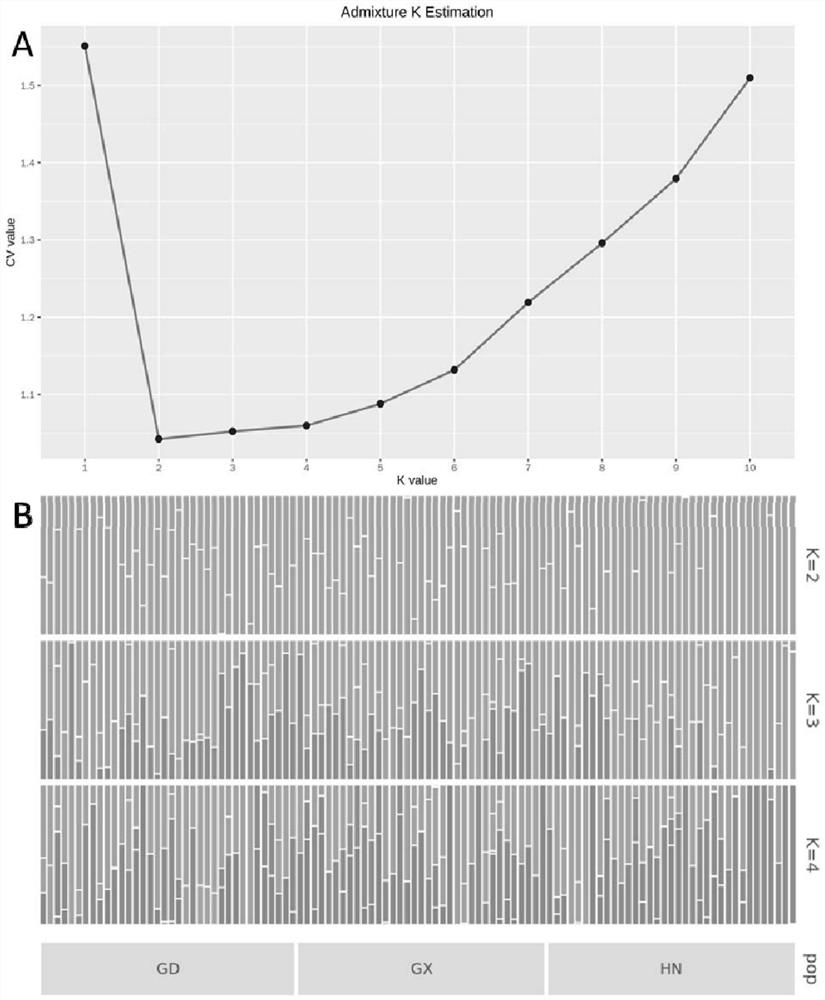
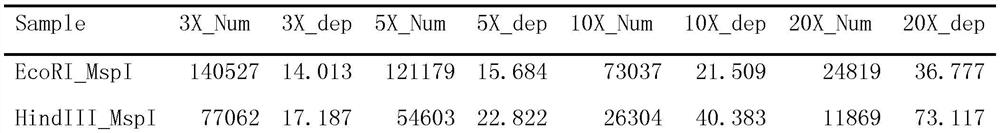
PendingCN114262747ADetermine the propagation pathReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenomic sequencingPuccinia graminis tritici
The invention provides a method for researching genetic and propagation paths of a corn southern rust group based on an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker. According to the method, DNA of different strains is subjected to enzyme digestion by using screened restriction enzymes EcoRI and MspI, so that a genome sequencing technology is simplified, SNP markers are mined by using Stacks software, and then the genetic structure and the propagation path of a puccinia multiflora population are researched; the restriction endonucleases EcoRI and MspI provided by the invention have a better cutting effect on the whole genome of puccinia multiflora, and compared with other combinations, more tags can be obtained under the condition of the same sequencing depth. At present, whole genome sequencing of puccinia multiflora is not performed yet, and the method for researching the population genetic structure and the propagation path of puccinia multiflora on the basis of the SNP sites obtained by simplifying genome sequencing and utilizing stacks software has important significance on comprehensive treatment and accurate prevention and control of diseases.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
EST-SSR (simple sequence repeat) fluorescent marker primers for scapharca broughtonii population genetic analysis and application
PendingCN111218517AEasy to operateGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsGenetic architecture
The invention provides EST-SSR (simple sequence repeat) fluorescent marker primers for scapharca broughtonii population genetic analysis and application and belongs to the field of molecular biologics. Sequences of the primers are shown in SEQ ID NO.1-10. The primers are adopted for genetic structure analysis on scapharca broughtonii populations, and effective tools can be provided for evaluatingand monitoring genetic structure variation of scapharca broughtonii populations in China.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Tea tree glutamine synthetase gene SSR molecular marker primer and application
ActiveCN114480697AEasy to synthesizeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention discloses a tea tree glutamine synthetase gene SSR molecular marker (SSR1-GS, SSR2-GS) primer and application of the tea tree glutamine synthetase gene SSR molecular marker primer. Researches show that the method for developing the SSR primer on the whole genome of the tea tree according to specific genes is feasible, and the obtained primer is high in polymorphism and good in repeatability and has good feasibility and pertinence. Therefore, the inventor develops research on genetic polymorphism of tea tree germplasm resources. In conclusion, the research method, the SSR molecular marker and the primer of the SSR molecular marker can be widely applied to tea tree variety identification, genetic structure and resource diversity analysis, genetic map construction, functional gene positioning and QTL positioning, seed purity identification and molecular marker-assisted seed selection research, and tea tree theanine synthesis and tea tree genetic polymorphism can be further researched conveniently; deep development of tea tree resources is promoted.
Owner:GUANGXI SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST GUANGXI SUBTROPICAL AGRI PROD PROCESSING RES INST
A method for analyzing genetic diversity of corn borer populations using issr system
ActiveCN109576377BAmplification reaction is stableAmplified fragments are clearMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic diversity
A method for analyzing the genetic diversity of corn borer population by using ISSR system, which relates to the method of genetic diversity of corn borer population; Corn borer, especially the genetic structure and kinship of different geographical populations of the Asian corn borer, so as to clarify the problem of the migration and change of the corn borer; the invention provides a method for analyzing the genetic diversity of the corn borer population using the ISSR system. This method is a simple and easy-to-operate molecular marker technology. The 14 ISSR primer sequences selected by this method have stable PCR amplification reactions in corn borer, clear amplified fragments, and high polymorphism, which can be used as corn borer resources. Provide technical support for scientific research such as identification and genetic diversity analysis. The invention is applied to the field of corn borer.
Owner:黑龙江省植检植保站
Method for classifying ctenopharyngodon idella based on expressed sequence tag-simple sequence repeats (EST-SSR) marker
InactiveCN102242222BAccurate identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetic architecture
The invention discloses a grass carp classification method based on EST-SSR markers. The method includes extracting the DNA of the grass carp, using EST-SSR markers to amplify, and analyzing the genetic structure of the grass carp according to the amplification result. Compared with the traditional method, the method of the invention has the advantages of strong purpose and direct effect. And the operation is simple, the detection is fast, the detection cost is low, and it is convenient to be popularized and used widely.
Owner:PEARL RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
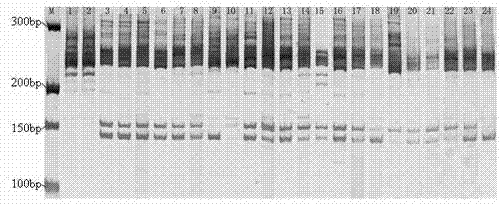
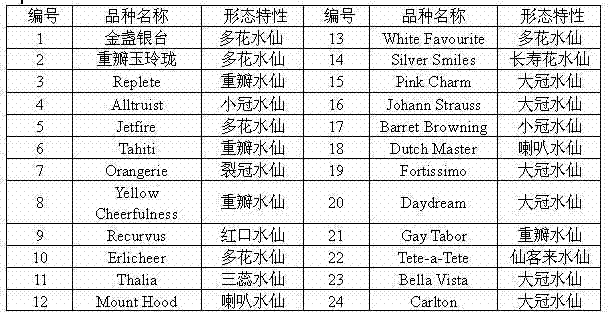
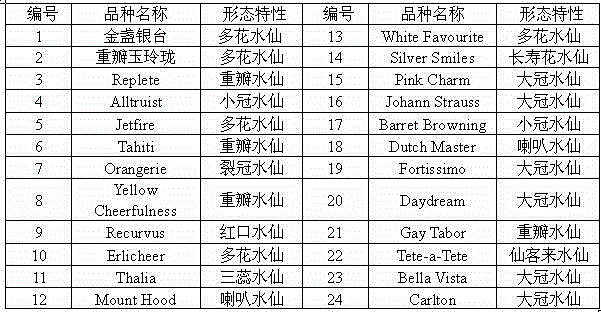
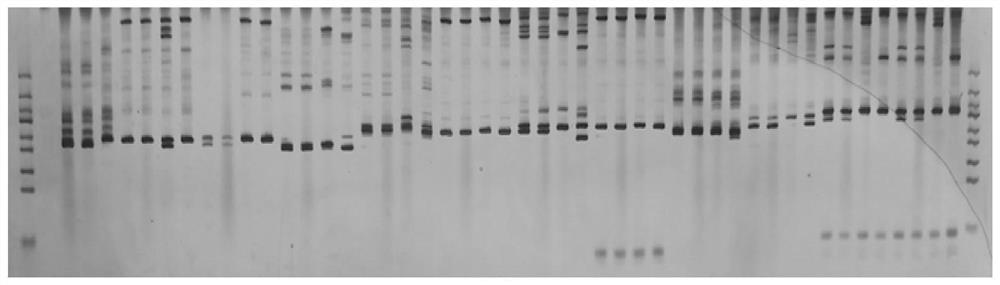
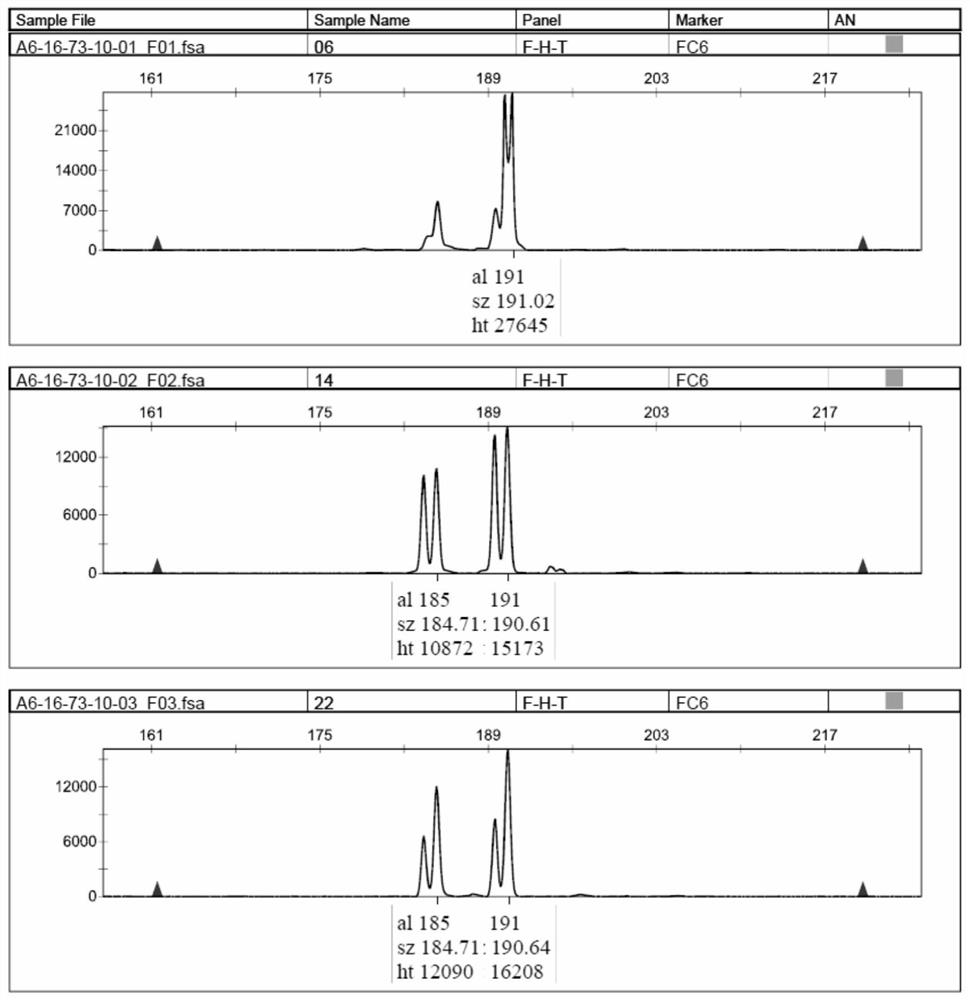
Narcissus bes-ssr marker primer ag9 and method for identifying narcissus varieties
InactiveCN103555854BGood polymorphismClear bandMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityGermplasm
The present invention relates to Narcissus BES-SSR marker primer AG9 and a method for identifying Narcissus varieties, including the design and synthesis of Narcissus BES-SSR marker primer AG9, extraction of total DNA from Narcissus genome, establishment of PCR overall reaction system, PCR amplification program, polyacrylamide Gel electrophoresis conditions and detection and identification of PCR amplification products. The Narcissus BES-SSR marker developed by the BAC-terminal sequence of the Narcissus genome in the present invention has the characteristics of high accuracy, easy judgment, good repeatability, no influence of environmental factors, and clear bands, and is an effective and reliable molecule. The marker is used for the identification of Narcissus germplasm, and has the advantages of small sampling volume, convenient operation, and reliable results. Narcissus BES-SSR marker primer AG9 can also be used in technical fields such as drawing fingerprints of narcissus varieties, analyzing genetic diversity, studying the genetic structure of gregarious populations, and analyzing genetic linkage maps.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Genes, SNP markers and their applications significantly correlated with cotton clothing traits
ActiveCN109628630BEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFiber
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology of characters of fiber yield, in particular to a gene in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield, a SNP marker and application of theSNP marker. The gene in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield is a Gh_D05G1124 gene and / or a Gh_D05G0313 gene. 276 upland cotton materials are taken as raw materials and planted in multiple environments, a CottonSNP63k gene chip is adopted for genetic typing, and 10660 high-quality SNPs are obtained and used for analyzing of the genetic structureand GWAS. According to the result, 23 SNPs in significant correlation with the characters of the fiber yield are discovered to correspond to 15 QTLs. In addition, through Qrt-PCR analyzing, the Gh_D05G1124 gene andthe Gh_D05G0313 gene are taken as candidate genes for adjusting the characters of the fiber yield, the SNP marker in significant correlation with the fiber yield is obtained, and theoretical support is provided for research and application of the characters of the fiber yield.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
ssr primer set for analysis of genetic structure of powdery mildew of rubber tree and its application
ActiveCN113755632BGenetic Diversity RevealedConvenient statisticsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an SSR primer set for analyzing the genetic structure of the rubber tree powdery mildew population and its application. The SSR primer set for analyzing the genetic structure of the rubber tree powdery mildew population includes 16 pairs of primers, and the nucleotide sequences of the primers are shown in SEQ ID NO. 17-48. The invention also provides the application of the primer set in the analysis of the genetic structure of the rubber tree powdery mildew population. The primer set has the characteristics of good specificity, stable amplification, rich polymorphism, good repeatability, convenient statistics, etc., and provides a new technology and means for the research on the genetic structure of the rubber tree powdery mildew population.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Polymorphic primers and applications of ssr molecular markers in camphor nuclei genome
ActiveCN110724760BFully reveal the true level of genetic diversityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a polymorphic primer of a cinnamomum camphora nuclear genome SSR molecular marker and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of forestry molecular biology. Thenucleotide sequence of the primer is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO.14. The polymorphic primer is applied to the application of variety identification of cinnamomum camphora, and genetic structureand resource genetic diversity analysis of ancient cinnamomum camphora groups. A method includes the steps of genome DNA extraction, PCR amplification, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and data analysis. 186 individuals of 18 ancient cinnamomum camphora groups are subjected to genetic structure and resource genetic diversity study; the possibly forming reasons are analyzed according to existinggenetic structure and resource genetic diversity patterns of the cinnamomum camphora; and theoretical basis is provided for the wild cinnamomum camphora resource protection and utilization. The repeatability of the SSR molecular marker is high, and the real level of the genetic diversity of the cinnamomum camphora can be comprehensively disclosed.
Owner:INST OF BIOLOGICAL RESOURCES JIANGXI ACAD OF SCI +1
Narcissus BES-SSR marker primer GA19 and method for identifying narcissus species
InactiveCN103555855AGood repeatabilityClear bandMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic diversityGenetic architecture
The invention relates to a narcissus BES-SSR marker primer GA19 and a method for identifying narcissus species. The method comprises the following steps: design and synthesis of the narcissus BES-SSR marker primer GA19, extraction of total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from a narcissus genome, establishment of a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) total reaction system, establishment of PCR amplification programs, establishment of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis conditions, and detection and identification of PCR amplification products. A narcissus BES-SSR marker developed by a BAC-terminal sequence of the narcissus genome is adopted, has the characteristics of high accuracy, easiness in judgment, good repeatability, effect of not being affected by environmental factors, clear spectral band and the like, is an effective and reliable molecular marker, and further has the advantages of small sampling quantity, convenience in operation, reliable results and the like when used for identifying the narcissus species. The narcissus BES-SSR marker primer GA19 can also be used for drawing of a narcissus species fingerprint spectrum, analysis of genetic diversity, research of a population genetic structure, analysis of a genetic linkage map and other technical fields.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Polymorphic primers of ssr molecular markers in Zhejiang Phoebe genome and their application
ActiveCN113801959BRich number of markersHigh polymorphismMicrobiological testing/measurementInvasive species monitoringCapillary electrophoresisNucleotide
The invention discloses polymorphic primers for SSR molecular markers of the Zhejiang Phoebe nuclei genome and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of forestry molecular biology. The present invention has developed 15 pairs of polymorphic primers for SSR molecular markers of the Zhejiang Phoebe nucleus genome through PCR technology, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and capillary electrophoresis technology, and the nucleotide sequences of the primers are as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 to SEQ ID NO As shown in .30, the polymorphic primers of the SSR molecular markers of the Zhejiang Phoebe genome have good specificity and high polymorphism. Applying it to the analysis of the genetic structure of the Zhejiang Phoebe population and the genetic diversity of resources can reveal more comprehensively the The diversity and genetic structure of Phoebe zhejiang at the genetic level lay the foundation for the formulation of genetic conservation strategies.
Owner:JIANGXI ACAD OF FORESTRY
SSR marker primer set for identifying germplasm resource genetic relationship of halogeton glomeratus and application of SSR marker primer set
ActiveCN111647681AImprove stabilityHave multiple allelesMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationHalophyteGenetics
The invention discloses an SSR marker based primer set for identifying germplasm resource genetic relationship of halogeton glomeratus. A total of 33 pairs of SSR polymorphic molecular markers are identified, an accurate and efficient method for identifying the genetic structure of the halophyte germplasm from different sources is established, and reference can be provided for identifying the halophyte germplasm from different sources. The method for identifying the halophyte germplasm resources comprises the steps of halogeton glomeratus DNA extraction, SSR primer amplification, polymorphismscreening, classification of halogeton glomeratus materials according to amplification results and the like. The germplasm resource genetic relationship of the halogeton glomeratus can be identified accurately and efficiently.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Application of 32 soybean InDel markers in detection of soybean genetic diversity
ActiveCN113493851AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic diversity
The invention discloses an application of 32 soybean InDel markers in detection of soybean genetic diversity. The 32 soybean InDel markers are 32 DNA molecules obtained by performing PCR amplification on soybeans by using 32 pairs of primers as shown in sequences 1-64 in a sequence table. The 32 soybean InDel markers can be used for detecting the soybean genetic diversity, identifying soybean varieties or strains or developing molecular markers for identifying the soybean varieties or strains, preparing soybean genetic maps, analyzing soybean genetic structures and further breeding soybeans. The 32 soybean InDel markers and the complete set of primers for detecting the 32 soybean InDel markers have wide research prospects.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
A primer, kit and identification method for identifying the genetic relationship among individuals of the Yangtze finless porpoise
ActiveCN106591462BRapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationZooidHomolepis
The invention provides a primer, a kit and a method for identifying inter-individual half-sibling, full-sibling and parental relationships of Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis. The primer comprises 20 pairs of microsatellite primers for amplification. The method is capable of identifying the inter-individual half-sibling, full-sibling and parental relationships of the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis rapidly and accurately and is widely applied to genetic resource conservation of the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis. But previous microsatellite studies are mostly used for identifying genetic structures and paternity of Neophocaena asiaeorientalis asiaeorientalis species and does not involve identification of the inter-individual half-sibling, full-sibling and parental relationships.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Primers and method for constructing
PendingCN111778350AHigh polymorphismGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyCynodon
The invention discloses primers and a method for constructing cynodon dactylon core germplasm by using a SCoT molecular marker. The sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO: 1-19, and the primers are applied to construction of the cynodon dactylon core germplasm. The 19 primer strips disclosed by the invention are clear, high in polymorphism and good in repeatability, and a cynodon dactylonSCoT amplification result shows that the 19 primer strips have rich genetic diversity and are suitable for constructing core germplasm. The cynodon dactylon SCoTCore disclosed by the invention generally maintains the genetic structure of an original population, the redundant materials are effectively removed, and the cynodon dactylon SCoTCore is a qualified core germplasm and is representative ofthe original germplasm.
Owner:TROPICAL CORP STRAIN RESOURCE INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Plateau zokor polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers
ActiveCN113736892AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetic diversity
The invention provides a group of plateau zokor polymorphic microsatellite molecular markers, and belongs to the technical field of DNA molecular markers. The microsatellite molecular marker(s) is / are a nucleotide sequence(s) as shown in any one or more of SEQ ID NO: 1 to SEQ ID NO: 10. Through high-throughput sequencing technology and by using a bioinformatics method, the invention screens microsatellite-containing DNA sequences, designs specific primers, and performs polymorphism detection on these microsatellite loci, and develop a group of (10) plateau zokor microsatellite molecular markers with abundant polymorphisms, and provides a set of plateau zokor microsatellite primers. The plateau zokor microsatellite primer pair provided by the invention can perform specific amplification on microsatellite loci, has high polymorphism, can be applied to the research fields of genetic diversity, population genetic structure, pedigree geography, evolution and genetic relationship and the like of the plateau zokor and related species thereof, and has excellent application prospects.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com