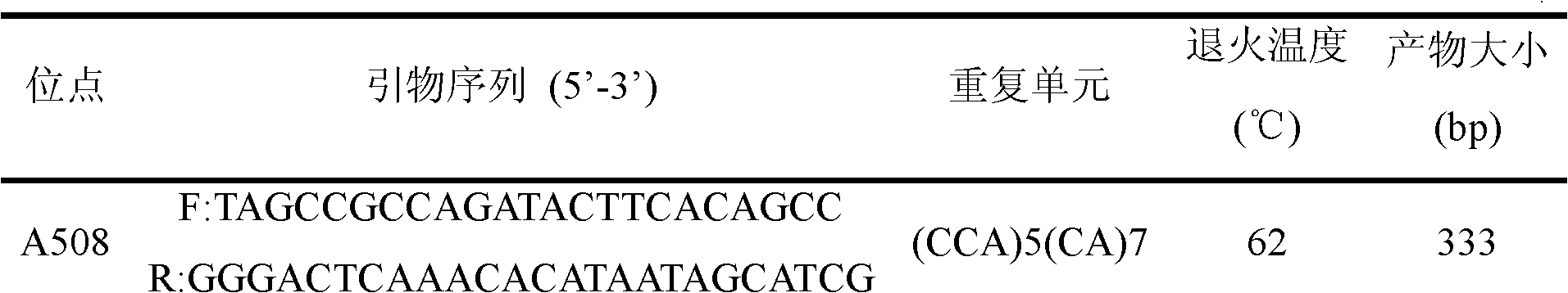Scylla paramamosain microsatellite DNA marker and screening method thereof
A technology of DNA markers and pseudo-cave crabs, applied in the field of DNA molecular markers, can solve the problems of scarcity, germplasm degradation of wild populations, loss of genetic diversity, etc., and achieve good reproducible results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Construction of a microsatellite enrichment library for Scylla pseudocavei
[0023] 1) Genomic DNA was extracted from the chelicer muscle tissue of 10 Scylla syringae by conventional methods and mixed in equal amounts to construct a genomic DNA pool of Scylla syringae, and the genomic DNA pool was digested with restriction endonuclease Mse I. The digested product was electrophoresed on 1.5% agarose gel, a 500-1000 bp DNA fragment was cut out under ultraviolet light, and the recovered digested product was purified with a gel recovery kit (purchased from Qiagen).
[0024] 2) Ligate the above-mentioned recovered fragment with the phosphorylated adapter at the 5' end with T4 DNA ligase, the first strand of the adapter sequence is 5'-GACGATGAGTCCTGAG-3', and the second strand is 5'-TACTCAGGACTCAT-3 '.
[0025] 3) Using the above-mentioned ligation product as a template and the long chain in the adapter (sequence 5'-GACGATGAGTCCTGAG-3') as a primer, amplify by PCR ...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 The sequencing of positive clones containing microsatellite sequences and the design of microsatellite primers
[0033] 1) Pick the monoclonal colonies on the Amp+LB plate and culture them in the Amp+LB liquid medium test tube.
[0034] 2) Using the long chain (GACGATGAGTCCTGAG) in the above linker as the forward and reverse primers, and using the bacterial solution as a template to perform PCR. PCR system 20μL, annealing temperature 55°C, extension time 30S, 30 cycles.
[0035] 3) Perform agarose electrophoresis detection on the PCR product of the bacterial liquid, the clone with the amplified product band in the range of 500-1000 bp is a successful clone, and the amplified product band in the range of about 100 bp is the vector self-ligation.
[0036] 4) Sequencing the clones with fragment insertions obtained by bacterial liquid PCR identification. Microsatellite screening was performed on the sequencing results using the microsatellite DNA site search sof...
Embodiment 3
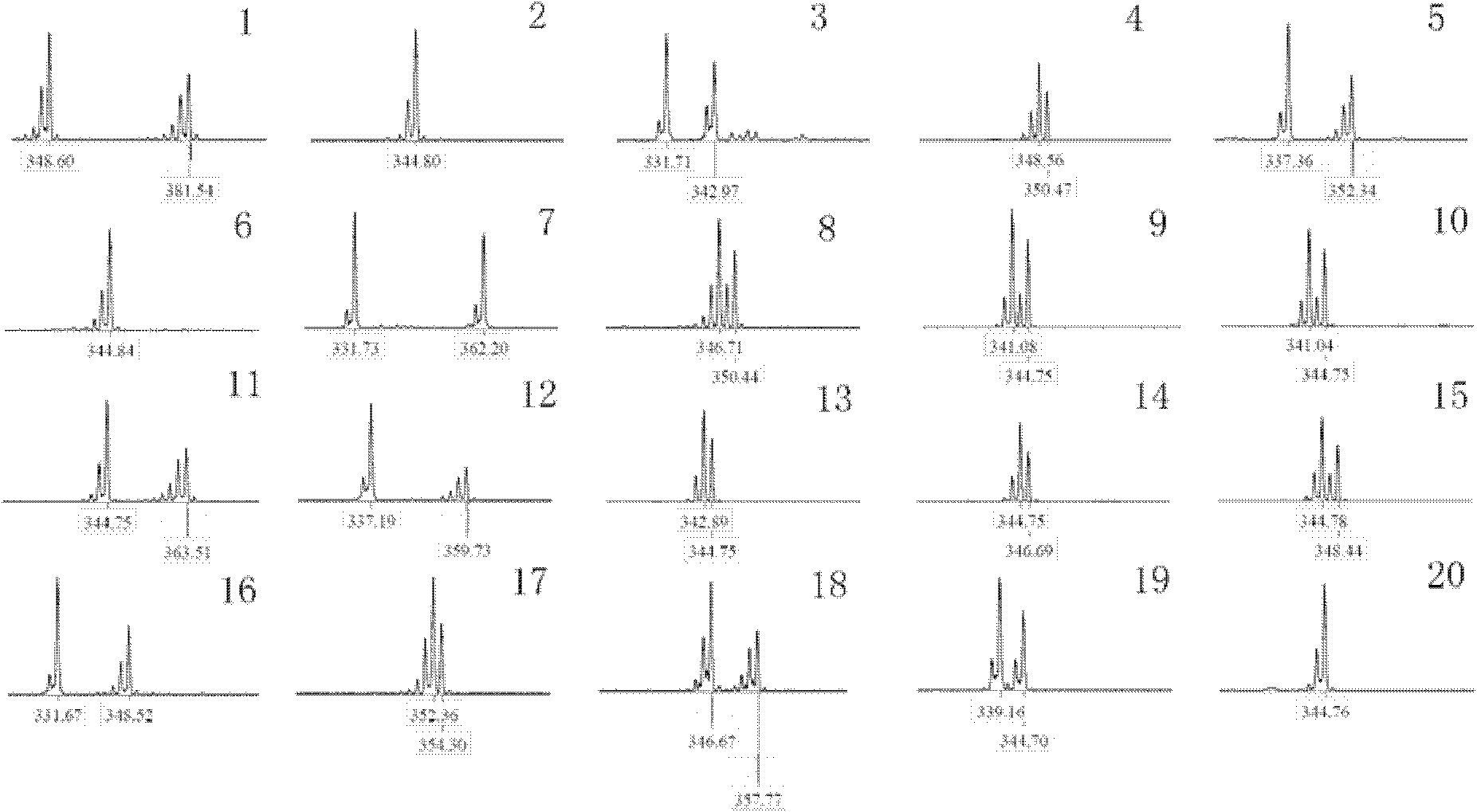
[0038] Example 3 Population genetics analysis using microsatellite DNA markers
[0039] Synthesis of fluorescently labeled primers for A508 microsatellite markers for population genetics analysis of Scylla burrowing crabs. The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0040] 1) Using a kit (purchased from Tiangen Company) to extract genomic DNA from a wild population of 20 individuals of Scylla pseudocarpus.
[0041]2) Amplify the DNA of these 20 individuals with the primers at the A508 site (see Table 1).
[0042] Table 1 A508 locus primer characteristic table
[0043]
[0044] Note: F indicates the forward primer, R indicates the reverse primer.
[0045] 3) Use ROX-500 molecular weight internal standard and GENEMAPPER version 3.2 software to measure the fragment length of each PCR product on ABIPRISM 3730 sequencer.
[0046] 4) Result analysis: Calculate the number of alleles, effective number of alleles, observed heterozygosity, expected heterozygosity, and Hardy-We...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com