Antagonistic PD-1, PD-L1 and LAG-3 binding proteins
A PD-L1 and binding protein technology, applied in the direction of anti-animal/human immunoglobulin, immunoglobulin, anti-receptor/cell surface antigen/cell surface determinant immunoglobulin, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0305] In the following, different aspects of the invention will be defined in more detail. Each aspect so defined may be combined with any other aspect or aspects unless clearly indicated to the contrary. In particular, any feature indicated as preferred or advantageous may be combined with any other feature or features indicated as preferred or advantageous.
[0306] In a first aspect, the invention provides an antagonistic antigen binding protein that specifically binds PD-1, wherein said antigen binding protein competes for binding to PD-1 with an antibody, said antibody
[0307] (i) comprising the amino acid sequence heavy chain variable region of SEQ ID NO: 2; and the amino acid sequence light chain variable region of SEQ ID NO: 3; or
[0308] (ii) comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:11 heavy chain variable region; and the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:12 light chain variable region.
[0309] Preferably, the present invention provides an antagonistic ant...
Embodiment 1
[0682] Example 1: Selection of scFv on activated human T lymphocytes
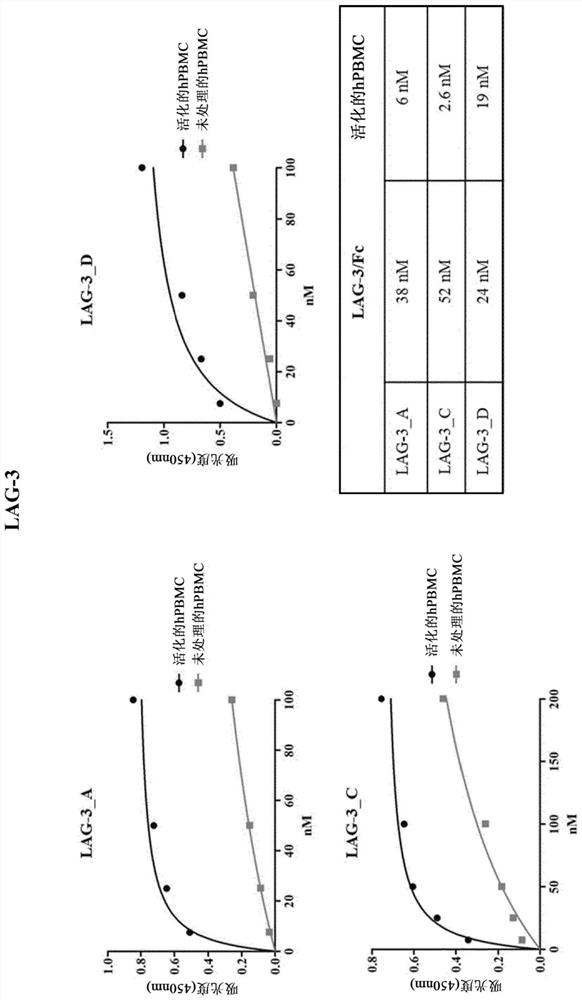
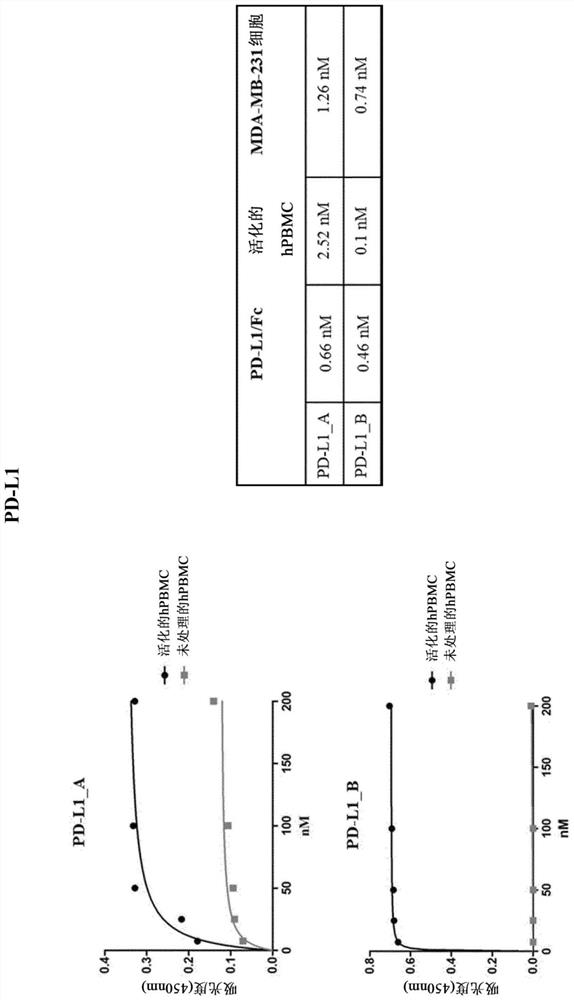
[0683] Our goal is to generate a library of human antibodies against immune checkpoints (ICs). Since many ICs are expressed on the surface of T lymphocytes and their expression increases when T cells are exposed to antigen-dependent or antigen-independent stimuli, we sought to use unfractionated human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (hPBMC) To screen a library of human single-chain antibody fragments (scFvs). To optimize the selection process, we first assessed the kinetics and expression levels of ten different ICs (shown in Table 1) after activation with anti-CD3 / CD28 beads in vitro. As shown in Table 1, peak expression measured by flow cytometry analysis varied among the different immunomodulators, however, most stimulators reached maximally displayed levels after 96 hours of stimulation (see Table 1). After 96 hours of stimulation, all ICs were well expressed in more than 50% of the gated populatio...
Embodiment 2
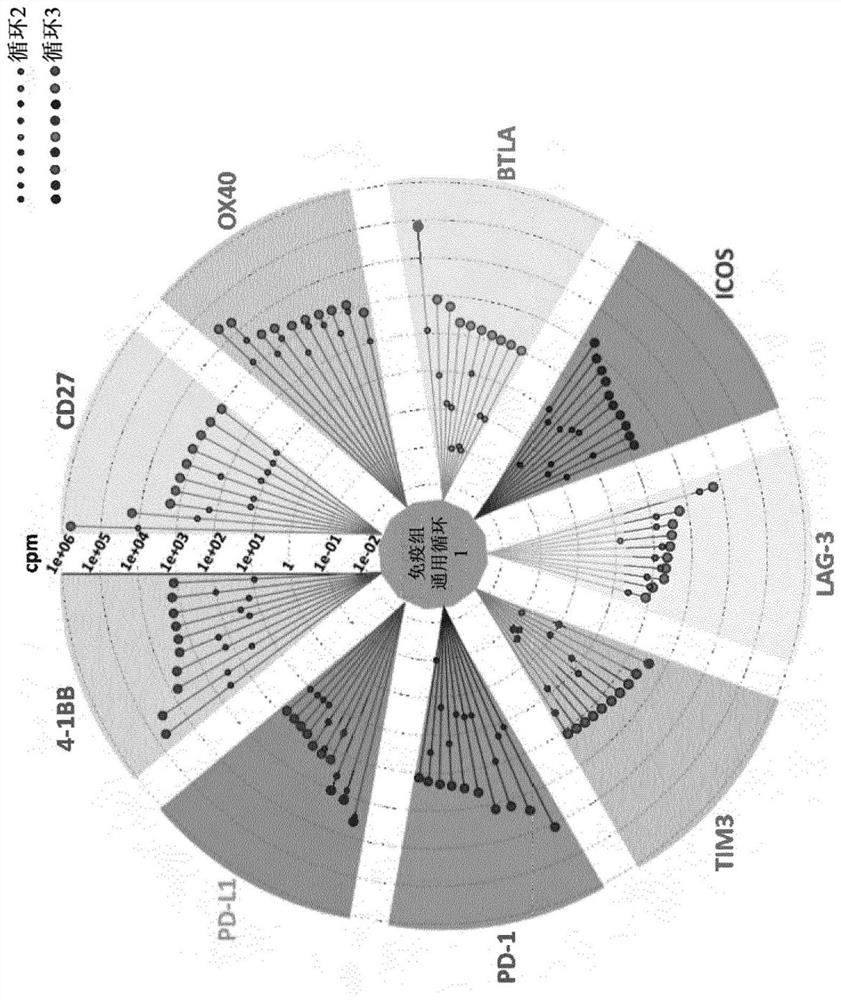
[0687] Example 2: Determination of scFv binders by next generation sequencing
[0688] To identify individual phage clones selected by the combined in vitro / in vitro approach, we sequenced the VH region of the IC-specific library by massively parallel sequencing on the MiSeqIllumina platform (see Materials and methods section for details). To ensure efficient enrichment of target-specific phage, starting from the immunome library (cycle 1), we performed two subsequent rounds of selection (cycle 2 and cycle 3) on Fc-fusion recombinant proteins. Sequence analysis of the entire selection sequence showed that enrichment had indeed occurred after cycle 2, but a higher level of enrichment (i.e.: at least 10-fold) was obtained after the third cycle ( figure 1 ). Analysis of the parallel sequencing data allowed us to remove all selected VH sequences that were shared, possibly due to the enrichment of Fc binders shared by the 10 biochemical baits. Similarly, non-specifically bioenric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com