A fixed-frequency model predictive current control method for single-phase grid-connected inverters
A model prediction and current control technology, applied in AC network circuits, single-network parallel feeding arrangements, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increased output signal fluctuation error, heavy calculation burden, high harmonic pass rate, etc. Dynamic responsiveness, improved waveform quality, and the effect of suppressing harmonic spectrum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
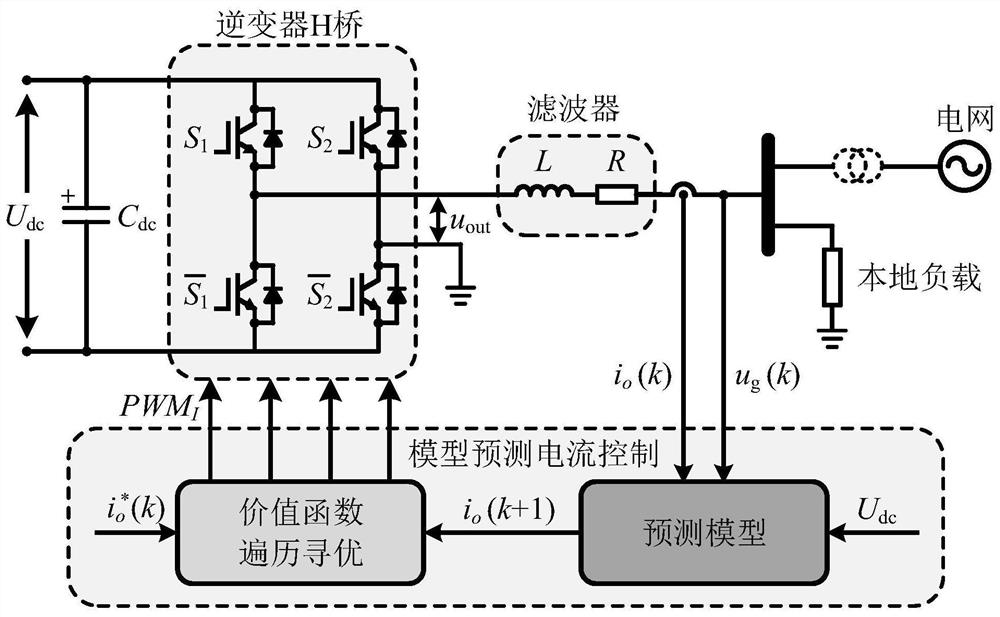
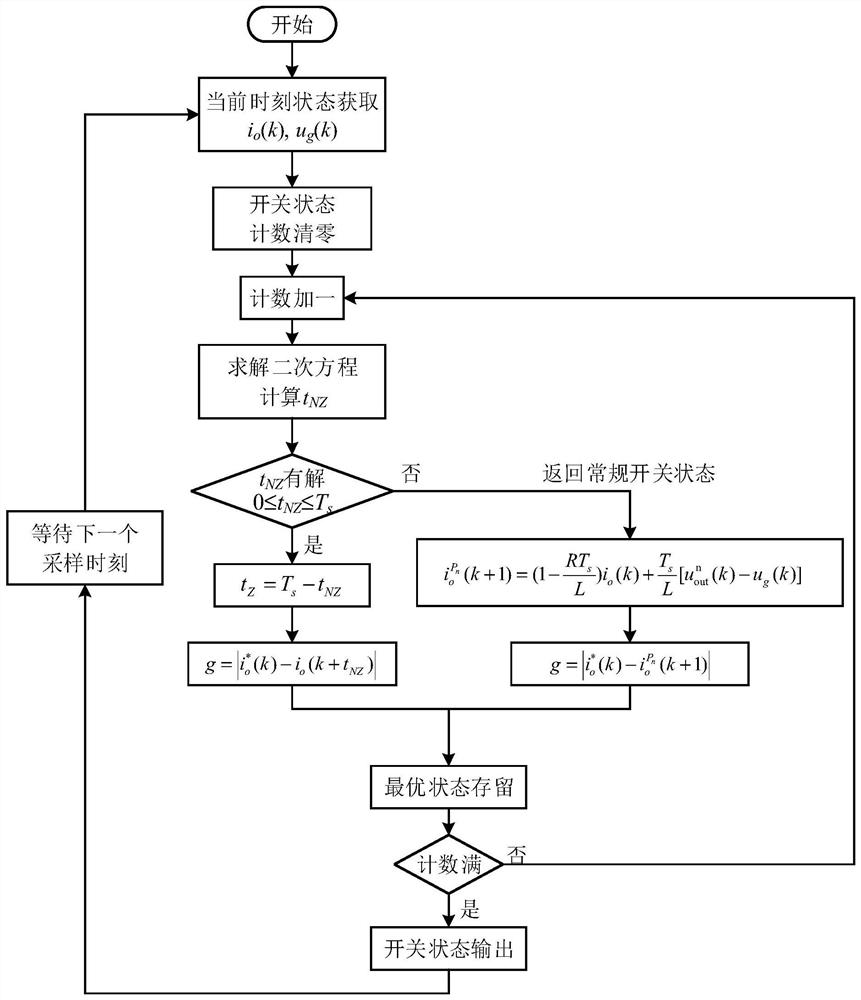
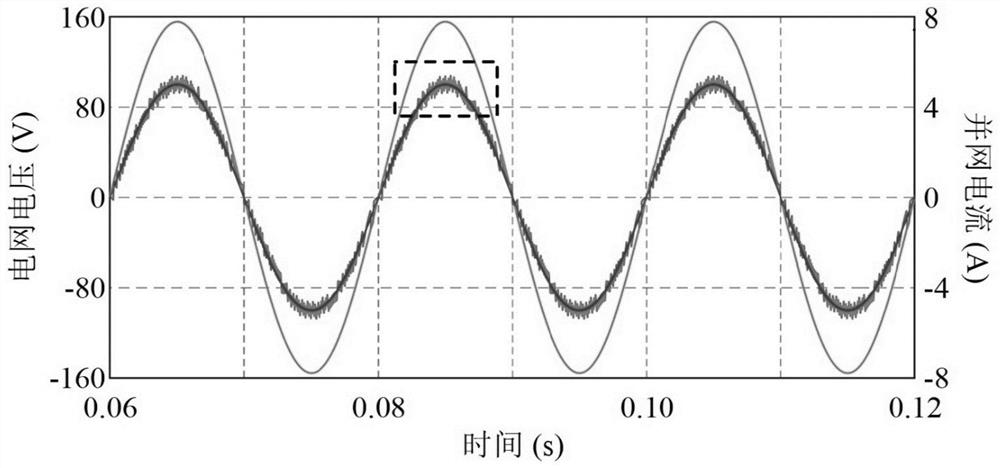
[0052] According to the above technical scheme, the structure of the single-phase grid-connected inverter fixed-frequency model predictive current control system designed by the present invention is as follows: figure 1 shown. The DC side adopts a stabilized DC voltage source and connects bus capacitors in parallel. The four switching tubes of the power conversion circuit part integrate anti-parallel diodes, and the switching states of the two tubes in the same bridge arm are complementary conduction, so as to avoid direct-current side power supply short circuit due to direct current.
[0053] The method of the present invention includes a voltage source type single-phase grid-connected inverter, and the voltage source type single-phase grid-connected inverter includes a bus capacitor connected in parallel with the inverter H-bridge, and the inverter H-bridge is composed of four integrated Anti-parallel diode switching tube S 1 , S 2 , Composition, the switch state of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com