Non-woven fabric of crimped composite fiber and laminate thereof, and article including the laminate
A technology of composite fiber and woven fabric layer, applied in the field of non-woven fabric and its laminates and articles containing the laminates, can solve the problems of bulkiness deterioration, urine leakage, ulceration and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1 to 6 and comparative example 1 to 5
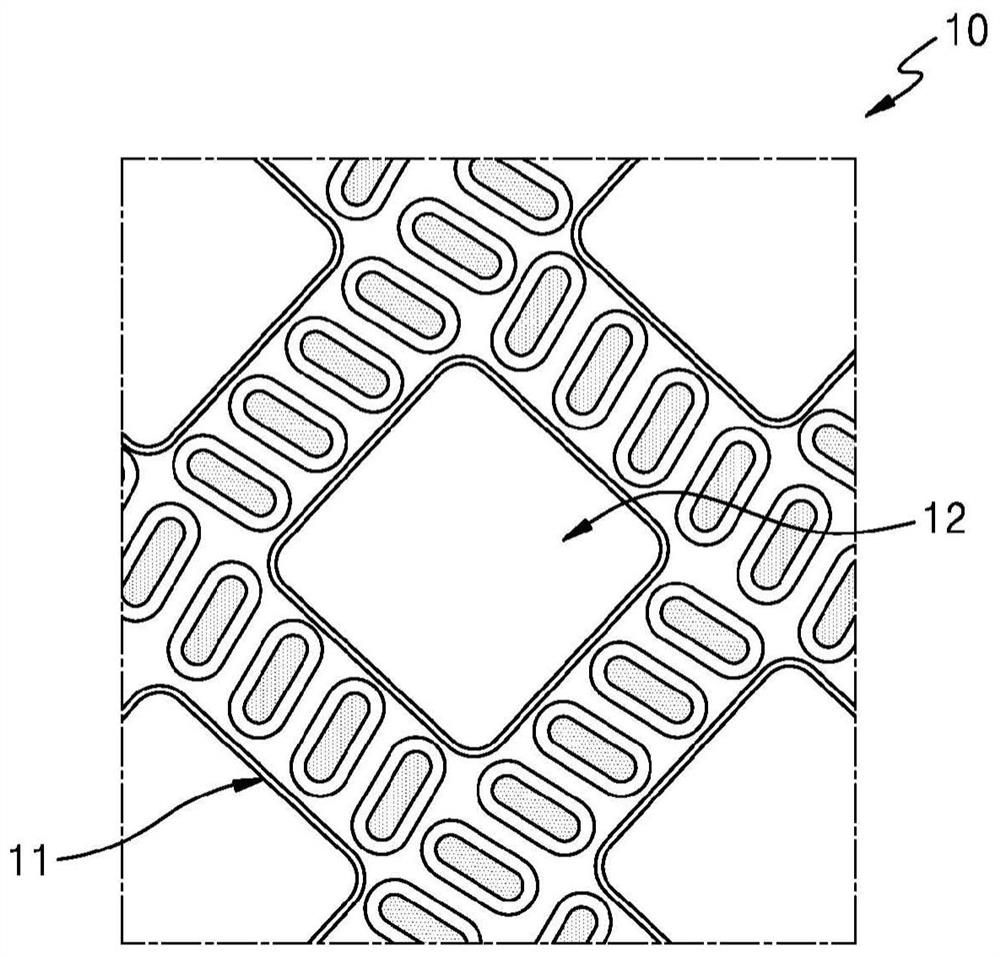
[0090] The first propylene-based polymer (A) containing erucamide slip agent therein and the second propylene-based polymer (B) containing erucamide slip agent therein are subjected to composite melt spinning by a spunbonding method to have figure 2 The side-by-side composite fibers of the structure were deposited on a collecting surface, and the composite fibers were subjected to the figure 1 Embossing of the embossing pattern shown in , in order to produce a nonwoven fabric comprising crimped conjugated fibers. The types, physical properties and content ratios of the first propylene-based polymer (A) and the second propylene-based polymer (B), the amount of erucamide slip agent and the characteristics of the embossed pattern are given in Table 1 below. In the table, MFR refers to a melting index measured according to ASTM D1238 under the conditions of a temperature of 230° C. and a load of 2.16 kg, and the amount of slip refers to a weight relative to the total weight of th...
example 1
[0102] Evaluation example 1: Evaluation of physical properties of spunbond nonwoven fabrics
[0103] The physical properties of the spunbonded nonwoven fabrics prepared in Examples 1 to 6 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5 were evaluated as follows, and the results thereof are given in Table 2 below.
[0104] (1) Measure the weight per unit area according to ASTM D 3776-1985 (weight: g / m 2 ).
[0105] (2) Tensile strength: by using a tensile strength measuring device ( Instron) perform a tensile test to obtain a maximum tensile load.
[0106] (3) Tensile elongation: When the nonwoven fabric is stretched to the maximum value, the elongation is measured by the method (2) above.
[0107] (4) Measure the thickness (mm) according to KSK 0506.
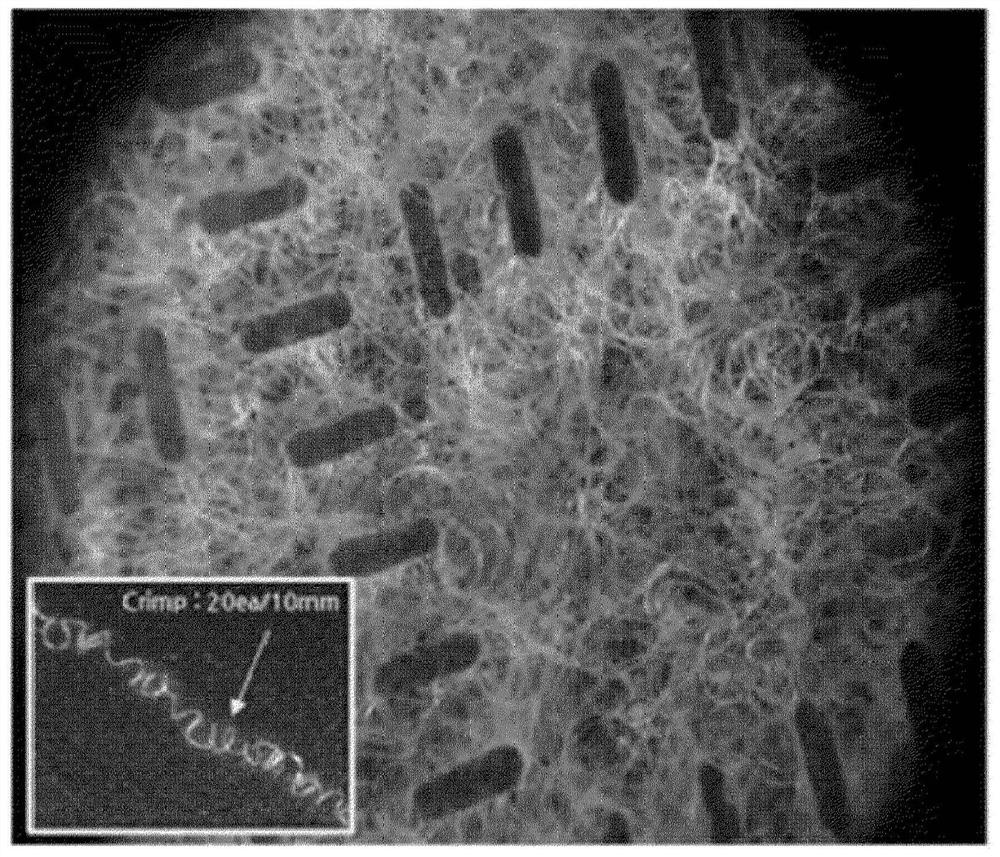
[0108] (5) Number of crimps: directly measure the number of crimps of filaments in a range of 10 mm using a microscope.
[0109] (6) Spinnability: Filament vibration was visually observed during melt spinning, and polymer dripping was de...
example 2
[0115] Evaluation Example 2: Evaluation of Physical Properties of Nonwoven Fabric Laminates Comprising Spunbonded Nonwoven Fabrics
[0116] The spunbonded nonwoven fabrics prepared in Examples 1 to 6 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5 were laminated in four layers to produce nonwoven fabric laminates. Next, the physical properties of each of the nonwoven fabric laminates were evaluated by the following methods, and the results thereof are given in Table 3 below.
[0117] (1) Uniformity (CV%) is determined by cutting the non-woven laminate into 1m 2 The size is evaluated as a percentage of a value obtained by dividing the weight deviation of 30 test samples by the average weight of 30 test samples after making 30 test samples. The smaller the uniformity (CV%) value, the better the uniformity.
[0118] (2) Measure the thickness (mm) according to KSK 0506.
[0119] (3) Number of crimps: directly measure the number of crimps in a range of 10 mm using a microscope.
[0120] (4) ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com