Rapid breeding method of imidazolinone herbicide resistant rice germplasm
An imidazolinone- and herbicide-resistant technology is applied in the field of rapid breeding of rice germplasm resistant to imidazolinone-type herbicides. It can solve the problems of manual removal, time-consuming and labor-intensive offspring materials, and few offspring groups, so as to improve efficiency and Accuracy, save manpower time, improve the effect of selection efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023]The invention provides a rapid breeding method for rice germplasm resistant to imidazolinone herbicides. The offspring is separated by crossing the herbicide-resistant material and the non-resistant material by using a specific concentration of herbicide to soak seeds and spray during the seedling period, which is fast and accurate Excluding non-resistant offspring materials, the surviving plants are herbicide-resistant and can grow normally, which is convenient for selection. The invention includes the use of specific concentration and herbicide to soak seeds, the specific concentration of herbicide is sprayed in the seedling stage, the concentration of soaking seeds is 0.03%, the time is 72 hours, and the spray concentration is 0.1%. Specifically include the following:
[0024]a. Use the selected imidazolinone-resistant herbicide varieties Jinjing 818 or Jindao 372 as the resistant gene donor parent, and the other parent is selected according to the breeding requirements, and t...
Embodiment 2
[0031]Use herbicides of different concentrations to soak the seeds to kill the non-herbicide resistant materials, and set the herbicide concentration: 0, 0.0005%, 0.001%, 0.003%, 0.005%, 0.007%, 0.01%, 0.03%, 0.05%, 0.07%, 0.1%, 0.3%, 0.5%, 0.7%. The results are shown in Tables 1 and 2. 0-13 means 0-0.7% from left to right.
[0032]Table 1 Survival of materials under 14 concentration gradients of 0-0.7% (sow 50 seeds)
[0033] concentration 012345678910111213 Kenyu 60 50504037282251000000 Tsuda 372 5050505050505050403530211010
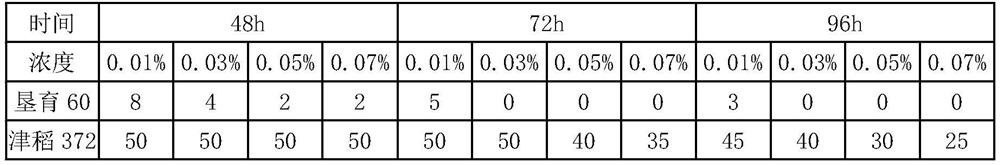
[0034]Table 2 Survival amount of material for 3 seed soaking time under 4 concentration gradients of 0.01%-0.07% (sowing 50 seeds)
[0035]
[0036]The experimental results show that the use of 0.03% herbicide, soaking seeds for 72 hours, can effectively kill non-herbicide-resistant materials with the best effect.
Embodiment 3
[0038]Planting seedling trays to simulate rice seedlings by spraying herbicides to remove non-resistant materials. Set herbicide concentrations: 0, 0.04%, 0.06%, 0.08%, 0.1%, 0.12%, and spray weeds when the rice grows to two leaves and one heart. Spray twice in a row with an interval of 3 days. The results are shown in Table 3.
[0039] Table 3 Seedling survival rate after spraying herbicide in seedling tray
[0040] Variety / concentration00.04%0.06%0.08%0.10%0.12% Kenyu 60 100%78%43%5%0%0% Tsuda 372 100%100%100%100%100%95%
[0041] The experimental results show that the herbicide with a concentration of 0.1% can be used during the seedling stage to kill materials that are not resistant to herbicides.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com