A Classical Flutter Suppression Wind Turbine Blade Structure and Flutter Suppression System
A technology of wind turbine blades and flutter, which is applied in the control of wind turbines, wind turbines that are consistent with the wind direction, wind turbines, etc., can solve the problems of classic flutter fracture failures, etc., and achieve light weight, convenient installation, and simple driving Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
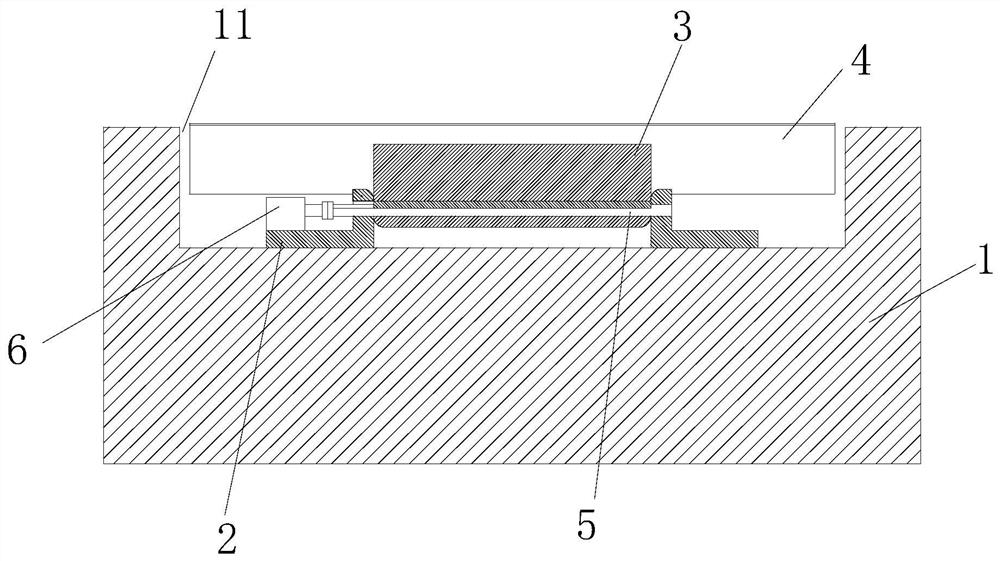
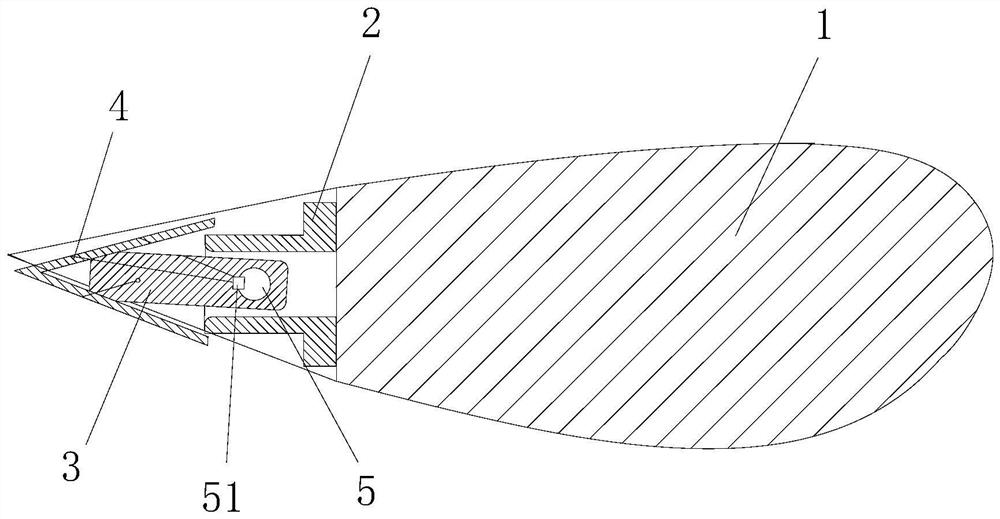
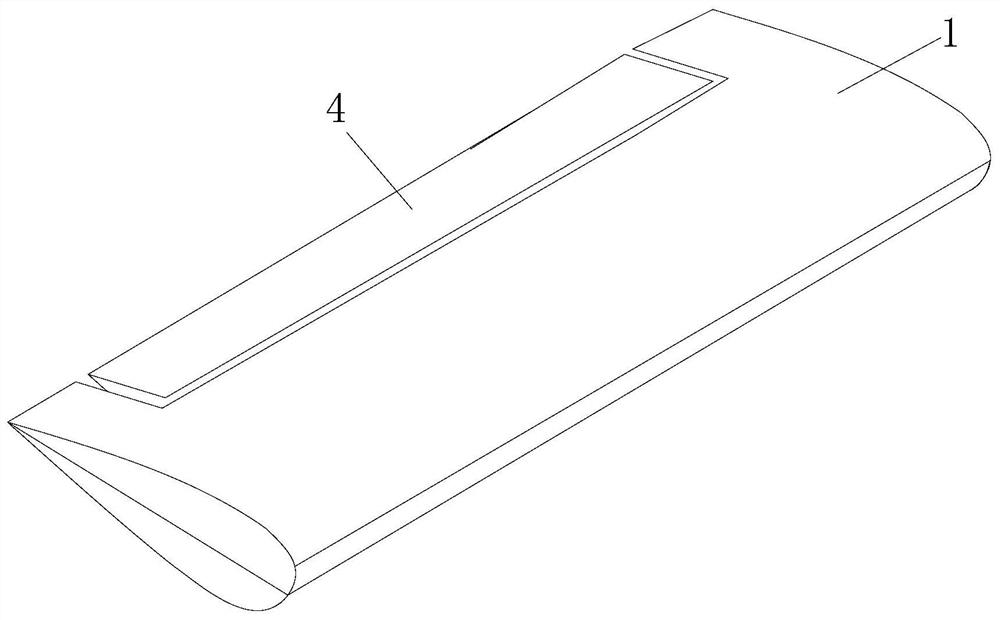
[0042] combine Figure 1 to Figure 6, a classic flutter suppression wind turbine blade structure, including a blade matrix 1, a blade notch 11 is provided on the trailing edge side of the blade matrix 1, and a flutter suppression device is arranged in the blade notch 11; the flutter suppression device includes a first A positioning base 2, a swing bracket 3 and a rigid trailing edge flap 4. The first positioning base 2 is positioned in the blade notch 11, the outer end of the first positioning base 2 is connected to the swing bracket 3 through the first rotating shaft rod 5, the rigid trailing edge flap 4 is connected to the swing bracket 3, and the first positioning base 2 is connected with a stepper motor 6 that drives the first rotating shaft 5 to rotate.
[0043] The blade parent body 1 is a solid plate-like structure, and the cross-section of the blade parent body 1 is a circumferential antisymmetric surface; the tail edge of the blade parent body 1 is flat plate-shaped,...
Embodiment 2
[0051] combine Figure 1 to Figure 6 A wind turbine blade flutter suppression system includes a wind frame and a wind machine head connected to the wind frame. A plurality of above-mentioned classic flutter suppression wind turbine blade structures are adapted and connected to the wind turbine head.
[0052] The wind machine head is equipped with a system controller. When the system controller detects that the wind speed is greater than or equal to the critical wind speed and continues to occur, it starts the stepping motor, and uses the first rotating shaft to drive the swing bracket to swing. After the swing bracket swings, the rigid tail The deflection of the edge flap changes the distribution of the aerodynamic force along the rigid trailing edge flap, thereby further changing the distribution of the aerodynamic force on the blade parent body; the system controller controls the swing amplitude of the rigid trailing edge flap through the flap control method .
[0053] The...
Embodiment 3
[0065] In the above-mentioned classic flutter-suppressed wind turbine blade structure, the rigid trailing edge flap occupies 90% to 95% of the span length of the solid blade. The chordwise (transverse) length of each section of the rigid trailing edge flap is approximately measured by the distance from the center of the first rotating shaft to the tip of the flap, and its length is 1 / 7 to 1 / 6 of the chord length of the blade. One end of the blade is fixed on the hub of the wind turbine head, and the other end is a free end. The flapping displacement refers to the displacement of the free end of the blade, and its direction is perpendicular to the rotation plane of the impeller.
[0066] Torsional displacement refers to the twist angle of the free end relative to the root of the blade and centered on the axial direction of the blade. As mentioned above, the torsional displacement range of the blade itself is relatively small through the limitation of the parameters of the blade...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com