Hepatitis b antibodies
An antibody, human antibody technology, applied in the direction of antibodies, antiviral agents, antiviral immunoglobulins, etc., can solve problems such as inability to eliminate viruses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0286] Example 1: Generation of anti-HBsAg viral antibodies
[0287] Human memory B cells from HBV-vaccinated donors were expanded in vitro and selected for their ability to secrete IgG antibodies against HBsAg. Specific B cells were lysed and the VH (heavy) and VL (light) chains were amplified by RT-PCR and then sequenced and analyzed to identify key post-translational modification (PTM) sites. The plasmids for the VH and VL chains are then transfected into an IgG1 backbone vector in a CHO mammalian cell line to express intact IgG1 antibodies.
[0288]Methods for generating monoclonal antibodies using phage display technology are known in the art (Antibody Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology Vol. 901, 2012, Chapter 3:33). Briefly, by complexing with biotinylated recombinant HBsAg (TRINA Bioreactives AG, Cat. No. C028-3001994774 (AD serotype), C028-3001994774 (AY serotype) or Biorbyte, Cat. No. orb82536 (AD isotype)) Solution panning with streptavidin-conju...
example 2
[0294] Example 2: Binding of anti-HBsAg antibody to HBsAg
[0295] Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) was used to determine the binding affinity interactions (K D ). HBsAg particles were immobilized on the S-series CM5 sensor chip at approximately 800 RU, and anti-HBsAg antibodies were flowed in 2-fold serial dilutions starting from 128 nM to utilize a Biacore T200 instrument (GEHeathcare, catalog number 28975001, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania) assesses the combination. K was determined by fitting the curve with a 1:1 fit model D (O'Shannessy et al. Anal.Biochem [Analytical Biochemistry] 1993; 212:457-468; Karlsson, J. Immunol. Methods. 1997; 200:121-133).
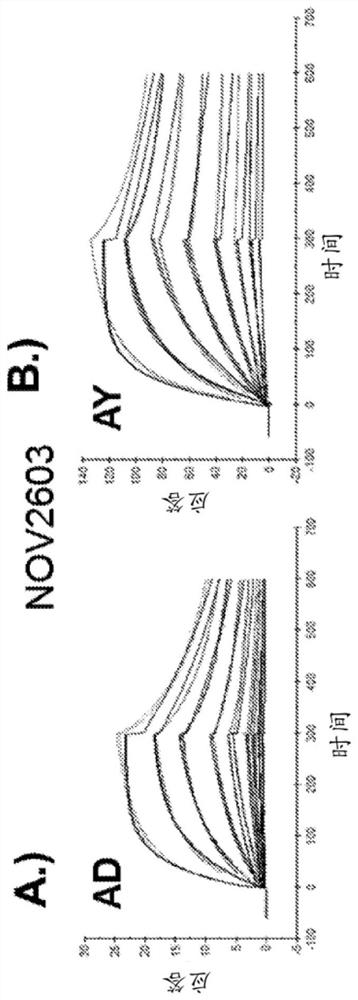
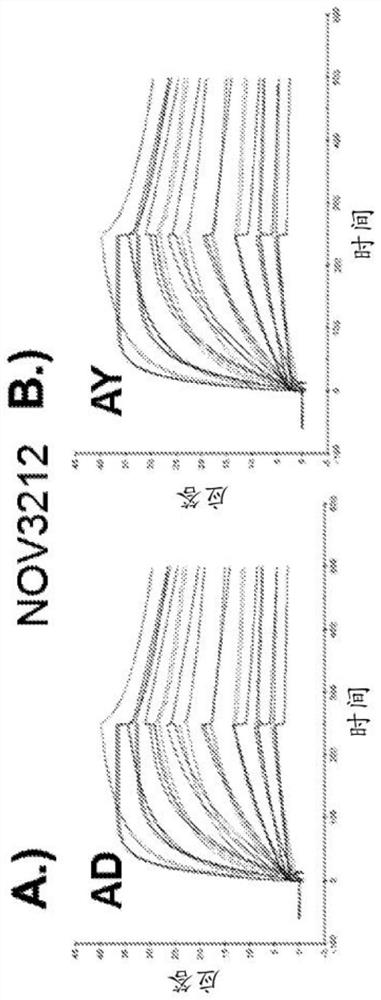
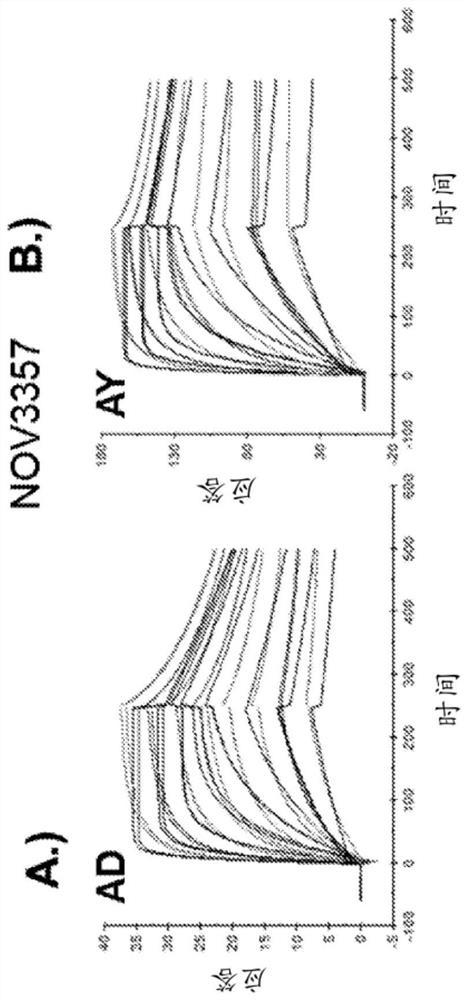
[0296] K of anti-HBsAg antibody measured by Biacore D Values ranged from 110 pM to 40 nM and were comparable between the two major serotypes (AD and AY) for each antibody tested. The Biacore affinity data summary of the anti-HBsAg antibody is shown in Table 4, and the SPR curve is shown in figure 1 A / B-16A / B.
[029...
example 3
[0300] Example 3: Neutralization of hepatitis B virus infection by anti-HBsAg antibodies
[0301] Infectious HBV virus was purified from genotype D, serotype ayw cell culture-derived HBV as described (Meier et al., J. Virol Hepat. 2017;24:662-671). Anti-HBsAg antibodies were pre-incubated with virus for 1 hour at 37°C to allow binding and neutralization. HepG2-hNTCP1 cells generated in-house as described (Tropberger et al, Proc. Fresh medium was replaced and incubated for an additional 6 days to allow virus entry, cccDNA establishment and viral protein expression. Supernatants were recovered and analyzed for HBeAg levels by a custom in-house eAg AlphaScreen assay (Perkin Elmer, Bridgeville, PA). Data were analyzed using an Envision plate reader (PerkinElmer, Cat. No. 2105-0010, Bridgeville, PA) and expressed as percent infection relative to untreated control wells.
[0302] All antibodies were able to neutralize HBV infection, EC 50 Values ranged from 17pM to 740pM, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com