Similarity analysis method of negative sequence mode based on biological sequence, implementation system and medium
A similarity analysis and biological sequence technology, applied in the application field of high-utility negative sequence rules, can solve problems such as lack of similarity measurement methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
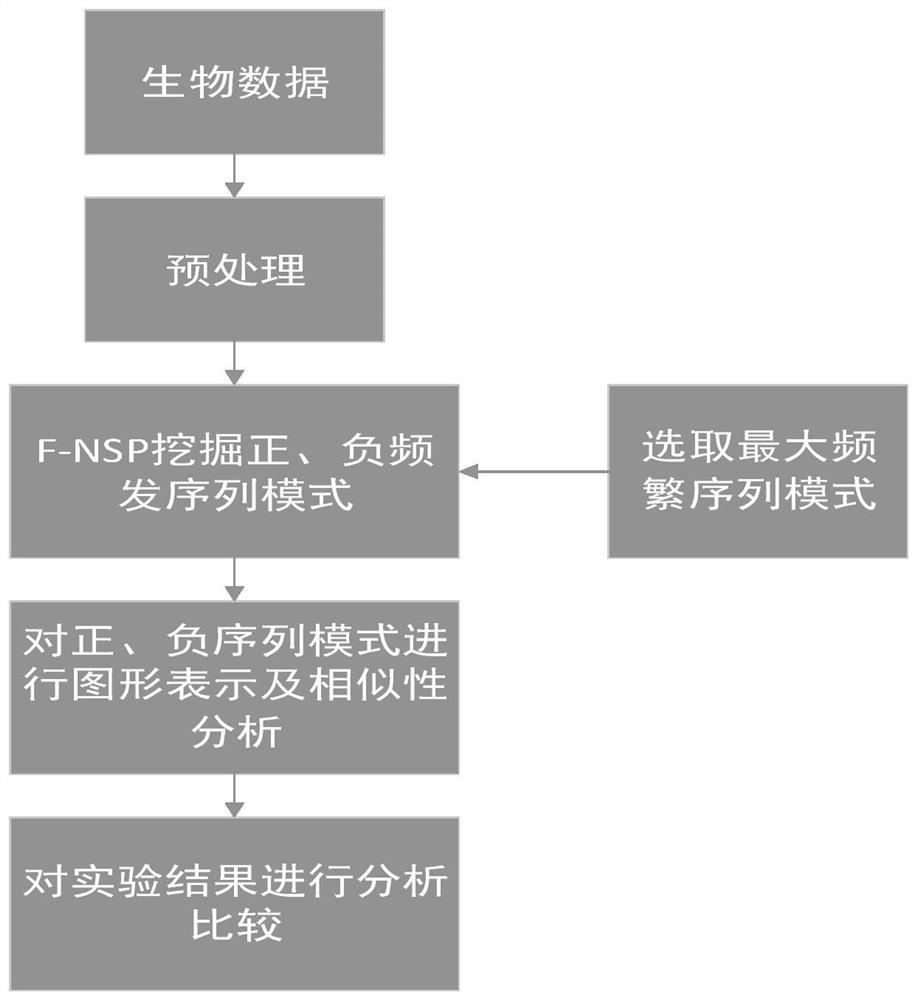
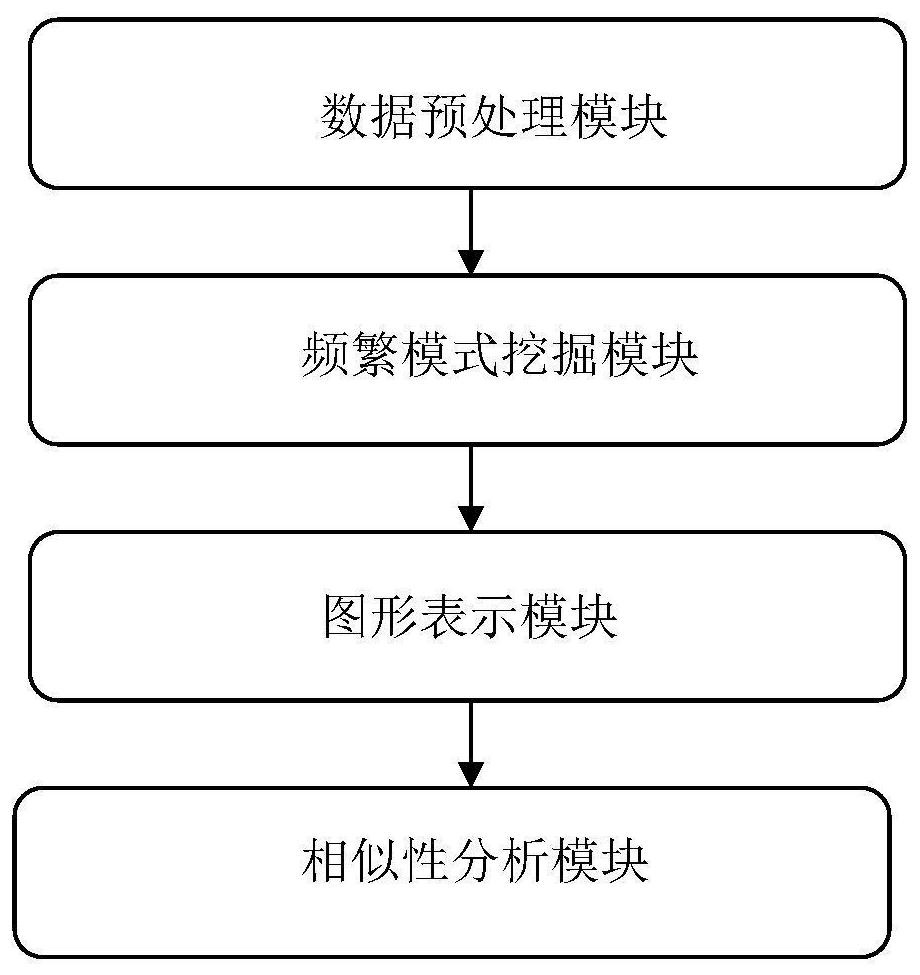
[0083] A similarity analysis method based on negative sequence patterns of biological sequences, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0084] (1) Data preprocessing
[0085] For each sequence or genome to be processed, preprocessing is performed before it is subjected to frequent pattern mining. The letters in the DNA sequence are represented by numbers; since the length of the DNA sequence is very long, the DNA sequence represented by the number is divided into several blocks, and the number of bases in each block is the same, and the obtained blocks are used as frequent pattern mining. data set;
[0086] In the present invention, each sequence is first divided into several blocks, and each block is composed of the same number of continuous bases. These blocks are independent of each other, and the block size can vary in practice. Note that if the size of the last block is smaller than the specified block size, then this block will be discarded. To mak...
Embodiment 2
[0099] According to a kind of similarity analysis method based on the negative sequence pattern of biological sequence described in embodiment 1, its difference is:
[0100] In step (2), the f-NSP algorithm is used to mine the data set, the data set is D, and the steps are as follows:
[0101] A. Use the GSP algorithm to obtain all positive and frequent sequences, and store the bitmap corresponding to each positive and frequent sequence in the hash table; including:
[0102] a. Scan the data set to get all sequence patterns with a length of 1 and put them into the original seed set P 1 middle;
[0103] b. From the original seed set P 1 Obtain sequence patterns with a length of 1, and connect them to generate a candidate sequence set C with a length of 2 2 ; Use the Apriori property on the candidate sequence set C 2 Perform pruning, and then scan the candidate sequence set C 2 Determine the support of the remaining sequences, save the sequence patterns whose support is hig...
Embodiment 3
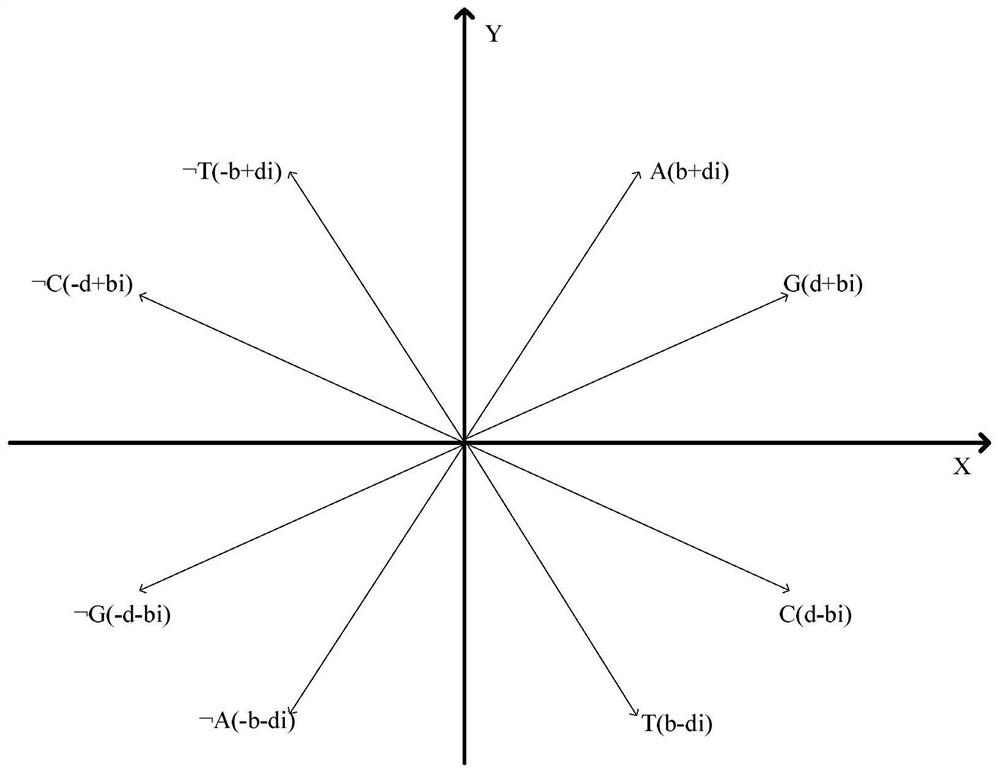
[0116] According to the similarity analysis method of a negative sequence pattern based on a biological sequence described in Example 1, the difference is that in step (3), the maximum frequent positive and negative sequence patterns are graphically represented, including: constructing in the complex plane A purine-pyrimidine diagram, in the purine-pyrimidine diagram, the first and second quadrants are purines, including A, G and The third and fourth quadrants are pyrimidines, including T, C and
[0117] (b+di)→A(Ⅰ)
[0118] (d+bi)→G(Ⅱ)
[0119] (b-di)→T(Ⅲ)
[0120] (d-bi)→C(Ⅳ)
[0121]
[0122]
[0123]
[0124]
[0125] A unit vector of the four nucleotides A, G, T, C and their corresponding negative sequences As shown in formula (Ⅰ) to formula (Ⅷ):
[0126] In formula (I) to formula (VIII), b and d are non-zero real numbers, A and T are conjugated, and so are G and C, ie, A, T, C, G represent actual base pairs, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com