A goat pregnancy-associated glycoprotein nucleic acid aptamer and its application
A technology of nucleic acid aptamers and glycoproteins, applied in instruments, biochemical equipment and methods, analytical materials, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
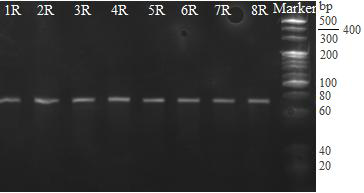
[0031] Example 1: Screening of goat PAG nucleic acid aptamers
[0032] 1. Synthetic random single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) library and primers:
[0033] Random single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) library:
[0034] 5'-CTACGGTGCCTTGAAGTGAC-N36-CATAGCAGGTCACTTCCAGG-3', wherein, N36 represents 36 random nucleotides, and the library was synthesized by Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.;
[0035] Upstream primer: 5'-FAM-CTACGGTGCCTTGAAGTGAC-3',
[0036] Downstream primer: 5'- 20A-spacer18-CCTGGAAGTGACCTGCTATG-3',
[0037] Among them, in the downstream primers, 20A represents a polyA tail composed of 20 adenosine (A), and Spacer 18 represents an 18-atom hexaethylene glycol interarm. The above primers were synthesized by Nanjing GenScript Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
[0038] Binding buffer solution (BB: NaCl 136.89mM, KCl 2.68 mM, Na 2 HPO 4 8.09 mM, KH 2 pH 4 1.47 mM, CaCl 2 0.9 mM, MgCl 6H 2 O 0.49 mM; PH 7 .4) were dissolved and stored at -20°C for later use.
[0039] 2. Magne...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2: Nucleic acid aptamer dissociation constant ( K d ) Determination
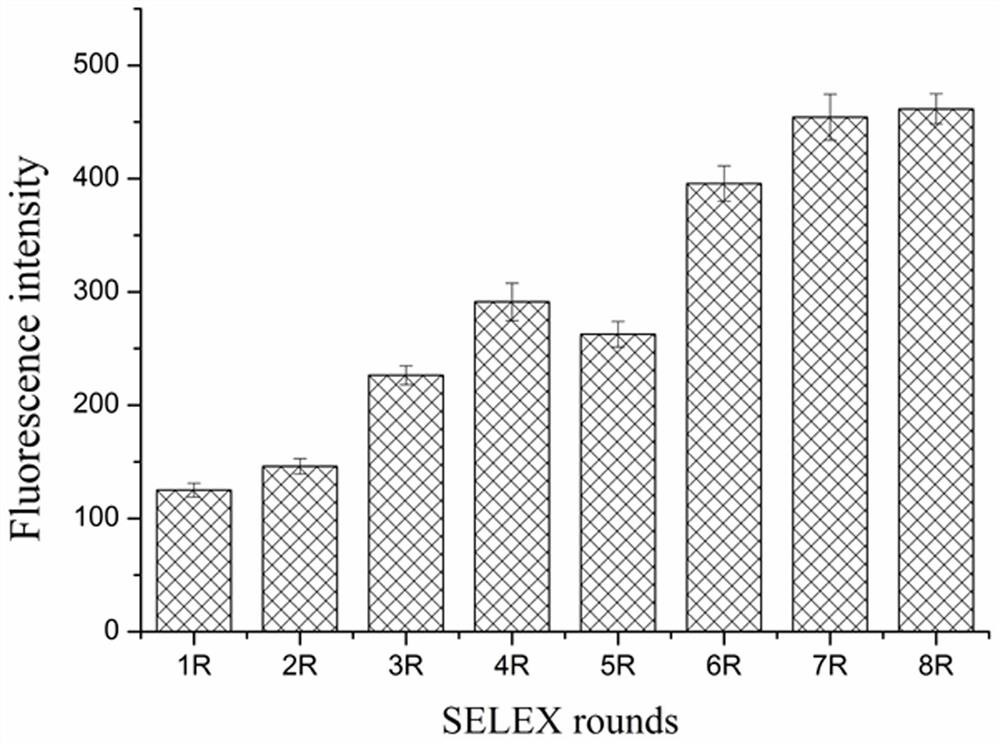
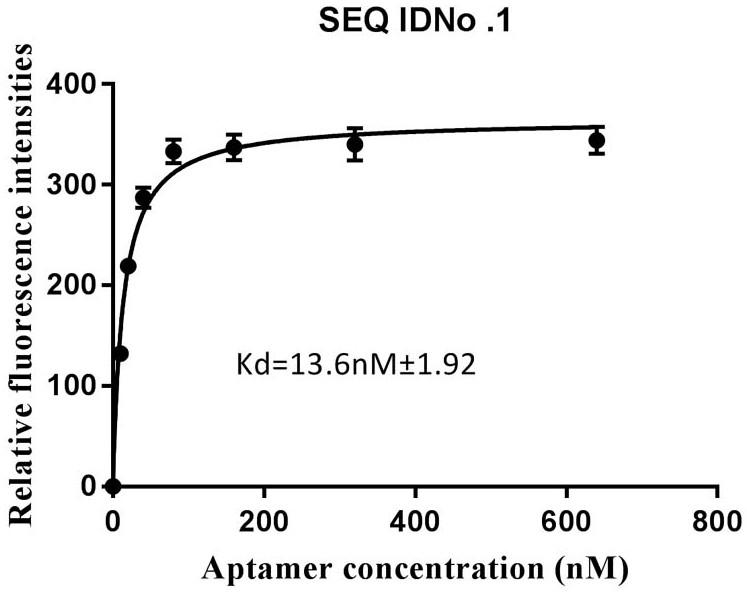
[0053] Select the nucleic acid aptamer with the highest binding ability in Example 1, and use BB buffer to prepare a series of aptamer solutions with gradient concentrations (0, 100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, 3200, 6400 nM); according to the example In Step 5 of 2, analyze the binding situation of the nucleic acid aptamer to MB-ovPAG7, use GraphPad Prism 7.0 software to fit the binding curve, and calculate the dissociation constant of the nucleic acid aptamer ( K d value). image 3 It is the saturation binding curve of the aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1 after truncating part of the X and Y sequences to the target protein ovPAG7, and its dissociation constant reaches 13.6 nM. Online Mfold was used to predict the secondary structure of the aptamer sequence, and the results were as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the aptamer has a typical stem-loop structure.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3: the specificity analysis of nucleic acid aptamer
[0055] The nucleic acid aptamer shown in SEQ ID No. 1 was truncated by 10 bases at both ends, and sent to Shanghai Sangong for synthesis, and the biotin group was labeled at the 5' end. Proteins such as ovPAG7, bPAG6, BSA, and OVA were diluted to 3 μg / mL with 10 mM PBS, then coated on a 96-well plate, and coated overnight at 4°C. Then the plate was washed 3 times with 200 μL of PBST (10 mM PBS, 0.05% Tween-20, pH 7.0), blocked by adding 200 μL of blocking solution (1% BSA) for 2 h, and washed 3 times with PBST. Add 100 μL of biotin-modified aptamer (100 nM), incubate for 20 min, wash 3 times with PBST, and pat dry. Add 100 μL of SA-HRP (0.5 U / mL) to each well, wash with PBST 3-5 times, pat dry, add 100 μL of TMB substrate chromogenic solution, and react for 5-7 min. Finally, 100 μL of stop solution was added to terminate the reaction, and the microplate reader was used at 450 nm (OD 450nm ) to measure i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com