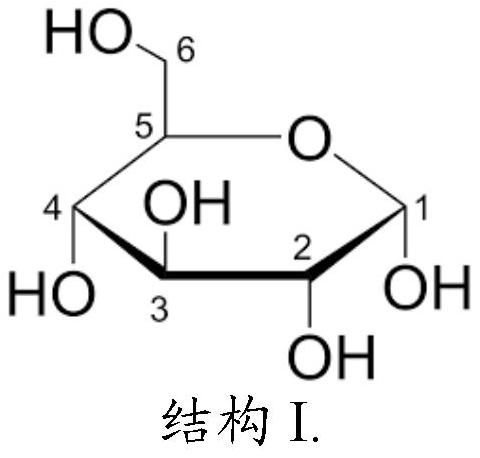
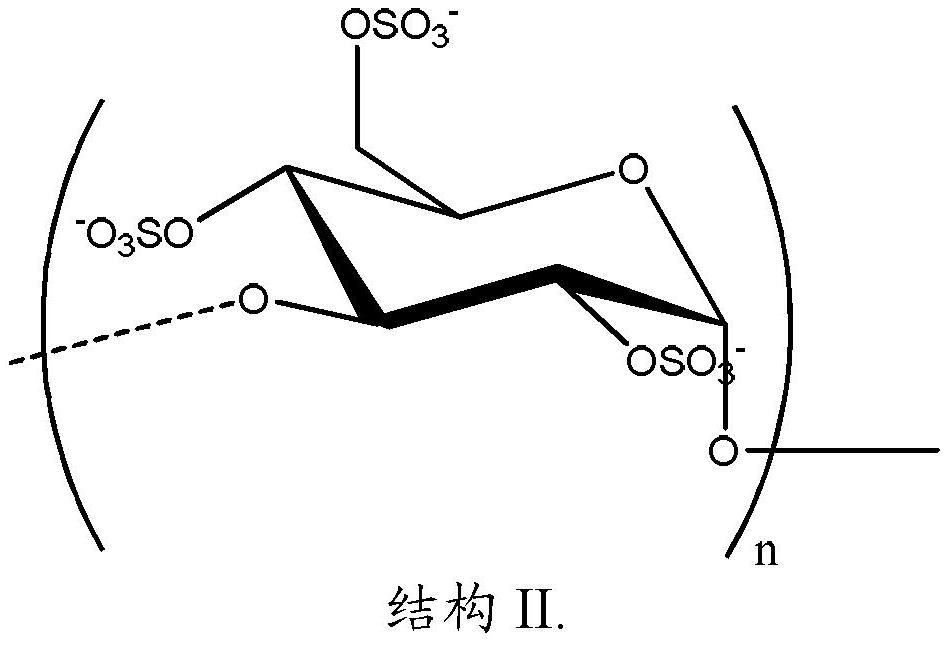
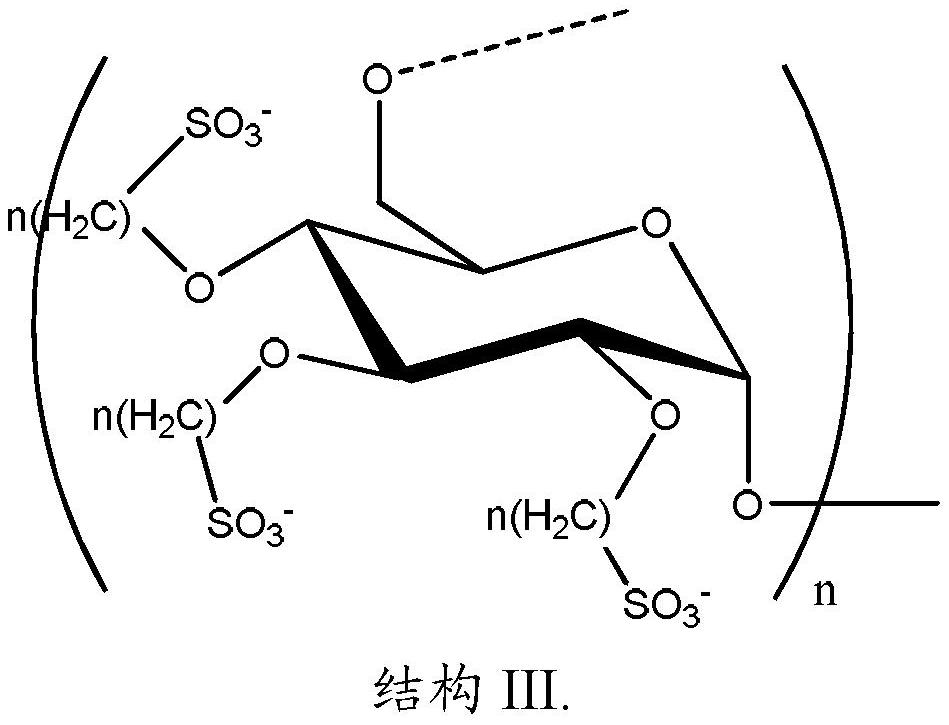
A product comprising polysaccharide derivatives
A technology of polysaccharide derivatives and products, which is applied in the preparation of detergent mixture compositions, detergent compositions, surface-active detergent compositions, etc., and can solve problems such as reducing rheological stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0253] Reaction of Poly α-1,6-Glucan with Sodium Vinyl Sulfonate
[0254] This example describes poly alpha-1,6 glucan functionalized with ethanesulfonic acid groups. In a 1 L round bottom flask equipped with an overhead stirrer, addition funnel, and nitrogen inlet, poly alpha-1,6 glucan (20 g), prepared as described above, was suspended in 200 mL of isopropanol. Sodium vinylsulfonate (187 mL of a 25% by weight solution) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred for 10 minutes. 59 g of 50% by weight sodium hydroxide were added thereto. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. The mixture was then heated to 80°C with stirring for 5 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and neutralized with 18.5 wt% HCl. The product was purified by ultrafiltration (MWCO 5 kDa, PES membrane). The degree of substitution is 1.0, as determined by 1 Measured by H NMR analysis.
Embodiment 2
[0256] Reaction of poly α-1,6-glucan with 1,3-propane sultone :
[0257] This example describes poly alpha-1,6 glucan functionalized with propanesulfonic acid groups. Poly alpha-1,6 glucan (20 g), prepared as described above, was dissolved in 50 mL of distilled deionized water in a 1 L round bottom flask equipped with an overhead stirrer, addition funnel, and nitrogen inlet. Cool the mixture with an ice / water bath. To this was added 9.9 g of a 50% by weight hydroxide solution via an addition funnel under a nitrogen purge. After the addition, the mixture was further stirred on ice / water for 30 minutes. 14.6 g of 1,3-propane sultone was added thereto. The mixture was heated at 45°C-50°C under nitrogen for 3 hours. The mixture was cooled and neutralized with 18.5 wt% HCl. The product was purified by ultrafiltration (MWCO 5K, PES membrane, 3X). The degree of substitution is 0.3, as determined by 1 Measured by HNMR analysis.
Embodiment 3
[0259] Reaction of poly α-1,6-glucan with 1,4-butane sultone :
[0260] This example describes poly alpha-1,6 glucan functionalized with butanesulfonic acid groups. In a 1 L round bottom flask equipped with an overhead stirrer, addition funnel, and nitrogen inlet, poly alpha-1,6 glucan (20 g), prepared as described above, was dissolved with 50 mL of distilled deionized water. Cool the mixture with an ice / water bath. To this was added 7.4 g of a 50% by weight hydroxide solution via an addition funnel under a nitrogen purge. After the addition, the mixture was further stirred on ice / water for 30 minutes. 16 g of 1,4-butane sultone was added thereto. The mixture was heated at 40°C-45°C under nitrogen for 2 days. The mixture was cooled and neutralized with 18.5 wt% HCl. The polymer was purified by ultrafiltration (MWCO 5K, PES membrane, 3X). The degree of substitution is 0.8, as determined by 1 Measured by H NMR analysis.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com