Rectifier circuit, power source device, and method for driving rectifier circuit
A technology of a rectifier circuit and a driving method, which is applied in the directions of measuring devices, measuring current/voltage, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing transient currents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach 〕
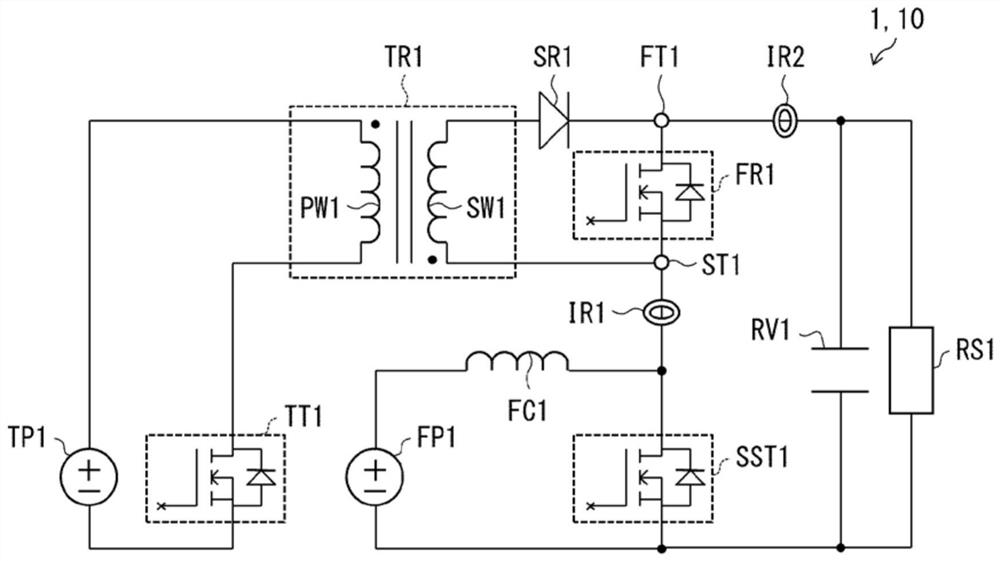
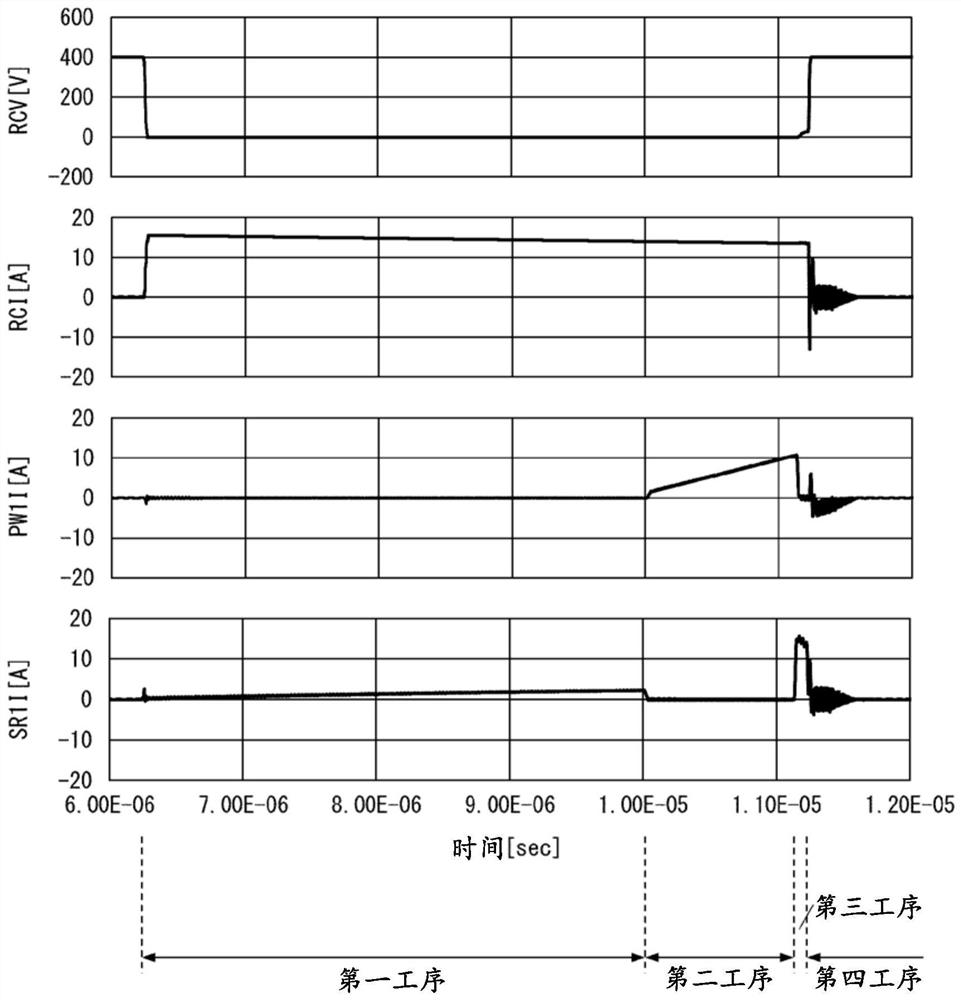
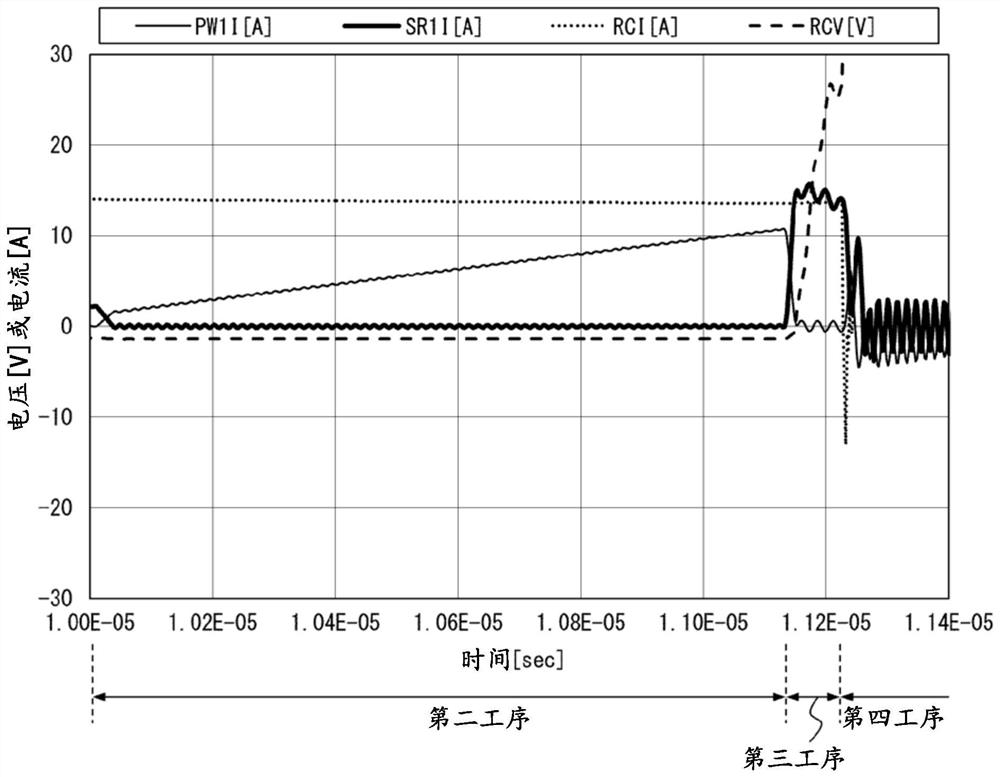
[0029] Hereinafter, the rectifier circuit 1 of the first embodiment will be described. For convenience of description, members having the same functions as those described in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals in the subsequent embodiments, and description thereof will not be repeated.
[0030] (One purpose of rectification circuit 1)
[0031] As described above, a transient current flows through the rectifying element having the PN junction. On the other hand, as an example of a rectifier element made of a compound semiconductor that does not have a PN junction, SiC-SBD (Schottky Barrier Diode, Schottky barrier diode) or GaN-HEMT (High Electron Mobility Transistor, High Electron Mobility Transistor) are exemplified. mobility transistors), etc. In this rectifying element, no transient current originates from the PN junction.
[0032] However, there is a parasitic capacitance in this rectifying element. Therefore, when a voltage in a direction t...
no. 2 approach 〕
[0198] Figure 9 It is a figure which shows the power supply circuit 20 of 2nd Embodiment. The rectification circuit of the second embodiment is referred to as a rectification circuit 2 . In the rectification circuit 2, the power supply TP1 of the rectification circuit 1 is replaced with a power supply FP1. That is, in the power supply circuit 20 , the input power supply (power supply FP1 ) of the step-up chopper unit is also used as the power supply of the rectification circuit 2 . According to this configuration, the total number of power supplies of the power supply circuit 20 can be reduced, which is advantageous in terms of cost.
[0199] In addition, in the rectification circuit 2 , switching elements TT2 , TT3 , and TT4 are provided instead of the switching element TT1 of the rectification circuit 1 . The transformer of the rectification circuit 2 is called a transformer TR2 (Transformer). The primary winding and the secondary winding of the transformer TR2 are refe...
no. 3 approach 〕
[0209] Figure 10 It is a figure which shows the power supply circuit 30 of 3rd Embodiment. The rectification circuit of the third embodiment is referred to as a rectification circuit 3 . In the rectification circuit 3, the power supply TP1 of the rectification circuit 1 is replaced with a capacitor RV1. That is, the smoothing capacitor (capacitor RV1 ) of the step-up chopper unit can be used as the power source of the rectification circuit 3 . According to this configuration, since the total number of power supplies of the power supply circuit 30 can be reduced, it is advantageous in terms of cost.
[0210] In addition, in the rectification circuit 3 , switching elements TT5 , TT6 , and TT7 are provided instead of the switching element TT1 of the rectification circuit 1 . The transformer of the rectification circuit 3 is called a transformer TR3 (Transformer). The primary winding and the secondary winding of the transformer TR3 are referred to as primary winding PW3 and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com