Method for recovering mercury in nonferrous smelting solid waste
A technology of solid waste and recovery method, applied in the field of mercury resource recovery, can solve the problem of high energy consumption cost, and achieve the effects of recycling, avoiding environmental pollution, and avoiding volatilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
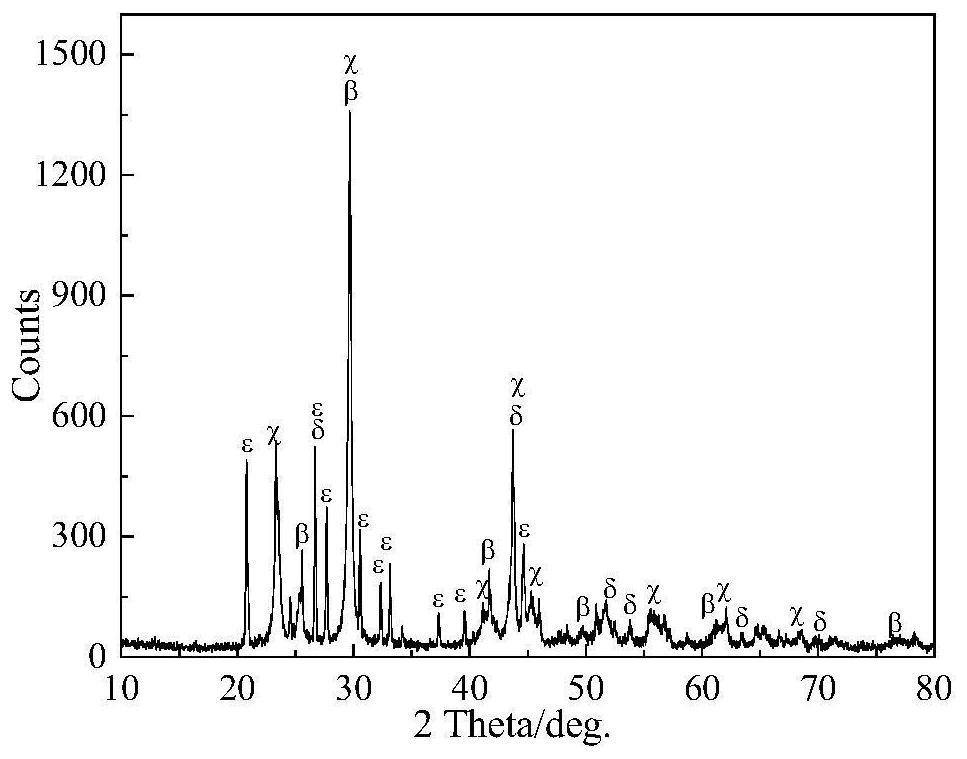
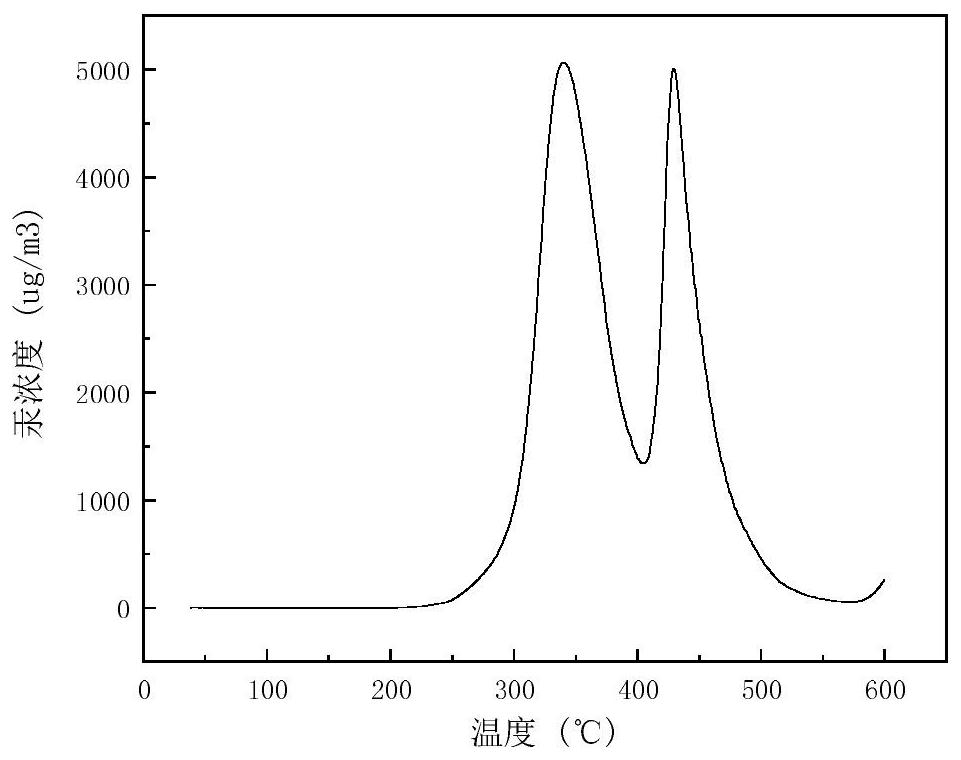
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
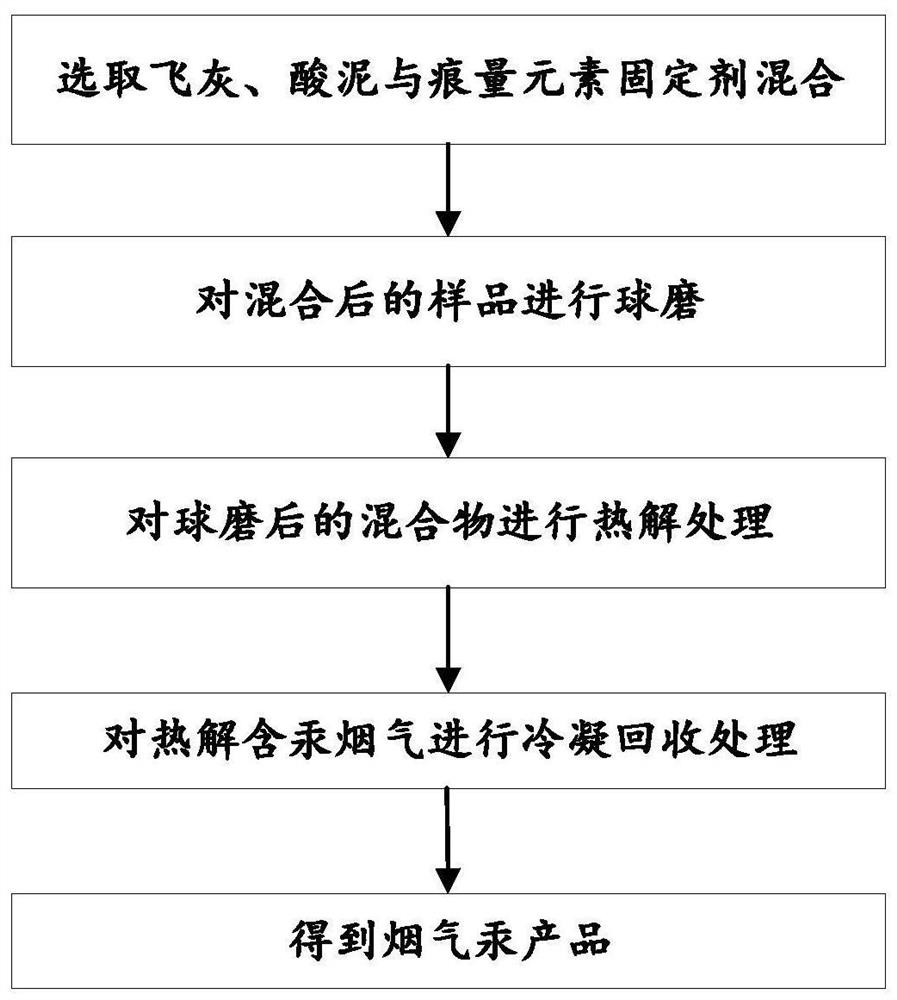
[0028] A method for recovering mercury in non-ferrous smelting solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0029] (1) Take solid waste and calcium oxide with a mass ratio of 1:0.1 for ball milling for 2 hours. The ball-to-material ratio of the above ball milling process is 4:1, and the ball milling speed is 400r / min. The main components of the above solid waste are Mercury-containing solid waste such as fly ash and acid mud produced by non-ferrous smelting, the mercury content in this solid waste is 1%, and the content of arsenic and selenium are both 0.01%.
[0030] (2) Put the solid waste and calcium oxide after ball milling into industrial furnaces. Among them, the input amount of solid waste is 50kg / h, and the input amount of calcium oxide is 10kg / h. At an air flow rate of 20m 3 / h, under the condition that the pyrolysis treatment temperature is 500°C, the solid waste is pyrolyzed for 0.5h to obtain the pyrolysis flue gas, and the calcium oxide in the industrial furna...
Embodiment 2
[0033] A method for recovering mercury in non-ferrous smelting solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0034] (1) Take solid waste and iron oxide with a mass ratio of 1:2 and perform ball milling treatment for 6 hours. The ball-to-material ratio of the ball milling process is 12:1, and the ball milling speed is 800r / min. The main components of the above solid waste are Mercury-containing solid wastes such as fly ash and acid sludge produced by non-ferrous smelting, the mercury content in the above-mentioned solid wastes is 20%, and the arsenic and selenium contents are both 5%.
[0035] (2) Put the solid waste and iron oxide after ball milling into industrial furnaces. Among them, the input amount of solid waste is 1000kg / h, and the input amount of iron oxide is 300kg / h. At an air flow rate of 100m 3 / h, under the condition that the pyrolysis treatment temperature is 600°C, the solid waste is pyrolyzed for 3 hours to obtain the pyrolysis flue gas. The iron oxide in th...
Embodiment 3
[0038] A method for recovering mercury in non-ferrous smelting solid waste, comprising the following steps:
[0039] (1) Take solid waste and alumina with a mass ratio of 1:0.1 for ball milling treatment for 6 hours. The ball-to-material ratio of the ball milling process is 4:1, and the ball milling speed is 800r / min. The main components of the above solid waste are Mercury-containing solid wastes such as fly ash and acid sludge produced by non-ferrous smelting. The mercury content in the above solid wastes is 20%, and the content of arsenic and selenium are both 0.01%.
[0040] (2) Put the solid waste and alumina after ball milling into industrial furnaces. Among them, the input amount of solid waste is 50kg / h, and the input amount of alumina is 10kg / h. At an air flow rate of 100m 3 / h, under the condition that the pyrolysis treatment temperature is 500°C, the solid waste is pyrolyzed for 0.5h to obtain pyrolysis flue gas. The alumina in the industrial furnace can absorb th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com